Infographics
Governance
Govt Jobs for Acquitted Individuals in Criminal Cases
For Prelims: Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP), Protection of Children from Sexual Offenses (POCSO) Act, 2012, Moral Turpitude, Indian Penal Code, 1860, Central Armed Police Forces (CAPF),
For Mains: Consideration of acquittals in cases involving moral turpitude and its impact on employment decisions.
Why in News?
Recently, The Punjab and Haryana High Court directed the Centre to reconsider the appointment of a person from Haryana as a constable in the Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP), given his acquittal in 2019 case under the Protection of Children from Sexual Offenses (POCSO) Act, 2012.
- Order issued by the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) cancelled the person’s appointment on grounds of moral turpitude.
What is the Moral Turpitude?
- The term "moral turpitude," as noted by the Supreme Court in the case of P. Mohanasundaram vs. the President, 2013, lacks a specific definition.
- It encompasses actions contrary to justice, honesty, modesty, or good morals, suggesting a depraved and wicked character or disposition of the individual accused of such conduct.
What is the Concerning Case?
- The constable, appointed on compassionate grounds in 2022, faced the revocation of his appointment after revealing his acquittal in a 2018 criminal case under Section 4 of the POCSO Act, 2012, concerning penetrative sexual assault.
- In addition to this, he faced charges under several sections of the Indian Penal Code, 1860, including offences related to causing harm by poison, kidnapping, and criminal intimidation, among others.
- Despite being acquitted of all charges by a Kaithal Court (Haryana) in 2019, he faced the cancellation of his appointment.
- This action was taken according to a policy issued by the Ministry of Home Affairs for appointments in the Central Armed Police Forces (CAPF), for individuals with criminal cases registered, under trial, or under inquiry.
- Individuals faced serious charges or moral turpitude in a criminal case, even if acquitted later due to benefit of doubt or witness intimidation, are generally deemed unsuitable for appointment in the CAPF.
What Mandates has the Court Set for Appointing Individuals with Criminal Cases in Public Jobs?
- A three-judge bench of the Supreme Court in Avtar Singh vs. Union of India, 2016 dealt with the appointment of a candidate involved in a criminal case.
- It ruled that information given to the employer about a candidate’s conviction, acquittal, arrest, or pendency of a criminal case must be true and without suppression or false information.
- For conviction in cases that aren’t trivial, the employer may cancel the employee’s candidature or terminate his services.
- If an acquittal has occurred in a case involving moral turpitude or a serious offence on technical grounds, and it's not a clear acquittal or based on reasonable doubt, the employer can assess all pertinent information regarding the individual's background and make a suitable decision regarding the employee's continuation.
- Supreme Court in Satish Chandra Yadav vs. Union of India, 2023 case “acquittal in a criminal case would not automatically entitle a candidate for appointment to the post” and it would be still open to the employer to consider their antecedents and examine their suitability as a candidate.
What is the Protection of Children From Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012?
- About:
- The POCSO Act came into effect on 14th November 2012 which was enacted in consequence to India’s ratification of the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child in 1992.
- The aim of this special law is to address offences of sexual exploitation and sexual abuse of children, which were either not specifically defined or adequately penalised.
- The Act defines a child as any person below the age of 18 years. The Act provides punishment as per the gravity of the offence.
- The Act was further reviewed and amended in 2019 to Introduce more stringent punishment including the death penalty for Committing sexual crimes on children, with a view to deter the perpetrators & prevent such crimes against children.
- The Government of India has also notified the POCSO Rules, 2020.
- Features:
- Gender-Neutral Nature:
- The Act recognises that both girls and boys can be victims of sexual abuse and that such abuse is a crime regardless of the gender of the victim.
- This is in line with the principle that all children have the right to protection from sexual abuse and exploitation and that laws should not discriminate based on gender.
- The Act recognises that both girls and boys can be victims of sexual abuse and that such abuse is a crime regardless of the gender of the victim.
- Ease in Reporting Cases:
- There is sufficient general awareness now to report cases of sexual exploitation of children not only by individuals but also by institutions as non-reporting has been made a specific offence under the POCSO Act. This has made it comparatively difficult to hide offences against children.
- Gender-Neutral Nature:
What is the Indo-Tibetan Border Police Force (ITBPF)?
