Maps
Governance
Custodial Death
Prelims: Fundamental Rights, Indian Penal Code, Code of Criminal Procedure
Mains: Reasons for Custodial Deaths, Reforms in Policing, Technology and Interrogation, Measures to avoid custodial deaths
Why in News?
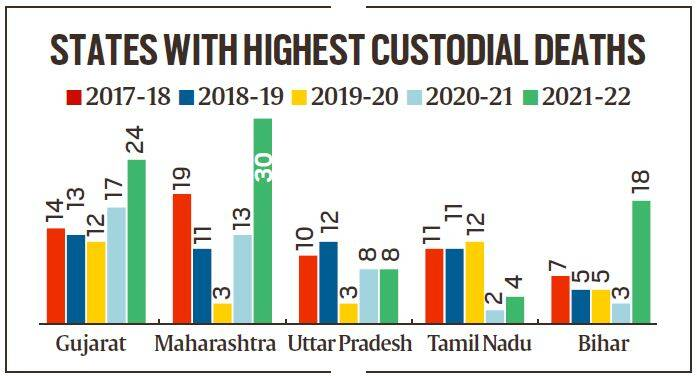
According to the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) in the last five years, the highest number of custodial deaths have been reported in Gujarat at 80.
What is Custodial Death?
- About:
- Custodial death is a death that occurs while a person is in the custody of law enforcement officials or in a correctional facility. It can occur due to various causes such as use of excessive force, neglect, or abuse by the authorities.
- According to the Law commission of India, the crime by a public servant against the arrested or the detained person who is in custody amounts to custodial violence.
- Custodial Death in India:
- A total of 146 cases of death in police custody were reported during 2017-2018,
- 136 in 2018-2019,
- 112 in 2019-2020,
- 100 in 2020-2021,
- 175 in 2021-2022.
- In the last five years, the highest number of custodial deaths (80) has been reported in Gujarat, followed by Maharashtra (76), Uttar Pradesh (41), Tamil Nadu (40) and Bihar (38).
- National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) has recommended monetary relief in 201 cases, and disciplinary action in one case.
- A total of 146 cases of death in police custody were reported during 2017-2018,
What are the Possible Reasons for Custodial Deaths?
- Absence of Strong Legislation:
- India does not have an anti-torture legislation and is yet to criminalise custodial violence, while action against culpable officials remains illusory.
- Institutional Challenges:
- The entire prison system is inherently opaque giving less room to transparency.
- India also fails in bringing the much desired Prison Reforms and prisons continue to be affected by poor conditions, overcrowding, acute manpower shortages and minimal safety against harm in prisons.
- Excessive Force:
- The use of excessive force including torture to target marginalised communities and control people participating in movements or propagating ideologies which the state perceives as opposed to its stature.
- Lengthy Judicial Processes:
- Lengthy, expensive formal processes followed by courts dissuade the poor and the vulnerable.
- Not Adhering to International Standard:
- Although India has signed the United Nations Convention against Torture in 1997 its ratification still remains.
- While signing only indicates the country’s intention to meet the obligations set out in the treaty, Ratification, on the other hand, entails bringing in laws and mechanisms to fulfil the commitments.
- Other Factors:
- Medical neglect or lack of medical attention, and even suicide.
- Poor training or lack of accountability among law enforcement officials.
- Inadequate or substandard conditions in detention centers.
- Underlying health conditions or pre-existing medical conditions that are not adequately addressed or treated while in custody.
What are the Provisions Available Regarding Custody?
- Constitutional Provisions:
- Article 21:
- Article 21 states that “No person shall be deprived of his life or personal liberty except according to procedure established by law”.
- Protection from torture is a fundamental right enshrined under Article 21 (Right to Life) of the Indian constitution.
- Article 21 states that “No person shall be deprived of his life or personal liberty except according to procedure established by law”.
- Article 22:
- Article 22 provides “Protection against arrest and detention in certain cases”.
- The right to counsel is also a fundamental right under Article 22(1) of the India constitution.
- Article 22 provides “Protection against arrest and detention in certain cases”.
- Article 21:
- Role of State Government:
- Police and public order are State subjects as per the Seventh Schedule of the Constitution of India.
- It is primarily the responsibility of the state government concerned to ensure the protection of human rights.
- Role of Central Government:
- The Central Government issues advisories from time to time and also has enacted the Protection of Human Rights Act (PHR), 1993.
- It stipulates establishment of the NHRC and State Human Rights Commissions to look into alleged human rights violations by public servants.
