India’s Slowing Exports
For Prelims: Status of India’s Exports, Initiatives related to Export Promotion.
For Mains: Concerns over India’s Slowing Exports.
Why in News?
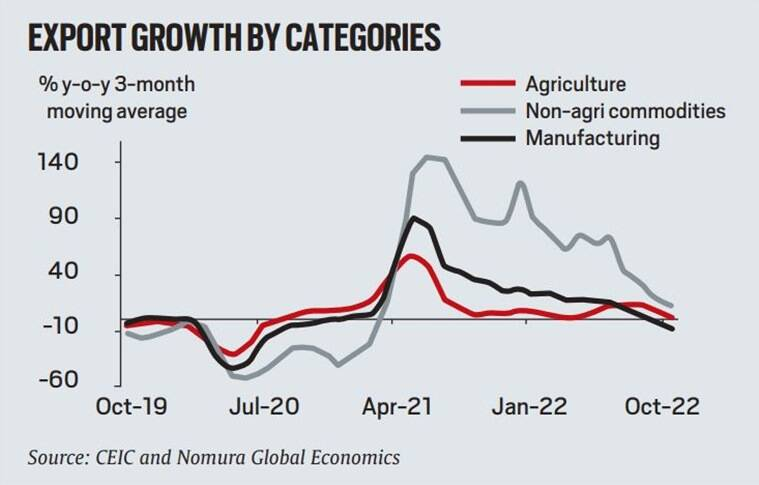
India’s exports declined about 16.7% in October 2022 compared with the same period 2021, raising concerns over slowing exports.
- For October, USD 2 billion worth of exports declining was seen in steel and allied products.
- Electronic goods exports remained among a handful of segments to witness a rise in exports growing about 38% to USD 1.8 billion.
What are the Factors of Slowing Export Demand?
- Weaker Global Demand:
- The global economic growth is decelerating sharply in the wake of persistently high inflation across developed countries and, as a result, as sharp tightening of monetary policy .
- With growth contraction across the board — UK and US are set to see recession while the euro area is likely to stall even as China struggles to grow — the demand for Indian goods has plummeted. That is why exports have contracted.
- Inflation:
- Inflation has been driven up more by local factors, including higher food prices, than imported reasons and that those pressures are set to dampen thanks to easing international commodity prices and the arrival of Kharif crop.
- Retail inflation has been consistently above 7% these past few months, but stood at 6.8% for October, 2022.
- Fall in Oil and other Export:
- Oil export growth fell to -11.4% y-o-y from 43.0% in September 2022, partly reflecting lower global crude oil prices, while non-oil exports plunged -16.9% y-o-y, with the decline broad-based across iron ore, handicrafts, textiles, some agricultural goods, plastics, gems & jewellery, engineering goods, chemicals, pharmaceuticals and leather goods.
- Engineering goods, which have lent a strong shoulder to India’s goods exports in recent years, slid 21%.
- Rising Global Trade Tension:
- Recent trade war between the US and China and other global trade wars has impacted growth all over the world.
- It has impacted manufacturing and exports in different parts of the world, including the Indian economy too.
What are the Positive Signals to the Economy?
- Despite the slowing export scenario, it is likely that domestic demand will carry through.
- The investment cycle will be reinvigorating which will spur growth and job creation in the coming days.
- The private sector capital expenditure is on track to touch six lakh crore this fiscal 2022-23 which would make it the highest of the past six years.
- Private capex typically depends on credit, or loans, from the banking system.
- And that has seen a healthy growth in the recent past touching a high of 18% in September, 2022.
What about other Exporting Nations?
- Vietnam, an export-dominated country, recorded a 4.5% growth in exports from a year earlier to USD 29.18 billion amid ‘sustained foreign demand’.
- Similarly, exports by the Philippines grew 20% in October, 2022.
- The government there had said that exports rose for the first time in three months in September amid what it calls ‘signs of reviving foreign demand’.
- China is an outlier in 2022 because of stringent lockdowns that are impacting manufacturing output, though lockdowns are being eased currently following protests against restrictions.
How has the Indian Forex Reserve been?
- For the week ended December 2, foreign exchange reserves stood at about USD 561 billion.
- October imports stood at USD 56.7 billion (an eight-month low) as a benchmark, and there about 9-10 months’ worth of import cover which isn’t as healthy as the 14-to-15-month cover that we had seen during the pandemic.
- However, economists feel this isn’t as bad as 2013 when foreign investors began pulling out of India’s financial markets.
- At that time, India had less than seven months’ worth of import cover.
- And if anything, forex reserves have been rising in recent weeks signalling hope for the future.
Note
- Import Cover is a measure of how many months of imports can be covered by foreign exchange reserves held by a country's central bank.
- It is an important indicator of the stability of the currency.
What are India’s Export Promotion Schemes?
- Merchandise Exports from India Scheme:
- MEIS was introduced in the Foreign Trade Policy (FTP) 2015-20, under MEIS, the government provides duty benefits depending on product and country.
