Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) Summit
For Prelims: Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) Summit, AIRAWAT, NITI Aayog, Cloud Computing Platform
For Mains: Significance of GPAI Summit for the Better Regulation and Functioning of Artificial Intelligence Technology.
Why in News?
The Prime Minister of India inaugurated the Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) Summit.
- India is the lead chair of GPAI in 2024. The GPAI is an alliance of 28 countries; the European Union adopted the ‘New Delhi Declaration’ of the GPAI.
What are the Key Highlights of the GPAI Summit?
- The Prime Minister of India discussed the national AI portal, highlighting the AIRAWAT initiative and raising concerns over the potential misuse of deep fake technology.
- YUVAi was prominently featured at the GPAI Summit, and the winners of the YUVAi initiative and start-ups showcased their AI models and solutions.
- The Prime Minister suggested using AI to make digital services available in local languages to increase digital inclusion.
- Responsible AI, data governance, future of work, and innovation and commercialization are the four different themes of four sessions organized in the GPAI.
- The summit also included various side events showcasing AI progress and engaging in discussions, such as industry panel discussions, workshops, research symposiums, hackathons, and the Global AI Expo.
What is the Delhi Declaration of the GPAI?
- It acknowledges the need to harness new opportunities and mitigate the risks arising from the development, deployment, and use of Artificial Intelligence (AI).
- Affirms the commitment to uphold human dignity, human rights, and democratic values.
- Emphasizes the importance of fostering trust, transparency, accountability, and inclusiveness in AI.
- Recognizes the potential of AI to contribute to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals and address global challenges.
- Encourages international cooperation and coordination on AI research, innovation, and policy.
- Supports the development of a comprehensive framework that encompasses shared principles for safe and trusted AI.
- Endorses India’s proposal to establish and maintain a Global Digital Public Infrastructure Repository (GDPIR) to share digital public goods.
- GDPIR was established under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), to serve as an extensive repository, consolidating crucial insights and knowledge from both G20 members and guest nations.
- Calls for further dialogue on AI governance and ethics among stakeholders.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
- AI is the ability of a computer, or a robot controlled by a computer to do tasks that are usually done by humans because they require human intelligence and judgement.
- Although no AI can perform the wide variety of tasks an ordinary human can do, some AI can match humans in specific tasks.
- The ideal characteristic of AI is its ability to rationalize and take actions that have the best chance of achieving a specific goal. A subset of AI is Machine Learning (ML).
- Deep Learning (DL) techniques enable this automatic learning through the absorption of huge amounts of unstructured data such as text, images, or video.
What is AIRAWAT?
- NITI Aayog circulated the cabinet note to establish a cloud computing platform called AIRAWAT (Artificial Intelligence Research, Analytics and Knowledge Assimilation Platform in 2019.
- The move to create a cloud computing platform is part of the government’s goal of making India a pioneer amongst emerging economies with regard to AI and transforming sectors like education, health, agriculture, urbanization and mobility.
What is DeepFake?
- Deepfakes are synthetic media that use AI to manipulate or generate visual and audio content, usually with the intention of deceiving or misleading someone.
- Deepfakes are created using a technique called generative adversarial networks (GANs), which involve two competing neural networks: a generator and a discriminator.
- The generator tries to create fake images or videos that look realistic, while the discriminator tries to distinguish between the real and the fake ones.
- The generator learns from the feedback of the discriminator and improves its output until it can fool the discriminator.
- Deepfakes require a large amount of data, such as photos or videos, of the source and the target person, which are often collected from the internet or social media without their consent or knowledge.
- The generator tries to create fake images or videos that look realistic, while the discriminator tries to distinguish between the real and the fake ones.
- Deepfakes are a part of Deep Synthesis, which uses technologies, including deep learning and augmented reality, to generate text, images, audio and video to create virtual scenes.
What is the YUVA Ai initiative?
- About:
- The National e-Governance Division (NeGD) partnered with Intel India to launch ‘YUVAi- Youth for Unnati and Vikas with AI’ program.
- Aims:
- To foster a deeper understanding of AI, equip school students from classes 8 to 12 across the nation with relevant mindset and skill sets, and empower them to become human-centric designers and users of AI.
- The program offers an applied learning experience for students to understand and identify how AI technology can be used to tackle critical problems and lead to inclusive development of the nation.
- The program will be ongoing throughout the year to give a maximum number of students a chance to empower themselves to be future-ready.
Conclusion
- India launched the GPAI Summit, where India seeks to equip school students with AI skills for inclusive development. The New Delhi Declaration emphasizes a global AI framework grounded in democracy, human rights, and responsible practices.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Q. The terms ‘WannaCry, Petya and EternalBlue’ sometimes mentioned in the news recently are related to (2018)
(a) Exoplanets
(b) Cryptocurrency
(c) Cyber attacks
(d) Mini satellites
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. What are the main socio-economic implications arising out of the development of IT industries in major cities of India? (2022)
Q. “The emergence ofthe Fourth Industrial Revolution (Digital Revolution) has initiated e-Governance as an integral part of government”. Discuss. (2020)
Unorganised Labour Initiatives and Migrant Workers Children Welfare
For Prelims: Unorganised Labour, Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana, Pradhan Mantri Shram Yogi Maan-dhan Yojana, Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act, India’s migrant workers, Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PM-JAY).
