Governance
National Organ Transplantation Guidelines
Prelims: National Organ Transplantation Guidelines, National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organization, Transplantation of Human Organs Act, 1994.
Mains: Need for Promoting Organ Donations.
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has modified National Organ Transplantation Guidelines, allowing those above 65 years of age to receive an organ for transplantation from deceased donors.
- In India, Transplantation of Human Organs Act, 1994 provides various regulations for the removal of human organs and its storage. It also regulates the transplantation of human organs for therapeutic purposes and for the prevention of commercial dealings in human organs.
What are the Highlights of the New Guidelines?
- Removed Age Cap:
- The upper age limit has been removed as people are now living longer.
- Earlier, according to the NOTTO (National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organization) guidelines, an end-stage organ failure patient above 65 years of age was prohibited from registering to receive the organ.
- The upper age limit has been removed as people are now living longer.
- No Domicile Requirement:
- The ministry has removed the domicile requirement to register as an organ recipient in a particular state under a ‘One Nation, One Policy’ move.
- Now a needy patient can register to receive an organ in any state of his or her choice and will also be able to get the surgery done there.
- No Fees for Registration:
- There will be no registration fee that states used to charge for this purpose, the Centre has asked states that used to charge for such registration to not do so.
- Among the states that sought money for registration were Gujarat, Telangana, Maharashtra, and Kerala.
- Certain states asked for anything between Rs 5,000 and Rs 10,000 to register a patient on the organ recipient waitlist.
Note
- NOTTO is set up under Directorate General of Health Services, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, located in New Delhi.
- National Network division of NOTTO functions as apex centre for all India activities for procurement, distribution and registry of organs and tissues donation and transplantation in the country.
What is the Purpose of New Guidelines?
- The Centre is planning to make changes in the rules of Transplantation of Human Organs (Amendment) Act 2011 towards creating a national policy for transplantation.
- Currently, different states have different rules; the Union government is considering changes to the rules so that there is a standard criterion followed in all states across the country.
- However, Health being a state subject, the rules formed by the central government will not be binding on the states.
- The steps are aimed at better and more equitable access to organs and also to promote cadaver donations, which currently form a minuscule fraction of all organ transplants carried out in India.
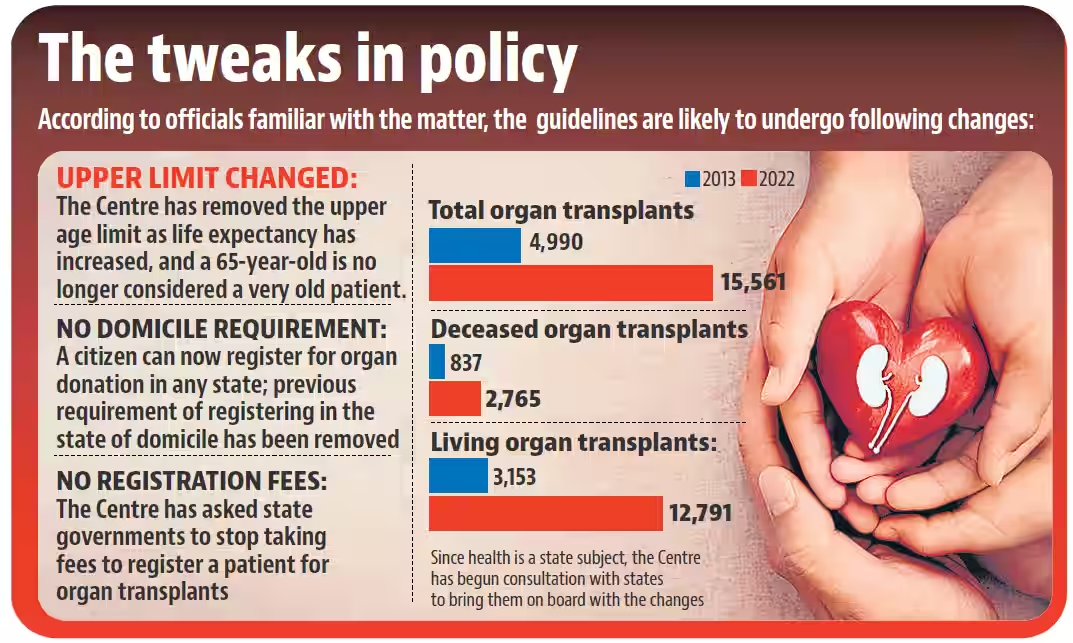
What is the Scenario of Organ Transplantation in India?
- India conducts the third highest number of transplants in the world.