- Rewards under the scheme are payable as percentage of realised free-on-board value (of 2%, 3% and 5%) and MEIS duty credit scrip can be transferred or used for payment of a number of duties including the basic customs duty.
- Service Exports from India Scheme:
- It was introduced in April 2015 for 5 Years under the Foreign Trade Policy of India 2015-2020.
- Earlier, this Scheme was named as Served from India Scheme (SFIS Scheme) for Financial Year 2009-2014.
- Under it, incentives are given by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry to Service Exporters based in India to promote the export of services from India.
- It was introduced in April 2015 for 5 Years under the Foreign Trade Policy of India 2015-2020.
- Remission of Duties or Taxes on Export Product (RoDTEP):
- It is a fully automated route for Input Tax Credit (ITC) in the GST (Goods and Service Tax) to help increase exports in India.
- ITC is provided to set off tax paid on the purchase of raw materials, consumables, goods or services that were used in the manufacturing of goods or services. This helps in avoiding double taxation and the cascading effect of taxes.
- It was started in January 2021 as a replacement for the MEIS, which was not compliant with the rules of the World Trade Organisation.
- It is a fully automated route for Input Tax Credit (ITC) in the GST (Goods and Service Tax) to help increase exports in India.
- Rebate of State and Central Taxes and Levies (RoSCTL):
- Announced in March, 2019, RoSCTL was offered for embedded state and central duties and taxes that are not refunded through GST.
- It was available only for garments and made ups. It was introduced by the Ministry of Textiles.
- Previously, it was Rebate for State Levies (ROSL).
Way Forward
- The weakness in India’s exports is likely to sustain because global growth is likely to remain weak. Weaker exports, in turn, will have a dampening effect on the growth of India’s gross domestic product (GDP).
- The government urgently needs to bring out a revised foreign policy to address both our historical trade imbalance, and the slowing of exports, rather than wait out the tumult as it intends to, having again deferred the new policy release till April next.
- The government should take appropriate measures to improve the credit cycle through investment and savings and promotion of foreign investment will bring the economy from slowdown in future.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q1. Which one of the following is not the most likely measure the Government/RBI takes to stop the slide of Indian rupee? (2019)
(a) Curbing imports of non-essential goods and promoting exports
(b) Encouraging Indian borrowers to issue rupee denominated Masala Bonds
(c) Easing conditions relating to external commercial borrowing
(d) Following an expansionary monetary policy
Ans: (d)
Q2. Which of the following best describes the term ‘import cover’, sometimes seen in the news? (2016)
(a) It is the ratio of value of imports to the Gross Domestic Product of a country.
(b) It is the total value of imports of a country in a year.
(c) It is the ratio between the value of exports and that of imports between two countries.
(d) It is the number of months of imports that could be paid for by a country’s international reserves.
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. Account for the failure of manufacturing sector in achieving the goal of labour-intensive exports. Suggest measures for more labour-intensive rather than capital-intensive exports. (2017)
Base Editing
For Prelims: Base Editing, CRISPR-Cas9 Technique, Cancer, T-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (T-ALL), Genetic Code, Genetic Engineering, Gene Editing.
For Mains: Base Editing Technique and its Significance.
Why in News?
Recently, scientists in the United Kingdom (UK) have successfully tested a new form of cancer therapy, ‘Base Editing’ for the time in a patient with T-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (T-ALL).
What is Base Editing?
- Bases are the language of life. Just as letters in the alphabet spell out words that carry meaning, the billions of bases in our Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) spell out the instruction manual for our body.
- A mis-arrangement in the sequence of bases may cause cancer.
- Using the technique of base editing, the molecular structure of just one base in a genetic code can be altered, effectively changing its genetic instructions.
- Genetic code refers to the instructions contained in a gene that tell a cell how to make a specific protein.
- Each genetic code uses the four nucleotide bases of DNA: Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G) and Thymine (T) — in various ways to spell out three-letter “codons” that specify which amino acid is needed at each position within a protein.
- Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR) technology is one of the most popular approaches that allows the genes to be altered, thereby, fixing the errors.
- This method has been further improvised to be able to directly change certain bases such as a C can be changed into a G and T into an A.
What is CRISPR Technology?