- Legal Provisions:
- Criminal Procedure Code (CrPC):
- Section 41 of Criminal Procedure Code (CrPC) was amended in 2009 to include safeguards so that arrests and detentions for interrogation have reasonable grounds and documented procedures, arrests are made transparent to family, friends and public, and there is protection through legal representation.
- Indian Penal Code:
- Sec 330 & 331 of the Indian Penal Code 1860 provides punishment for injury inflicted for extorting confession.
- Crime of custodial torture against prisoners can be brought under Sec 302, 304, 304A, and 306 of IPC.
- Protection under Indian Evidence Act, 1872:
- Section 25 of the Act provides that a confession made to the police cannot be admitted in Court.
- Section 26 of the Act provides that a confession made to the police by the person cannot be proved against such person unless it is made before the Magistrate.
- Indian Police Act, 1861:
- Sections 7 & 29 of the Police Act, 1861 provide for dismissal, penalty or suspension of police officers who are negligent in the discharge of their duties or unfit to perform the same.
- Criminal Procedure Code (CrPC):
Way Forward
- Ensuring strict adherence to human rights laws and regulations, including the prevention of torture and cruel, inhuman, or degrading treatment or punishment.
- Implementing comprehensive and effective training programs for law enforcement officials on the proper use of force and non-lethal methods of controlling suspects.
- Establishing independent and impartial investigations into all custodial deaths to determine the cause of death and hold responsible parties accountable.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q.1 Instances of the President’s delay in commuting death sentences has come under public debate as denial of justice. Should there be a time specified for the President to accept/reject such petitions? Analyse. (2014)
Q.2 National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) in India can be most effective when its tasks are adequately supported by other mechanisms that ensure the accountability of a government. In light of above observation assess the role of NHRC as an effective complement to the judiciary and other institutions in promoting and protecting human rights standards. (2014)


Governance
ChatGPT-Powered WhatsApp Chatbot
Prelims: Generative Artificial Intelligence, Google’s Bard, Artificial Intelligence.
Mains: ChatGPT-Powered WhatsApp Chatbot and Associated Concerns.
Why in News?
The Ministry of Electronics and IT’s (MeitY) BHASHINI is working on a ChatGPT-Powered WhatsApp Chatbot to help Indian farmers learn about various government schemes.
- BHASHINI (BHASHa INterface for India) is India’s Artificial Intelligence (AI) led language translation platform.
- The launch of the WhatsApp chatbot may take time as ChatGPT currently relies on input in English, and the support for local languages is limited.
What are the Intended Features?
- It will let users send a question via voice notes.
- A user could simply ask a question using voice notes and receive a voice-based response generated by ChatGPT.
- The chatbot has been developing with the view of India’s rural and agrarian population that most depend on government schemes and subsidies.
- These potential users speak a wide range of languages, which makes it important to build a language model that can successfully identify and understand them.
- This will help numerous farmers in India who may not be familiar with typing on smartphones.
- The ChatGPT-powered WhatsApp chatbot will support 12 languages, including English, Hindi, Tamil, Telugu, Marathi, Bengali, Kannada, Odia, and Assamese.
- The majority of those who will use this chatbot would not know English, for which the Government's Bhasha Daan Initiative will be used.
- Bhasha Daan is an initiative to crowdsource language inputs for multiple Indian languages as part of Project BHASHINI. It calls upon citizens to help build an open repository of data to digitally enrich his/her own language.
What are the Concerns Related to Such Models?
- Responses of generative AI models like ChatGPT, Google’s Bard may not always be accurate.
- Recently, Bard made a factual error about James Webb Space Telescope. The company’s shares dropped by USD 100 billion after the mistake was spotted.
- In its current testing phase, the WhatsApp chatbot can only respond to simple queries about government schemes, etc.
- This is primarily due to the current limitation of ChatGPT itself — the fact that it cannot access information from the Internet in real time.
- ChatGPT’s language model was trained on a dataset that only includes information until 2021.
- However, this could soon change. Recently, Microsoft announced a new version of its search engine Bing, powered by an upgraded version of the same AI technology that underpins ChatGPT.
- The feature will be powered by an updated version of GPT 3.5, the AI language model created by OpenAI that powers ChatGPT.
- It called this the “Prometheus Model”, and said it was more powerful than GPT 3.5 and better able to answer search queries with more up-to-date information and annotated answers.
What is ChatGPT?
- About:
- ChatGPT is a variant of GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) which is a large-scale neural network-based language model developed by OpenAI.
- GPT models are trained on vast amounts of text data to generate human-like text.
- It can generate responses to a wide range of topics, such as answering questions, providing explanations, and engaging in conversations.