For Mains: Migration centric policy, Unorganised Labour in India and Related Initiatives
Why in News?
The Ministry of Labour & Employment recently highlighted measures designed to safeguard the interests of unorganised labour in a written response presented in the Rajya Sabha.
- Additionally, the ministry addressed welfare facilities for the children of migrant workers.
What are the Highlighted Initiatives Related to Unorganised Labour?
- Life and Disability Cover:
- Provided through Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY) and Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY).
- PMJJBY:
- Rs. 2.00 Lakh in case of death of insured, due to any reason, at an annual premium of Rs. 436/-.
- PMSBY:
- Rs. 2.00 Lakh in case of accidental death or total permanent disability and Rs. 1.00 lakh for partial permanent disability due to accident at a premium of Rs. 20/- per annum.
- PMJJBY:
- Provided through Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY) and Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY).
- Health and Maternity Benefits:
- The health and maternity benefits are insured through Ayushman Bharat- Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY) under deprivation and occupation criteria.
- It provides health insurance coverage up to Rs. 5.00 lakhs per family for secondary and tertiary care-related hospitalization.
- Old Age Protection:
- To provide old age protection to unorganised sector workers, the Government of India launched a pension scheme in 2019 namely Pradhan Mantri Shram Yogi Maan-dhan Yojana (PM-SYM) to provide a monthly pension of Rs. 3000/- after attaining the age of 60 years to unorganized workers.
- Other Schemes:
- Public Distribution System through One Nation One Ration Card scheme under the National Food Security Act (NFSA) 2013.
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act,2005.
- Deen Dayal Upadhyay Gramin Kaushal Yojana.
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana.
- Pradhan Mantri Gareeb Kalyan Rojgar Yojana.
- Mahatma Gandhi Bunkar Bima Yojana.
- Deen Dayal Antyodaya Yojana.
- Prime Minister Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM-SVANidhi).
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana.
Note
- Unorganised Workers’ Social Security Act, 2008, mandates the Government to provide Social Security to the workers of the unorganized sector by formulating suitable welfare schemes on matters relating to life and disability cover, health and maternity benefits, old age protection etc.
- The term unorganized worker has been defined under the Unorganized Workers' Social Security Act, 2008, as a home-based worker, self-employed worker or a wage worker in the unorganized sector.
- As per the survey carried out by the National Sample Survey Organization in the year 2011-12, the total employment in both organized and unorganized sectors in the country was of the order of 47 crore. Out of this, about 39 crore are in the unorganized sector.
What are the Welfare Facilities for Children of Migrant Workers?
- Inter-State Migrant Workmen (Regulation of Employment and Conditions of Services) Act, 1979:
- The act protects the interests of migrant workers. The act provides for registration of certain establishments employing Interstate Migrant Workers, licensing of contractors etc.
- Workers employed with such establishments are to be provided payment of minimum wages, journey allowance, displacement allowance, residential accommodation, medical facilities, protective clothing etc.
- The act protects the interests of migrant workers. The act provides for registration of certain establishments employing Interstate Migrant Workers, licensing of contractors etc.
- Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education (RTE) Act, 2009:
- It mandates the appropriate Government to provide free and compulsory elementary education to every child aged 6 to 14 years in a neighbourhood school, which is also applicable to children of inter-state migrant workers.
Persistence of Synchronized Extreme Rainfall in Changing Climates
For Prelims: Persistence of Synchronized Extreme Rainfall in Changing Climates, Global Warming, Indian Summer Monsoon Rainfall (ISMR).
For Mains: Persistence of Synchronized Extreme Rainfall in Changing Climates, Factors Affecting the Rainfall in India.
Why in News?
Recently, a new study has been published by Advancing Earth and Space Sciences (AGU) titled- Geographical Trapping of Synchronous Extremes Amidst Increasing Variability of Indian Summer Monsoon Rainfall, highlighting that Indian Monsoon has undergone significant alterations due to Global Warming.
- The study investigates synchronous extreme rainfall events during the Indian Summer Monsoon Rainfall (ISMR) from 1901 to 2019. It highlights the consistent presence of interconnected extreme hubs in Central India, suggesting the geographical concentration of these concurrent events in the region.
How have been the Rainfall Trends in India?
- Consistent Spatial Concentration:
- Despite the rising variability in Indian Summer Monsoon Rainfall (ISMR) over the past century, synchronous extreme rainfall events have consistently concentrated within a specific geographical region, primarily in Central India (CI) that extends from parts of West Bengal and Odisha to parts of Gujarat and Rajasthan.
- This corridor has remained unchanged from 1901 to 2019!
- This indicates a stable pattern of synchronized extreme events despite overall increased variability.
