Governance
Remote Voting for Migrants
Prelims: ECI, VVPAT, Remote Electronic Voting Machine, e-SHRAM portal, EVM, Supreme Court.
Mains: Remote Voting for Migrants and Associated Concerns.
Why in News?
Recently, the Election Commission of India (ECI) has proposed a new Remote Electronic Voting Machine (RVM), which will allow domestic migrants to vote in national and regional elections.
- The EC proposed using this in a State Assembly election as a pilot so internal migrants within a state can cast their ballots.
Why the Need for Remote Voting?
- Decrease in Voting Turnout:
- In 2019 general election, over 91% of its eligible citizens were registered with 67% of them coming out to vote, which is the highest voter turnout in the nation’s history.
- It is, however, worrying that a third of the eligible voters, a whopping 30 crore people, do not vote.
- Internal Migration:
- One of the reasons for less voter turnout remained the internal migration that took electors away from their home constituencies.
- Electors can have their names added to the electoral rolls of the constituency they ordinarily reside in, but many chose to retain the Voter ID from their home constituencies for various reasons.
- Supreme Court’s Direction:
- Hearing a petition on the alleged denial of voting opportunities to migrants, the Supreme Court (SC) had in 2015 directed the EC to explore options for remote voting.
- Increasing Registrations of Unorganised Workers:
- There are nearly 10 million migrant workers, which is for the unorganised sector, registered with the government’s e-SHRAM portal. If the remote voting project is implemented, it will have far reaching ramifications.
What is the Current Proposal for Remote Voting?
- RVM:
- RVM is a modified version of the existing Electronic Voting Machine (EVM).
- The special remote polling booths would be set up in different states when elections are on in the home state of migrants.
- The RVM can handle multiple constituencies from a single remote polling booth.
- For this, instead of a fixed ballot paper sheet, the machine has been modified to have an electronic dynamic ballot display which will present different candidate lists corresponding to the constituency number of the voter read by a constituency card reader.
- Security:
- The system would have a device similar to the so voters can verify their votes.
- The units will save the number of votes for each candidate for each of the constituencies, to be tallied on counting day.
- The results would then be shared with the home RO (Returning Officer).
- A returning officer is responsible for overseeing elections in one or more constituencies.
How do Existing EVMs Work?
- EVMs have been used on a large scale in India since 1992 and have been used in all Lok Sabha and State Assembly elections since 2000.
- The latest iteration of the machine is the M3 model, which has been manufactured since 2013. In 2010, multiple political parties approached the ECI to develop a mechanism to verify that the EVM had recorded the vote correctly.
- As a result, the ECI developed the Voter Verified Paper Trail Audit (VVPAT) machine, which has become universal in elections since mid-2017.
- The current EVM setup includes a Balloting Unit (BU), which is connected to the VVPAT printer and is located inside the voting compartment.
- The VVPAT is connected to the Control Unit (CU), which sits with the Presiding Officer (PO) and totals the number of votes cast.
- The VVPAT prints a slip with the poll symbol and candidate name once the voter presses the key on the BU, which is visible to the voter for seven seconds before being dropped off in a box inside the VVPAT.
What are the Concerns and Challenges Ahead?
- The Multi-Constituency RVM for migrant voting will have the same security system and voting experience as the EVM. This essentially means that the challenges with regard to the current EVMs will persist when it comes to the RVMs.
- Besides machine related concerns, remote voting will also face logistical and administrative challenges. These include questions on how voter registration will take place in remote locations, how names will be removed from the electoral rolls of the home constituency, how remote voting applications will be made transparent etc.
- The current VVPAT system is not voter verified in its full sense, meaning, while the voter sees their vote slip behind the VVPAT’s glass for seven seconds, it does not mean they have verified it. That would happen if the voter got the printout in their hand, was able to approve it before the vote was finally cast, and was able to cancel if there was an error.
- Under the current system, if the voter disputes what they have seen behind the screen, they are allowed a test vote in the presence of an election officer, and if the outcome of the test vote is correct, the voter can be penalized or even prosecuted. The same may persist with remote voting.
