International Relations
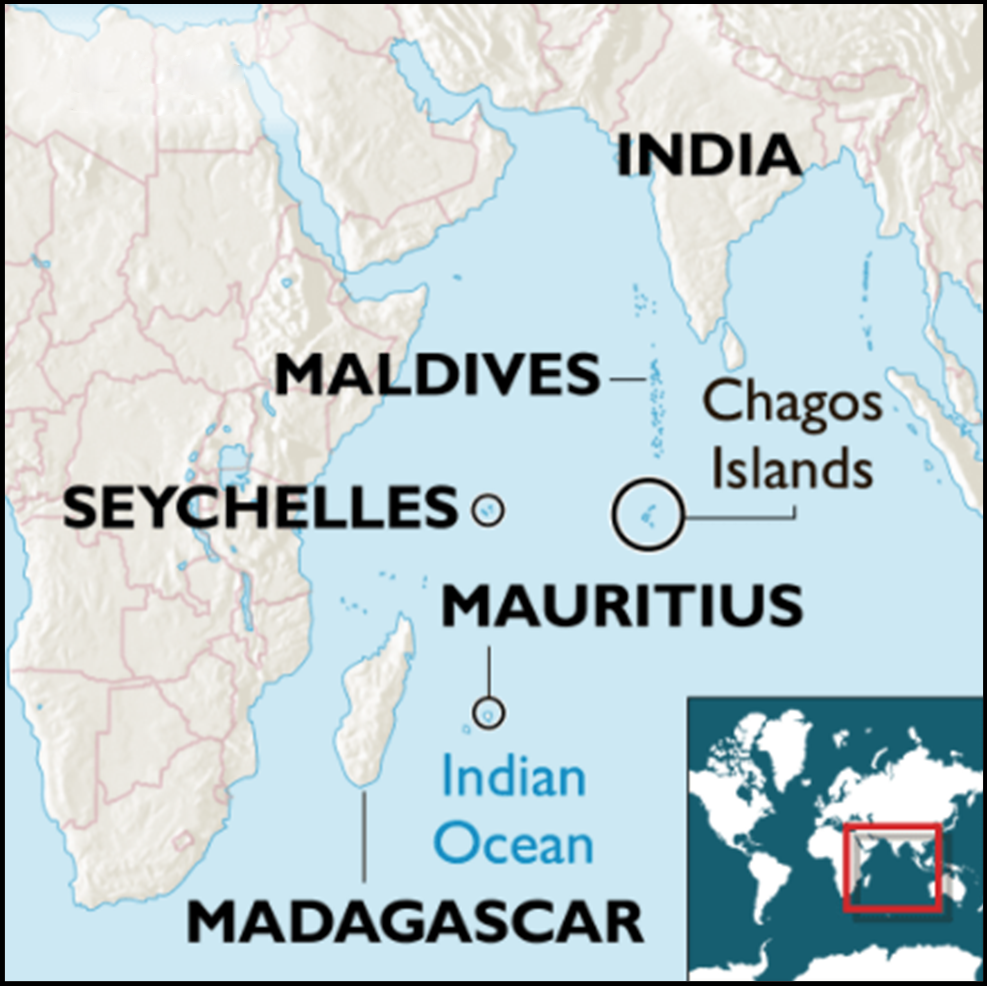
India-Mauritius Relations
For Prelims: Agalega Island, Chagos Archipelago, Colombo Security Conclave, IORA, Indian Ocean Conference, Dandi March, SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region), Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) Program, National Centre for Good Governance (NCGG).
For Mains: Significance of Mauritius as international partner, India-Mauritius relations.
Why in News?
During the Indian Prime Minister’s visit to Mauritius, both nations signed multiple agreements on trade, maritime security, and defense, emphasizing regional cooperation and elevating their ties to an enhanced strategic partnership.
- PM also received the highest national award of Mauritius, the 'Grand Commander of the Order of the Star and Key of the Indian Ocean.'
What are the Key Outcomes of India’s PM Visit to Mauritius?
- Enhanced Strategic Partnership: Both elevated their ties to an Enhanced Strategic Partnership, strengthening security, trade in local currencies, and development while reaffirming their commitment to a free and secure Indian Ocean.
- Both countries agreed to ratify the protocol amending the Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) to align with international treaty standards.
- ‘Mahasagar’ Vision: India introduced the MAHASAGAR (Mutual and Holistic Advancement for Security and Growth Across Regions) initiative for the Global South.