- Organs from deceased donors accounted for nearly 17.8% of all transplants in 2022.
- The total number of deceased organ transplants climbed from 837 in 2013 to 2,765 in 2022.
- The total number of organ transplants – with organs from both deceased and living donors – increased from 4,990 in 2013 to 15,561 in 2022.
- Every year, an estimated 1.5-2 lakh people need a kidney transplant.
- Only around 10,000 got one in 2022. Of the 80,000 people who required a liver transplant, less than 3,000 got one in 2022.
- And, of the 10,000 who needed a heart transplant, only 250 got it in 2022.
Way Forward
- Promoting Organ donations is an important initiative that can save lives and benefit society as a whole.
- By increasing awareness, educating the public, and improving the donation process, we can make organ and tissue donation more accessible and increase the number of potential donors.
- For increasing accessibility of donated organs to weaker sections, the public hospitals need to increase the infrastructural capacity to carry out transplantation and provide affordable proper treatment to the poor.
- It is suggested that cross-subsidization will increase accessibility to the weaker section. For every 3 or 4 transplants, the private hospitals should carry out free of cost transplantation to the section of the population that donates a majority of organs.


Governance
Vibrant Villages Programme
Prelims: ITPB, Vibrant Villages Programme, Shinku-La tunnel, LAC, Centrally Sponsored Scheme.
Mains: Infra Push for the Bordering Villages.
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Cabinet has approved raising of seven new ITBP (Indo-Tibetan Border Police) battalions and allocated Rs 4,800 crore under the Vibrant Villages Programme (VVP) to bolster the social and security framework along the China border.
- The Cabinet has also cleared a 4.1-km Shinku-La tunnel on the Manali-Darcha-Padum-Nimmu axis to allow all-weather connectivity to Ladakh.
What is the Significance?
- It is aimed at strengthening the security grid on the Line of Actual Control (LAC). It will also provide a window for the ITBP to rest, recuperate and train its personnel.
- The decision to raise additional battalions was taken keeping an eye on the need for effective monitoring in the border areas and the battalion.
- The government's decision to approve a financial package for border villages and upgrade security comes at a time when issues with China are still to be resolved along the LAC in Ladakh. PLA troops are still squatting in the Depsang Plains and Demchok. China is also upgrading its infrastructure along the LAC.
What is the Vibrant Villages Programme?
- About:
- It is a Centrally sponsored scheme, announced in the Union Budget 2022-23 (to 2025-26) for development of villages on the northern border, thus improving the quality of life of people living in identified border villages.
- It will cover the border areas of Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim and Ladakh.
- It will cover 2,963 villages with 663 of them to be covered in the first phase.
- Vibrant Village Action Plans will be created by the district adminstration with the help of Gram Panchayats.
- There will not be overlap with Border Area Development Programme.
- Objective:
- The scheme aids to identify and develop the economic drivers based on local, natural, human and other resources of the border villages on the northern border;
- Development of growth centres on ‘hub and spoke model’ through promotion of social entrepreneurship, empowerment of youth and women through skill development and entrepreneurship;
- Leveraging the tourism potential through promotion of local, cultural, traditional knowledge and heritage;
- Development of sustainable eco-agri businesses on the concept of ‘one village-one product’ through community-based organisations, cooperatives, NGOs.
What are the Key Points of the Shinku-La tunnel?
- It is a 4.1-km tunnel on the Nimu-Padam-Darcha Road link to provide all-weather connectivity to the border areas of Ladakh.
- The tunnel will be completed by December 2025.
- It is very important as far as the security and safety of the country is concerned.
- It will also help in the movement of security forces in that region.


Social Issues
Impact of Covid-19 on Human Capital
Prelims: World Bank, Covid-19, Cognitive Deficit.
Mains: Impact of Covid-19 on Human Capital.
Why in News?
Recently, the World Bank has released a report titled- “Collapse and Recovery: How COVID-19 Eroded Human Capital and What to Do”, stating that the Covid-19 caused a massive collapse in human capital, primarily affecting children and young people.
- It analyzed global data on the pandemic’s impacts on young people at key developmental stages: early childhood (0-5 years), school age (6-14 years) and youth (15-24 years).
Note: Human capital consists of the knowledge, skills, and health that people invest in and accumulate throughout their lives, enabling them to realize their potential as productive members of society.
What are the Findings of the Report?
- Impact of Pandemic:
- The Covid-19 caused massive damage to human capital at critical moments in the life cycle, primarily affecting children and young people in underdeveloped and developing countries.
