Maps
Geography
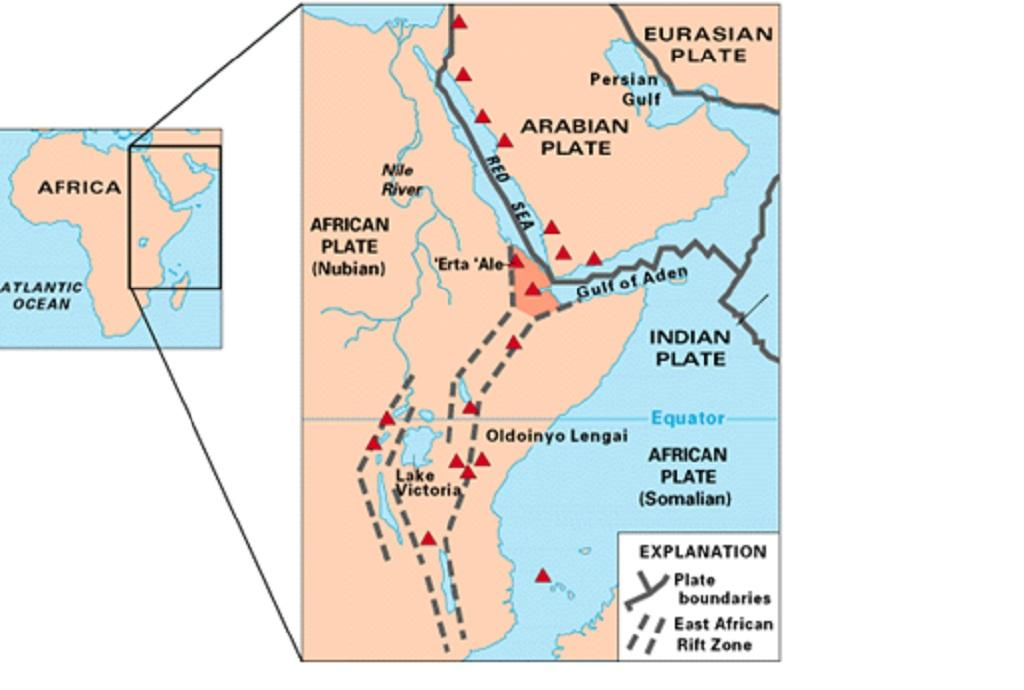
Africa's Rift Valley and the Creation of a New Ocean Basin
For Prelims: Red Sea, Rift Valley, Nubian African Plate, Arabian Plate, Gulf of Aden.
For Mains: Tectonic Plates, Factors Responsible for Africa’s Rifting Plates.
Why in News?
In 2020, a study revealed that the gradual separation of the African continent is leading to the formation of a new ocean basin.
- The division of the continent is connected to the East African Rift (also called the Great Rift Valley), a crack that stretches 56 kilometres and appeared in the desert of Ethiopia in 2005, triggering the formation of a new sea.
What are the Factors Responsible for Africa’s Rifting Plates?
- Factor:
- The three plates — the Nubian African Plate, Somalian African Plate and Arabian Plate — are separating at different speeds.
- The Arabian Plate is moving away from Africa at a rate of about an inch per year, while the two African plates are separating even slower, between half an inch to 0.2 inches per year.
- In the past 30 million years, the Arabian Plate has been gradually moving away from Africa, which has already led to the creation of the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden.
- Possible Outcome:
- As the Somali and Nubian tectonic plates continue to pull apart from each other, a smaller continent will be created from the rift, which will include present-day Somalia and parts of Kenya, Ethiopia, and Tanzania.
- The Gulf of Aden and the Red Sea will eventually flood into the Afar region in Ethiopia and the East African Rift Valley, leading to the formation of a new ocean.
- This new ocean will result in East Africa becoming a separate small continent with its own unique geographic and ecological characteristics.
- The necessary separation of the Somali and Nubian tectonic plates will take 5 to 10 million years to create a new ocean basin.
- Current Situation:
- While the rifting process has been occurring for some time, the potential division made headlines worldwide in 2018 when a large crack emerged in the Kenyan Rift Valley.
What are the Opportunities and Challenges of this Rifting?