Way Forward
- For the voting process to be verifiable and correct, it should be machine-independent, or software and hardware independent, meaning, the establishment of its veracity should not depend solely on the assumption that the EVM is correct.
- The “voter should have full agency to cancel a vote if not satisfied; and that the process to cancel must be simple and should not require the voter to interact with anybody”.
- It is important that any system of remote voting has to take into account the confidence and acceptability of all the stakeholders of the electoral system – voters, political parties and election machinery, the officials are learnt to have informed the committee while political consensus is the way forward to introduce remote voting.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Right to vote and to be elected in India is a (2017)
(a) Fundamental Right
(b) Natural Right
(c) Constitutional Right
(d) Legal Right
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- Right to Vote is implicit in Article 326 of the Constitution, which states that the elections to the House of the People and to the Legislative Assembly of every State shall be on the basis of adult suffrage. Every person who is a citizen of India and who is not less than eighteen years of age and not disqualified under the Constitution or any law made by the appropriate Legislature on the ground of nonresidence, unsoundness of mind, crime or corrupt or illegal practice, shall be entitled to be registered as a voter at any such election.
- Right to be elected is implicit in the Constitution in a way that it provides for the minimum qualifications required to be the Member of Parliament (Article 84), Member of State Legislatures (Article 173), President and Vice-President. Article 84 provides that a citizen of India who is not less than thirty years of age is eligible to fill a seat in the Council of State (Rajya Sabha) and a person who is not less than twenty-five years of age is eligible to fill the seat in the House of the People (Lok Sabha).
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Science & Technology
Hyderabad: Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution
For Prelims: World Economic Forum (WEF), Fourth Industrial Revolution, Big data, Cybersecurity, Internet of things (IoT), Xenobots, Pacemaker, Microplastics, Energy Transition Index, Global Competitiveness Report, Global Gender Gap Report.
For Mains: Applications of Fourth Industrial Revolution(4IR), Challenges Associated with 4IR.
Why in News?
Recently, the World Economic Forum (WEF) has chosen Hyderabad, Telangana for establishing its Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (C4IR).
- The C4IR Telangana will be an autonomous, non-profit organisation with a thematic focus on healthcare and life sciences.
What is the Fourth Industrial Revolution?
- About:
- It is characterised by the use of technology to blur the boundaries between the digital, physical, and biological worlds, and is driven by data.
- Key technologies include cloud computing, big data, autonomous robots, cybersecurity, simulation, additive manufacturing, and the internet of things (IoT).
- The term 4IR was coined by Klaus Schwab, executive chairperson of the WEF, in 2016.
- Major Examples of its Application:
- Pacemaker: The pacemaker is a near-perfect example of the ongoing fourth industrial revolution (4IR).
- The four wireless sensors of the pacemaker monitor vitals such as temperature, oxygen levels and the heart’s electrical activity.
- The device then analyses the vitals and decides when to pace the heart and at what rate. Doctors can wirelessly access the information on a tablet or smartphone.
- Xenobots: Xenobots, which are less than a millimetre long, are known to be the first living robot, were created in 2020 from the stem cells of the African clawed frog and can be programmed using artificial intelligence.
- It has a reproductive ability demonstrated in October 2021 by a team of US scientists.
- When the researchers put the xenobots into a petri dish, they were able to gather hundreds of tiny stem cells inside their mouths and create new xenobots a few days later.
- Once perfected, xenobots could be useful for tasks like cleaning up microplastics and regrowing or replacing dead cells and tissues inside human bodies.
- Smart Railway Coaches: In November 2020, the Modern Coach Factory (MCF) at Raebareli, Uttar Pradesh, rolled out smart railway coaches that are fitted with a battery of sensors to provide a comfortable experience to passengers.
- The sensors monitor odour levels in toilets, check if the doors are safely closed, avoid fire outbreaks and stop unauthorised travel using CCTV cameras with face recognition capabilities, among other technologies.