- The development of millions in low- and middle-income countries has been derailed.
- Impact on School Children:
- Preschool-age children in multiple countries have lost more than 34% of learning in early language and literacy and more than 29% of learning in mathematics compared to pre-pandemic cohorts.
- In many countries, even after schools had reopened, preschool enrollment had not recovered by the end of 2021; it was down by more than 10% in multiple countries.
- Children also faced greater food insecurity during the pandemic.
- Reductions in Healthcare:
- Millions of children faced reductions in health care—including missed critical vaccines.
- They also faced more stress in their care environments—orphanhood, domestic violence, suboptimal nutrition—which led to declines in school readiness and declines in social and emotional development.
- Youth Employment:
- Forty million people who would have had a job in the absence of the pandemic did not have one at the end of 2021, worsening youth unemployment trends. Youth earnings contracted by 15% in 2020 and 12% in 2021.
- New entrants with lower education will have 13% fewer earnings during their first decade in the labour market.
- In Brazil, Ethiopia, Mexico, Pakistan, South Africa, and Vietnam 25% of all young people were neither in education, employment, nor training in 2021.
- Challenges in Future:
- The cognitive deficit in today’s toddlers could translate into a 25% decline in earnings at their prime working age.
- Today’s students in low- and middle-income countries could lose up to 10% of their future average annual earnings due to the COVID-related education shocks. Globally, this generation of students risks losing USD 21 trillion in potential lifetime earnings.
- Losses of lifetime earnings at this scale can mean lower productivity, greater inequality, and possibly greater social unrest for decades to come.
What are the Recommendations?
- Countries should act urgently to recover these losses and invest better in their people.
- Human capital is a key driver of poverty reduction and inclusive growth. It is imperative for building resilience in the face of current and future crises and shocks.
- Some of the Policy Actions can include,
- Vaccinations and nutritional supplementation campaigns; increasing coverage of parenting programs; increasing access to pre-primary education, expanding coverage of cash transfers for vulnerable families.
- Increasing instructional time; assessing learning and matching instruction to students’ learning level; and streamlining the curriculum to focus on foundational learning.
- For youth, support for adapted training, job intermediation, entrepreneurship programs, and new workforce-oriented initiatives are crucial.
- In the longer term, countries need to build agile, resilient, and adaptive human development systems that can better prepare for and respond to current and future shocks.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2018)
Human capital formation as a concept is better explained in terms of a process which enables
- individuals of a country to accumulate more capital.
- increasing the knowledge, skill levels and capacities of the people of the country.
- accumulation of tangible wealth.
- accumulation of intangible wealth
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 4
(d) 1, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. COVID-19 pandemic accelerated class inequalities and poverty in India. Comment. (2020)


Biodiversity & Environment
Deep Sea Fish Conservation
Prelims: Purse Seine Fishing, Exclusive Economic Zone, UNCLOS, Total allowable catch
Mains: Purse Seine Fishing Technique and its concerns, Conservation Efforts for Marine Animal Resources
Why in News?
Supreme Court (SC) has given permission to fishermen using Purse Seine Fishing gear to fish beyond territorial waters (12 nautical miles) and within the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) (200 nautical miles) of Tamil Nadu but observing certain restrictions.
- This comes in the backdrop against the banning of purse seine fishing by the Tamil Nadu Government in February 2022.
- SC has restricted the purse seiner to fish on two days, Monday and Thursday from 8am to 6pm revoking the complete ban imposed by Tamil Nadu government.
What are the Concerns?
- Insufficient Conservation Efforts:
- Court’s order seems to be more concerned about regulating fishing with administrative and transparency measures than about the conservation measures and obligations under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS).
- Under UNCLOS, coastal states have sovereign rights to ensure that the living and non-living resources of the EEZ are used, conserved and managed, and not subject to overexploitation.
- In order to prevent overexploitation, coastal States must determine the total allowable catch (TAC) in the EEZ.
- Restricting the purse seiner to fish on two days is not sufficient without regulating fishing methods.
- Threatens Livelihood of Traditional Fishers:
- Purse seiners tend to overfish, unlike traditional fishermen using traditional fish gear, thus endangering the livelihood of the traditional fisher.
- It is a non-targeted fishing gear and catches all sorts of fishes which come in the way of the net, including juveniles. Hence, they are very much detrimental to marine resources.
- Threat to Food Security:
- A major concern is the dwindling availability of oil sardines, a favourite of Kerala fish eaters.
- In 2021, Kerala recorded a catch of just 3,297 tonnes of sardine, a sharp decrease from the haul of 3.9 lakh tonnes in 2012.