- Despite the rising variability in Indian Summer Monsoon Rainfall (ISMR) over the past century, synchronous extreme rainfall events have consistently concentrated within a specific geographical region, primarily in Central India (CI) that extends from parts of West Bengal and Odisha to parts of Gujarat and Rajasthan.
- Network Cohesiveness:
- There is a persistent network of highly interconnected extreme rainfall hubs in CI. These hubs exhibit strong local connections, emphasizing a stable synchronization of extreme events in this region over the long term.
- Correlation with Climatic Patterns:
- India’s monsoon forecasts rely heavily on its relation to the El Niño and the La Niña phenomena, although this relation holds only about 60% of the time.
- Indian Rainfall events are correlated with El Niño Southern Oscillations (ENSO), with more synchronization during strong El Niño periods and less during La Niña conditions.
- Implications for Predictability:
- The findings suggest that despite the increasing variability and complexity of ISMR, understanding the persistent nature of extreme rainfall synchronization in CI provides insights crucial for predicting synchronous extremes.
- This knowledge can aid in developing effective adaptation strategies and risk management during the monsoon season.
What are the Implications of the Findings on the Forecast?
- Revisiting Stationarity:
- Despite the belief that stationary elements in climate systems no longer exist due to global warming, the Indian monsoon's ability to synchronize heavy rain events challenges this notion.
- It suggests that certain consistent patterns, such as synchronized extreme rainfall events along specific corridors, persist even in a changing climate.
- Understanding Corridor Dynamics:
- The identification of a geographic corridor, primarily the mountain ranges along the west coast and across Central India, as the potential trapping zone for synchronized extreme rainfall events and monsoon depressions provides a crucial insight.
- This hypothesis would significantly enhance the understanding of how and where these events occur, aiding in more accurate forecasts.
- The identification of a geographic corridor, primarily the mountain ranges along the west coast and across Central India, as the potential trapping zone for synchronized extreme rainfall events and monsoon depressions provides a crucial insight.
- Forecast Improvement:
- The research suggests that improving forecasts of synchronized extreme rainfall events doesn't necessarily require increased model resolution or higher computational costs.
- Instead, focusing on understanding the dynamics of synchronization within the existing models could lead to more accurate predictions. This highlights a strategic shift in forecasting approaches.
- Risk Reduction Strategies:
- Accurate forecasts of these large-scale extreme rainfall events are vital for minimizing risks across various sectors like agriculture, water management, energy, transportation, and public health.
- The findings offer an opportunity to refine risk reduction strategies at a smaller scale, leveraging better forecasts for preparedness and mitigation.
- Accurate forecasts of these large-scale extreme rainfall events are vital for minimizing risks across various sectors like agriculture, water management, energy, transportation, and public health.
- Leveraging India's Resources:
- The study emphasizes India's strong modelling capacity and computational resources, positioning the country well to exploit this potential for better forecasting.
- It highlights the capacity to delve deeper into understanding synchronization dynamics and optimizing forecasts, potentially minimizing the impacts of extreme rainfall events on various sectors.
What are the Factors Affecting the Indian Monsoon?
- Himalayan Mountains:
- The Himalayas are a major factor in the formation of the monsoon winds in India.
- During the summer months, the landmass over the Indian subcontinent heats up rapidly, leading to the formation of a low-pressure system.
- The Himalayas, which act as a barrier, prevent the cool, dry air from the north from flowing into the region, resulting in a pressure gradient that draws in warm, moist air from the Indian Ocean.
- Thar Desert:
- The Thar Desert, also known as the Great Indian Desert, is a crucial factor in the formation of monsoon winds in India.
- It acts as a rain shadow area for the Bay of Bengal branch of the monsoon, meaning that it receives very little rainfall due to the barrier created by the Aravalli Mountain range.
- Thus, the Arabian branch of the monsoon, which moves parallel to the Thar Desert, also leads to very little rainfall in the nearby regions.
- This lack of rainfall can have significant impacts on agriculture and the local economy in the region.
- The hot and dry air from the desert creates a low-pressure zone in the whole northwest parts of India, which draws in moisture-laden winds from the Indian Ocean, resulting in heavy rainfall during the summer months.
- Thus, the Arabian branch of the monsoon, which moves parallel to the Thar Desert, also leads to very little rainfall in the nearby regions.
- Indian Ocean:
- The Indian Ocean is a significant contributor to the formation of monsoon winds in India.
- The ocean's warm and moist air interacts with the low-pressure system over the Indian subcontinent, resulting in the formation of the monsoon winds.
- The Indian Ocean is a significant contributor to the formation of monsoon winds in India.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. With reference to ‘Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)’ sometimes mentioned in the news while forecasting Indian monsoon, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2017)
- IOD phenomenon is characterised by a difference in sea surface temperature between tropical Western Indian Ocean and tropical Eastern Pacific Ocean.
- An IOD phenomenon can influence an El Nino’s impact on the monsoon.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Exp;
- The Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) is an atmosphereocean coupled phenomenon in the tropical Indian Ocean (like the El Nino is in the tropical Pacific), characterised by a difference in Sea-Surface Temperatures (SST).