- Pacemaker: The pacemaker is a near-perfect example of the ongoing fourth industrial revolution (4IR).
- Challenges Associated with 4IR:
- Job Displacement: As automation and artificial intelligence become more prevalent, there is a concern that many jobs will be replaced by machines, leading to widespread job loss and unemployment.
- Privacy Concern: The increasing connectivity of devices and systems in Industry 4.0 increases the risk of cyber-attacks, which can have significant consequences for both businesses and individuals.
- Ethical Concerns: As artificial intelligence and automation become more advanced, there are also concerns about ethical issues such as accountability, bias, and transparency.
- Lack of Digital Infrastructure: Not all countries have the digital infrastructures for Industry 4.0, leading to digital divide and uneven economic growth.
What are the Other Industrial Revolutions?
- First Industrial Revolution (1800s): It used water and steam power to mechanise production. Example: Steam engine.
- Second Industrial Revolution (early 1900s): It used electric power to create mass production. Example: Electricity.
- Third Industrial Revolution (late 1900s): It used electronics and information technology to automate production. Example: Computer and Internet.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question
Q. “The emergence of the Fourth Industrial Revolution (Digital Revolution) has initiated e-Governance as an integral part of government”. Discuss. (2020)
Indian Economy
State Finances: A Study of Budgets of 2022-23
For Prelims: Reserve Bank of India (RBI), Gross Fiscal Deficit (GFD), Informal sector, State Finances: A Study of Budgets of 2022-23, Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM).
For Mains: Significance of the State Finances: A Study of Budgets of 2022-23 in Debt improvement of the states.
Why in News?
Recently, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has released a report stating that the Gross Fiscal Deficit (GFD) of states is expected to decrease to 3.4% of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in 2022-23, from 4.1% in 2020-21.
- This is due to a broad-based economic recovery and an increase in revenue collections.
What is the Report "State Finances: A Study of Budgets of 2022-23"?
- About:
- The report titled "State Finances: A Study of Budgets of 2022-23" is a comprehensive analysis of the financial position of the Indian states, including the trends and challenges in their revenue and expenditure.
- Finding of the Report:
- According to the RBI report, states' debt is expected to decrease to 29.5% of GDP in 2022-23, compared to 31.1% in 2020-21.
- However, the report also highlights that this is still higher than the 20% recommended by the Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Review Committee in 2018.
- States are anticipating an increase in non-tax revenue, which is generated from sources such as fees, fines, and royalties. This increase is likely to be driven by revenue from industries and general services.
- The report notes that states are expecting to see an increase in revenue from various sources such as State GST, excise taxes, and sales taxes in the 2022-2023 fiscal year.
- Measures Suggested in the Report:
- This suggests that debt consolidation should be a priority for state governments.
- Debt consolidation refers to the process of combining multiple debts into a single, more manageable debt. This can help to lower overall interest costs, simplify payments, and make it easier to pay off the debt.
- Allocating more resources to key sectors such as healthcare, education, infrastructure, and green energy, the states can promote economic growth and development.
- The report is proposing that it would be beneficial to establish a fund that would be used to buffer capital expenditure during periods of strong revenue growth.
- The purpose of this fund would be to maintain a consistent level of spending on capital projects, and to ensure that spending on these projects is not drastically reduced during economic downturns.
- In order to attract private investment, state governments should focus on creating a favorable environment for the private sector to operate and grow.
- This can be achieved by implementing policies and regulations that make it easy for private companies to do business, as well as providing incentives and support for private investment.
- States also need to encourage and facilitate higher inter-state trade and commerce to realize the full benefit of spillover effects of state capex across the country.
- This suggests that debt consolidation should be a priority for state governments.
What is Gross Fiscal Deficit (GFD)?
- GFD measures the overall financial health of the state government and is calculated by subtracting total revenue from total expenditure.
- A decrease in GFD is generally considered a positive sign as it indicates that the state government is able to balance its revenue and expenditure more effectively.