- Threatens Endangered Species:
- Non-selective fishing methods by purse seiners resulting in the by-catch of other marine living species (which could include endangered species too) may threaten with a potential trade embargo.
What is UNCLOS?
- The UNCLOS, 1982 is an international agreement that establishes the legal framework for marine and maritime activities.
- It is also known as Law of the Sea. It divides marine areas into five main zones namely- Internal Waters, Territorial Sea, Contiguous Zone, Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) and the High Seas.
- It is the only international convention which stipulates a framework for state jurisdiction in maritime spaces. It provides a different legal status to different maritime zones.
- It provides the backbone for offshore governance by coastal states and those navigating the oceans.
- It not only zones coastal states’ offshore areas but also provides specific guidance for states’ rights and responsibilities in the five concentric zones.
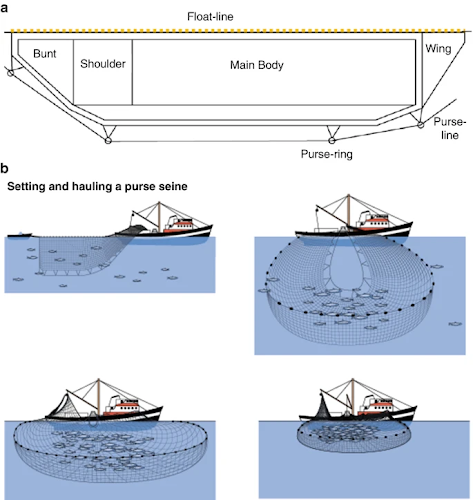
What is Purse Seine Fishing?
- A purse seine is made of a long wall of netting framed with floating and leadline and having purse rings hanging from the lower edge of the gear, through which runs a purse line made from steel wire or rope which allow the pursing of the net.
- The technique is considered to be an efficient form of fishing and has been widely deployed on India’s western coasts.
- It is used in the open ocean to target dense schools of single-species pelagic (midwater) fish like tuna and mackerel.
What are the Conservation Efforts for Marine Animal Resources?
- The United Nations General Assembly passed Resolutions in 1989 and 1991:
- It called for a moratoria on all large-scale pelagic drift net fishing vessels in high seas.
- UN (United Nations) Ocean Conference 2022:
- To ensure global cooperation towards protection and sustenance of the Ocean ecosystem of the world.
- One Ocean Summit:
- Combating illegal fishing, decarbonising shipping and reducing plastic pollution.
- Convention for the Conservation of Southern Bluefin Tuna 1993 (SBT):
- The objective of this Convention is to ensure, through appropriate management, the conservation and optimum utilisation of southern bluefin tuna
- Convention for the Prohibition of Fishing with Long Drift Nets 1989:
- It is a regional convention in the South Pacific to restrict port access for drift net fishing vessels.
- Tarawa Declaration 1989:
- It is a declaration of the South Pacific Forum to prohibit the use of large drift nets or at least call for their prohibition.
Conclusion
Garrett Hardin's concept of the 'Tragedy of the Commons,' which suggests that "Freedom in a commons brings ruin to all," should serve as a compelling argument for authorities, fishermen, particularly purse seiners, to work together and adhere to conservation efforts.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Other than poaching, what are the possible reasons for the decline in the population of Ganges River Dolphins? (2014)
- Construction of dams and barrages on rivers
- Increase in the population of crocodiles in rivers
- Getting trapped in fishing nets accidentally
- Use of synthetic fertilizers and other agricultural chemicals in crop-fields in the vicinity of rivers.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
- Habitat of Ganges River Dolphins is freshwater mainly the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna and Karnaphuli-Sangu River systems of Nepal, India, and Bangladesh. They are essentially blind. They hunt by emitting ultrasonic sounds, which bounces off of fish and other prey, enabling them to “see” an image in their mind.
- As per the study conducted by WWF-India, the causes of decline in population of Gangetic River Dolphins are:
- Construction of dams and barrages on the rivers; hence, 1 is correct.
- Dolphins getting trapped in fishing nets; hence, 3 is correct.
- Use of synthetic fertilizers and other industrial pollutants around the vicinity of rivers. hence, 4 is correct.
- The increased population of crocodiles in the rivers has not been cited as a reason for the decline in population of Ganges River Dolphins. Hence, 2 is not correct. Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. Defining blue revolution, explain the problems and strategies for pisciculture development in India. (2018)


Indian Economy
Current Account Deficit
For Prelims: Current account deficit (CAD), Fiscal Deficit, Government Budgeting, Foreign Exchange Reserves
For Mains: Issues Related to CAD, Recent Status of India’s CAD.