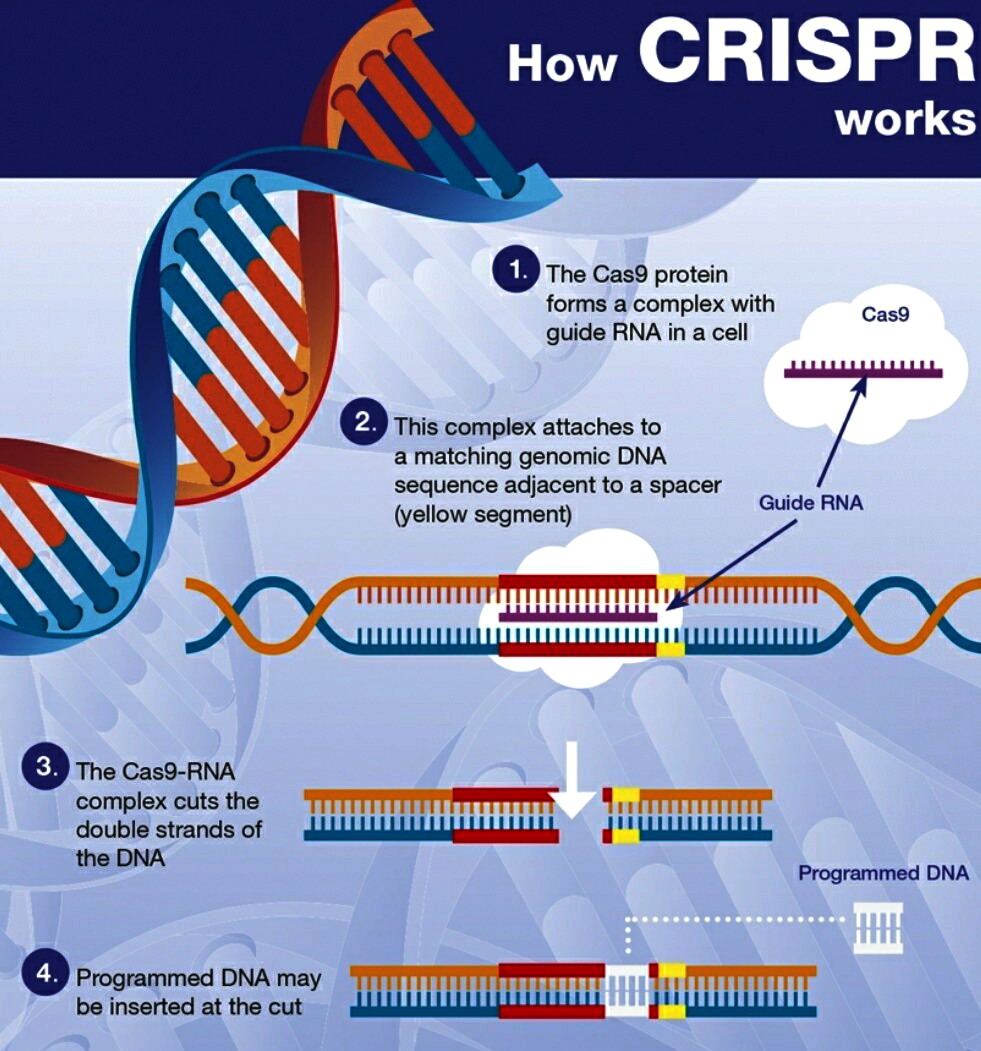
- CRISPR is a gene editing technology, by which research scientists selectively modify the DNA of living organisms using a special protein called Cas9.
- CRISPR/Cas9 edits genes by precisely cutting DNA and then letting natural DNA repair processes to take over. The system consists of two parts: the Cas9 enzyme and a guide Ribonucleic Acid (RNA).
- Cas9: a CRISPR-associated (Cas) endonuclease, or enzyme, that acts as “molecular scissors” to cut DNA at a location specified by a guide RNA.
- Guide RNA (gRNA): a type of RNA molecule that binds to Cas9 and specifies, based on the sequence of the gRNA, the location at which Cas9 will cut DNA.
- CRISPR-Cas9 technology is often described as ‘Genetic Scissors’.
- Its mechanism is often compared to the ‘cut-copy-paste’, or ‘find-replace’ functionalities in common computer programmes.
- A bad stretch in the DNA sequence, which is the cause of disease or disorder, is located, cut, and removed and then replaced with a ‘correct’ sequence.
- The technology replicates a natural defence mechanism in some bacteria that uses a similar method to protect itself from virus attacks.
What is T-ALL?
- It affects the stem cells in the bone marrow that produce a particular kind of White Blood Cells (WBCs) called T lymphocytes (T-cells).
- T-cells provide a person with immunity by killing cells carrying infections, activating other immune cells, and regulating the immune response.
- T-ALL is a rapid and progressive type of blood cancer in which the T-cells start destroying healthy cells instead of helping in immunity (that’s T-cells’ normal function).
- It is usually treated by chemotherapy, radiation therapy and stem cell/bone marrow transplant.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. What is Cas9 protein that is often mentioned in news? (2019)
(a) A molecular scissors used in targeted gene editing
(b) A biosensor used in the accurate detection of pathogens in patients
(c) A gene that makes plants pest-resistant
(d) A herbicidal substance synthesized in genetically modified crops
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- CRISPR-Cas9 is a unique technology that enables geneticists and medical researchers to edit parts of the genome by removing, adding or altering sections of the DNA sequence.