What are the Measures of Government Deficit?
- Revenue Deficit: It refers to the excess of government’s revenue expenditure over revenue receipts.
- Revenue Deficit = Revenue expenditure – Revenue receipts
- Fiscal Deficit: It is the gap between the government’s expenditure requirements and its receipts. This equals the money the government needs to borrow during the year. A surplus arises if receipts are more than expenditure.
- Fiscal Deficit = Total expenditure – (Revenue receipts + non-debt creating capital receipts).
- Primary Deficit: Primary deficit equals fiscal deficit minus interest payments. This indicates the gap between the government’s expenditure requirements and its receipts, not taking into account the expenditure incurred on interest payments on loans taken during the previous years.
- Primary deficit = Fiscal deficit – Interest payments
- Effective Revenue Deficit: It is the difference between revenue deficit and grants for creation of capital assets.
- The concept of effective revenue deficit has been suggested by the Rangarajan Committee on Public Expenditure.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question
Q1. Which one of the following is likely to be the most inflationary in its effect? (2021)
(a) Repayment of public debt
(b) Borrowing from the public to finance a budget deficit
(c) Borrowing from the banks to finance a budget deficit
(d) Creation of new money to finance a budget deficit
Ans: (d)
Q2. Consider the following statements: (2018)
- The Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Review Committee Report has recommended a debt to GDP ratio of 60% for the general (combined) government by 2023, comprising 40% for the Central Government and 20% for the State Governments.
- The Central Government has domestic liabilities of 21% of GDP as compared to that of 49% of GDP of the State Governments.
- As per the Constitution of India, it is mandatory for a State to take the Central Government’s consent for raising any loan if the former owes any outstanding liabilities to the latter.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Q3. Which of the following is/are included in the capital budget of the Government of India? (2016)
- Expenditure on acquisition of assets like roads, buildings, machinery, etc.
- Loans received from foreign governments
- Loans and advances granted to the States and Union Territories
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Indian Economy
Sugar Exports
For Prelims: Indian Sugar Mills Association (ISMA), Sugar Industry, Agro-based industry, Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) Programme, Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP), Pesticide, Remote Sensing Technologies.
For Mains: Present Status of the Sugar Industry in India, Growth Drivers for Sugar Industries, Problems Associated with the Sugar Industry.
Why in News?
According to the Indian Sugar Mills Association (ISMA), sugar mills in India have entered into contracts to export 55 lakh tonnes of sweetener.
- The government has allowed sugar mills to export 60 lakh tonnes of sugar till May in the 2022-23 marketing year (October-September).
What is the Present Status of the Sugar Industry in India?
- About:
- Sugar industry is an important agro-based industry that impacts the rural livelihood of about 50 million sugarcane farmers and around 5 lakh workers directly employed in sugar mills.
- In (Oct-Sep) 2021-22 India emerges as the world’s largest producer and consumer of sugar and world’s 2nd largest exporter of sugar.
- Geographical Conditions for the Growth of Sugar:
- Temperature: Between 21-27°C with hot and humid climate.
- Rainfall: Around 75-100 cm.
- Soil Type: Deep rich loamy soil.
- Top Sugarcane Producing States: Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, Karnataka.
- Growth Drivers for Sugar Industries:
- Impressive Sugar Season (Sep-Oct): All records of sugarcane production, sugar production, sugar exports, cane procured, cane dues paid and ethanol production was made during the season.
- High exports: The exports were the highest at about 109.8 LMT without any financial assistance and earned foreign currency of about Rs. 40,000 crores in the year 2021-22.
- Indian Government Policy Initiatives: Timely government initiatives in the last 5 years have taken them out of financial distress in 2018-19 to the stage of self-sufficiency in 2021-22.
- Encouraging Ethanol Production: The Government has encouraged sugar mills to divert sugar to ethanol and also export surplus sugar so that mills may have better financial conditions to continue their operations.
- Ethanol Blending with Petrol (EBP) Programme: The National Policy on Biofuels 2018, provides an indicative target of 20% ethanol blending under the Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) Programme by 2025.
- Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP): The FRP is the minimum price that sugar mills have to pay to sugarcane farmers for procurement of sugarcane.
- It is determined on the basis of recommendations of the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP) and after consultation with State Governments and other stakeholders.
- Problems Associated:
- Competition from Other Sweeteners: The Indian sugar industry is facing increasing competition from other sweeteners such as high fructose corn syrup, which is cheaper to produce and has a longer shelf life.
- Lack of Modern Technology: Many of the sugar mills in India are outdated and lack the modern technology needed to produce sugar efficiently. This makes it difficult for the industry to compete with other sugar-producing countries.
- Environmental Impact: Sugarcane cultivation requires large amounts of water and pesticides, which can have a negative impact on the environment.
- Additionally, sugar mills often release pollutants into the air and water, which can harm nearby communities.
- Political interference: Sugar industry in India is heavily influenced by politics, with the state and central government having a significant role in determining the prices, production, and distribution of sugar. This often leads to a lack of transparency and inefficiency.
What is the Indian Sugar Mills Association (ISMA)?
- Indian Sugar Mills Association (ISMA) is a premier sugar organisation in India.
- It is the interface between the Government and sugar industry (both private and public sugar mills) in the country.
- The prime objective is to ensure that the functioning and interest of both the private and public sugar mills in the country are safeguarded through conducive and growth-oriented policies of the Government.
Way Forward
- Remote Sensing Technology: Despite the importance of sugarcane in the water, food and energy sectors in India, there are no reliable sugarcane maps for recent years and in time series.
- There is a need to deploy remote sensing technologies to map sugarcane areas.
- Diversification: The sugar industry in India should diversify its operations by exploring other products such as biofuels and organic sugar.
- This would help to reduce the risk associated with fluctuations in sugar prices.
- Encouraging Research and Development: The industry should invest in research and development to improve crop yields and reduce the environmental impact of sugar production.
- Encouraging Sustainable Practices: The industry should encourage sustainable practices, such as water conservation, integrated pest management, and reduced use of pesticides, in order to reduce the negative impact of sugar production on the environment.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. According to India’s National Policy on Biofuels, which of the following can be used as raw materials for the production of biofuels? (2020)
- Cassava
- Damaged wheat grains
- Groundnut seeds
- Horse gram
- Rotten potatoes
- Sugar beet
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 5 and 6 only
(b) 1, 3, 4 and 6 only
(c) 2, 3, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6
Ans: (a)
Important Facts For Prelims
Solitary Wave in Martian Magnetosphere
Why in News?
Recently, Indian Institute of Geomagnetism (IIG), an autonomous institute of the Department of Science and Technology (DST) has found evidence of "solitary waves" in the weak magnetic field around Mars for the first time.
- Scientists used high-resolution electric field data from NASA's MAVEN spacecraft to make the discovery of solitary waves.
What are the Key Highlights of the Discovery?
- Unlike Earth, the planet Mars does not have any intrinsic magnetic field. This allows the high-speed solar wind to interact directly with the Mars atmosphere, like an obstacle in flow.
- It has been suggested that even in a weak and thin magnetosphere as that of Mars, frequent occurrences of solitary waves can be observed.
- However, despite several missions to Mars, the presence of solitary waves in the Martian magnetosphere has never been reported earlier.
- The waves were found mostly in the morning and evening on Mars, at altitudes of 1000-3500 km, and their exact cause is still unknown.
What are Solitary Waves?
- About:
- Solitary waves are the distinct electric field fluctuations (bipolar or monopolar) that follow constant amplitude-phase relations.
- Their shape and size are less affected during their propagation.
- Significance:
- Solitary waves have been found to play a significant role in the dynamics of various physical systems, such as in the Earth's magnetosphere and in the Martian magnetosphere.
- In the Earth's magnetosphere, they are known to be responsible for the energization and transport of plasma particles, which can affect the behaviour of satellites and other space-borne equipment.