Why in News?
Recently, the government released data showing that India's exports and imports decreased by 6.59% and 3.63%, respectively, in January 2023, there are indications that the country's current account deficit (CAD) will moderate despite the global slowdown triggered by the rising inflation and interest rates.
- The moderation in CAD is expected to be aided by the fall in commodity prices, rising workers remittances and services exports, and abatement of selling pressure by foreign investors.
What is the Current Account Deficit?
- About:
- Current account deficit (CAD) is when the value of a country's imports of goods and services is greater than its exports.
- CAD and fiscal deficit together make up twin deficits that can impact the stock market and investors.
- Fiscal Deficit is the gap between the government’s expenditure requirements and its receipts. This equals the money the government needs to borrow during the year.
- Implication:
- The CAD is significant because it affects the economy, stock markets, and people's investments.
- A lower CAD can boost investor sentiment and make the country's currency more attractive to investors.
- A surplus in the current account indicates that money is flowing into the country, which can boost foreign exchange reserves and the value of the local currency.
- Recent Status of India’s CAD:
- The CAD for the first half of 2022-23 was 3.3% of GDP, but the situation improved in Quarter 3:2022-23 due to lower commodity prices and moderated imports.
- Negative Effects of CAD on Economy:
- Weaker Currency: When a country's imports exceed its exports, it can cause a decrease in demand for its currency, leading to a weaker currency value (depreciation).
- This can make imports more expensive, leading to higher inflation and a reduction in purchasing power.
- Debt Accumulation: If a country is unable to finance its current account deficit with foreign investment, it may need to borrow to cover the gap.
- This can lead to an increase in debt levels, which can further harm the economy.
- Weaker Currency: When a country's imports exceed its exports, it can cause a decrease in demand for its currency, leading to a weaker currency value (depreciation).
How India can Moderate Current Account Deficit?
- Encourage Exports: Increasing exports is one of the most effective ways to reduce CAD.
- The government can provide incentives for export-oriented industries, streamline export procedures and regulations, and negotiate better trade agreements with other countries.
- Promote Import Substitution: Encouraging domestic production of goods that are currently being imported can help to reduce the trade deficit.
- This can be achieved by providing incentives for domestic manufacturers and by imposing tariffs or import duties on certain goods.
- Improve Productivity and Competitiveness: Improving the productivity and competitiveness of the domestic economy can help to increase exports and reduce the trade deficit.
- This can be achieved through various measures such as investments in infrastructure, technology, and education.
Conclusion
The reduction in CAD in January 2023, driven by a fall in imports, is seen as a positive sign by experts, but it needs to be sustained over many more months to alleviate concerns about the country's external account. Maintaining a healthy CAD is important for the value of the currency and the overall health of the economy.
UPSC Civil Services, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. Consider the following actions which the Government can take: (2011)
- Devaluing the domestic currency.
- Reduction in the export subsidy.
- Adopting suitable policies which attract greater FDI and more funds from FIIs.
Which of the above action/actions can help in reducing the current account deficit?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 3 only
(d) 1 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q2. With reference to Balance of Payments, which of the following constitutes/constitute the Current Account? (2014)
- Balance of trade
- Foreign assets
- Balance of invisibles
- Special Drawing Rights
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1, 2 and 4
Ans: (c)


Biodiversity & Environment
Lead Poisoning
Prelims: Lead Poisoning, Lead, anaemia, hypertension, renal impairment, United Nations Environment Programme
Mains: Environmental Pollution & Degradation, Lead Poisoning and related concerns
Why in News?
The widespread use of Lead has resulted in extensive environmental contamination, human exposure and significant public health problems in many parts of the world.
What is Lead Poisoning?
- About:
- Lead poisoning is a type of poisoning that occurs when lead accumulates in the body, often over a period of months or years.
- It is caused by the absorption of Lead in the system and is characterised especially by fatigue, abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhoea, loss of appetite, anaemia, a dark line along the gums, and muscle paralysis or weakness of limbs.
- Children are particularly vulnerable to lead poisoning because their bodies are still developing.