- CRISPR is an acronym for “Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats.”
- Cas9 is basically an enzyme that is used like a pair of scissors to cut two strands of DNA at a specific location to add, remove or repair bits of DNA.
- Hence, option (a) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. What are the research and developmental achievements in applied biotechnology? How will these achievements help to uplift the poorer sections of society? (2021)
Methane Emissions
For Prelims: Methane Gas, Related Initiatives
For Mains: Wetland emission and atmospheric sink changes explain methane growth in 2020.
Why in News?
Recently a study has been published titled- “Wetland emission and atmospheric sink changes explain methane growth in 2020’, which states that low nitrogen oxide pollution and warming wetlands likely drove global methane emissions to record high levels in 2020.
What are the Findings?
- Overview:
- Global methane emissions reached roughly 15 parts per billion (ppb) in 2020 from 9.9 ppb in 2019.
- In 2020, methane emissions from human activities decreased by 1.2 teragrams (Tg) per year.
- Contributors:
- Methane emissions from oil and natural gas decreased by 3.1 Tg per year compared to 2019. Contributions from coal mining decreased by 1.3 Tg per year. Fire emissions, too, dropped by 6.5 Tg per year.
- Globally, fire emissions appear to have fallen in 2020 compared to 2019, the researchers wrote in the study.
- Contributions from the agricultural sector went up by 1.6 Tg per year.
- Wetland emissions rose by 6.0 Tg per year.
- Methane emissions from oil and natural gas decreased by 3.1 Tg per year compared to 2019. Contributions from coal mining decreased by 1.3 Tg per year. Fire emissions, too, dropped by 6.5 Tg per year.
- Causes:
- Water‐logged soils make conditions ripe for soil microorganisms, allowing them to produce more methane.
- Nitrogen oxide levels fell by 6% in 2020 from 2019. Less nitrogen oxide pollution means less hydroxyl and more methane.
- Nitrogen oxide enters the atmosphere from exhaust gasses of cars and trucks as well as electrical power generation plants.
- Nitrogen oxide (NOx) can impact methane levels. In the troposphere — the upper part of the atmosphere — NOx combines with ozone to form hydroxyl radicals.
- These radicals, in turn, remove 85 % of methane annually from the atmosphere.
- The contribution of hydroxyl radicals in removing methane decreased by roughly 7.5 Tg per year.
- Roughly 53 % of the methane growth can be attributed to lower hydroxyl sink, and the remaining 47 % from natural sources, predominantly wetlands.
What is the Significance of the Study?
- It can help unravel a puzzle concerning why globally methane increased when many other greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide decreased during 2020.
- The results have significant implications for our ability to reliably predict methane changes in a future world with lower anthropogenic emissions of pollutants like nitrogen oxides and also if we have a wetter world.
What is Methane?
- About:
- Methane is the simplest hydrocarbon, consisting of one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms (CH4).
- It is flammable, and is used as a fuel worldwide.
- Methane is a powerful greenhouse gas.
- Methane has more than 80 times the warming power of carbon dioxide over the first 20 years of its lifetime in the atmosphere.
- The common sources of methane are oil and natural gas systems, agricultural activities, coal mining and wastes.
- Methane is the simplest hydrocarbon, consisting of one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms (CH4).
- Impact:
- More Global Warming Potential: It is nearly 80-85 times more potent than carbon dioxide in terms of its global warming capacity.
- This makes it a critical target for reducing global warming more quickly while simultaneously working to reduce other greenhouse gases.
- Promotes Generation of Tropospheric Ozone: Increasing emissions are driving a rise in tropospheric ozone air pollution, which causes more than one million premature deaths annually.
- More Global Warming Potential: It is nearly 80-85 times more potent than carbon dioxide in terms of its global warming capacity.
What are the Initiatives to Tackle Methane Emissions?
- Indian:
- ‘Harit Dhara’ (HD): Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) has developed an anti-methanogenic feed supplement ‘Harit Dhara’ (HD), which can cut down cattle methane emissions by 17-20% and can also result in higher milk production.
- India Greenhouse Gas Program: The India GHG Program led by WRI India (non-profit organization), Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) and The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI) is an industry-led voluntary framework to measure and manage greenhouse gas emissions.
- The programme builds comprehensive measurement and management strategies to reduce emissions and drive more profitable, competitive and sustainable businesses and organisations in India.
- National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC): NAPCC was launched in 2008 which aims at creating awareness among the representatives of the public, different agencies of the government, scientists, industry and the communities on the threat posed by climate change and the steps to counter it.
- Bharat Stage-VI Norms: India shifted from Bharat Stage-IV (BS-IV) to Bharat Stage-VI (BS-VI) emission norms.
- Global:
- Methane Alert and Response System (MARS):
- MARS will integrate data from a large number of existing and future satellites that have the ability to detect methane emission events anywhere in the world, and send out notifications to the relevant stakeholders to act on it.