- Opportunities:
- The emergence of new coastlines will unlock a myriad of opportunities for economic growth in countries (e.g., landlocked countries, such as Uganda and Zambia), that will have access to new ports for trade, as well as fishing grounds and subsea internet infrastructure.
- Challenges:
- Displacement and Habitat Loss: Displacement of communities, settlements, and habitat loss of various flora and fauna are consequences that will lead to environmental degradation.
- The necessary evacuation of people and the potential loss of lives will be an unfortunate cost of this natural phenomenon.
- As of 2015, more than 15 million people were internally displaced in Africa, according to the United Nations Environment Programme report on displacement and environment.
- Pressure on Natural Resources: Rapid urbanisation and increased settlements will put pressure on natural resources, leading to a scarcity of water, energy, and food.
- Uncontrolled waste disposal will also be a significant concern.
- New Faults: The separation of the Nubian and Somali plates can result in the formation of new faults, fissures, and cracks or the reactivation of pre-existing faults, leading to seismic activity.
- Displacement and Habitat Loss: Displacement of communities, settlements, and habitat loss of various flora and fauna are consequences that will lead to environmental degradation.
What is Rifting?
- The Earth's lithosphere is divided into several tectonic plates that move in relation to each other at varying speeds.
- Tectonic forces not only move the plates but also have the potential to cause them to rupture, resulting in the formation of a rift and potentially leading to the creation of new plate boundaries.
- Rifting refers to the geological process in which a single tectonic plate is split into two or more plates separated by divergent plate boundaries.
- This process leads to the emergence of a lowland region known as a rift valley.
- Example: Narmada Rift Valley(India), Baikal Rift Valley(Russia).
What is Great Rift Valley?
- The Great Rift Valley is a massive geological formation that stretches around 6,400 kilometers from northern Syria to central Mozambique in East Africa.
- The valley is home to the Jordan River, which flows through the Jordan Valley and eventually empties into the Dead Sea on the border between Israel and Jordan.
- The Gulf of Aden is an eastward continuation of the Rift, and from there it extends southeastward as part of the mid-oceanic ridge of the Indian Ocean.
- In eastern Africa, the valley divides into the Eastern Rift and the Western Rift. The Western Rift, also known as the Albertine Rift, contains some of the deepest lakes in the world.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. The Narmada river flows to the west, while most other large peninsular rivers flow to the east. Why? (2013)
1. It occupies a linear rift valley.
2. It flows between the Vindhyas and the Satpuras.
3. The land slopes to the west from Central India.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) None
Ans: (a)
Social Issues
Reservation for Women in Politics
For Prelims: Right to Equality, Women Reservation bill, constitutional provisions related to women empowerment.
For Mains: Issue of Under-representation of Women in Politics, Issues Related to Women, Women's Issues, Inclusive Growth, Human Resource, Government Policies & Interventions.
Why in News?
A political party recently called for the long-delayed Women's Reservation Bill to be introduced in Parliament.
- The Rajya Sabha passed the Women's Reservation Bill on 9 March 2010. However, the Lok Sabha never voted on the bill. The bill lapsed since it was still pending in Lok Sabha.
What is the Background of the Reservation for Women in Politics in India?
- The issue of reservation for women in politics can be traced back to the Indian national movement. In 1931, in their letter to the British Prime Minister, submitting the official memorandum jointly issued on the status of women in the new Constitution by three women’s bodies, leaders Begum Shah Nawaz and Sarojini Naidu.
- The National Perspective Plan for Women recommended in 1988 that reservation be provided to women right from the level of the panchayat to that of Parliament
- These recommendations paved the way for the historic enactment of the 73rd and 74th amendments to the Constitution which mandate all State governments to reserve one-third of the seats for women in Panchayati Raj Institutions and one-third of the offices of the chairperson at all levels of the Panchayati Raj Institutions, and in urban local bodies, respectively. Within these seats, one-third are reserved for Scheduled Caste/Scheduled Tribe women.
- Many States such as Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand and Kerala have made legal provisions to ensure 50% reservation for women in local bodies.
What is Women Representation Bill?
- About the Bill:
- The Women’s Reservation Bill proposes to reserve 33% of seats in the Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assemblies for women.
- Reserved seats may be allotted by rotation to different constituencies in the state or union territory.