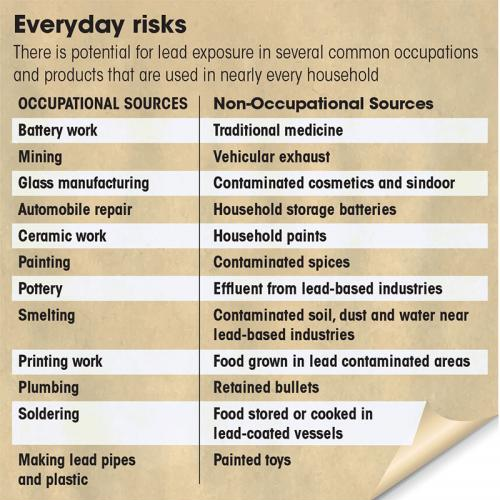
- Source:
What are the Implications of Lead Poisoning?
- High Blood Lead Levels:
- According to a 2020 report by the UN Children’s Fund (UNICEF) and Pure Earth, half the children in India report high blood lead levels.
- The report says 275 million children in India record blood lead levels beyond the tolerable limit of 5 µg/dL.
- Of these, 64.3 million children’s blood lead levels exceed 10 µg/dL.
- In terms of average blood lead levels among the population, some 23 states exceed the 5 µg/dL margin; levels in the remaining 13 states and Union Territories cannot be determined as there is a lack of research and screening mechanisms to collect data.
- According to a 2020 report by the UN Children’s Fund (UNICEF) and Pure Earth, half the children in India report high blood lead levels.
- Disability-Adjusted Life Years:
- According to a 2016 analysis by the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME), Lead toxicity in India contributes to 4.6 million Disability-Adjusted Life Years (number of years lost due to disease burden) and 165,000 deaths annually.
- IHME is an independent population health research center at the University of Washington School of Medicine.
- According to a 2016 analysis by the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME), Lead toxicity in India contributes to 4.6 million Disability-Adjusted Life Years (number of years lost due to disease burden) and 165,000 deaths annually.
- Adverse Health Impact:
- Once lead enters the bloodstream, it goes directly to the brain, particularly in children.
- It can be transferred to the foetus during pregnancy, leading to low birth weight and slow growth. Lead poisoning can cause anemia and various illnesses in children and adults, affecting neurological, skeletal, and neuromuscular systems.
What are the Challenges to Cope with Lead Poisoning?
- Less Attention:
- In India, lead does not get as much attention as other potential public health concerns.
- India lacks systems to screen populations for possible exposure. India has some 48 national referral centres for lead projects where blood lead levels can be tested, but screening is usually done on a voluntary basis or at health camps by non-profits.
- Poor Recycling Laws:
- Many developing countries, including India and under-developing countries have a lack of stringent laws over informal recycling sectors.
- As a result, enormous quantities of (lead)-acid batteries are recovered without using scientific techniques in an unregulated and uncontrolled way.
- Management of lead-acid batteries came under the Batteries (Management and Handling) Rules, 2001. But enforcement capacity to ensure safe and environmentally sound recycling has been inadequate.
- In 2022, The government notified the Battery Waste Management Rules, 2022, but it remains to be seen whether the government can successfully implement this.
- High demand for Cheap Products:
- Many low-cost products in India contain lead, and people may not be willing or able to pay more for lead-free alternatives.
Way Forward
- Regular screening and testing of lead sources will inform about region-wise prevalence and help tailor interventions, such as “regulations and enforcement, changes in industry practices, training of government officials to assess lead contamination, and changes in public education and consumer behaviour.
- As recycling of used lead-acid batteries risks exposure, discouraging informal operations and regulating the sector will help.
- India must enhance capacity for testing, currently done for blood lead levels, and the government should create facilities for blood lead level screenings at every district hospital.
- Lead poisoning needs to be a part of the narrative of India’s health status.
- There is a need to devise strategies on a state level, through regional bureaucracy, local press and vernacular language to have tangible impact.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Lead, ingested or inhaled, is a health hazard. After the addition of lead to petrol has been banned, what still are the sources of lead poisoning? (2012)
- Smelting units
- Pens and pencils
- Paints
- Hair oils and cosmetics
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)


Biodiversity & Environment
Marine Spatial Planning Framework
Prelims: MSP framework, Blue Economy, Exclusive Economic Zone.
Mains: Government Policies & Interventions, Significance of the Oceans, India-Norway Cooperation
Why in News?
Puducherry has launched the country’s first Marine Spatial Planning (MSP) framework as part of a pact under the Indo-Norway Integrated Ocean Initiative.
- Puducherry and Lakshadweep were chosen as coastlines to pilot the MSP initiative after a 2019 Memorandum of understanding (MoU) between India and Norway.
What is Marine Spatial Planning?
- MSP is an ecosystem-based spatial planning process for analysing current and anticipated ocean and coastal uses and identifying areas most suitable for various activities.