- Global Methane Pledge:
- At the Glasgow climate conference (UNFCCC COP 26) in 2021, nearly 100 countries had come together in a voluntary pledge, referred to as the Global Methane Pledge, to cut methane emissions by at least 30% by 2030 from the 2020 levels.
- Global Methane Initiative (GMI):
- It is an international public-private partnership focused on reducing barriers to the recovery and use of methane as a clean energy source.
- Methane Alert and Response System (MARS):
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q1. Which of the following statements is/are correct about the deposits of ‘methane hydrate’? (2019)
- Global warming might trigger the release of methane gas from these deposits.
- Large deposits of ‘methane hydrate’ are found in Arctic Tundra and under the sea floor.
- Methane in atmosphere oxidizes to carbon dioxide after a decade or two.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- Methane hydrate is a crystalline solid that consists of a methane molecule surrounded by a cage of interlocking water molecules. It is an “ice” that only occurs naturally in subsurface deposits where temperature and pressure conditions are favourable for its formation.
- Regions with suitable temperature and pressure conditions for the formation and stability of methane hydrate– sediment and sedimentary rock units below the Arctic permafrost, sedimentary deposits along continental margins, deep-water sediments of inland lakes and seas, and, under Antarctic ice. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- Methane hydrates, the sensitive sediments, can rapidly dissociate with an increase in temperature or a decrease in pressure. The dissociation produces free methane and water, which can be triggered by global warming. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- Methane is removed from the atmosphere in about 9 to 12 year period by oxidation reaction where it is converted into Carbon Dioxide. Hence, statement 3 is correct.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer
Q2. Consider the following: (2019)
- Carbon monoxide
- Methane
- Ozone
- Sulphur dioxide
Which of the above are released into atmosphere due to the burning of crop/biomass residue?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (d)
Vijay Diwas and Indo Bangladesh Relations
For Prelims: Indo-Pak War 1971, Vijay Diwas, Operation Jackpot, India-Bangladesh Relations
For Mains: India’s role in Bangladesh Liberation War, India-Bangladesh Ties and major irritants in it
Why in News?
Every year 16th December is observed by Indian Armed Forces and Bangladesh as Vijay Diwas (Bijoy Dibos) to mark India's victory over Pakistan in the 1971 war and the birth of Bangladesh as an independent nation.
What are the Key Points about the Indo-Pak War for Bangladesh Liberation?
- Background:
- Pakistan right after India’s independence consisted of East and West Pak where a major problem was the geographical disconnect between the two regions.
- Cultural conflicts and negligence of East Pak’s administration were also challenges.
- In the mid-1960s, leaders such as Sheikh Mujibur Rahman (the founding father of Bangladesh), actively began protesting against the policies of West Pak which was followed by a brutal crackdown by the Pakistani military.
- Pakistan right after India’s independence consisted of East and West Pak where a major problem was the geographical disconnect between the two regions.
- India’s Role:
- On 15 May 1971, India launched Operation Jackpot to recruit, train, arm, equip, supply and advise Mukti Bahini fighters engaged in guerrilla warfare against the Pakistan military.
- On 3rd December 1971, India decided to go on a war with Pakistan to save Bengali Muslims and Hindus in East Pakistan. The war lasted for 13 days.
- After that, a written agreement between India, Pakistan and the provisional government of Bangladesh came into effect bringing an end to the Bangladesh Liberation War.
- Significance:
- 51 years ago, on 16th December, the largest surrender of military personnel took place since the end of World War II.
- The chief of the Pakistani forces surrendered unconditionally to the Indian Army and Mukti Bahini in Dhaka.
- Victory Day celebrations are of importance to not only Bangladesh but also marks a special occasion celebrated across India which bears testimony to the pivotal role of the Indian military and its contribution to the war.
- 51 years ago, on 16th December, the largest surrender of military personnel took place since the end of World War II.
How are India’s Relations with Bangladesh since Its Independence?
- India’s Immediate Recognition:
- India was one of the first countries to recognize Bangladesh and establish diplomatic relations immediately after its independence in December 1971.
- The UN member nations were also quick to recognise Bangladesh’s independent identity.
- Defence Cooperation:
- India and Bangladesh share 4096.7 km. of border; the longest land boundary that India shares with any of its neighbours.
- Assam, West Bengal, Mizoram, Meghalaya, and Tripura share borders with Bangladesh.
- The two also conduct Joint exercises - Army (Exercise Sampriti) and Navy (Exercise Milan).
- India and Bangladesh share 4096.7 km. of border; the longest land boundary that India shares with any of its neighbours.
- Economic Relations:
- In 2021-22, Bangladesh has emerged as the largest trade partner for India in South Asia and the fourth largest destination for Indian exports worldwide.
- Exports to Bangladesh grew more than 66% from USD 9.69 billion in FY 2020-21 to USD 16.15 billion in FY 2021-22.