- A ‘positive IOD’ is associated with cooler than normal sea-surface temperatures in the eastern equatorial Indian Ocean and warmer than normal sea-surface temperatures in the western tropical Indian Ocean.
- The opposite phenomenon is called a ‘negative IOD’, and is characterised by warmer than normal SSTs in the eastern equatorial Indian Ocean and cooler than normal SSTs in the western tropical Indian Ocean.
- Also known as the Indian Nino, it is an irregular oscillation of sea-surface temperatures in the Indian Ocean in which the western Indian Ocean becomes alternately warmer and colder than the eastern part of the Indian Ocean. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- The IOD is one aspect of the general cycle of global climate, interacting with similar phenomena like the El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) in the Pacific Ocean. An IOD can either aggravate or weaken the impact of El Nino on Indian monsoon. If there is a positive IOD, it can bring good rains to India despite of an El Nino year. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer
Mains:
Question: How far do you agree that the behaviour of the Indian monsoon has been changing due to humanizing landscape? Discuss. (2015)
Southeast Asia Opium Survey 2023: UNODC
For Prelims: Southeast Asia Opium Survey 2023: UNODC, United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), Golden Triangle, Southeast Asia, Opium cultivation, Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB).
For Mains: Southeast Asia Opium Survey 2023: UNODC, Drug Menance: Threats, Challenges, Initiatives taken, challenges.
Why in News?
Recently, the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) has released a report titled-Southeast Asia Opium Survey 2023 - Cultivation, Production, and Implications, highlighting that there is a significant increase in Opium Cultivation in the Golden Triangle, Southeast Asia.
Note
- The Golden Triangle typically refers to a region in Southeast Asia known for the production of illicit drugs, particularly Opium. It's an area where the borders of three countries meet: Myanmar (formerly Burma), Laos, and Thailand.
- Originally, the term "Golden Triangle" referred to the opium-producing region covering parts of these three countries. However, it has evolved to denote a broader area associated with drug production, trafficking, and organized crime.
- One more infamous region for illicit drugs is Golden Crescent or “Death crescent”, this crescent region includes Afghanistan and Iran – making it a natural transit point for drugs being smuggled out of Pakistan.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- Opium Cultivation Increase in Myanmar:
- Opium cultivation in the Golden Triangle continued to expand over the past year 2022, with a significant increase in Myanmar.
- There's been a 18% increase in Opium cultivation in Myanmar, reaching 47,100 hectares.
- This surge has made Myanmar the world's largest source of opium, particularly due to disruptions following the Military Takeover in 2021.
- Increased Yield and Investment:
- The average estimated opium yield per hectare expanded by 16% to 22.9 kilograms/hectare.
- This reflects advancements in farming practices and increased investments in irrigation systems and fertilizers, signaling a more sophisticated approach by farmers and buyers.
- Rising Opium Prices:
- Despite an expanding supply, the price paid to farmers increased by 27% to approximately USD 355 per kilogram.
- This price surge underscores the attractiveness of opium as a crop and commodity, indicating strong demand that fuels the opium trade in the Golden Triangle.
- Impact of the Afghanistan Opium Ban:
- The report anticipates that a protracted ban on opium in Afghanistan will likely lead to sustained high prices and further increases in cultivation in Southeast Asia.
- The Taliban’s ban has led to a 95% drop in the cultivation of opium poppies in Afghanistan
- Contribution to Illicit Economy:
- The expansion of opium cultivation contributes to a broader illicit economy in the Mekong region (Cambodia, the People's Republic of China (specifically Yunnan Province and Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region), Lao People's Democratic Republic , Myanmar, Thailand, and Viet Nam).
- It fuels synthetic drug production and a convergence of drug trafficking, money laundering, and online criminal activities, generating significant profits for organized crime groups.
- Recommendations:
- The crisis in Myanmar exacerbates crime and governance challenges in the region. Addressing these issues necessitates comprehensive solutions considering the complex realities faced by people in opium-cultivation areas. Providing viable alternatives to opium cultivation and improving socio-economic conditions are crucial to mitigate this trend.
- Given the insecurities and economic hardships faced by farming communities, the UNODC's direct engagement with these communities in Myanmar and Laos becomes more critical than ever.
- Building resilience and offering sustainable income generation alternatives are vital to combat the allure of opium cultivation.
What are the Key Facts about Opium Poppy Plants?
- Scientific Name: Papaver somniferum
- Uses: Opium derived from the sap of the opium poppy has been used for centuries as a pain reliever, sedative, and in the production of various opioids, including morphine, codeine, and heroin. Medicinally, it has been employed to alleviate severe pain, suppress coughs, and induce sleep.
- Global Production: India is the sole country authorized by the United Nations Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs (1961) to produce gum opium. Additionally, other countries like Australia, Austria, France, China, Hungary, the Netherlands, Poland, Slovenia, Spain, Turkey, and the Czech Republic cultivate opium poppies. However, these countries do not extract gum but instead use the Concentrate of Poppy Straw process (CPS).
- This process involves cutting the bulb with 8 inches of the stalk for processing in its entirety.
What is the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime?