- Indo-Tibetan Border Police Force (ITBPF) is a Central Armed Police Force functioning under the Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India.
- The ITBP was raised on 24th October 1962 during the India-China War and is a border guarding police force specialising in high-altitude operations.
- Presently, ITBP is deployed on border guarding duties from Karakoram Pass in Ladakh to Jachep La in Arunachal Pradesh covering 3488 km of the Indo-China Border.
- The Force is also deployed for Anti-Naxal Operations and other internal security duties.


Geography
Implications of No Snowfall In Kashmir
For Prelims: Implications of No Snowfall In Kashmir, Western Disturbance, Climate Change, Himalayan region, El Nino.
For Mains: Important Geophysical Phenomena, Geographical features and their location, Impacts of Climate Change.
Why in News?
The absence of Snowfall in Kashmir during the winter season is not only affecting the region's tourism industry, particularly in popular destinations like Gulmarg, but it also has significant implications for various aspects of the local environment and economy.
What Causes No Snowfall In Kashmir?
- Climate and Weather Patterns:
- The entire Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh regions have seen a lack of rains or snow this winter, with a notable 80% rainfall deficit in December 2023 and 100% (no rain) deficit in January 2024 so far.
- Winter precipitation in these regions, crucial for the local climate, is mainly in the form of snowfall.
- Decline in Western Disturbance:
- The overall trend of decreasing snowfall has been attributed to a decline in Western Disturbance events and a gradual rise in temperatures, likely influenced by Climate Change.
- Western Disturbances are the primary source of winter precipitation in the Himalayan region.
- The number of Western Disturbance events has been showing a declining trend, contributing to less overall precipitation during the winter months.
- Western Disturbance are large eastward-moving rain-bearing wind systems that originate beyond Afghanistan and Iran, picking up moisture from as far as the Mediterranean Sea and even the Atlantic Ocean.
- Role of Climate Change and El Nino:
- Climate change is considered a contributing factor to the declining snowfall in Kashmir, as indicated by various studies.
- The rate of temperature increase is higher in upper elevation areas than in the plains, further impacting snowfall.
- The current El Nino event in the eastern Pacific Ocean is suggested as an additional factor affecting global atmospheric circulation and contributing to the deficit precipitation in the region.
- There have been several years in the last one decade — 2022, 2018, 2015 — when winters have been relatively dry in Jammu and Kashmir, and snowfall has been very low.
What are the Implications of No Snowfall in Kashmir?
- Short and Long Term Impact:
- Short-term effects include an increase in forest fires, agricultural drought, and a drop in crop production.
- Long-term consequences include a reduction in hydroelectricity generation, an increase in glacier melting, and adverse effects on drinking water supply due to less recharge of groundwater.
- Vital for Winter Crops:
- The winter snow, crucial for moisture in the soil, is vital for winter crops, particularly horticulture. The yields of apples and Saffron, significant contributors to the local economy, are adversely affected in the absence of sufficient snowfall.
- Impact on Tourism:
- Gulmarg, a key winter tourism spot in Kashmir, is witnessing a sharp decline in tourist visits this season due to insufficient snow. Despite substantial tourist numbers in 2023, officials project at least a 60% reduction in footfall.
- The scarcity of snow is adversely affecting ski resorts and related businesses, impacting the local economy.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to ‘Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)’ sometimes mentioned in the news while forecasting Indian monsoon, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2017)
- IOD phenomenon is characterised by a difference in sea surface temperature between tropical Western Indian Ocean and tropical Eastern Pacific Ocean.
- An IOD phenomenon can influence an El Nino’s impact on the monsoon.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Most of the unusual climatic happenings are explained as an outcome of the El-Nino effect. Do you agree? (2014)


Indian Polity
Prior Approval for Investigation Against Government Officials
For Prelims: Prior Approval, Supreme Court (SC), FIR (First Investigation Report), Skill Development Scam case, Crime Investigation Department (CID).
For Mains: Prior Approval.
Why in the News?
Recently, the Supreme Court (SC) has delivered a split verdict in former Andhra Pradesh Chief Minister’s plea to quash an FIR (First Investigation Report) in the alleged Skill Development Scam case.