- In the Martian magnetosphere, their significance is not fully understood yet, but it has been suggested that they may play a role in the loss of atmospheric ions on Mars.
- Solitary waves have been found to play a significant role in the dynamics of various physical systems, such as in the Earth's magnetosphere and in the Martian magnetosphere.
What are the Key Points Related to Mars?
- Size and Distance:
- It is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System.
- Mars is about half the size of Earth.
- Similarity to the Earth (Orbit and Rotation):
- As Mars orbits the Sun, it completes one rotation every 24.6 hours, which is very similar to one day on Earth (23.9 hours).
- Mars' axis of rotation is tilted 25 degrees with respect to the plane of its orbit around the Sun.
- This is similar to Earth, which has an axial tilt of 23.4 degrees.
- Mars has distinct seasons like Earth, but they last longer than seasons on Earth.
- Various Mars Missions:
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2016)
The Mangalyaan launched by ISRO
- is also called the Mars Orbiter Mission
- made India the second country to have a spacecraft orbit the Mars after USA
- made India the only country to be successful in making its spacecraft orbit the Mars in its very first attempt
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Important Facts For Prelims
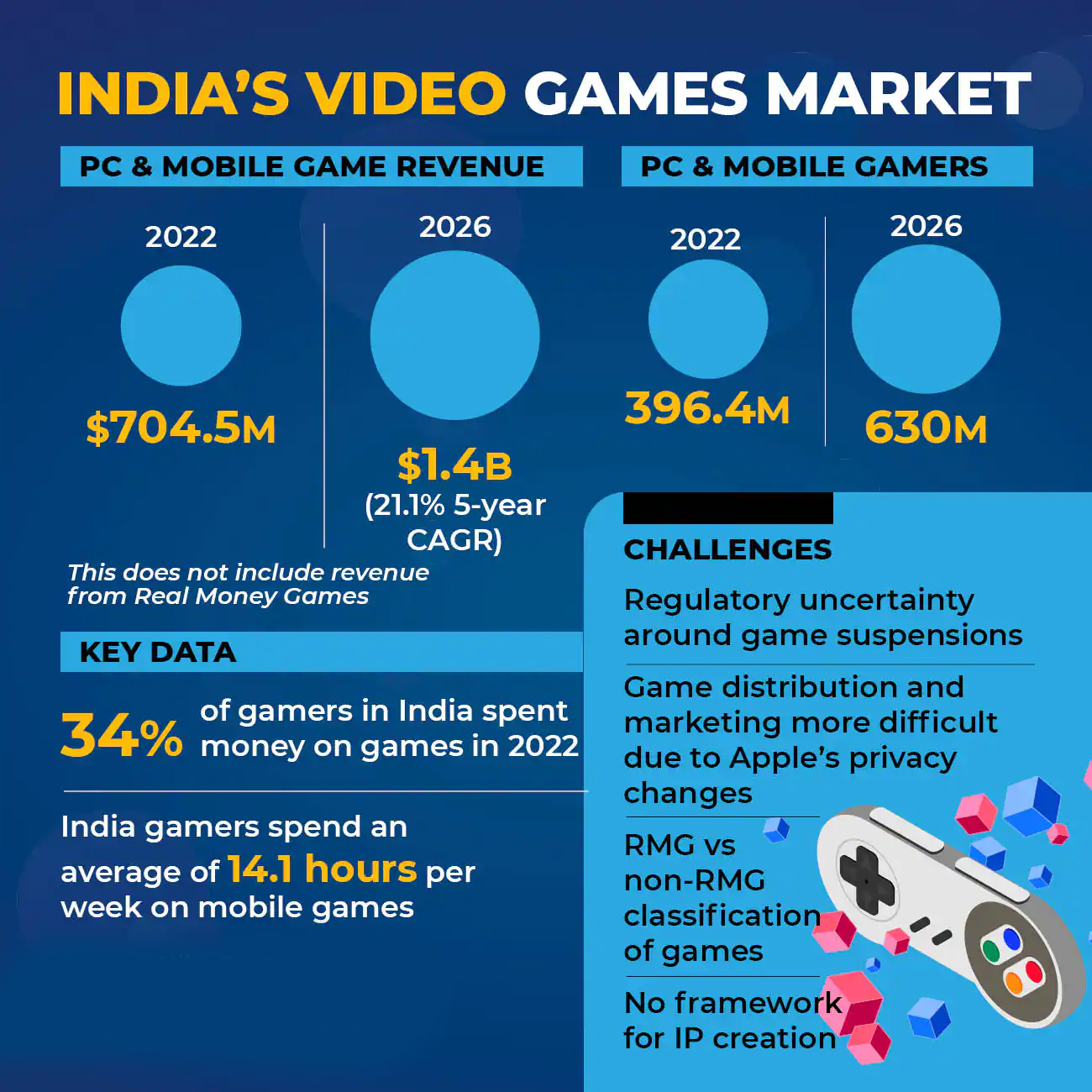
Segregate Video Games from Money Games
Why in News?
