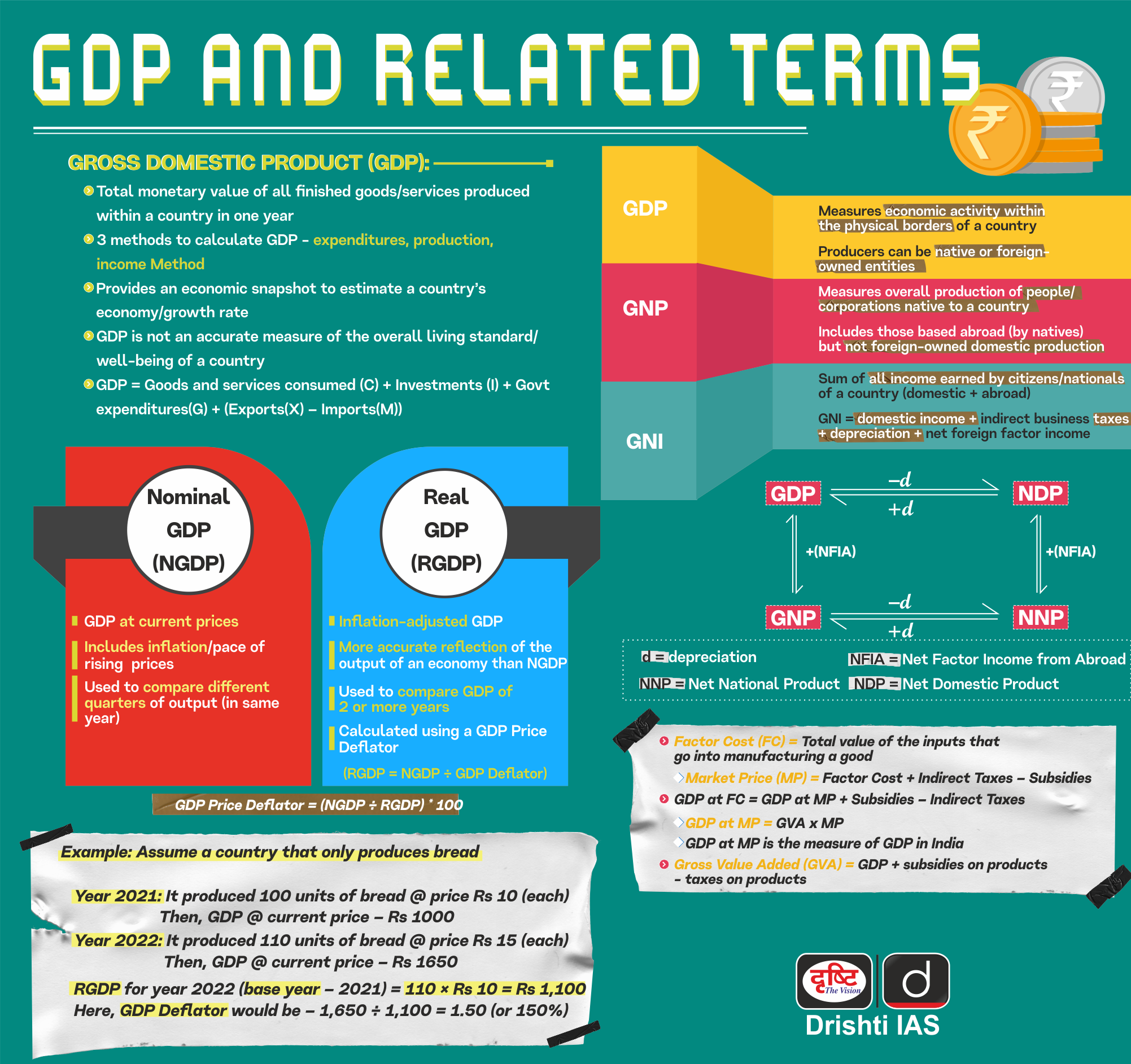
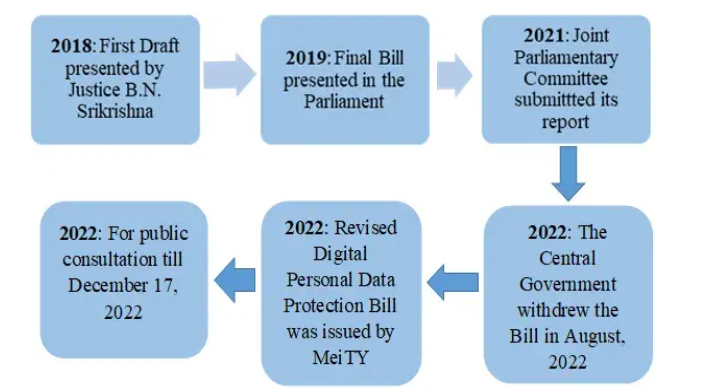
Infographics
Governance
The Places of Worship Act, 1991
For Prelims: The Places of Worship (Special Provisions) Act, 1991
For Mains: Indian Constitution, The Places of Worship (Special Provisions) Act, 1991, Related Provisions
Why in News?