- In addition to being able to "admit its mistakes, challenge false premises, and refuse unsuitable requests," the ChatGPT can also "answer follow-up questions."
- The chatbot was also trained using Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF).
- Usage:
- It can be used in real-world applications such as digital marketing, online content creation, answering customer service queries or as some users have found, even to help debug code.
- The bot can respond to a large range of questions while imitating human speaking styles.
- It is being seen as a replacement for basic emails, party planning lists, CVs, and even college essays and homework.
- It can also be used to write code, as examples have shown
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)


Indian Polity
The Missing Deputy Speaker
Prelims: Position of speaker and Deputy speaker, Provisions for Presiding Officers Of the parliament.
Mains: Significance of Deputy Speaker.
Why in News?
Supreme Court sought response from Centre on a Public Interest Litigation (PIL) that contends that not electing a Deputy Speaker to the 17th (present) Lok Sabha, since 2019, is “against the letter and spirit of the Constitution".
- The post has also been lying vacant in the five state Assemblies including Rajasthan, Uttarakhand, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, and Jharkhand.
What are the Constitutional Provisions?
- Article 93 says that the House of the People (Lok Sabha) shall, as soon as may be, choose two members to be Speaker and Deputy Speaker so often as the offices become vacant. However, it does not provide a specific time frame.
- Article 178 contains the corresponding position for Speaker and Deputy Speaker of the Legislative Assembly of a state.
What are the Different Viewpoints on the Matter?
- Experts:
- Experts point out that both Articles 93 and 178 use the word “shall”, indicating that the election of Speaker and Deputy Speaker is mandatory under the Constitution.
- Union Government:
- Government argues that there is no “immediate requirement” for a Deputy Speaker as “bills are being passed and discussions are being held” as normal in the House.
- Further, there is a panel of nine members selected from different parties who can act as chairpersons to assist the Speaker to run the House.
Can the Judiciary Intervene in the Matter?
- Article 122 says, “The validity of any proceedings in Parliament shall not be called in question on the ground of any alleged irregularity of procedure.”
- Courts usually don’t intervene in the procedural conduct of Parliament. However, Experts argue that the courts do have jurisdiction to at least inquire into why there has been no election to the post of Deputy Speaker since the Constitution does envisage an election “as soon as may be".
What are the Provisions Regarding Deputy Speaker?
- Election:
- In Lok Sabha, the election of Deputy Speaker is governed by Rule 8 of The Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in Lok Sabha.
- The Deputy Speaker is elected by the Lok Sabha from amongst its members right after the election of the Speaker. The date of election of the Deputy Speaker is fixed by the Speaker.
- Time Frame:
- The election of the Deputy Speaker usually takes place in the second session and is generally not delayed further in the absence of genuine and unavoidable constraints.
- Term of Office and Removal:
- Like the Speaker, the Deputy Speaker remains in office usually for the entire duration of the House (5 years).
- The Deputy Speaker may vacate his/her office earlier in any of the following three cases:
- If he ceases to be a member of the Lok Sabha.
- If he resigns by writing to the Speaker.
- If he is removed by a resolution passed by a majority of all the then members of the Lok Sabha. Such a resolution can be moved only after giving 14 days’ advance notice.
- Position of the Deputy Speaker:
- Under article 95 The Deputy Speaker performs the duties of the Speaker’s office when it is vacant and acts as the Speaker when the latter is absent from the sitting of the House. In both the cases, he assumes all the powers of the Speaker.
- Deputy Speaker is not subordinate to the Speaker. He is directly responsible to the House. Consequently, if either of them wishes to resign, they must submit their resignation to the House which implies that Speaker gives resignation to deputy Speaker.
What is the Need of Deputy Speaker?
- Maintains Continuity: Deputy Speaker maintains continuity of the office whenever speaker is absent or the office becomes vacant.
- Represents The House: If Speaker resigns, he/she tenders resignation to Deputy Speaker.
- If the post of Deputy Speaker is vacant the Secretary-General receives the letter of resignation and informs the House about it. The resignation is notified in the Gazette and the Bulletin, as per the Rules for Presiding Officers of Lok Sabha.
- Strengthens the Opposition: Since 2011, convention has been to offer the position of deputy Speaker to Opposition party.
- Though Constitutionally, Deputy speaker can be from Opposition or Majority party.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. Consider the following statements: (2017)
- In the election for Lok Sabha or State Assembly, the winning candidate must get at least 50 percent of the votes polled, to be declared elected.