- Reservation of seats for women shall cease to exist 15 years after the commencement of this Amendment Act.
- Need:
- According to Global Gender Gap Report 2022, India ranks 48th out of 146 in Political Empowerment (Percentage of Women in Parliament and in Ministerial Positions) dimension.
- Notwithstanding its rank, its score is quite low at 0.267. Some of the best-ranking countries in this category score much better. For instance, Iceland is ranked 1 with a score of 0.874 and Bangladesh is ranked 9 with a score of 0.546.
- Women’s right to self-representation and self-determination;
- The various surveys do indicate that women representatives from Panchayati Raj have worked commendably in the development and overall well-being of society in villages and many of them would definitely want to work on the larger scale, however, they face various challenges in the political structure prevalent in India.
- According to Global Gender Gap Report 2022, India ranks 48th out of 146 in Political Empowerment (Percentage of Women in Parliament and in Ministerial Positions) dimension.
- Arguments Against the Bill:
- Women are not a homogeneous community say like, a caste group. Therefore, the same arguments made for caste-based reservations cannot be made for women.
- Reserving seats for women is opposed by some who claim that doing so violates the Constitution's guarantee of equality. If there is a reserve, they claim, women won't be competing on merit, which could decrease their status in society.
- Arguments in Favour of the Bill:
- Affirmative action is necessary to better the condition of women, as political parties are inherently patriarchal.
- Women are still under-represented in Parliament, and reservations will ensure that women form a strong lobby to fight for issues that are often ignored.
- More women in decision-making positions are needed to address the high percentage of crimes against women, low participation of women in the workforce, low nutrition levels, and skewed sex ratio.
What is the Status of Women Representation in Politics in India?
- Prior to Independence:
- Patriarchal social norms and mindsets have historically allowed women to be marginalized and exploited in India.
- Beginning of social reforms and involvement in the struggle for freedom: The Indian freedom movement, which began with the swadeshi in Bengal (1905-08), also saw the impressive participation of women, who organized political protests, mobilized resources, and held leadership positions in those movements.
- Post Independence:
- India's Constitution stipulated that all political, social, and economic spheres would treat men and women equally.
- At present, only about 14.4% of the members of the Indian Parliament are women, the highest so far. According to the Inter-Parliamentary Union, India has a fewer percentage of women in the lower House than its neighbors such as Nepal, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, and Bangladesh.
- As per the latest Election Commission of India (ECI) data as of October 2021, Women represent 10.5% of the total members of the Parliament.
- The scenario for women Members of Legislative Assemblies (MLAs) across all state assemblies in India is even worse, with the national average being a pitiable 9%. In the last 75 years of independence, women’s representation in Lok Sabha has not even increased by 10%.
What are the Criteria to Evaluate Women's Political Participation in India?
- Women as Voter:
- Almost as many women as men cast ballots in the most recent Lok Sabha election in 2019, marking a turning point in India's journey towards gender equality in politics and what has been dubbed a "quiet revolution of self-empowerment." There are many reasons for the growing participation, notably during the 1990s.
- Women as Candidates:
- Generally, the proportion of female candidates in parliamentary elections has increased over time but has remained low when compared to male candidates. Less than 9% of the 8,049 candidates running in the 2019 Lok Sabha elections were female.
How can Women's Representation in Politics be Improved in India
- Women's representation in politics in India has been a topic of discussion for several years, and although progress has been made, there is still a long way to go. Here are some ways forward to improve women's representation in politics in India:
- Reservation of Seats: The reservation of seats for women in local bodies and legislative assemblies has been a successful way to increase women's representation in politics. More such reservation policies could be implemented to provide women with more opportunities to participate in decision-making processes.
- Increasing Awareness and Education: Creating awareness among women about their rights and the importance of their participation in politics is essential. Educational programs and awareness campaigns can help to increase women's political participation.
- Addressing Gender-based Violence and Harassment: Gender-based violence and harassment are major obstacles to women's participation in politics. Addressing these issues through policy and legal measures can create a safer and more supportive environment for women in politics.
- Reforms in the Electoral Process: Reforms such as introducing proportional representation and preferential voting systems can help to increase women's representation in politics by ensuring that more women get elected.