Recently, Representatives from the video gaming industry have written a letter to the Ministry of Electronics, Information and Technology (MeitY) seeking to treat video games separately from real money games that involve wagering real money.
- Earlier, the MeitY released the Draft Rules for Online Gaming as an amendment to the Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021.
- The letter requests and recommends that MeitY as “the nodal agency for ‘online gaming’” should recognise the difference between the two industries.
What are the Concerns over Video Games?
- Same Regulatory Purview:
- As part of the amendments of IT Rules, 2021, there is a proposal for a self-regulatory body which will certify a permitted online game in India.
- The current draft notification combines ‘video games’ and ‘online games played for stakes’ into the same regulatory purview.
- There are no countries in the world which recognise and regulate” these two categories of games similarly.
- But gaming companies are worried about the lack of distinction between them and ‘real money games’ (RMG), which are often in the gray zone due to state rules and laws around gambling.
- Purely Entertainment:
- Video game companies state that their “games do not involve staking money and are purely played for entertainment.”
- They point out that Real Money Games and Fantasy Sports are collectively referred to as the “iGaming Industry” in other countries.
What are their Demands?
- To make world-class video games in India for a global audience, it is crucial to have a suitable framework which respects the nuances of the industry and aligns with global best practices.
- This will go a long way to attract capital, enhance market access, increase foreign technology collaboration, build talent pools and help develop India’s global champions.
- Video games are regulated through an India-specific age and content rating mechanism by setting up a video games industry-specific self-regulatory body (SRB), in line with global standards such as PEGI (Pan-European Game Information) in the European Union and ESRB (Entertainment Software Rating Board) in North America.
- Create a robust framework to deal with issues such as children’s addiction to video games, their exposure to in-game purchases, age-inappropriate content and online harm, which will be regulated by video games industry-specific self-regulatory body in line with global standards such as COPPA (Children's Online Privacy Protection Rule) in the USA and GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in the European Union.
Important Facts For Prelims
Revival of Village Defence Committees
Why in News?
Lieutenant Governor of the Jammu and Kashmir declared to revive Village Defence Committees (VDC) amid recent militant attacks.
What are Village Defence Committees (VDC)?
- About:
- The VDC were set up in the mid - 1990s as a force multiplier against militant attacks.
- Its aim was to provide residents of remote hilly villages with weapons and give them arms training to defend themselves.
- Need to Setup VDCs:
- The militancy that began in Kashmir in the early 1990s had spread to the adjoining Doda district by mid 1990s.
- The demand for arming the civilian population first rose after the massacre of 13 people in Kishtwar in 1993.
- The Home Ministry in 1995 decided to set up the VDCs. Later, the scheme was expanded to other areas of the Jammu division as militants extended their activities to Udhampur, Reasi, Rajouri, Poonch, Kathua and Samba districts.
- The militancy that began in Kashmir in the early 1990s had spread to the adjoining Doda district by mid 1990s.