- According to the provisions laid down in the Constitution of India, in Lok Sabha, the Speaker’s post goes to the majority party and the Deputy Speaker’s to the Opposition.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
- The system of first-past-the-post (FPTP) is used in India for direct elections to the Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assemblies. In this voting method, the candidate with the highest number of votes (not necessarily more than 50%) in a constituency is declared the winner. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- According to the Constitution, the Speaker and the Deputy Speaker in the Lok Sabha are elected from amongst its members. They can be from either the majority party or the opposition party. Hence, statement 2 is not correct. Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Q2. Regarding the office of the Lok Sabha speaker, consider the following statements: (2012)
- He/She holds the office during the pleasure of the President.
- He/She need not be a member of the House at the time of his/her election but has to become a member of the House within six months from the date of his/her election.
- If he/she intends to resign, the letter of his/her resignation has to be addressed to the Deputy Speaker.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) None
Ans: (b)
- The Speaker is elected by the members of Lok Sabha from amongst its members (as soon as may be, after its first sitting). Hence, statement 2 is not correct.
- Whenever the office of the Speaker falls vacant, the Lok Sabha elects another member to fill the vacancy. The date of election of the Speaker is fixed by the President. Usually, the Speaker remains in office during the life of the Lok Sabha. However, he has to vacate his office earlier in any of the following three cases:
- if he ceases to be a member of the Lok Sabha.
- if he resigns by writing to the Deputy Speaker; Hence, statement 3 is correct.
- if he is removed by a resolution passed by a majority of all the members of the Lok Sabha. Such a resolution can be moved only after giving 14 days advance notice. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.


Biodiversity & Environment
Global Sea-level Rise and Implications: WMO
Prelims: WMO, Climate Crisis, Global Warming, Coastal Ecosystems.
Mains: Global Sea-level Rise and Implications.
Why in News?
According to the World Meteorological Organisation ‘s (WMO) Report “Global Sea-level Rise and Implications”, India, China, Bangladesh and the Netherlands face the highest threat of sea-level rise globally.
- Several big cities on all continents are threatened by the rise in sea level.
- These include Shanghai, Dhaka, Bangkok, Jakarta, Mumbai, Maputo, Lagos, Cairo, London, Copenhagen, New York, Los Angeles, Buenos Aires and Santiago.
What are the Highlights of the Report?
- Trends and Projections:
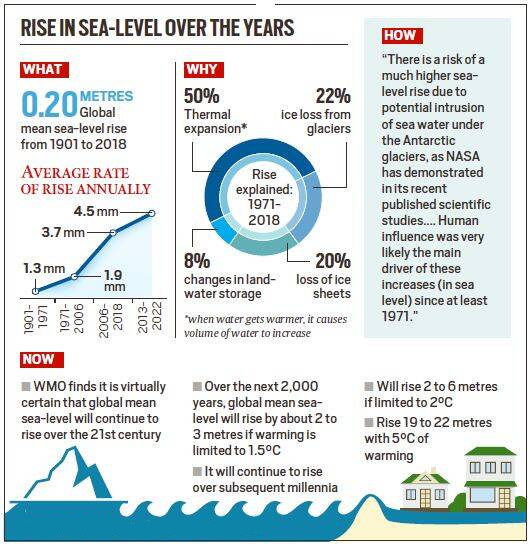
- Between 2013 and 2022, Global mean sea-level was 4.5 mm/year and human influence was likely the main driver of these increases since at least 1971.
- Global mean sea-level increased by 0.20m between 1901 and 2018,
- 1.3 mm/ year between 1901 and 1971,
- 1.9 mm/year between 1971 and 2006
- 3.7 mm/year between 2006 and 2018.
- Even if global heating is limited to 1.5 degrees Celsius over pre-industrial levels, there will still be a sizable sea level rise.
- But every fraction of a degree counts. If temperatures rise by 2 degrees, that level rise could double, with further temperature increases bringing exponential sea level increases.
- Between 2013 and 2022, Global mean sea-level was 4.5 mm/year and human influence was likely the main driver of these increases since at least 1971.
- Contributors to Sea Level Rise:
- Thermal expansion contributed to 50% of sea level rise during 1971-2018, while ice loss from glaciers contributed to 22%, ice-sheet loss to 20% and changes in land-water storage 8%.
- The rate of ice-sheet loss increased by a factor of four between 1992-1999 and 2010-2019. Together, icesheet and glacier mass loss were the dominant contributors to global mean sea level rise during 2006-2018.
- Impacts:
- At sustained warming levels between 2-3 degree Celcius, the Greenland and West Antarctic ice sheets will be almost completely and irreversibly lost over multiple millennia causing potentially multimeter sea-level rise.