- These are only a few approaches to increase the number of women in Indian politics. To effect long-lasting change, a multifaceted strategy addressing multiple challenges is required.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. “The reservation of seats for women in the institutions of local self-government has had a limited impact on the patriarchal character of the Indian Political Process.” Comment. (2019)
Science & Technology
Green and Self-Powered Desalination Plant in Lakshadweep
For Prelims: National Institute of Ocean Technology, Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion Plant, Deep Sea Mining, Deep Ocean Mission,
For Mains: Significance of harnessing Ocean Thermal Energy, Deep Ocean Mission (DOM), Government Policies & Interventions, Scientific Innovations.
Why in News?
Recently, the National Institute of Ocean Technology (NIOT), an autonomous institute under the Union Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) is establishing a Green and Self-powered Desalination Plant in Lakshadweep.
- The NIOT is working on an initiative to provide potable water in six islands of Lakshadweep using Low Temperature Thermal Desalination (LTTD) technology. The NIOT is now trying to make this process emission-free.
- Currently, the desalination plants, each of which provides at least 100,000 litres of potable water every day, are powered by diesel generator sets.
What is the Green and Self-powered Desalination Plant?
- About:
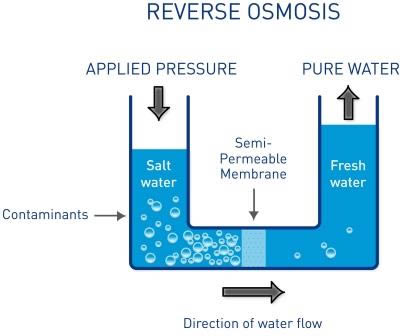
- The proposed desalination plant will use a combination of renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and wave energy to power the plant. The plant will be equipped with reverse osmosis (RO) technology to desalinate seawater and produce potable water. The NIOT plans to set up the plant in one of the islands, where there is a high potential for renewable energy generation.
- The plant is the first of its kind in the world as it will generate drinking water from sea water using indigenous technology, green energy and environmentally friendly processes and it is self-powered.
- Need:
- The process of LTTD is not fossil-fuel free and also consumes diesel and works by diesel generator sets, a precious commodity in the islands that has to be shipped from the mainland critical for powering the electric grid.
What is Low Temperature Thermal Desalination Technology?
- LTTD is a desalination technique that turns seawater into drinkable water.
- This method is based on the idea that ocean water 1,000 to 2,000 feet below the surface is 4–8°C colder than surface water. Therefore, a tank is used to collect and apply high pressure to salty surface water (via an external power source).
- The vaporized water under pressure is contained in tubes or a chamber. Cold ocean water is drawn up via these tubes, where the vapour condenses to create fresh water and the salt that results is diverted away and the condensed fresh water can be used for drinking.
What is Desalination Plant?
- A desalination plant turns salt water into water that is fit to drink.
- Desalination is the process of removing salts from water to produce water that meets the quality (salinity) requirements of different human uses.
- Most commonly used technology for the process is reverse osmosis.
- An external pressure is applied to push solvents from an area of high-solute concentration to an area of low-solute concentration through a semi-permeable membrane.
- The microscopic pores in the membranes allow water molecules through but leave salt and most other impurities behind, releasing clean water from the other side.
- These plants are mostly set up in areas that have access to sea water.
Conclusion
- The successful implementation of NIOT's self-powered desalination plant in Lakshadweep will require a concerted effort from all stakeholders involved and the project can become a sustainable solution to the water scarcity problem in the region and a model for other coastal communities facing similar challenges.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Where was the first desalination plant in India to produce one lakh litres freshwater per day based on low temperature thermal desalination principle commissioned? (2008)
(a) Kavaratti
(b) Port Blair
(c) Mangalore
(d) Valsad
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- The National Institute of Ocean Technology (NIOT), Chennai has developed the world’s first Low Temperature Thermal Desalination (LTTD) plant in Kavaratti, the capital of Lakshadweep to cater to the requirements of the local population of Karavatti, Minicoy and Agatti.
- The reverse osmosis, a membrane process which is globally accepted technology suitable for desalination of saline water, is quite different from LTTD technology.
- The LTTD is a process under which the warm surface sea water is flash evaporated at low pressure and the vapour is condensed with cold deep-sea water.