- The MAHASAGAR vision builds on SAGAR, enhancing engagement with the Global South through technology sharing, concessional loans, grants, trade, and mutual security cooperation.
- Security Cooperation: India and Mauritius agreed to enhance the use of Agalega Island's new runway and jetty, developed by India.
- India also reaffirmed support for Mauritius’s sovereignty over the Chagos Archipelago.
- Cooperation will be strengthened in white shipping, blue economy, and hydrography.
- Developmental Support: India announced its first-ever rupee-denominated Line of Credit to support Mauritius in replacing its water pipelines.
- India will help Mauritius establish a police academy and a maritime information-sharing center.
- The Mauritius President inaugurated the Atal Bihari Vajpayee Institute of Public Service and Innovation, a health center, and 20 Indian-funded community projects.
- New Parliament Building: India will construct a new Parliament building for Mauritius, which India described as a gift from the “Mother of Democracy”.
- Multilateral Engagements: India reaffirmed its commitment to working with Mauritius in regional and international forums like the Colombo Security Conclave, IORA, and the Indian Ocean Conference.
Historical Connection Between India and Mauritius
- Pre-Independence of India: The first Indians in Mauritius arrived during French colonial rule (1700s) as artisans and masons from Puducherry (Mauritius was once a French colony, before being taken over by the British).
- Under British rule, about 500,000 Indian indentured workers migrated between 1834 and the early 1900s, with two-thirds settling in Mauritius.
- Mahatma Gandhi visited Mauritius in 1901, advocating education and political empowerment for the Indian community.
- As a tribute to Gandhi, Mauritius celebrates its National Day on 12th March, marking the Dandi March.
- Post-Independence of India: India and Mauritius established diplomatic ties in 1948, two decades before Mauritius gained independence (1968).
- Mauritius' first Prime Minister, Seewoosagur Ramgoolam, was closely associated with Indian leaders like Gandhiji, JL Nehru, and Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose.
Why are India and Mauritius Important for Each Other?
Importance of Mauritius for India
- Maritime Significance: Mauritius' strategic location in the western Indian Ocean makes it a key maritime partner under India’s SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region) initiative (now MAHASAGAR).
- Countering China’s Presence: With China's expanding presence in the Indian Ocean, India's strong ties with Mauritius help safeguard securing Sea lines of communication (SLOC) and India’s strategic interests.
- Economic Relations: Mauritius is a gateway for India’s trade and investment in Africa, being part of the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA).
- India is one of Mauritius’s largest trading partners, and Mauritius is the 2nd-largest FDI source into India (FY 2023-24) after Singapore.
- Cultural Links: About 70% of Mauritius population are of Indian origin that help promote Indian culture, language, and heritage.
- Mauritius shares strong cultural ties with India, with grand Maha Shivratri celebrations and Ganga Talao as a revered Hindu pilgrimage site.
Importance of India for Mauritius
- Leading Development Partner: India has been Mauritius’s key development partner since its independence (1968), providing USD 1.1 billion in the last decade alone.
- India has supported Mauritius in implementing key infrastructure projects, including the Metro Express, Supreme Court Building, Hospitals, etc.
- Maritime Security Assistance: India is Mauritius’s key security partner, supporting EEZ protection through naval patrols, joint maritime surveillance, and hydrographic surveys.
- Disaster Assistance: India has been Mauritius’s first responder in crises, providing aid during Cyclone Chido (2024), the Wakashio Oil Spill (2020), and the Covid-19 pandemic.
- Capacity Building: Mauritius is a key beneficiary of India’s Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) program, with 4,940 Mauritians trained since 2002.
- India also offers customized training to civil servants of Mauritius through National Centre for Good Governance (NCGG).
|
Click Here to Read: |
Conclusion
India and Mauritius have reinforced their strategic partnership through agreements in trade, security, and development. India’s "Mahasagar" vision and infrastructural support strengthen regional cooperation, counter external influences, and enhance economic ties. Their shared history, cultural bonds, and geopolitical alignment make this partnership crucial for regional stability and prosperity.
|
Drishti Mains Question: How does India’s strategic partnership with Mauritius contribute to its maritime security and regional influence in the Indian Ocean? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to ‘Indian Ocean Rim Association for Regional Cooperation (IOR-ARC)’, consider the following statements: (2015)
- It was established very recently in response to incidents of piracy and accidents of oil spills.
- It is an alliance meant for maritime security only.