- Contribution:
- During the peak of militancy in most parts of Jammu division, especially areas falling in Chenab Valley and Pir Panjal regions, the hills of Udhampur, and Reasi and Kathua districts, the VDCs played a significant role in combating militancy.
- They were the most-feared armed groups among militants in areas where poor road networks delayed the arrival of security forces.
- The villagers, well-versed with the local topography, averted many militant attacks and helped in their capture and killings.
- During the peak of militancy in most parts of Jammu division, especially areas falling in Chenab Valley and Pir Panjal regions, the hills of Udhampur, and Reasi and Kathua districts, the VDCs played a significant role in combating militancy.
- Issues Associated:
- Along with the successes, the VDCs also faced allegations of human rights violations and other crimes, including murder, rape and extortions.
- Recent Developments:
- The VDCs have now been renamed as Village Defence Guards (VDG). The new scheme to set up VDGs in vulnerable areas of J&K was approved by the Union Ministry of Home Affairs in March 2022.
- The VDGs will function under the direction of the Senior superintendent of police (SSP)/superintendent of police (SP) of the district concerned.
- Similarities and Differences in VDC and VDG:
- Similarity: Like a VDC member, each VDG will be provided a gun and 100 rounds of ammunition.
- Difference: Under the new scheme, the persons leading the VDGs will be paid Rs 4,500 per month by the government, while others will get Rs 4,000 each.
- In the VDCs, only the Special Police Officers (SPOs) leading them were provided a remuneration of Rs 1,500 monthly.
Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
UNSC 1267 Committee
The ISIL and Al Qaida Sanctions Committee of the UNSC (1267 Committee) has placed Abdul Rehman Makki - the key planner of the Pakistan-based Lashkar-e-Taiba (LeT), on its sanctions list.
The move was made possible after China withdrew the “technical hold” that it had imposed in June 2022 when the US and India tried to get Makki on the global terror blacklist.
Read More - India-US proposed to list Makki under UNSC 1267 Committee
IT Amendment Rules 2022
Under the notified amendments to the IT Rules, 2021, MeitY proposed a draft rule [Rule 3(1)(b)(v)] under which social media platforms will have to take down content that has been “fact-checked” as false by the PIB’s (Press Information Bureau) fact check unit.
The notified amendments to IT Rules 2021 aim to impose a legal obligation on intermediaries to make reasonable efforts to prevent users from uploading certain categories of harmful/unlawful content. The new provision will ensure that the intermediary’s obligation is not a mere formality.
Read More - Amendments to the Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021
Windfall Tax
The Government has reduced the windfall profit tax levied on domestically-produced crude oil as well as on the export of diesel and Aviation Turbine Fuel (ATF), in line with softening international oil prices.
Windfall taxes are designed to tax the profits a company derives from an external, sometimes unprecedented event. These profits can’t be attributed to something the firm actively did, like an investment strategy or an expansion of business but are rather unearned and unanticipated gains.
The government levies tax on windfall profits made by oil producers on any price they get above a threshold of USD 75 per barrel. The levy on fuel exports is based on margins that refiners earn on overseas shipments.
Read More - Windfall Tax
Saudi and Houthi Rebels Revive Talks
Amid Yemen's longest ever pause in fighting - more than 9 months - Saudi Arabia and Iran-backed Houthi rebels have revived back-channel talks in an informal ceasefire.
The roots of the Houthi movement can be traced to “Believing Youth”, a Zaydi (oldest branch of the Shia sect) revivalist group founded by Hussein al-Houthi and his father, Badr al-Din al-Houthi (early 1990s). However, the movement turned political and started attacking the “corrupt” regime of Ali Abdullah Saleh (in Yemen) and his support for the US’ war on terror.
The rapid rise of the Houthis in Yemen set off alarm bells in Saudi Arabia which saw them as Iranian proxies which led to Saudi begin a military campaign in Yemen in March 2015.
Read More - Houthi Rebels, India’s Operation Rahat in Yemen