- It was established in 1997 and was named as a United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) in 2002.
- It acts as the Office for Drug Control and Crime Prevention by combining the United Nations International Drug Control Program (UNDCP) and the Crime Prevention and Criminal Justice Division of the United Nations Office at Vienna.
What are the Related Initiatives to Tackle Drug Abuse ?
- Indian:
- Global Initiatives:
- Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, 1961.
- The Convention on Psychotropic Substances, 1971.
- The UN Convention against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances, 1988.
- India is a signatory to all three and has enacted the Narcotics Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act, 1985.
- Every year, the UN publishes a World Drug Report, Global Drug Policy Index.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements:
- The United Nations Convention against Corruption (UNCAC) has a ‘Protocol against the Smuggling of Migrants by Land, Sea and Air’.
- The UNCAC is the ever-first legally binding global anti-corruption instrument.
- A highlight of the United Nations Convention against Transnational Organized Crime (UNTOC) is the inclusion of a specific chapter aimed at returning assets to their rightful owners from whom they had been taken illicitly.
- The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) is mandated by its member States to assist in the implementation of both UNCAC and UNTOC.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. In one of the districts of a frontier state, narcotics menace has been rampant. This has resulted in money laundering, mushrooming of poppy farming, arms smuggling and near stalling of education. The system is on the verge of collapse. The situation has been further worsened by unconfirmed reports that local politicians as well assume senior police officers are providing surreptitious patronage to the drug mafia. At that point of time a woman police officer, known for her skills in handling such situations is appointed as Superintendent of Police to bring the situation to normalcy.
If you are the same police officer, identify the various dimensions of the crisis. Based on your understanding, suggest measures to deal with the crisis. (2019)
IUCN Red List Update 2023
Why in News?
Recently, the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List underwent an update, featuring thousands of new species assessments and reassessments.
- This information was presented at the 28th Conference of Parties, shedding light on the escalating impacts of climate change on a diverse range of species.
- The IUCN Red List now includes 157,190 species, of which 44,016 are threatened with extinction.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- Climate Change Threatens Diverse Species:
- Species ranging from Atlantic salmon to green turtles face growing threats due to climate change.
- IUCN Director General, emphasises the urgency of ambitious climate action to combat species decline.
- The IUCN Red List update underscores the interlinked nature of climate and biodiversity crises, urging joint efforts for sustainable solutions.
- Freshwater Fish Assessment:
- The first comprehensive assessment of global freshwater fish species is revealed.
- 25% of assessed freshwater fish species are at risk of extinction.
- Climate change, pollution, overfishing, and invasive species contribute to the decline.
- The first comprehensive assessment of global freshwater fish species is revealed.
- Impact on Atlantic Salmon:
- Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) are ray-finned fish that can grow up to a meter long, found in the North Atlantic Ocean basin. They are anadromous, meaning they live in both fresh and saltwater.
- Atlantic salmon population declined by 23% (2006-2020), moving them from Least Concern to Near Threatened.
- Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) are ray-finned fish that can grow up to a meter long, found in the North Atlantic Ocean basin. They are anadromous, meaning they live in both fresh and saltwater.
- Green Turtles Facing Extinction:
- Central South Pacific and East Pacific green turtle populations are respectively Endangered and Vulnerable.
- Climate change poses threats throughout their life cycle, impacting hatching success and food sources.
- Central South Pacific and East Pacific green turtle populations are respectively Endangered and Vulnerable.
- Mahogany Trees Facing Endangerment:
- The big-leaf mahogany (Swietenia macrophylla), a sought-after timber tree, shifts from Vulnerable to Endangered.
- Unsustainable harvest, urban encroachment, and illegal logging contribute to a 60% reduction over 180 years.
- The big-leaf mahogany (Swietenia macrophylla), a sought-after timber tree, shifts from Vulnerable to Endangered.
- Conservation Success Stories:
- Scimitar-horned oryx, a desert antelope moves from Extinct in the Wild to Endangered, showcasing successful reintroduction efforts in the Republic of Chad.
- Saiga antelope improves from Critically Endangered to Near Threatened due to conservation measures.
International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List
- The IUCN Red List is the foremost global resource for assessing the risk of extinction among animals, fungi, and plant species.
- Accessible to all, it serves as a crucial indicator of global biodiversity health, it offers comprehensive insights into species' characteristics, threats, and conservation measures, playing a pivotal role in shaping informed conservation decisions and policies.
- The IUCN Red List Categories define the extinction risk of species assessed. Nine categories extend from NE (Not Evaluated) to EX (Extinct). Critically Endangered (CR), Endangered (EN) and Vulnerable (VU) species are considered to be threatened with extinction.
- It is also a key indicator for the Sustainable Development Goals and Aichi Targets.
- The IUCN Red List includes the IUCN Green Status of Species, which assesses the recovery of species’ populations and measures their conservation success.
- There are eight Green Status Categories: Extinct in the Wild, Critically Depleted, Largely Depleted, Moderately Depleted, Slightly Depleted, Fully Recovered, Non-Depleted and Indeterminate.