- Sea-level rise will bring cascading and compounding impacts resulting in losses of coastal ecosystems and ecosystem services, groundwater salinization, flooding and damage to coastal infrastructure that cascade into risks to livelihoods, settlements, health, well-being, food, displacement and water security, and cultural values in the near to long-term.
What is the Scenario for India?
- Rate of Sea Level Rise:
- According to the Ministry of Earth Sciences, on average, the sea level along the Indian coast was observed to be rising at a rate of about 1.7 mm/year during the last century (1900-2000).
- A 3 cm sea level rise could cause the sea to intrude inland by about 17 meters. At future rates of 5 cm/decade, this could be 300 metres of land taken by the sea in a century.
- India is more Susceptible:
- India is most vulnerable to compounding impacts of sea level rise.
- In the Indian ocean half of sea level rise is due to the volume of water expanding since the ocean is warming up rapidly.
- The contribution from glacier melt is not as high.
- The Indian Ocean is the fastest warming ocean in terms of surface warming.
- Implications:
- India is facing compound extreme events along our coastline. Cyclones are intensifying rapidly due to more moisture and heat from ocean warming.
- The amount of flooding also increases because storm surges are compounding sea level rise decade by decade.
- Cyclones are bringing more rain than earlier. Super Cyclone Amphan (2020) caused large-scale flooding and inundated tens of kms inland with saline water intruding.
- Over time, the Indus, Ganga and Brahmaputra rivers may shrink, and rising sea levels combined with a deep intrusion of saltwater will make large parts of their huge deltas simply uninhabitable.
What are the Recommendations?
- There is a need to address the climate crisis and broaden our understanding of the root causes of insecurity.
- It is imperative to actively support grassroots resilience efforts to tackle climate change and improve Early Warning Systems.
What is the World Meteorological Organization (WMO)?
- The WMO is an intergovernmental organization with a membership of 192 Member States and Territories.
- India is a member of WMO.
- It originated from the International Meteorological Organization (IMO), which was established after the 1873 Vienna International Meteorological Congress.
- Established by the ratification of the WMO Convention on 23rd March 1950, WMO became the specialized agency of the United Nations for meteorology (weather and climate), operational hydrology and related geophysical sciences.'
- WMO is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. ‘Climate change’ is a global problem. How India will be affected by climate change? How Himalayan and coastal states of India will be affected by climate change? (2017)


International Relations
Japan’s Reaching Out to the Global South
Prelims: G7 agenda, G20 summit, Cold War, Climate Change, Indo-Pacific.
Mains: Japan’s Reaching Out to the Global South.
Why in News?
Japan has taken the initiative to raise the Global South to the top of the G7 agenda.
- Japan is hosting G7 summit 2023 at Hiroshima. With India wanting to make the voice of the Global South heard at this year’s G20 summit, there is much new room for global political collaboration between Delhi and Tokyo.
What is Global South?
- The term ‘Global South’ began by loosely referring to those countries that were left out of the industrialisation era and had a conflict of ideology with the capitalist and communist countries, accentuated by the Cold War.
- It includes countries that are mostly in Asia, Africa and South America.
- Moreover, Global North is defined essentially by an economic division between the rich and poor countries.
- Global North’ refers loosely to countries like the US, Canada, Europe, Russia, Australia and New Zealand.
- ‘Global South’ is significant because of its large population, rich cultures, and abundant natural resources.
- Understanding the Global South is important for addressing global issues such as poverty, inequality, and climate change.
What are the Concerns of the Global South?
- Poverty and Inequality:
- Many countries in the Global South struggle with extreme poverty, which can manifest in a range of issues such as malnutrition, lack of access to education, and inadequate healthcare.
- The Global South is often marked by significant inequalities, both within countries and between countries. For example, there may be significant disparities in wealth and access to resources between urban and rural areas, or between different ethnic or socioeconomic groups.
- Environmental Challenges:
- Many countries in the Global South are particularly vulnerable to environmental challenges such as climate change, deforestation, and pollution. These issues can have a significant impact on the health and well-being of local communities.
- Political Instability:
- Political instability is one of the major issues in some countries in the Global South, with challenges ranging from coups and civil wars to corruption and weak governance.
- Lack of Infrastructure, Education and Health:
- Many countries struggle to provide access to quality education for their populations, which can limit economic opportunities and perpetuate poverty and inequality.
- Health issues are also a major concern, where access to quality healthcare may be limited or non-existent. This can lead to a range of health issues, including infectious diseases, malnutrition, and chronic conditions.
Why Does Japan Want to Reach Out to the Global South?
- Japan Fears Ukraine-Like Implications:
- Japan has transformed its foreign and security policies, since it fears similar Ukraine-Like Implications.