- Recently, the Prime Minister of Bangladesh visited India and held talks with Indian Prime Minister where India and Bangladesh signed 7 agreements for cooperation in various areas.
- Key Challenges in Relations:
- Despite the remarkable progress, the unresolved Teesta water sharing issue looms large.
- The problem of Bangladeshi civilians being shooted at the border has also dented relations; these shootings occur as many Bangladeshi people try to illegally migrate into India.
- Despite its ‘Neighbourhood First Policy’, India has been losing its influence in the region to China; Bangladesh is an active partner of the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
Way Forward
- Bangladesh is South-Asian region’s fastest growing economy, with social indicators that other countries, including India, can learn. This is the vital link with which India can realise the full potential of either the economic or strategic underpinnings of its Neighbourhood First policy.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. With reference to river Teesta, consider the following statements: (2017)
- The source of river Teesta is the same as that of Brahmaputra but it flows through Sikkim.
- River Rangeet originates in Sikkim and it is a tributary of river Teesta.
- River Teesta flows into Bay of Bengal on the border of India and Bangladesh.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Critically examine the compulsions which prompted India to play a decisive role in the emergence of Bangladesh. (2013)
Drug Menace
For Prelims: Drug Menace, Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan/Drugs-Free India Campaign, World Drug Report 2022
For Mains: Problem of drug abuse and related Initiatives, World Drug Report 2022.
Why in News?
Kerala is using sports to tackle drug menace, for which its Excise department has created clubs near college campuses and hostels in Kerala.
- Apart from making students motivated to participate in sports, awareness classes are conducted and information on substance abuse is shared.
What is the Status of Drug Menace in India?
- The menace of drug addiction has spread fast among the youth of India.
- India is sandwiched between two largest Opium producing regions of the world that is the Golden triangle on one side and the Golden crescent on other.
- The golden triangle area comprises Thailand, Myanmar, Vietnam and Laos.
- The golden crescent area includes Pakistan, Afghanistan and Iran.
- India is sandwiched between two largest Opium producing regions of the world that is the Golden triangle on one side and the Golden crescent on other.
- India is one of the world's single largest opiate markets in terms of users and would likely be vulnerable to increased supply.
- This is because of the intensification of trafficking in opiates originating in Afghanistan may be taking place eastwards, in addition to southwards and westwards along the traditional Balkan route.
- According to World Drug Report 2022, India has the fourth largest quantity of opium seized in 2020 at 5.2 tons and the third-highest amount of morphine was also seized in the same year at 0.7 tons.
- According to the World Drug Report 2021, prescription drugs and their ingredients or 'precursors' are being increasingly diverted for recreational use in India--the largest manufacturer of generic drugs in the world.
- India is also linked to shipment of drugs sold on the 19 major darknet markets analysed over 2011-2020.
What are the Initiatives to Cope with Drug Menace?
- Indian:
- Narco-Coordination Centre: The Narco-Coordination Centre (NCORD) was constituted in November, 2016 and the scheme of “Financial Assistance to States for Narcotics Control” was revived.
- Seizure Information Management System (SIMS): SIMS is a e-portal created by the Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) to create a complete online database of drug offences and offenders.
- National Drug Abuse Survey: The government is also conducting a National Drug Abuse Survey to measure trends of drug abuse in India through the Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment with the help of National Drug Dependence Treatment Centre of AIIMS.
- Project Sunrise: It was launched by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare in 2016, to tackle the rising HIV prevalence in north-eastern states in India, especially among people injecting drugs.
- NDPS Act: It prohibits a person from producing, possessing, selling, purchasing, transporting, storing, and/or consuming any narcotic drug or psychotropic substance.
- The NDPS Act has since been amended thrice – in 1988, 2001 and 2014.
- The Act extends to the whole of India and it applies also to all Indian citizens outside India and to all persons on ships and aircraft registered in India.
- Nasha Mukt Bharat: Government has also announced the launch of the ‘Nasha Mukt Bharat’, or Drug-Free India Campaign which focuses on community outreach programs.
- International Treaties and Conventions to Combat Drug Menace:
- India is signatory of the following international treaties and conventions to combat the menace of Drug Abuse:
- United Nations (UN) Convention on Narcotic Drugs (1961)
- UN Convention on Psychotropic Substances (1971).
- UN Convention against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (1988)
- UN Convention against Transnational Organized Crime (UNTOC) 2000.
- India is signatory of the following international treaties and conventions to combat the menace of Drug Abuse:
Way Forward
- While steps must be taken to stop supply by tamping down on cross-border trafficking, imposing harsher penalties under the NDPS Act, or improving drug enforcement, India must also address the problem on the demand side.
- Addiction should not be seen as a character flaw, but as an ailment that any other person could be struggling with. Therefore, the stigma associated with drug taking needs to be reduced. Society needs to understand that drug-addicts are victims and not criminals.
- Certain crop drugs which have more than 50% alcohol and opioids need to be contained. Strict action is required from police officers and the excise and narcotics department to curb the problem of drug menace in the country.