- A Green Status assessment examines how conservation actions have affected the current Red List status.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. ‘Invasive Species Specialist Group’ (that develops Global Invasive Species Database) belongs to which one of the following organizations?(2023)
(a) The International Union for Conservation of Nature
(b) The United Nations Environment Programme
(c) The United Nations World Commission for Environment and Development
(d) The World Wide Fund for Nature
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- The Invasive Species Specialist Group (ISSG) is a global network of scientific and policy experts on invasive species, organized under the auspices of the Species Survival Commission (SSC) of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). Hence, option (a) is correct.
- It was established in 1994.
- The ISSG manages the Global Invasive Species Database (GISD), which provides information on invasive alien species worldwide. The ISSG also maintains other online resources such as the Aliens-L listserv, the Invasive Species Compendium, the Global Register of Introduced and Invasive Species, and the Environmental Impact Classification for Alien Taxa.
Green Hydrogen Projects and SEZs
Why in News?
The Indian government is considering amendments to current regulations that could pave the way for significant fiscal benefits for renewable energy projects focused on producing green hydrogen within Special Economic Zones (SEZs).
What are the Key Proposed Amendments?
- Expanding SEZs for Green Hydrogen Projects: The Ministry of Commerce is contemplating permitting SEZs to span multiple non-contiguous areas, specifically catering to green hydrogen initiatives.
- Presently, SEZs require a contiguous land area of 50 hectares or more. The commerce ministry is open to relaxing this criterion for green hydrogen projects.
- Allowing multi-locational SEZs will enable developers to use wind energy for which turbines are placed at a considerable distance (250 to 400 metres) from each other.
- Eligibility for Fiscal Benefits: The proposed amendment aims to grant fiscal benefits to renewable energy plants used for captive consumption within SEZs.
- Currently, SEZ rules do allow fiscal benefits only for renewable energy plants set up as SEZ units and meant for selling power outside of SEZs.
- However, renewable energy plants become ineligible for benefits when used for captive consumption.
- Currently, SEZ rules do allow fiscal benefits only for renewable energy plants set up as SEZ units and meant for selling power outside of SEZs.
- These changes, if approved, will enable export-oriented green hydrogen ventures to access tax breaks for establishing and operating renewable energy facilities dedicated to green hydrogen production.
Note
Captive consumption refers to the utilization of goods or services within the premises of the producing entity or within a designated area, without their transfer or sale to external markets.
What is a Special Economic Zone?
- About: A Special Economic Zone (SEZ) is a geographical region that has economic laws that are more liberal than a country's domestic economic laws.
- The category 'SEZ' covers a broad range of more specific zone types, including, but not limited to:
- Free Trade Zones (FTZs)
- Export Processing Zones (EPZs)
- Free Zones (FZs)
- Industrial Estates (IEs)
- India was one of the first in Asia to recognize the effectiveness of the Export Processing Zone model in promoting exports, with Asia's first EPZ set up in Kandla, Gujarat in 1965.
- The category 'SEZ' covers a broad range of more specific zone types, including, but not limited to:
- SEZs in India: Special Economic Zones Policy in India was announced in April 2000 to enhance foreign investment, creation of employment opportunities and provide an internationally competitive and hassle-free environment for exports along with the development of infrastructure facilities.
- All laws of India are applicable in SEZs unless specifically exempted as per the SEZ Act/ Rules.
- Each Zone is headed by a Development Commissioner and is administered as per the SEZ Act, 2005 and SEZ Rules, 2006.
- Units may be set up in the SEZ for manufacturing, trading or for service activity.
- All laws of India are applicable in SEZs unless specifically exempted as per the SEZ Act/ Rules.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. With reference to green hydrogen, consider the following statements : (2023)
- It can be used directly as a fuel for internal combustion.
- It can be blended with natural gas and used as fuel for heat or power generation.
- It can be used in the hydrogen fuel cell to run vehicles.
How many of the above statements are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
Ans: (c)
Pompe Disease
Why in News?
India’s first Pompe disease patient, passed away at the age of 24 years after battling the disease in a semi-comatose state.
- A semi-comatose state is characterized by partial coma, manifesting as disorientation and stupor without reaching a complete coma. Individuals in a semi-comatose state may exhibit responsiveness to stimuli, such as groaning and mumbling.
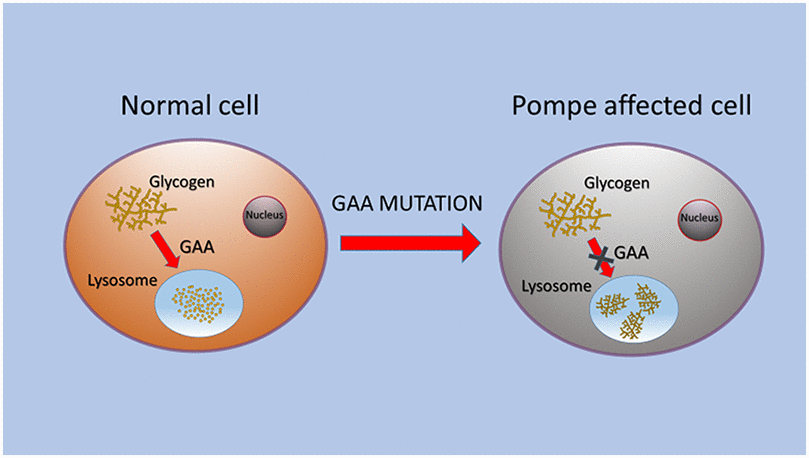
What is Pompe Disease?