- The disagreement between Judges revolves around whether the Andhra Pradesh Crime Investigation Department (CID) was required to seek 'Prior Approval' from the state government before conducting an inquiry against public officials accused of corruption.
What Was the Verdict of the Supreme Court?
- The Supreme Court delivered a split verdict on the interpretation and applicability of Section 17A of the Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988.
- One Judge stated that prior approval for conducting a probe for alleged offenses under the PC Act against the former CM was necessary. However, he refused to quash the remand order and granted liberty to the state to seek such approval.
- Wherever another Judge held that Section 17A would not apply retrospectively and upheld the high court order refusing to quash the FIR.
- The Justice also stated that the impugned order of remand and the high court judgment did not suffer from any illegality.
- Due to the divergent opinions, the matter has been referred to the Chief Justice of India (CJI) for appropriate directions.
What was Skill Development Scam In Andhra Pradesh?
- The skill development scam in Andhra Pradesh involves allegations against former Chief Minister Chandrababu Naidu and the misappropriation of funds earmarked for a skill development program.
- In 2021, the skill development project, worth Rs 3,356 crores, came under scrutiny
- An FIR was filed against Chandrababu Naidu in December 2021. The Crime Investigation Department (CID) alleged that around Rs 241 crores allocated for the project were diverted to five shell companies.
What is Prior Approval For Investigation Against Government Officials?
- About:
- Prior Approval refers to the requirement for investigators, particularly agencies like the Crime Investigation Department (CID) or the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI), to obtain approval from the government or a competent authority before initiating an inquiry or investigation into allegations of corruption against public officials.
- This approval is necessary before any formal action, such as lodging an FIR (First Information Report) or conducting a detailed investigation, can take place.
- Legal Provisions:
- The need for 'Prior Approval' is rooted in legal provisions introduced through amendments to the Delhi Special Police Establishment Act, 1946, and later incorporated into the Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988.
- Originally, the requirement was introduced in 2003, stipulating that approval from the central government was necessary before investigating offenses under the Prevention of Corruption Act if the accused held a rank higher than joint secretary.
- However, the SC struck down this requirement in 2014. Subsequently, in 2018, a similar provision (Section 17A) was reintroduced through an amendment to the Prevention of Corruption Act.
- According to this provision, approval from the central or state government or a competent authority is required before initiating an inquiry or investigation if a public servant is accused of committing an offense under the Act while discharging their official duties.
- Rationale:
- The rationale behind the 'prior approval' requirement is to balance the need for investigating corruption cases involving public officials with the protection of officials from potentially baseless or politically motivated inquiries.
- It is seen as a procedural safeguard to ensure that investigations are conducted judiciously and with appropriate oversight, preventing misuse of investigative powers.
What are the Challenges to the Provision of Prior Approval?
- Requiring 'prior approval' makes it extremely difficult to determine if an offense was committed by a public official while they were discharging their duties.
- Without the ability to conduct an initial investigation, it becomes challenging to gather evidence and establish whether there is a valid case against the official.
- Placing the burden of obtaining 'prior approval' on police officers and investigating agencies may hinder their ability to promptly and effectively address corruption allegations.
- This burden could slow down the investigative process, potentially allowing corrupt officials to evade scrutiny or continue their activities.
Way Forward
- There is a need to conduct a comprehensive review of existing legislation related to 'Prior Approval' and consider amendments to address concerns raised by stakeholders.
- Seek a balance between the oversight provided by 'Prior Approval' and the need for expeditious investigations. Consider refining the criteria for seeking approval to ensure that it does not unduly delay the initiation of inquiries.
- Establish clear and transparent criteria for granting 'Prior Approval' to investigate public officials. This can include specifying the threshold for the seriousness of allegations or the rank of the official involved.


Social Justice
Global Surgery
For Prelims: Low- and Middle-Income Countries (LMICs), Disease Control Priorities Network (DCPN), World Bank (WB), World Health Organization (WHO), Universal Health Coverage.
For Mains: Global Surgery, Government Initiatives Related to Healthcare.
Why in News?
Global surgery is the neglected stepchild in global health. The neglect is more shocking in South Asia which has the largest population globally lacking access to essential surgery.
What is Global Surgery?