The Supreme Court of India has adjourned the case regarding the validity of the Places of Worship Act of 1991, allowing the Centre until October 31, 2023, to clarify its stand on the matter.
What is the Places of Worship Act?
- About:
- It was enacted to freeze the status of religious places of worship as they existed on August 15, 1947, and prohibits the conversion of any place of worship and ensures the maintenance of their religious character.
- Major Provisions of the Act:
- Prohibition of Conversion (Section 3):
- Prevents the conversion of a place of worship, whether in full or part, from one religious' denomination to another or within the same denomination.
- Maintenance of Religious Character (Section 4(1)):
- Ensures that the religious identity of a place of worship remains the same as it was on August 15, 1947.
- Abatement of Pending Cases (Section 4(2)):
- Declares that any ongoing legal proceedings concerning the conversion of a place of worship's religious character before August 15, 1947, will be terminated, and no new cases can be initiated.
- Exceptions to the Act (Section 5):
- The Act does not apply to ancient and historical monuments, archaeological sites, and remains covered by the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act, 1958.
- It also excludes cases that have already been settled or resolved and disputes that have been resolved by mutual agreement or conversions that occurred before the Act came into effect.
- The Act does not extend to the specific place of worship known as Ram Janmabhoomi-Babri Masjid in Ayodhya, including any legal proceedings associated with it.
- Penalties (Section 6):
- Specifies penalties, including a maximum imprisonment term of three years and fines, for violating the Act.
- Prohibition of Conversion (Section 3):
- Criticism:
- Bar on Judicial Review:
- Critics argue that the Act prevents judicial review, which is a fundamental aspect of the Constitution.
- They believe this restriction undermines the checks and balances system and limits the judiciary's role in protecting constitutional rights.
- Arbitrary Retrospective Cutoff Date:
- The Act is criticized for using an arbitrary date (Independence Day, 1947) to determine the status of religious places.
- Opponents argue that this cutoff date disregards historical injustices and denies redressal for encroachments before that date.
- Violation of the Right to Religion:
- Critics claim that the Act infringes upon the religious rights of Hindus, Jains, Buddhists, and Sikhs.
- They argue that it restricts their ability to reclaim and restore their places of worship, impeding their freedom to practice their religion.
- Violation of Secularism:
- Opponents argue that the Act violates the principle of secularism, which is a core component of the Constitution, and favours one community over others
- They contend that this undermines the equal treatment of religions under the law.
- Opponents argue that the Act violates the principle of secularism, which is a core component of the Constitution, and favours one community over others
- Exclusion of Ayodhya Dispute:
- The Act is specifically criticized for excluding the land involved in the Ayodhya dispute.
- Opponents question its consistency and raise concerns about the differential treatment of religious sites.
- Bar on Judicial Review:
- Supreme Court’s Stance on the Act:
- The Supreme Court views the Places of Worship Act as a legislative intervention that upholds the commitment to secularism, a fundamental aspect of the Indian Constitution.
- The Act enforces the constitutional obligation of the State to ensure equality among all religions. It guarantees the preservation of places of worship for every religious community.
Way Forward
- Undertake a thorough review of the Places of Worship Act to address criticisms and shortcomings.