- About:
- Pompe Disease (also known as Glycogen Storage Disease Type II) is characterized by the buildup of glycogen in the lysosomes of the body’s cells.
- This disease is a rare genetic disorder caused by a deficiency of the enzyme acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA). This enzyme is crucial for breaking down glycogen into glucose within the lysosomes of cells.
- Lysosomes are membrane-enclosed organelles that contain an array of enzymes capable of breaking down all types of biological polymers—proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids.
- Its prevalence estimates range from 1 in 40,000 to 1 in 300,000 births.
- Symptoms:
- Muscle weakness, Motor skill delay, Degenerative impact on bones, Respiratory complications, Cardiac involvement, Implications for daily living.
- Diagnosis:
- Enzyme assays are conducted to measure the activity of GAA, the deficient enzyme.
- Genetic testing identifies mutations in the responsible GAA gene. Genetic analysis confirms the presence of specific mutations associated with Pompe Disease.
- Treatment:
- Although there is presently no cure for Pompe disease, there are treatment alternatives accessible to address symptoms and enhance the patient's quality of life.
- Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT) is a common treatment method that entails infusing the deficient enzyme to mitigate glycogen accumulation.
Element Plutonium
Plutonium, a radioactive element, was first produced and isolated at the Berkeley Radiation Laboratory by Dr. Glenn T. Seaborg, Joseph W. Kennedy, Edwin M. McMillan, and Arthur C. Wahl in 1940.
- They produced it by bombarding uranium-238 with deuterium nuclei (alpha particles).
- Plutonium production was essential for the Manhattan Project (a top-secret program to make the first atomic bombs during World War II).
- Its basic chemistry is closely related to uranium.
- Plutonium-239, an isotope of plutonium, could undergo fission and be used as fuel for an atomic bomb.
- Plutonium is also a key material in the development of nuclear power. I
Pandemic Accord
Recently, the seventh round of deliberations on the Pandemic Accord was recently concluded by representatives from 28 countries.
- The accord aims to strengthen global prevention, preparedness, and response to disease outbreaks.
- The delegates failed to reach a consensus on Intellectual Property Rights and Relaxing Patents.
- The United States did not change its stance on the protection of Intellectual Property Rights (IPR), reiterating that canceling them would not improve access for poor countries during emergencies.
- Developed and developing countries had divergent opinions, with the former focusing on prevention and the latter demanding equitable access to medical products to be a guarantee in the treaty.
- The International Federation of Pharmaceutical Manufacturers and Associations was also in agreement when it came to retaining patent rights.
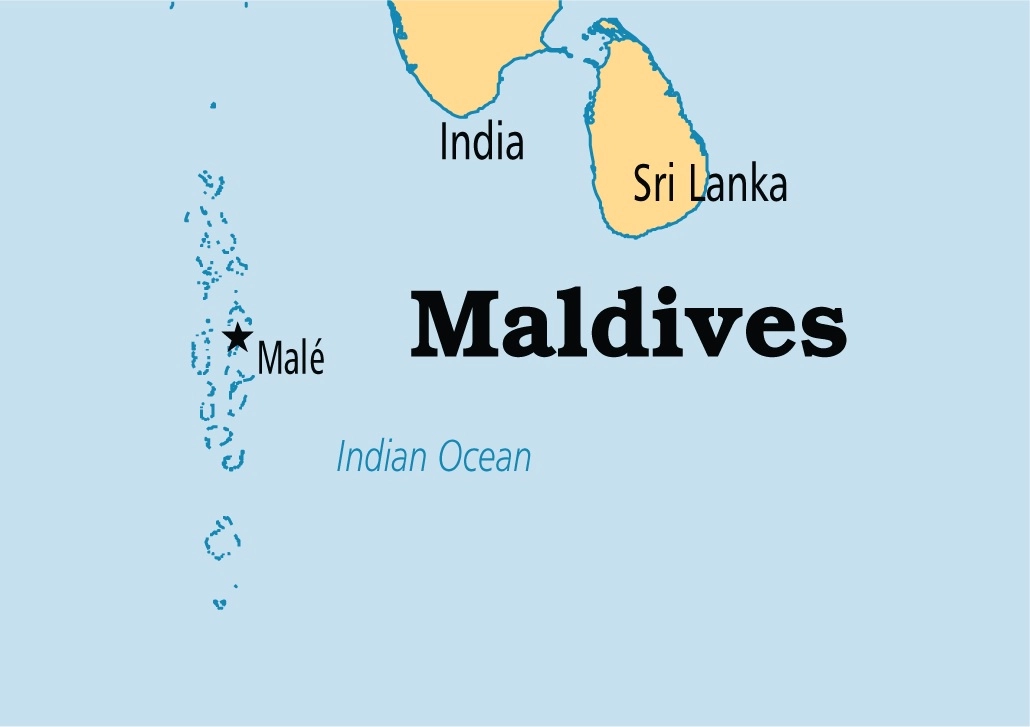
Maldives Ends India's Hydrography Agreement
The current Maldives’s government, steering away from the 'India First' policy, has opted not to renew the hydrography agreement with India citing national security concerns and the safeguarding of sensitive information.