- About:
- Global surgery focuses on Equitable Access to Emergency and essential surgery. While it predominantly focuses on Low- and Middle-Income Countries (LMICs), it also prioritises access disparities and under-served populations in high-income countries (HICs).
- These “surgeries” include essential and emergency surgeries such as surgery, obstetrics, trauma, and anaesthesia (SOTA).
- History:
- In 2015, often referred to as the "Annus Mirabilis" or miracle year for global surgery, key developments transformed the field. The Disease Control Priorities Network (DCPN) report sponsored by the World Bank (WB) highlighted the cost-effectiveness of essential surgery and the significant disease burden that could be addressed surgically.
- The Lancet Commission on Global Surgery (LCoGS) played a crucial role by assessing global surgical care access, defining indicators for readiness, and proposing strategies like the National Surgical, Obstetrics, and Anaesthesia Plan (NSOAP).
- This laid the groundwork for the World Health Organization (WHO) Declaration on Safe Surgery (WHO Resolution 68.15), emphasizing the essential role of surgical systems in achieving Universal Health Coverage.
What are the Challenges and Disparity in Global Surgery?
- Inaccessibility:
- As per the LCoGS, over 70% of the global population, or five billion people, lack timely access to safe and affordable surgical care when needed.
- In Low- and lower-middle-income countries (LLMICs), 99% and 96% of the population, respectively, face access gaps, compared to 24% in high-income countries (HICs).
- Particularly in South Asia, over 98% of the population lacks access to safe and affordable surgical care.
- Disease Burden:
- Surgically treatable conditions led to around 17 million deaths in 2010, surpassing the combined mortality burden of HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus)/AIDS (Acquired ImmunoDeficiency Syndrome), Tuberculosis, and Malaria.
- Low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) have over 77 million surgically avertable Disability-Adjusted Life-Years (DALY), constituting 3.5% of the total disease burden in these countries.
- South Asia has a higher DALY rate than the LMIC average, contributing significantly to surgically avertable burdens in neonatal and maternal diseases, congenital anomalies, digestive conditions, and injuries.
- Economic Burden:
- The absence of scaling up surgical care is projected to result in a cumulative loss of USD 20.7 trillion (in purchasing power parity terms) to global GDP across 128 countries by 2030.
- The annual loss in societal welfare is estimated to be about USD 14.5 trillion for 175 countries.
- South Asia contributes about 7% to the global lost welfare.
- Limited Representation in International Health Reports:
- Surgery contributes to less than 1% of indicators mentioned in major international health reports by organizations such as the World Bank, WHO, and UNICEF.
- This lack of representation may result in reduced prioritization in global health initiatives and resource allocation.
- Neglect in National Policy Making:
- National Health Strategic Plans from various countries, such as those in Africa and India, often exhibit limited attention to surgery. Some plans do not mention surgery or surgical conditions at all, while others mention them only sparingly.
- This lack of emphasis in national policies may hinder the development of comprehensive healthcare systems.
- Research Disparities:
- A significant disparity exists in research attention and funding between global surgery and broader global health topics.
- The limited number of 'global surgery' titles in databases like PubMed compared to 'global health' titles highlights the gap in research focus.
- This disparity may hinder the generation of evidence-based practices in surgical care
- Interconnected Challenges:
- Neglect in one aspect, such as policy or research, can perpetuate neglect in other areas, creating a cycle of under prioritization.
- The lack of representation in international reports may influence national policies, which, in turn, affects research funding and attention.
What are the Government Initiatives Related to Healthcare and Surgery?
Way Forward
- There is a need to support and encourage research in global surgery to generate evidence-based practices, innovations, and solutions. Prioritize research funding for surgical interventions, outcomes, and healthcare delivery models that can be adapted to resource-limited settings.
- There is a need to encourage countries to develop and implement NSOAPs, demonstrating a commitment to improving surgical care at the national level. NSOAPs provide a roadmap for strengthening surgical systems, infrastructure, and workforce.
- There is a need to advocate for sustained and increased financing for surgical care. Develop funding mechanisms that prioritize surgical infrastructure, training, and service delivery. Engage with international donors, governments, and philanthropic organizations to allocate resources for global surgery initiatives.