- The Ukraine war, coming on top of the long-standing threats from North Korea and mounting security challenges from China, has pushed Japan towards sweeping reform of Japan’s defence policy.
- Diplomacy and Defense:
- Japan thinks that the war in Ukraine has made it recognise the essential relationship between diplomacy and defence.
- Diplomacy needs to be backed by defence capabilities and reinforcing defence capabilities will also lead to persuasiveness in carrying out our diplomatic efforts.
- Acknowledging Negligence from West:
- The West has neglected political engagement with the Global South in recent decades.
- In the Cold War, the West competed fiercely with Russia for strategic influence across the Global South.
- After the collapse of the Soviet Union, the G7 simply took the Global South for granted and was more interested in lecturing rather than talking to the leaders of the Global South.
- This, in turn, left much room for China and Russia to play in the developing world.
- The West has neglected political engagement with the Global South in recent decades.
What is the Way Forward for India?
- Championing the Global South today would demand more active Indian engagement with the messy regional politics within the developing world.
- India must also come to terms with the fact that the Global South is not a coherent group and does not have a single shared agenda. There is much differentiation within the South today in terms of wealth and power, needs and capabilities.
- This demands a tailored Indian policy to different regions and groups of the developing world.
- India is eager to become a bridge between the North and the South by focusing on practical outcomes rather than returning to old ideological battles. If India can translate this ambition into effective policy, there will be no contradiction between the simultaneous pursuit of universal and particular goals.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. In which one of the following groups are all the four countries members of G20?
(a) Argentina, Mexico, South Africa and Turkey
(b) Australia, Canada, Malaysia and New Zealand
(c) Brazil, Iran, Saudi Arabia and Vietnam
(d) Indonesia, Japan, Singapore and South Korea
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- The G20 is an informal group of 19 countries and the European Union, with representatives of the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank.
- In order to achieve a robust global economic growth, the member countries which represent and contribute more than 80% of the global GDP came at the premier forum for international economic cooperation, which was agreed by leaders at the Pittsburgh Summit in Pennsylvania (USA) in September 2009.
- The G20 members include Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Mexico, Republic of Korea , Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, the United Kingdom, the United States and the European Union (EU).
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. ‘The long-sustained image of India as a leader of the oppressed and marginalised nations has disappeared on account of its new found role in the emerging global order.’ Elaborate. (2019)


Important Facts For Prelims
Air-Launched Unmanned Aerial Vehicle
Why in News?
Recently, a prototype of the Air-Launched Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (ALUAV) developed jointly by India and the United States is likely to be flight tested in 2023.
- The U.S. delegation to Aero India 2023 also mentioned the possible participation of the F-35 stealth aircraft in the air show.
What is Aero India 2023?
- On February 13, Prime Minister of India inaugurated Aero India 2023, a five-day event at India Air Force station in Bengaluru, India.
- This year's theme is 'The runway to a billion opportunities' and the focus is on showcasing India's growth in aerospace and defense capabilities.
- Aero India 2023 displays indigenous equipment/technologies and forge partnerships with foreign companies, aligning with the 'Make in India, Make for the World' vision.
- The major exhibitors at Aero India include Airbus, Boeing, Dassault Aviation, Lockheed Martin, Israel Aerospace Industry, BrahMos Aerospace, SAAB, Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) etc.
What is ALUAV Project?
- In 2021, the Indian Ministry of Defence and U.S. Department of Defense signed a Project Agreement for ALUAV, under the Joint Working Group Air Systems in the Defence Technology and Trade Initiative (DTTI).
- The ALUAV is being developed to be launched from an aircraft, specifically the C130J aircraft.
- The Bengaluru-based Aeronautical Development Establishment (ADE) and the Aerospace Systems Directorate at the U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory are the principal organizations involved in the project.
- The project agreement also involves technology transfer, which is seen as a great step in the relationship between India and the U.S.
- India and the U.S. are working together in various areas to ensure a free and open, prosperous, connected, and resilient Indo-Pacific region, where democracies can thrive.
What is an Air-Launched Unmanned Aerial Vehicle?
- An ALUAV is a type of drone or unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) that is launched from an aircraft, typically a military transport plane.
- The ALUAV is designed to provide aerial reconnaissance, surveillance, and intelligence gathering capabilities to the military.
- The ALUAV is typically equipped with advanced sensors and communication equipment, and can operate at high altitudes and for extended periods of time.
What is the Defence Trade and Technology Initiative (DTTI)?
- About:
- The DTTI is a bilateral program between India and the United States aimed at deepening their defence ties through cooperation in military technology development and trade.