Which of the statements given above is/ are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Q. A great deal of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) to India comes from Mauritius than from many major and mature economies like UK and France. Why? (2010)
(a) India has preference for certain countries as regards receiving FDI
(b) India has double taxation avoidance agreement with Mauritius
(c) Most citizens of Mauritius have ethnic identity with India and so they feel secure to invest in India
(d) Impending dangers of global climatic change prompt Mauritius to make huge investments in India.
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Why indentured labour was taken by British from India to other colonies? Have they been able to preserve their cultural identity over there? (2018)


Important Facts For Prelims
World Air Quality Report 2024
Why in News?
The World Air Quality Report 2024, released by Swiss company IQAir, ranked India as the 5th most polluted country globally.
What are the Key Findings of the World Air Quality Report?
- India: India is the 5th most polluted country in 2024, improving slightly from 3rd place in 2023.
- Polluted Cities: Delhi remains the most polluted capital globally with a Particulate matter (PM) 2.5 concentration of 91.6 µg/m³ (micrograms per cubic metre).
- 6 of the world's 10 most polluted cities and 13 of the top 20 are in India, with Byrnihat (Assam-Meghalaya border) topping the list at a PM2.5 concentration of 128.2 µg/m³.
- Other polluted cities include Mullanpur (Punjab), Gurugram, Faridabad, Bhiwadi, and Noida.
- 6 of the world's 10 most polluted cities and 13 of the top 20 are in India, with Byrnihat (Assam-Meghalaya border) topping the list at a PM2.5 concentration of 128.2 µg/m³.
- PM2.5 Reduction: India saw a 7% decrease in PM2.5 levels, averaging 50.6 µg/m³ in 2024, down from 54.4 µg/m³ in 2023.
- However, this is still 10 times higher than the World Health Organization (WHO's) recommended safe limit of 5 µg/m³. 35% of Indian cities reported PM2.5 levels exceeding this limit.
- Pollution Sources: Major contributors include vehicle emissions, industrial pollution, and the burning of biomass.