Important Facts For Prelims
Cabo Verde Declared A Malaria-Free Country
Why in News?
Recently, the World Health Organization (WHO) has declared Cabo Verde as a Malaria-free country.
- Cabo Verde now joins Mauritius and Algeria as the third country in the WHO African region to be certified as malaria-free.
What is the Malaria Elimination Certification Process?
- About:
- WHO certifies a country as malaria-free when it demonstrates the interruption of nationwide malaria transmission for at least 3 consecutive years and has a fully functional surveillance and response system preventing re-establishment of indigenous transmission.
- Global Status:
- Till now, WHO has awarded the ‘malaria-free’ certification to 43 countries and 1 territory.
- South East Asian Region: Maldives (2015) and Sri Lanka (2016) are certified malaria-free by WHO.
- India is not certified as Malaria free.
What is Malaria?
- Malaria is a life-threatening mosquito borne blood disease caused by plasmodium parasites.
- There are 5 Plasmodium parasite species that cause malaria in humans and 2 of these species – P. falciparum and P. vivax – pose the greatest threat.
- Malaria is predominantly found in the tropical and subtropical areas of Africa, South America as well as Asia.
- Malaria is spread by the bite of an infected female Anopheles mosquito.
- The mosquito becomes infected after biting an infected person. The malaria parasites then enter the bloodstream of the next person the mosquito bites. The parasites travel to the liver, mature, and then infect red blood cells.
- Symptoms of malaria include fever and flu-like illness, including shaking chills, headache, muscle aches, and tiredness. Notably, malaria is both preventable and curable.
What are the Initiatives Related to Malaria?
- Global:
- India:
- National Framework for Malaria Elimination 2016-2030
- National Vector-Borne Disease Control Programme
- National Malaria Control Programme (NMCP)
- High Burden to High Impact (HBHI) Initiative
- Malaria Elimination Research Alliance-India (MERA-India)
What are the Key Facts About Cabo Verde?
- Geographical Location:
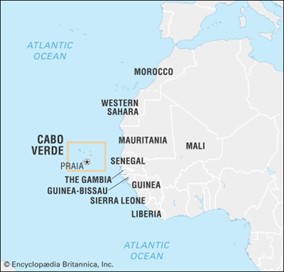
- Cabo Verde, also known as Cape Verde, is a group of islands situated off the west coast of Africa.
- It is located near Senegal and is the closest point to the African continent.
- Archipelago Structure:
- The country is composed of ten islands and five islets.
- These are divided into two main groups: the windward islands (Barlavento) and the leeward islands (Sotavento).
- Population:
- The majority of the population in Cabo Verde is of mixed European and African descent.
- People of this mixed heritage are often referred to as "mestiço" or "Crioulo."
- Capital:
- The capital city of Cabo Verde is Praia.
- Languages:
- Portuguese is the official language.
- Cape Verdean Creole, or simply Creole, is also widely spoken and is considered a significant part of the cultural identity.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Widespread resistance of malarial parasite to drugs like chloroquine has prompted attempts to develop a malarial vaccine to combat malaria. Why is it difficult to develop an effective malaria vaccine? (2010)
(a) Malaria is caused by several species of Plasmodium
(b) Man does not develop immunity to malaria during natural infection
(c) Vaccines can be developed only against bacteria
(d) Man is only an intermediate host and not the definitive host
Ans: (b)


Important Facts For Prelims
World Economic Forum
Why in News?
The World Economic Forum (WEF) is holding its Annual Meeting from 15th January to 19th January, 2024 in Davos, Switzerland.
What are the Major Points Related to the World Economic Forum (WEF)?
- About: WEF is the International Organization for Public-Private Cooperation. The Forum engages the foremost political, business, cultural and other leaders of society to shape global, regional and industry agendas.
- It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.
- Foundation: Klaus Schwab, a German professor with a background in mechanical engineering and a Master of Public Administration from Harvard, founded WEF in 1971, originally known as the European Management Forum.
- He introduced the concept of “stakeholder capitalism.”
- According to Schwab, “It is a form of capitalism in which companies do not only optimize short-term profits for shareholders, but seek long term value creation, by taking into account the needs of all their stakeholders, and society at large.”