- The LTTD technology does not require any chemical pre and post-treatment of seawater and thus the pollution problems are minimal and the process is suitable for island territories. Since no effluent treatment is required, it gives less operational maintenance problems compared to other desalination processes. Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Indian Economy
Trade Infrastructure for Export Scheme
For Prelims: Trade Infrastructure for Export Scheme (TIES), PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan (NMP), Duty Drawback Scheme, Russia-Ukraine War, Weaponization of Supply Chain, Special Economic Zones.
For Mains: Major Government Initiatives to Promote Export Growth, Challenges Related to Indian Export Growth.
Why in News?
The Department of Commerce, Government of India, has implemented the Trade Infrastructure for Export Scheme (TIES) to facilitate the growth of exports by creating appropriate infrastructure.
What are the Major Government Initiatives to Promote Export Growth?
- TIES Scheme:
- The TIES scheme provides grants-in-aid to central/state government-owned agencies or their joint ventures for infrastructure projects with significant export linkages.
- The infrastructure includes Border Haats, Land customs stations, quality testing and certification labs, cold chains, trade promotion centres, export warehousing and packaging, Special Economic Zones, and ports/airports cargo terminuses.
- The TIES scheme provides grants-in-aid to central/state government-owned agencies or their joint ventures for infrastructure projects with significant export linkages.
- PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan (NMP):
- The PM Gati Shakti NMP is a digital platform that integrates geospatial data related to infrastructure in the country and planning portraits of various ministries/departments of the government.
- This digital system helps in data-based decision-making for the synchronised implementation of infrastructure projects, aiming to reduce logistics costs and support economic activity in the country.
- The PM Gati Shakti NMP is a digital platform that integrates geospatial data related to infrastructure in the country and planning portraits of various ministries/departments of the government.
- Duty Drawback Scheme:
- The Duty Drawback Scheme rebates the incidence of customs duties on imported inputs and central excise duties on domestic inputs used in the manufacture of export goods.
- This scheme is operated in terms of provisions of the Customs Act, 1962, read with the Customs and Central Excise Duties Drawback Rules, 2017.
- The Duty Drawback Scheme rebates the incidence of customs duties on imported inputs and central excise duties on domestic inputs used in the manufacture of export goods.
What are the Challenges Related to Indian Export Growth?
- Rising Protectionism and Deglobalisation: Countries around the globe are moving towards protectionist trade policies due to disrupted global political order (Russia-Ukraine War) and weaponization of supply chain, that is in way shrinking India’s export capacities.
- Lack of Basic Infrastructure: India’s manufacturing sector lacks sufficient manufacturing hubs, internet facilities and transportation are costly when compared to developed nations which is a huge deterrence to Industries.
- India uses only 4.3% of its GDP for infrastructure construction each year, as compared to China’s 20% of its GDP. For infrastructure, Rs 10 lakh crore (3.3% of GDP) was allocated in the budget 2023-24, an increase of three times from 2019.
- Uninterrupted power supply is another challenge.
- Lack of Innovation Due to Low Spending On R&D: Currently, India spends about 0.7% of GDP on research and development. This prevents the manufacturing sector from evolving, innovating and growing.
Way Forward
- Filling Up Infrastructural Gaps: A robust infrastructure network - warehouses, ports, testing labs, certification centres, etc. will help Indian exporters compete in the global market.
- It also needs to adopt modern trade practices that can be implemented through the digitisation of export processes. This will save both time and cost.
- Exploring Joint Development Programmes: Amidst a wave of deglobalisation and slowing growth, exports cannot be the sole engine of growth.
- India can also explore joint development programmes with other countries in sectors like space, semiconductor, solar energy to improve India’s medium-term growth prospects.
- Frontlining MSME Sector: Currently, MSMEs contribute to one-third of the country's GDP, account for 48% of exports making them key players in achieving ambitious export targets.
- It is important for India to link Special Economic Zones with the MSME sector and incentivize small businesses.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q1. Increase in absolute and per capita real GNP do not connote a higher level of economic development, if (2018)
(a) Industrial output fails to keep pace with agricultural output.
(b) Agricultural output fails to keep pace with industrial output.
(c) Poverty and unemployment increase.
(d) Imports grow faster than exports.