- Northern India faced extreme pollution levels with crop stubble-burning contributing to 60% of PM2.5 levels.
- Polluted Cities: Delhi remains the most polluted capital globally with a Particulate matter (PM) 2.5 concentration of 91.6 µg/m³ (micrograms per cubic metre).
- Global: The most polluted countries by annual average PM2.5 levels are Chad (91.8 µg/m³), Bangladesh (78 µg/m³), Pakistan (73.7 µg/m³), and Congo (58.2 µg/m³).
- The report highlights that most of the global population is breathing polluted air, with only 12 countries, regions, or territories reporting PM2.5 concentrations below the WHO’s recommended limit.
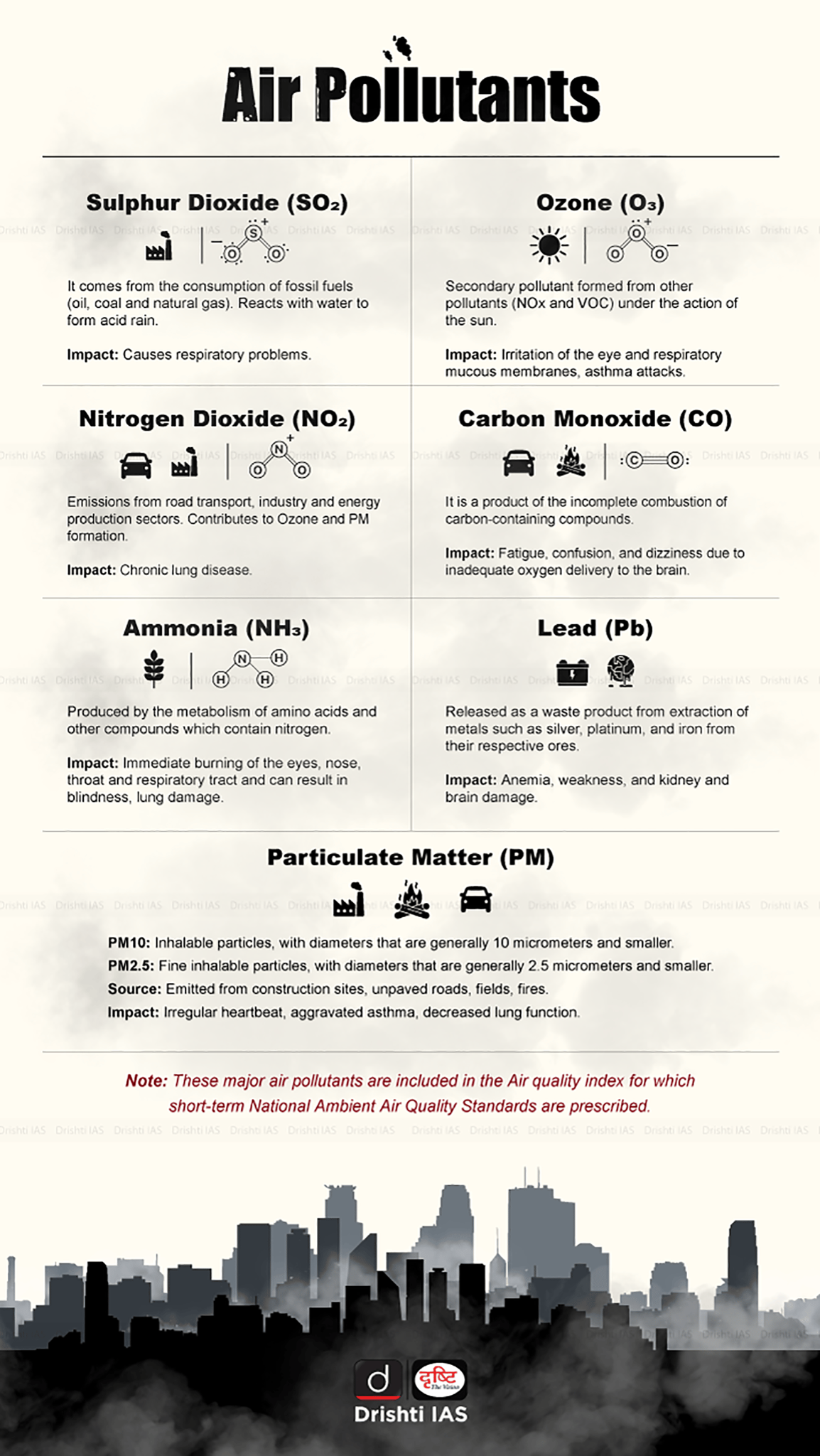
Air Pollution
- Air pollution is the contamination of air by chemical, physical, or biological agents that alter its natural composition.
- Major sources include combustion, vehicles, industries, and fires. Pollutants like PM, CO, O₃, NO₂, and SO₂ cause respiratory diseases and high mortality.
- WHO reports that 99% of the global population breathes polluted air, with low- and middle-income countries most affected.
- Prolonged PM2.5 exposure cuts life expectancy by 5.2 years in India, linked to 1.5 million annual deaths between 2009–2019, as per the Lancet Planetary Health Study.
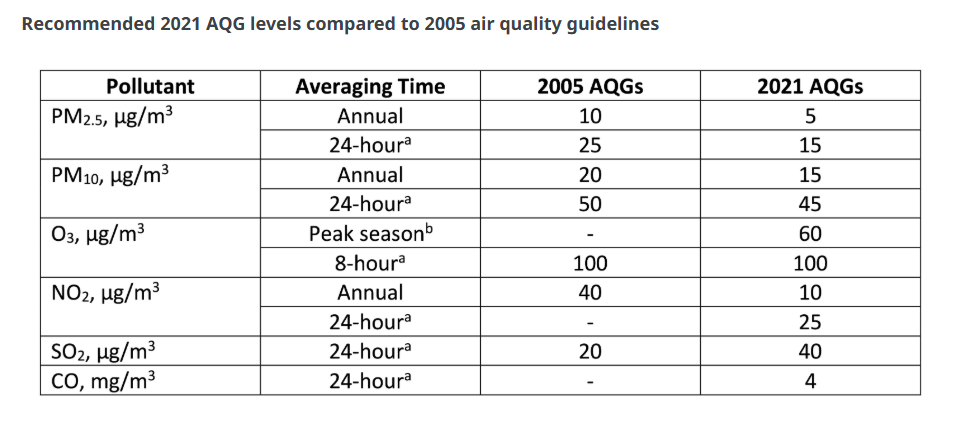
- WHO Air Quality Guidelines (AQG) aim to help governments reduce air pollution and improve public health.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
In the cities of our country, which among the following atmospheric gases are normally considered in calculating the value of the Air Quality Index? (2016)
- Carbon dioxide
- Carbon monoxide
- Nitrogen dioxide
- Sulphur dioxide
- Methane
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Mains
Describe the key points of the revised Global Air Quality Guidelines (AQGs) recently released by the World Health Organisation (WHO). How are these different from its last update in 2005? What changes in India’s National Clean Air Programme are required to achieve revised standards? (2021)


Rapid Fire
APAAR ID
The Automated Permanent Academic Account Registry (APAAR) ID, aims to standardize student records. However, concerns over implementation, data privacy have sparked debates among activists.