- Ensure the Act does not restrict judicial review, preserving the judiciary's role in upholding constitutional rights.
- Strike a balance between preserving religious character and respecting the rights of different communities.
- Involve public consultation, ensure transparency, and review the exclusion of specific sites to promote fairness and consistency.


Governance
Data Governance in India
For Prelims: DPDP 2022, GDPR, Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules 2021, Proposal of ‘Digital India Act’,2023.
For Mains: Data Governance in India.
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Cabinet has approved the Draft Digital Personal Data Protection Bill (DPDP), 2022, to introduce in the Monsoon session of Parliament with some significant changes, including lowering the age of consent for data processing and providing exemptions for certain companies.
- If passed, the law will become India’s core data governance framework, six years after the Supreme Court declared privacy as a fundamental right.
- The Bill is one of the four proposed legislations in the IT and telecom sectors to provide the framework for the rapidly growing digital ecosystem. Other three bills are,
- Digital India Bill: It aims to replace the Information Technology Act, 2000.
- Indian Telecommunication Bill, 2022: A new bill related to the telecommunications sector.
- Non-Personal Data Governance Policy: A policy focused on governing non-personal data.
What are the Expected Changes?
- Lowering Age of Consent:
- The Bill had fixed the age of consent at 18 years, requiring parental consent for processing data of individuals below 18.
- The upcoming Bill will adopt a graded approach, allowing a case-by-case determination of the age of consent.
- The change addresses concerns raised by social media companies, who argued that a fixed age of consent would disrupt their operations and hinder services targeted at users under 18.
- This aligns with data protection regulations in the European Union and the United States, where a lower age of consent is prescribed.
- Definition of a Child and Exemptions:
- The definition of child may include individuals below 18 or a lower age as determined by the Central Government.
- In the 2022 draft, the definition of a child was an “individual who has not completed eighteen years of age”.
- Certain entities dealing with children's data may be exempted from obtaining parental consent if they can demonstrate verifiably safe data processing practices.
- The Ministry of Women and Child Development, in collaboration with the Ministry of IT, will evaluate platforms' privacy standards for children to grant exemptions.
- The definition of child may include individuals below 18 or a lower age as determined by the Central Government.
- Relaxations on Cross-Border Data Flows:
- The upcoming Bill introduces further relaxations on cross-border data flows, shifting from a whitelisting approach to a blacklisting mechanism.
- The bill allows global data to flow by default to all jurisdictions other than a specified negative list of countries where such transfers would be restricted.
- This change aims to facilitate data transfers to international jurisdictions, streamlining the process for businesses.
- The upcoming Bill introduces further relaxations on cross-border data flows, shifting from a whitelisting approach to a blacklisting mechanism.
What are the Global Regulations Regarding Data Governance?
- General Data Protection Regulations (GDPR) of European Union (EU):
- The GDPR focuses on a comprehensive data protection law for processing of personal data.
- In the EU, the right to privacy is enshrined as a fundamental right that seeks to protect an individual’s dignity and her right over the data she generates.
- The fines imposed by the GDPR have prompted organizations worldwide to prioritize compliance. Notable companies, including Google, WhatsApp, British Airways, and Marriott, have faced substantial fines.
- Moreover, the GDPR's strict norms regarding data transfers to third countries have had a profound influence on data protection frameworks beyond the EU.
- Data Governance in US:
- There is no comprehensive set of privacy rights or principles in the US that, like the EU’s GDPR, addresses the use, collection, and disclosure of data.
- Instead, there is limited sector-specific regulation. The approach towards data protection is different for the public and private sectors.
- The activities and powers of the government vis-a-vis personal information are well-defined and addressed by broad legislation such as the Privacy Act, the Electronic Communications Privacy Act, etc.
- For the private sector, there are some sector-specific norms.
- There is no comprehensive set of privacy rights or principles in the US that, like the EU’s GDPR, addresses the use, collection, and disclosure of data.
- Data Governance in China:
- The Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL) grants Chinese individuals new rights to protect personal data.
- The Data Security Law (DSL) categorizes business data by importance and imposes restrictions on cross-border transfers. These laws aim to prevent misuse of personal data.