Ans: (c)
Q2. The SEZ Act, 2005 which came into effect in February 2006 has certain objectives. In this context, consider the following: (2010)
- Development of infrastructure facilities.
- Promotion of investment from foreign sources.
- Promotion of exports of services only.
Which of the above are the objectives of this Act?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Q3. A “closed economy” is an economy in which (2011)
(a) the money supply is fully controlled
(b) deficit financing takes place
(c) only exports take place
(d) neither exports or imports take place
Ans: (d)
International Relations
China, India and the Promise of the Power
Prelims: China, India and the Promise of the Power, SCO, G-20, GDP.
Mains: China, India and the Promise of the Power.
Why in News?
With India’s presidency of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) and the G-20 , its focus is also on China.
What are the Focus Areas of China’s Development?
- Steady Growth:
- In 2022, China’s economy grew by 3%.
- China’s GDP (Gross Domestic Product) increased to 121 trillion yuan (approximately USD 18 trillion), registering an annual growth rate of 5.2% over the past five years.
- People’s Well-Being:
- As a result of continued efforts of the past eight years, China has historically resolved absolute Poverty, with the alleviation of close to 100 million rural residents from poverty.
- Over 70% of the government’s expenditure went toward ensuring people’s well-being.
- Win-Win Cooperation:
- In the period 2013-2021, China’s contribution to global economic growth averaged 38.6%, higher than that of G7 countries combined (25.7%).
- Ever since the Chinese President proposed the Global Development Initiative (GDI) in a speech at the United Nations General Assembly in 2021, more than 100 countries have expressed their support and over 60 countries have joined the Group of Friends of the GDI.
What is the Scenario of Trade between India and China?
- China is India’s second biggest trading partner after the US.
- China and India are important trading partners, with bilateral trade volume reaching USD 135.984 billion in 2022.
- Though there is a trade deficit, India’s import of equipment and materials from China does reduce the overall cost of “Made-in-India” products, benefits Indian downstream industries and consumers, enhances the competitiveness of Indian exports, and in turn facilitates India’s integration into global industrial and supply chains.
- The Chinese market is open to India, and the Chinese side is happy to see more high-quality Indian goods, cultural and other products entering the Chinese market.
- Investments by Chinese enterprises have created a large number of jobs for the Indian people and contributed to India’s economic development.
Way Forward
- The development and revitalisation of China and India embody a boost to the force of developing countries; it is one that will change the destiny of a third of the world’s population and have bearing on the future of Asia and beyond.
- As two neighboring and ancient civilisations, with a combined population of 2.8 billion, China and India are representatives of developing countries and emerging economies.
- India and China are both in the process of national rejuvenation and a crucial period of modernisation where challenges need to be overcome and problems need to be solved.
- China and India have far more common interests than differences.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. “China is using its economic relations and positive trade surplus as tools to develop potential military power status in Asia”. In the light of this statement, discuss its impact on India as her neighbour. (2017)
Important Facts For Prelims
Defence Acquisition Council
Why in News?
The Defence Acquisition Council (DAC) accorded Acceptance of Necessity (AoN) for capital acquisition proposals worth Rs 70,500 crore for the Armed Forces & Indian Coast Guard under ‘Buy Indian-IDDM’ (Indigenously Designed, Developed and Manufactured).
What are the Highlights of Acquisition Proposals?
- Indian Navy:
- Out of the total proposals, Indian Navy proposals constitute more than Rs 56,000 crore, which largely includes indigenous BrahMos cruise missiles, Shakti Electronic Warfare (EW) systems, Utility Helicopters-Maritime among others.
- Air force:
- Long Range Stand-Off Weapon for the Indian Air Force gets a nod, which is to be integrated on SU-30 MKI aircraft.
- Army:
- Also, 155mm/52 Caliber Advanced Towed Artillery Gun System (ATAGS), along with High Mobility & Gun Towing Vehicles will be procured for the Indian Army.
- Hindustan Aeronautics:
- Hindustan Aeronautics is a big beneficiary of this announcement by DAC, as it shall supply Advance Light Helicopters MK-III to the Indian Coast Guard. The Helicopter will be able to carry a suite of surveillance sensors which will enhance the surveillance capabilities, along with giving full night capability and Instrument Flight Rules capability for operations of the Indian Coast Guard.