- Education curriculum should include chapters on drug addiction, its impact and also on de-addiction. Proper Counselling is another alternative.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. India’s proximity to the two of the world’s biggest illicit opium-growing states has enhanced her internal security concerns. Explain the linkages between drug trafficking and other illicit activities such as gunrunning, money laundering and human trafficking. What counter-measures should be taken to prevent the same? (2018)
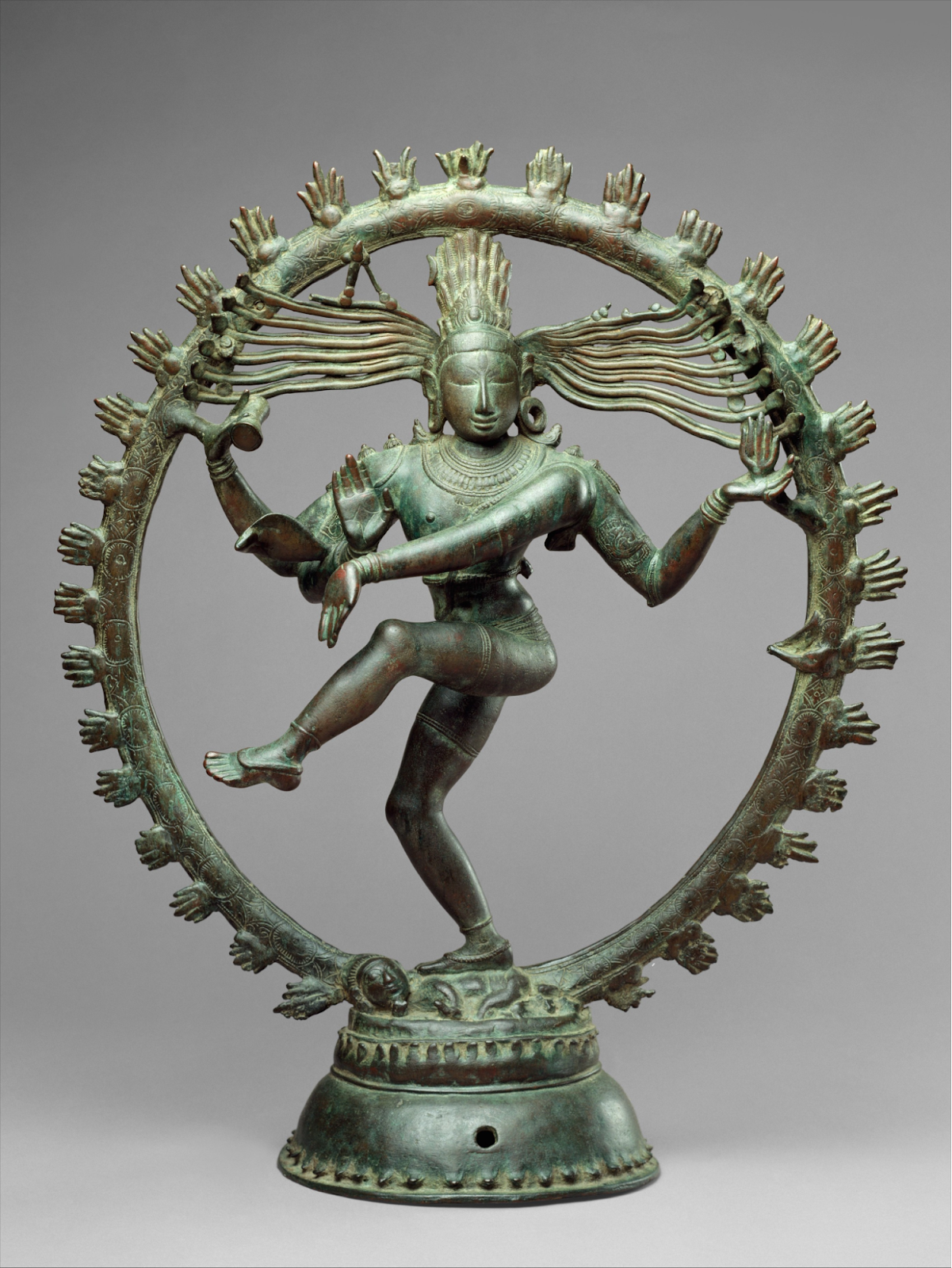
Lord Nataraja
Why in News?
Recently, the Tamil Nadu police successfully stopped the scheduled auctioning of a bronze idol of Nataraja by France.
- The rare variety bronze idol was suspected to have been stolen from Kayathar in Thoothukudi district half a century ago.
What are the Key Facts about Lord Nataraja?
- Nataraja (Lord of the Dance), the Hindu god Shiva in his form as the cosmic dancer, is represented in metal or stone in many Shaivite temples, particularly in South India.
- It is an important piece of Chola sculpture.