- The hydrographic survey agreement was signed on June 8, 2019, during the Indian Prime Minister's visit to the Maldives.
- Under the agreement, India was allowed to conduct a comprehensive study of the island nation's territorial waters, which includes reefs, lagoons, coastlines, ocean currents, and tide levels.
- The third Joint hydrographic survey by the Indian Navy and the Maldives National Defense Force (MNDF) was carried out by an Indian Naval Ship Investigator (INS Investigator) from 19th January to 26th February 2023.
- Earlier, the current Maldives’s government also requested India to withdraw its military personnel from the island.
Read more: India-Maldives Relations
Kashi Vishwanath Corridor
Recently, the Prime Minister of India has celebrated 2 years of Kashi Vishwanath Corridor.
- Kashi Vishwanath Corridor connects the iconic Kashi Vishwanath temple and the ghats along the river Ganga.
- Kashi Vishwanath Temple is one of the most famous Hindu temples dedicated to Lord Shiva.
- The temple stands on the western bank of the holy river Ganga and is one of the twelve Jyotirlingas, the holiest of Shiva temples.
- Kashi Vishwanath Dham has become one of the top pilgrimage spots in India as a record 12.9 crore devotees visited the shrine in two years.
Read more: Kashi Vishwanath Corridor
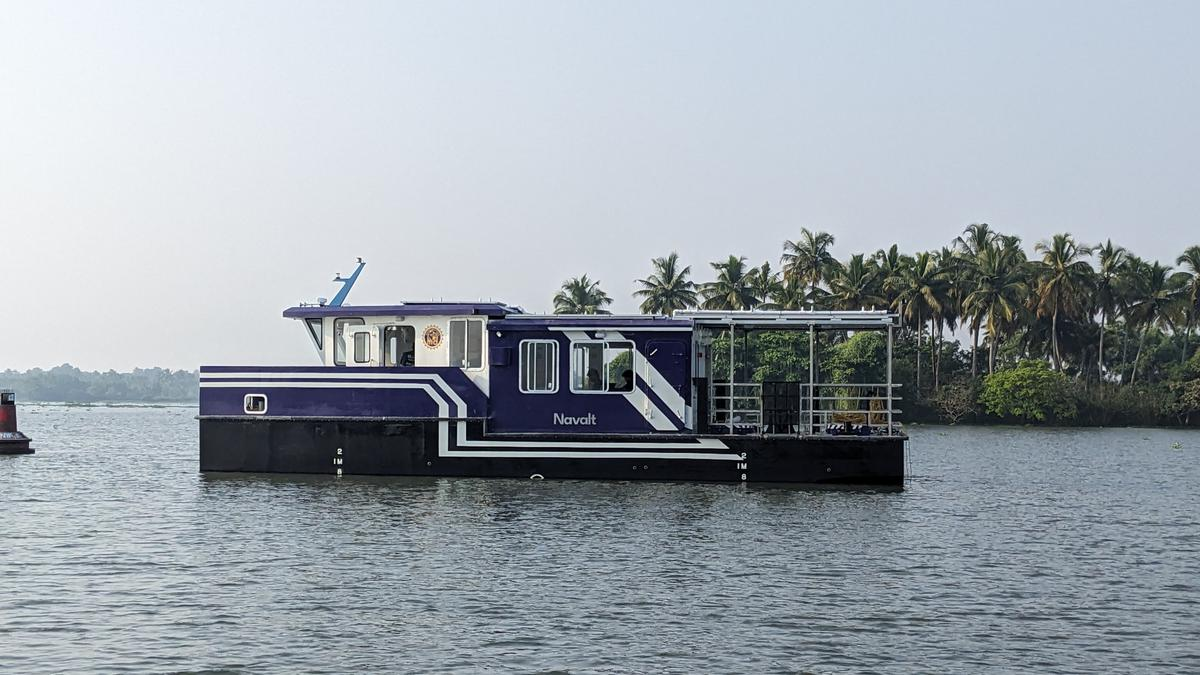
Barracuda: India's Solar-Electric Maritime Boat
The launch of Barracuda in Alappuzha, India's fastest solar-electric boat, marks a significant step forward in eco-friendly maritime transportation.
- Developed by Navalt Solar and Electric Boats, the 14-meter-long vessel embodies efficiency and sustainability, capable of ferrying up to 12 passengers and cargo even in rough seas.
- Engineered to navigate waves as tall as four meters, it operates silently without noise, vibration, or air pollution.
Read more: India's Maritime Doctrine