- The Medium Speed Marine Diesel Engine:
- Under the Make-I category, the Medium Speed Marine Diesel Engine will be manufactured indigenously.
What is the Defense Acquisition Council?
- The DAC is the highest decision-making body in the Defence Ministry for deciding on new policies and capital acquisitions for the three services (Army, Navy and Air Force) and the Indian Coast Guard.
- The Minister of Defence is the Chairman of the Council.
- It was formed, after the Group of Ministers recommendations on 'Reforming the National Security System', in 2001, post Kargil War (1999).
Important Facts For Prelims
Joint Anti-Submarine Warfare Drills
Why in News?
Recently, joint anti-submarine warfare drills are being held by the United States, Canada, India, Japan, and South Korea.
- As a part of it, the exercise named Sea Dragon 23 was started on March 15, 2023 and it aims to strengthen the alliance between the countries to tackle threats from China and North Korea.
How China is Expanding its Maritime Domain?
- China's navy is taking part in joint search and rescue exercises in the Gulf of Oman with Iran and Russia.
- China’s dispute with Japan over tiny islands in the East China Sea has also heated up, with both sides accusing the other of violating their maritime territory.
- China is holding Security Bond-2023 exercises with other nations as well.
What is Sea Dragon 23?
- Sea Dragon 23 is a coordinated anti-submarine warfare exercise being held between the US, Japan, Canada, South Korea, and India.
- The exercise aims to achieve high levels of synergy and coordination between the friendly navies based on their shared values and commitment to an open, inclusive Indo-Pacific region.
- The Indian Navy is represented by a P8I aircraft, along with P8A of the US Navy, P1 from the Japanese Maritime Self Defence Force, CP 140 from the Royal Canadian Air Force, and P3C from the RoKN.
Conclusion
The participation of the Indian Navy in Exercise Sea Dragon 23 reflects its commitment to enhancing its naval capabilities and strengthening cooperation with like-minded nations in the Indo-Pacific region.
Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
BIS Launches ‘Learning Science via Standards’ Series
Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), has launched a new initiative called ‘Learning Science via Standards’, aimed at helping students understand the practical applications of scientific concepts, principles, and laws in the manufacturing, functioning, and testing of products.
It is in line with BIS's earlier ‘Standards Clubs’ initiative, which has already formed over 4200 clubs with more than one lakh student members. Standards Clubs undertake student-centric activities like debates, quiz and competitions, including standards-writing competitions. BIS provides financial support to these clubs for up to three activities in a year.
The ‘Learning Science via Standards’ initiative is expected towards bridging the gap between theory and real-life use of science education and promoting a culture of quality and standardization in the country.
Atal Innovation Mission Launches ATL Sarthi
Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) NITI Aayog launched ATL Sarthi, a comprehensive self-monitoring framework to strengthen the ecosystem of Atal Tinkering Labs (ATL).
AIM is establishing ATLs in schools across India to foster curiosity, creativity, and imagination in young minds; and inculcate skills such as design thinking mindset, computational thinking, adaptive learning, physical computing etc. So far (March 2023), AIM has funded around 10,000 schools to establish ATLs.
ATL Sarthi is a tool to enable the ATLs to be efficient and effective. The initiative has four pillars ensuring the performance enhancement of ATLs through a self-reporting dashboard known as ‘MyATL Dashboard’ and Compliance SOPs for schools to ensure financial and non-financial compliances, on-ground enablement of ATLs in collaboration with relevant local authorities through Cluster-based Approach and providing ownership to schools to analyze their performance through Performance-Enablement (PE) Matrix.
Bumchu Festival: Sikkim
Bumchu is an annual holy water vase ritual commemorated in Tashiding Monastery, one of the most sacred Buddhist pilgrimage sites, located on a hilltop overlooking the Rangeet River in Sikkim.
Bumchu means “pot of sacred water” in Tibetan. The water inside the vase is shared among the worshippers. The water is thought to have healing qualities and to grant luck and riches to those who drink it. The celebration takes place on the 14th and 15th of the first lunar month, which often falls in February or March.
Legend has it that in the eighth century, a great Buddhist guru who brought Buddhism to Tibet, blessed the location of the monastery. Later the monastery was founded in the 17th century.

-01.png)