- The upper right hand holds the damru (drum), which signifies the sound of creation. All creations spring from the great sound of the damru.
- The upper left-hand holds the eternal fire, which represents the destruction. Destruction is the precursor and inevitable counterpart of creation.
- The lower right hand is raised in the gesture of Abhay mudra signifying benediction and reassuring the devotee to not be afraid.
- The lower left-hand points towards the upraised foot and indicates the path of salvation.
- Shiva is dancing on the figure of a small dwarf. The dwarf symbolises ignorance and the ego of an individual.
- Shiva is shown as the source of all movement within the cosmos and as the god whose doomsday dance, represented by the arch of flames, accompanies the dissolution of the universe at the end of an eon.
- The matted and flowing locks of Shiva represent the flow of river Ganges.
- In ornamentation, one ear of Shiva has a male earring while the other has a female. This represents the fusion of male and female and is often referred to as Ardhanarishwar.
- A snake is twisted around the arm of Shiva. The snake symbolises the kundalini power, which resides in the human spine in the dormant stage. If aroused, one can attain true consciousness.
- The Nataraja is surrounded by a nimbus of glowing lights which symbolises the vast unending cycles of time.
Agni-5 Ballistic Missile
Why in News?
Recently, India successfully carried out the night trials of the Agni-5 nuclear-capable ballistic missile.
What are the Features of the Missile?
- Agni-5 is an ingeniously built advanced surface-to-surface ballistic missile developed under the Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP).
- It is a fire-and-forget missile, which cannot be stopped without an interceptor missile.
- The missile has the capability of hitting targets beyond the range of 5000 km and is crucial for India's self-defense systems.
What are Agni Missiles?
- About:
- The Agni missile class is the backbone of India's nuclear launch capability, as are Prithvi short-range ballistic missiles, submarine-launched ballistic missiles, and fighter aircraft.
- Agni-1 to 5 missiles are designed & developed by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- Other Ranges of Agni Missiles:
- Agni I: Range of 700-800 km.
- Agni II: Range more than 2000 km.
- Agni III: Range of more than 2,500 Km
- Agni IV: Range is more than 3,500 km and can fire from a road mobile launcher.
- Agni-V: The longest of the Agni series, an Inter-Continental Ballistic Missile (ICBM) with a range of over 5,000 km.
What is the Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme?
- IGMDP was the brainchild of renowned scientist Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam.
- It was intended to attain self-sufficiency in the field of missile technology.
- After keeping in mind, the requirements of various types of missiles by the defense forces, the program recognized the need to develop five missile systems.
- The IGMDP formally got the approval of the Indian government in 1983.
- It brought together the country’s scientific community, academic institutions, R&D laboratories, industries and the three defence services in giving shape to the strategic, indigenous missile systems.
- The missiles developed under IGMDP are:
- Short-range surface-to-surface ballistic missile – Prithvi
- Intermediate-range surface-to-surface ballistic missile – Agni
- Short-range low-level surface-to-air missile – Trishul
- Medium-range surface-to-air missile – Akash
- Third generation anti-tank missile – Nag
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q1. What is “Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD)”, sometimes seen in the news? (2018)
(a) An Israeli radar system
(b) India’s indigenous anti-missile programme
(c) An American anti-missile system
(d) A defence collaboration between Japan and South Korea.
Ans: (c)
- Terminal High Altitude Area Defence (THAAD) is an American anti-missile system designed to intercept and destroy short and medium-range ballistic missiles during their “terminal” phase of flight when they are falling towards the target.
- They have the ability to intercept missile inside and outside the atmosphere.
- It is interoperable with other ballistic missile defence systems and is highly mobile and deployable worldwide.
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Q2. With reference to Agni-IV Missile, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2014)
- It is a surface-to-surface missile.
- It is fuelled by liquid propellant only.
- It can deliver one-tonne nuclear warheads about 7500 km away.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
- Agni-IV is a nuclear-capable long-range ballistic missile of India, with a strike range of 4,000 km.
- The indigenously developed Agni-IV is a two-stage surface-to-surface missile. It is 20 metres long with a weight of 17 tonnes. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- It is a two stage solid fuelled system that can carry a one-tonne nuclear warhead over a distance of 4,000 kilometres. Hence, statements 2 and 3 are not correct. Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Surya Kiran XVI
Why in News?
The 16th Edition of Indo-Nepal joint training Exercise “Surya Kiran” between India and Nepal is being conducted at Saljhandi, Nepal.
What is Surya Kiran?
- It is a military exercise conducted annually between India and Nepal.
- The objective of this exercise is to:
- Establish military relations in inaccessible mountainous areas by the soldiers of both countries,
- Provide humanitarian assistance under disaster management,
- Get training in anti-terrorist operations,
- Build interoperability and sharing expertise between the two countries.
- The 15th edition of Surya Kiran took place at Pithoragarh in Uttarakhand, India.

.png)