- It provides a public policy process for society to better determine how the ocean and coasts are sustainably used and protected - now and for future generations.
What is this Framework About?
- Ministry of Earth Sciences oversees the implementation of the MSP through National Centre for Coastal Research (NCCR), the National Centre for Sustainable Coastal Management, the Puducherry Coastal Zone Management Authority and Department of Science, Technology and Environment, Puducherry in collaboration with Norwegian Environment Agency.
- The two nations have agreed to provide continued assistance towards the sustainable use of ocean resources, with the aim of promoting economic and social development in coastal regions.
- After successful implementation of pilot project in Lakshadweep and Puducherry, the framework can be replicated to other coastal regions of the country.
What is the Significance of MSP Framework?
- An Ecosystem-based Approach: It aims to simultaneously enhance ocean health and economic growth in a manner consistent with principles of social equity and inclusion.
- Vital Governance Tool: it is a tool to ensure the emergence of a Blue economy characterised by a sustainable and equitable ocean resource management, instead of an environmentally unsustainable “brown economy.
- Tool in Balancing Conflicting Interests: It can be used to balance the demands for tourism growth with the livelihood concerns of fisher communities in terms of the use of coastal land and marine waters.
- In line with Blue Economy Policy: Blue economy policy seeks to enhance contribution of coastal areas to GDP while preserving Marine biodiversity.
- Currently, the blue economy comprises 4.1% of India’s economy.
- Vast Coastline: With a coastline of nearly 7500 kilometres, India has a unique maritime position with respect to environmental responsibilities and economic growth opportunities.


Important Facts For Prelims
HAL Ties Up HENSOLDT For Tech Transfer
Why in News?
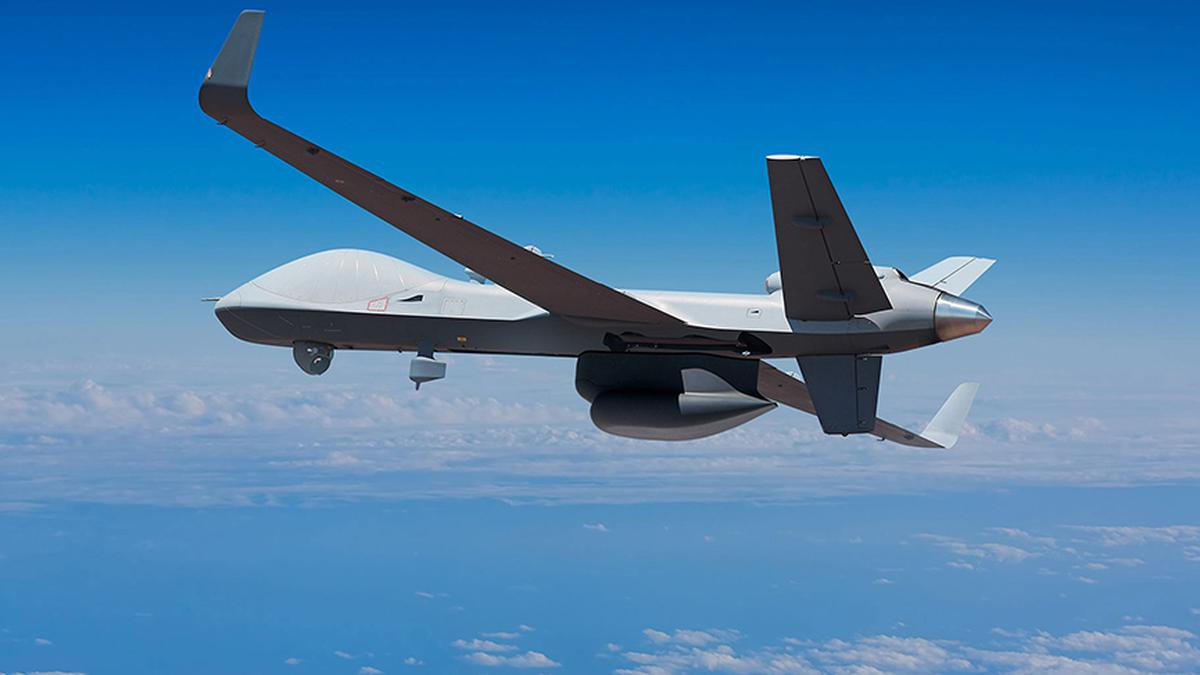
Hindustan Aeronautics Ltd (HAL) will provide Maintenance, Repair and Overhaul (MRO) services for engines of US’s MQ-9B Remotely Piloted Aircraft System as India is in discussions to buy 30 MQ-9B drones to enhance its surveillance capabilities along the China border and the Indian Ocean region.