Note: The European Management Forum was the first non-governmental institution to initiate a partnership with China’s economic development commissions, spurring economic reform policies in China.
- Evolution: Events in 1973, namely the collapse of the Bretton Woods fixed exchange rate mechanism and the Arab-Israeli War, saw the Annual Meeting expand its focus from management to economic and social issues.
- Two years later, the organization introduced a system of membership for ‘the 1,000 leading companies of the world.
- In 1987, the European Management Forum formally became the World Economic Forum and sought to broaden its vision to include providing a platform for dialogue
- In 2015, the Forum was formally recognised as an international organization.
- Funding: Primarily supported by partnering corporations, typically with annual turnovers exceeding USD 5 billion.
- Annual Meeting in Davos: Davos brings together around 3,000 participants (including paying members and select invitees): investors, business leaders, political leaders, economists, celebrities, and others to discuss global issues across 500 sessions
- Key Diplomatic Moments at WEF:
- Korean Diplomacy: North and South Korea held first ministerial-level meetings in Davos.
- German Reunification (1989): East German Prime Minister and German Chancellor met at WEF to discuss reunification.
- South African Milestone (1992): South African President de Klerk, Nelson Mandela, and Zulu prince Mangosuthu Buthelezi made their inaugural joint appearance outside South Africa, marking a significant milestone in the country's political transition.
- G20 Genesis(1998): WEF emphasized the need to involve major developing countries. Therefore, the concept of G20 emerged, initially limited to finance ministers.
- G20, born from WEF discussions, evolved into a summit.
- Major Reports: WEF regularly publishes globally recognized reports, including the Global Competitiveness Report and the Global Gender Gap Report, Energy Transition Index, Global Risk Report, Global Travel and Tourism Report.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q1. Which of the following gives ‘Global Gender Gap Index’ ranking to the countries of the world? (2017)
(a) World Economic Forum
(b) UN Human Rights Council
(c) UN Women
(d) World Health Organization
Ans: (a)
Q2. Who among the following is the founder of World Economic Forum? (2009)
(a) Klaus Schwab
(b) John Kenneth Galbraith
(c) Hobert Zoellick
(d) Paul Krugman
Ans (a)
Q3. The Global Competitiveness Report is published by the (2019)
(a) International Monetary Fund
(b) United Nations Conference on Trade and Development
(c) World Economic Forum
(d) World Bank
Ans: (c)


Important Facts For Prelims
NHAI Introduces 'One Vehicle, One FASTag' Initiative
Why in News?
National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) has launched the ‘One Vehicle, One FASTag’ initiative that aims to discourage user behavior of using single FASTag for multiple vehicles or linking multiple FASTags to a particular vehicle.
- NHAI is also encouraging FASTag users to complete the ‘Know Your Customer’ (KYC) process of their latest FASTag by updating KYC as per RBI guidelines.
- FASTags with valid balance but with incomplete KYC will get deactivated/blacklisted by banks post 31st January 2024.
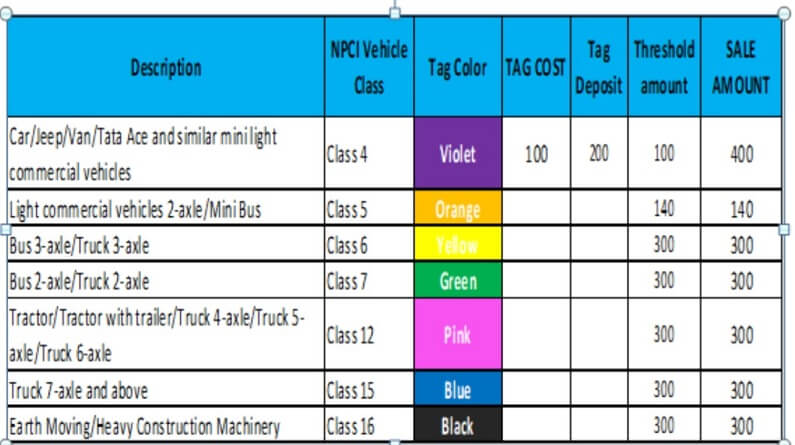
What is FASTag?
- About: FASTag is a device that employs Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology for making toll payments directly while the vehicle is in motion.