- The initiative was launched in 2012 and is designed to facilitate collaboration in defence manufacturing, research and development, and technology transfer.
- It seeks to enhance the interoperability of military forces and promote regional stability by building a strong defence partnership between the two countries.
- Projects: The projects under DTTI have been identified as the near, medium and long term projects.
- The near-term projects included so far are Air-launched Small Unmanned Systems, LightWeight Small Arms Technology and Intelligence-Surveillance-Targeting & Reconnaissance (ISTAR) systems.
- The medium-term projects identified are Maritime Domain Awareness Solution and Virtual Augmented Mixed Reality for Aircraft Maintenance or VAMRAM.
- The two long term projects are Terrain Shaping Obstacle (lethal munitions) and anti-drone technology called Counter-UAS, Rocket, Artillery & Mortar (CURAM) system for the Indian Army.


Important Facts For Prelims
Quasicrystals
Why in News?
Scientists have discovered a third natural source of quasicrystals in the Sand Hills of north central Nebraska, USA.
What are Quasicrystals?
- About:
- Quasicrystals are fascinating materials that possess a unique combination of properties. They are a testament to the beauty and power of irregularity in the natural world.
- Difference from Traditional Crystal:
- Unlike traditional crystals, the atoms in quasicrystals are arranged in a pattern that repeats itself at irregular intervals, rather than in a fixed, repetitive pattern.
- This deviation from the normal arrangement of atoms in solids makes quasicrystals a symbol of the power of irregularity.
- Common salt crystals, like those of Sodium chloride (NaCl), adopt a cubic pattern due to their chemical and physical properties.
- The cubic pattern allows the sodium and chloride ions to optimise for factors like density and thermal stability.
- Quasicrystals, on the other hand, form in a pattern that deviates from the cubic structure and is less optimal.
- The structure of their atomic lattice still contains the imprints of some stressful event.
- Unlike traditional crystals, the atoms in quasicrystals are arranged in a pattern that repeats itself at irregular intervals, rather than in a fixed, repetitive pattern.
- Application:
- They are used in manufacturing non-stick frying pans, needles for acupuncture and surgery, dental instruments and razor blades.
How Quasicrystals were Discovered?
- The discovery of quasicrystals was made by American-Israeli scientist Dan Shechtman in 1982 in the lab.
- Dan Shechtman received the 2011 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for discovering quasicrystals.
- The first natural quasicrystal was discovered in the Khatyrka meteorite in Russia in 2009.
- The Khatyrka meteorite is believed to have gone through several collisions in space over millions of years, which would have subjected it to intense pressure and heat.
- Inspired by these conditions, physicists conducted experiments to create new quasicrystals in the lab using "shock synthesis."
- In 2021, scientists discovered a quasicrystal in the remains of the first-ever detonated atomic weapon, the Trinity test of the Manhattan Project.
- These findings suggest that intense, fiery conditions like those experienced by the Khatyrka meteorite and the Trinity test are the birthplace of natural quasicrystals.


Important Facts For Prelims
Uttarakhand’s Anti Cheating Law
Why in News?
On February 11 2023, a protest in Dehradun over paper leaks and scams in government recruitment tests turned violent.
- On the following day, the Uttarakhand Governor gave his assent to the Uttarakhand Competitive Examination (Measures for Control and Prevention of Unfair Means in Recruitment) Ordinance, 2023 to prevent the use of unfair means in exams.
What are the Provisions Related to Uttarakhand’s Anti Cheating Laws?
- The ordinance has provisions for fines up to Rs 10 crore and life imprisonment for the guilty
- The ordinance is aimed at preventing offences related to obstructing the sanctity of examinations, use of unfair means, leakage of question papers, and other irregularities.
- It covers public examinations for recruitment to posts under the state government, autonomous bodies run by the government, and authorities, corporations, and institutions operated with grants of the state government.
- The offences are cognizable, non-bailable, and non-compoundable. The law is expected to prevent irregularities in recruitment exams and ensure that they are conducted transparently and fairly.
What are the Other Growing Concerns Related to Unfair Practises in Examination?
- The use of technology for cheating is also a growing concern, with cases of impersonation, hacking, and the use of electronic devices during exams.
- In this context, the use of generative AI (artificial intelligence) has also raised concerns about its potential to create fake identities, images, and even written content that can be used to cheat.
- Generative AI is a technology that uses algorithms to create new content that mimics human-generated content, such as images, text, and even voice.
- While this technology has many legitimate uses, it can also be misused to create fake identities and content that can be used for cheating.
- Therefore, as technology advances, it is important for authorities and governments to also keep up with the latest developments and implement measures to prevent its misuse.