- In another announcement, Germany based HENSOLDT and HAL announced a collaboration agreement covering design/IPR Transfer for design and manufacturing of Obstacle Avoidance System (OAS) for Indian helicopters.
What is the MQ-9B Sea Guardian?
- The MQ-9B Sea Guardian has changed the game in maritime domain awareness. It’s the first unmanned aerial system of its kind that can search the ocean surface and the depths in support of naval intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance.
- It is designed to fly over the horizon via SATCOM for up to 30 hours (depending on configuration) in all types of weather.
- General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, Inc (GA-ASI) of US is the manufacturer of the MQ-9Bs.
- Indian Navy operates two MQ-9B Sea Guardians taken on lease in 2020.
What are the Highlights Related to Tech-Transfer Between India and Germany?
- HAL and HENSOLDT will collaborate on the design and manufacturing of Obstacle Avoidance Systems (OAS) for Indian helicopters, primarily the Advanced Light Helicopter (ALH), with potential future exports.
- The OAS system will provide smart visual cues to pilots to reduce their workload, increasing flight safety, and mission effectiveness, particularly in crucial mission phases under adverse visual conditions.
- The system is a LiDAR-based sensor with synthetic vision and 3D conformal symbology to detect objects and terrain, providing assistance to the pilot through safety lines, enhancing situational awareness to increase flight safety.
What is LiDAR Technology?
- LiDAR, or light detection and ranging, is a popular remote sensing method used for measuring the exact distance of an object on the earth’s surface.
- LiDAR uses a pulsed laser to calculate an object’s variable distances from the earth surface.
- These light pulses — put together with the information collected by the airborne system — generate accurate 3D information about the earth surface and the target object.


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Aadi Mahotsav
Recently, the Prime Minister of India inaugurated the tribal festival "Aadi Mahotsav", a two-week-long exhibition in New Delhi.
The Mahotsav celebrates the spirit of tribal culture, crafts, cuisine, commerce and traditional art is an annual initiative of the Tribal Cooperative Marketing Development Federation Limited (TRIFED) under the Ministry of Tribal Affairs.
TRIFED was established in 1987 under the Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act, 1984 by the Government of India as a National level Cooperative body under the administrative control of the then Ministry of Welfare of India, with the basic mandate of bringing about socio-economic development of tribals of the country by institutionalizing the trade of Minor Forest Produce (MFP) & Surplus Agricultural Produce (SAP) collected/ cultivated by them.
Read More: TRIFED, Initiatives & Constitutional Provisions Related to Tribes in India
Snow Leopard
A snow leopard has been sighted for the first time at a height of about 11,120 feet in the Darma valley in Uttarakhand's Pithoragarh district.
Snow leopards are also known as “Ghost of Mountains”. They act as an indicator of the health of the mountain ecosystem in which they live, due to their position as the top predator in the food web. They are listed as vulnerable on the International Union for Conservation of Nature's (IUCN) Red List. They are listed in appendix I of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) and Schedule-I of the Indian Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
They have a vast but fragmented distribution across the mountainous landscape of central Asia, which covers different parts of the Himalayas such as Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and Sikkim.
Read More: Indian Initiatives to Protect Snow Leopard
International Engineering and Technology Fair (IETF) 2023
 |
 |
The President of India inaugurated the International Engineering and Technology Fair (IETF) 2023 in New Delhi.
IETF is a platform for buyer-seller meets, international conferences and seminars, business networking, technology assessments, strategic partnerships, vendor development and is attended by visitors from around the globe. The event is not just a celebration of India’s growth story in the engineering and manufacturing sector, but also a testimony to the nation’s collaboration with the best in the world in advanced technologies.
IETF-2023 covers 11 areas of emerging technologies that would have a profound impact on our economy and society.
Read More: India and Advanced Computing Technologies
Exercise Dharma Guardian
The 4th edition of the joint military exercise, Exercise Dharma Guardian, between India and Japan is being conducted in Japan from 17th February to 2nd March 2023.
The exercise is an annual training event with Japan and is crucial and significant in terms of security challenges faced by both nations in the backdrop of the current global situation.
The exercise will further enhance the level of defence co-operation between The Indian Army and Japanese Ground Self Defence Forces, furthering the bilateral relations between the two nations.
Other Military Exercises between India and Japan are JIMEX (naval), SHINYUU Maitri (Air Force) and Exercise Veer Guardian.