- NHAI launched two mobile Apps – MyFASTag and FASTag Partner to facilitate the availability of FASTags.
- The tag is valid for 5 years from the date of issuance and comes in seven different colour codes.
- Benefits of FASTag:
- For Road Users
- Near non-stop motion through toll plazas
- Convenience for cashless payment of toll fee
- Less traffic congestion and reduced commute times
- For Toll Operator
- Lower operating costs
- Better audit control through centralized user accounts
- Improved capacity without being required to build more infrastructure
- For Government
- Savings on fuel and reduction of emissions from idling and repeated stops at toll plazas.
- Improves transparency of toll transactions
- For Road Users
Note
Radio Frequency Identification is a technology that uses radio waves to passively identify a tagged object. The system has two basic parts: tags and readers.
- The reader gives off radio waves and gets signals back from the RFID tag, while the tag uses radio waves to communicate its identity and other information.
What is the National Highways Authority of India?
- NHAI was constituted by an Act of Parliament in 1988 under the administrative control of the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways as a Central Authority to develop, maintain and manage the National Highways entrusted to it by the Government of India.
- The authority, however, became operational in February, 1995.
- The Authority consists of a full time Chairman, and not more than five full time Members and four part time Members who are appointed by the Central Government.
What is the National Electronic Toll Collection Programme?
- The National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) has created the National Electronic Toll Collection (NETC) program to fulfill India's electronic tolling needs.
- This program provides a nationwide, interoperable toll payment solution, covering clearing house services for settlement and dispute resolution.
- In the context of NETC, interoperability means a standardized set of processes and technical specifications, allowing FASTag users to use their tags for payment at any toll plaza, regardless of the plaza's operator.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
1. Consider the following communication technologies: (2022)
- Closed-circuit Television
- Radio Frequency Identification
- Wireless Local Area Network
Which of the above are considered Short-Range devices/technologies?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)


Rapid Fire
ANUBHAV Awards Scheme 2024
Government of India has notified the ANUBHAV Awards Scheme 2024. To participate in the scheme, retiring Central Government employees/pensioners are required to submit their Anubhav write ups, 8 months prior to retirement and up to 1 year after their retirement.
- The published write-ups will be shortlisted for Anubhav Awards and Jury Certificates.
- The Department of Pension & Pensioners' Welfare launched Anubhav Portal in 2015, allowing retired Central Government employees to share their experiences online.


Rapid Fire
PFRDA notifies Point of Presence (PoP) Regulations
Recently, the Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA) notified the Point of Presence (PoP) Regulations 2023,
- This regulation makes it easier for people to join the National Pension System (NPS) by simplifying the registration process.
- Banks and non-banks can serve as Points of Presence (PoPs) to help people join the NPS.
- Now, people require only single Registration for NPS, instead of multiple registrations as earlier required and can operate with just one branch with wider digital presence.
- The Central Government has introduced the National Pension System (NPS) with effect from January 2004.
- National Pension System Trust (NPST) established by PFRDA is the registered owner of all assets under NPS.


Rapid Fire
Jallikattu
Recently, Alanganallur Jallikattu was inaugurated in Madurai district of Tamil Nadu.
- Jallikattu is a bull taming sport in which contestants attempt to tame a bull for a prize, if they fail, the bull owner wins the prize.
- It is celebrated as a part of Pongal (harvest) festival and is revered majorly across Madurai, Tiruchirappalli, Theni, Pudukkottai and Dindigul districts of Tamil Nadu, known as the Jallikattu belt.
- In May 2023, the Supreme Court of India upheld the validity of Jallikattu.
Read more: Jallikattu


Rapid Fire
Navy to Have Mixed Marching Contingent at Republic Day Parade
The Indian Navy is set to make history at the Republic Day Parade, showcasing a groundbreaking mixed-gender marching contingent of 144 men and women Agniveers.
- This year's parade marks the debut of a triservice women marching contingent and features the first-ever appointment of a woman officer as a Commanding Officer of a warship.
- The Navy's tableau highlights two key themes - 'Nari Shakti' and indigenisation, spotlighting the achievements of Bharat in naval capabilities.
Read more: Equal Benefits for Women in Armed Forces