- This includes investing in new technologies and training personnel to detect and prevent the use of unfair means in exams and other contexts.


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Mpox
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), as many as 85,765 confirmed and 1,382 probable cases of mpox (monkeypox) were reported from 110 countries since 1st January, 2022. The United States was the most affected, recording 29,948 confirmed cases.
WHO assessed the global risk as ‘Moderate’ and also announced that it would prefer to refer to the disease as mpox rather than monkeypox.
Monkeypox is a zoonotic viral disease with symptoms similar to smallpox but is less contagious. It was first diagnosed in humans in 1970 in the Democratic Republic of Congo in Africa. Vaccines used to eradicate smallpox provides protection against mpox. New vaccines against the disease have also been developed and approved.
Read More: Monkeypox, Smallpox, World Health Organisation (WHO)
Marburg Virus
Equatorial Guinea, Central Africa has confirmed its first-ever outbreak of Marburg virus disease.
According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), the Marburg virus disease is highly contagious and causes haemorrhagic fever. It begins abruptly, with high fever, severe headache and severe malaise. Of every 100 people who contract the virus, 88 are likely to die. The virus is transmitted to people from fruit bats and spreads among humans through direct contact with the bodily fluids of infected people, surfaces and materials.
The rare virus was first identified in 1967 after it caused simultaneous outbreaks of disease in laboratories in Marburg, Germany and Belgrade, Serbia.
Read More: Marburg Virus
Judicial Review
Recently, the Supreme Court explained that “suitability” of a candidate cleared by the Collegium for appointment as a judge in a constitutional court cannot be a subject of judicial review.
Judicial Review is a type of court proceeding in which a judge reviews the lawfulness of a decision or action made by a public body. It is the power exerted by the courts of a country to examine the actions of the legislatures, executive and administrative arms of government and to ensure that such actions conform to the provisions of the nation’s Constitution.
Judicial review is considered a basic structure of the constitution (Indira Gandhi vs Raj Narain Case 1975).
Some of the provisions that support Judicial Review: Article 372 (1), Article 13, Articles 32 and 226, Article 251 and 254, Article 246 (3), Article 245, Articles 131-136, Article 137
Read More: Judicial Review, Supreme Court, Basic Structure of the Constitution, Collegium System
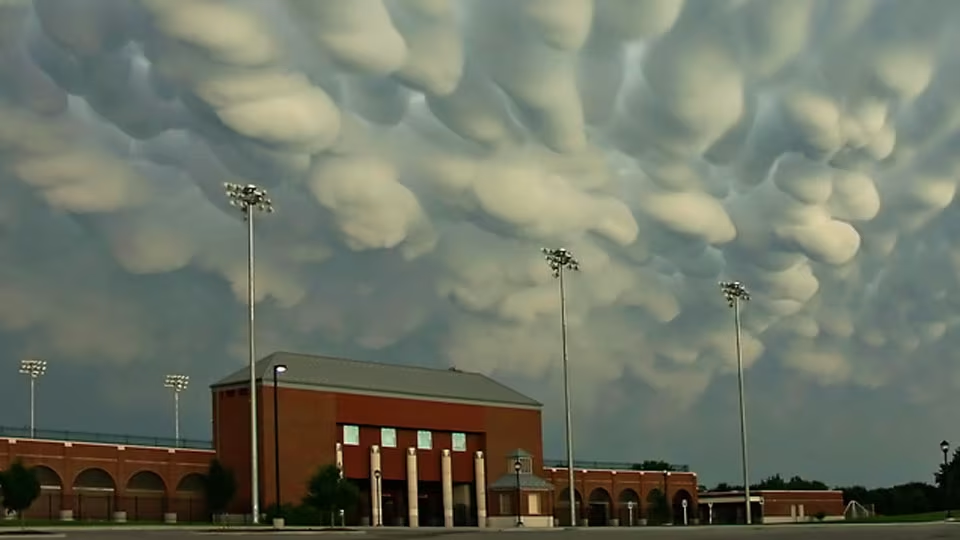
Mammatus Clouds
Recently, a cluster of clouds that appear like bubbles from the bottom are observed hovering over Nebraska, United States.
The cloud bottoms appear like bubbles because moist warm air that rises and cools will condense into water droplets at a specific temperature, which usually corresponds to a very specific height. As water droplets grow, an opaque cloud forms. Under some conditions, however, cloud pockets can develop that contain large droplets of water or ice that fall into clear air as they evaporate. Such pockets may occur in turbulent air near a thunderstorm. Resulting in the appearance of mammatus clouds.