- APAAR ID: Introduced under the National Education Policy 2020 and aligned with the National Credit Framework, it aims to establish a "One Nation, One Student ID" system to streamline academic records and facilitate transitions between educational levels.
- APAAR assigns a 12-digit ID, linking academic records to DigiLocker and Academic Bank of Credits for storage and verification.
- Schools record data, while Higher Education Institutions & Skill Institutes access verified academic records for admissions and recruitment.
- Concerns About APAAR ID: APAAR's Aadhaar linkage is causing issues due to spelling mismatches, necessitating updates.
- While the Education Ministry claims APAAR is voluntary, Central Board of Secondary Education’s push for 100% enrolment of APAAR raises concerns of implicit mandates, contradicting the Supreme Court ruling in Justice (Retd.) K.S. Puttaswamy v. Union of India (2019), which held that Aadhaar cannot be required for basic education access.
- The Advocacy groups are concerned about risks in handling minors’ sensitive personal data without robust data protection.
- The Data Protection Act, 2023 (not yet enforced) mandates that consent must be free, informed, and unambiguous, which activists argue is being ignored.
| Read more: APAAR: One Nation One Student ID Card |


Rapid Fire
Mycelium Bricks
In the face of climate change, the construction industry is seeking low-carbon alternatives, and mycelium bricks have emerged as a promising innovation.
- Mycelium Bricks: Created from fungal spores, husk, and sawdust, mycelium bricks form a lightweight, fibrous structure with a low environmental impact compared to traditional fired clay bricks, which emit nearly 300 million tonnes of CO₂ annually.
- They are biodegradable, fire-resistant, lightweight, and good heat insulators, making them suitable for interior panelling, filters, and electronics.
- Potential applications include interior panelling, liquid filters, sports equipment, and electronic components.
- Challenges Hindering Adoption: Mycelium bricks have low load-bearing capacity, high moisture absorption, and a short lifespan due to biodegradability and vulnerability to termites, making them less durable than concrete.
- Tropical weather conditions, high humidity, and lack of infrastructure in India make large-scale manufacturing expensive and impractical.
- Potential Solutions: Flame retardants and Ultra Violet Coatings can improve fire resistance and durability, while R&D and policy support can enhance competitiveness with clay bricks.
| Read more: Energy Efficiency in Construction Sector |


Rapid Fire
PM-YUVA 3.0
The Ministry of Education launched PM-YUVA 3.0 (Young, Upcoming and Versatile Authors)-Prime Minister’s Scheme for Mentoring Young Authors.
- It aims to train young authors (below 30 years) to promote reading, writing, and book culture while projecting Indian literature globally.
- Themes:
- Contribution of Indian Diaspora in Nation Building
- Indian Knowledge System
- Makers of Modern India (1950-2025)
- National Book Trust (NBT), under the Ministry of Education, is the implementing agency.
- Books to be published by NBT and translated into multiple Indian languages under Ek Bharat Shreshtha Bharat.
- It aligns with NEP 2020 to support empowerment of young minds and prepares future leaders.
| Read More: YUVA Scheme for Young Writers |


Rapid Fire
Railways’ Work Under Mission Amrit Sarovar
The Indian Railways has been integrated into the Mission Amrit Sarovar initiative to aid in water conservation by constructing and rejuvenating ponds across the country.
- Indian Railways will desilt, excavate, or create water bodies near railway lines in coordination with district authorities and the Ministry of Rural Development.
About Mission Amrit Sarovar: It was launched in April 2022 to construct or rejuvenate 75 ponds per district. As of October 2024, over 68,000 ponds have been completed.
- It ensures long-term water availability through community participation, and climate resilience to secure sustainable water resources.
- It is an initiative of the Ministry of Rural Development and Bhaskaracharya National Institute for Space Application and Geo-informatics (BISAG-N) is the Mission's technical partner.
- It is implemented through convergence with schemes like MGNREGA, 15th Finance Commission Grants, PMKSY, and state programs.
| Read More: Mission Amrit Sarovar |