What are the Challenges with Data Governance in India?
- Insufficient Awareness:
- The limited understanding among individuals and organizations regarding the significance of data protection and the potential risks linked to data breaches.
- Weak Enforcement Mechanisms:
- The existing legal framework concerning data protection in India lacks robust mechanisms for enforcing compliance. This deficiency makes it difficult to hold organizations accountable for data breaches and non-compliance with data protection regulations.
- Lack of Standardization:
- A significant hurdle in implementing and enforcing data protection regulations in India is the absence of standardized practices among organizations. The lack of uniformity in data protection protocols poses challenges when attempting to establish and adhere to consistent data protection practices.
- Inadequate Safeguards for Sensitive Data:
- The current data protection framework in India fails to offer sufficient safeguards for sensitive data, such as health data and biometric data.
- As organizations increasingly collect these types of data, the lack of adequate protection measures becomes a concern.
How is Data Governed in India??
- IT amendment Act, 2008.
- Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules 2021
- Proposal of ‘Digital India Act’,2023 to replace IT act, 2000
- Justice K. S. Puttaswamy (Retd) vs Union of India 2017
- B.N. Srikrishna Committee 2017
Way Forward
- The government should lead by example in prioritizing data protection as it plays a significant role as a data fiduciary and processor.
- Creating an independent and empowered data protection board with parliamentary or judicial oversight is crucial for effective governance and enforcement of data protection regulations.
- Finding the right balance between stringent regulations to safeguard personal data and fostering innovation is essential. Overly prescriptive and restrictive norms can stifle innovation and impede cross-border data flows.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q1. ‘Right to Privacy’ is protected under which Article of the Constitution of India? (2021)
(a) Article 15
(b) Article 19
(c) Article 21
(d) Article 29
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- In Puttaswamy v. Union of India case, 2017, the Right to Privacy was declared a fundamental right by the Supreme Court as an intrinsic part of the Right to Life and Personal Liberty under Article 21.
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Q2. Right to Privacy is protected as an intrinsic part of Right to Life and Personal Liberty. Which of the following in the Constitution of India correctly and appropriately imply the above statement? (2018)
(a) Article 14 and the provisions under the 42nd Amendment to the Constitution.
(b) Article 17 and the Directive Principles of State Policy in Part IV.
(c) Article 21 and the freedoms guaranteed in Part III.
(d) Article 24 and the provisions under the 44th Amendment to the Constitution.
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. Examine the scope of Fundamental Rights in the light of the latest judgement of the Supreme Court on Right to Privacy. (2017)


Governance
Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban
For Prelims: Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban, open defecation, Garbage Free Star Ratings
For Mains: Swachh Bharat Mission, Government Policies and Interventions
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) organized a review-cum-workshop to evaluate and accelerate the planning and implementation of the second phase of Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban (SBM-U 2.0) across the country.
- The issue of open defecation has once again garnered attention following the recent release of the Joint Monitoring Program (JMP) report on water, sanitation, and hygiene by the World Health Organization and the United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) for the year 2022. The report stated that approximately 17% of the total population in India continues to practice open defecation.
What is Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban?
- About:
- Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban (SBM-U) was launched on October 2, 2014, by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs as a national campaign to promote cleanliness, sanitation, and proper waste management in urban areas.
- It aimed to make cities and towns across India clean and free from open defecation.
- Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban 1.0:
- The first phase of SBM-U focused on achieving the target of making urban India ODF by providing access to toilets and promoting behavioral change.
- SBM-U 1.0 was successful in achieving the target and 100% of urban India was declared ODF.
- Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban 2.0 (2021-2026):
- SBM-U 2.0, announced in Budget 2021-22, is the continuation of SBM-U first phase.
- The second phase of SBM-U aimed to go beyond ODF to ODF+, and ODF++, and focus on making urban India garbage-free.
- It emphasized sustainable sanitation practices, waste management, and the promotion of a circular economy.
- Achievements:
- Open Defecation Free (ODF):
- Urban India has become Open Defecation Free (ODF), with all 4,715 Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) completely ODF.
- 3,547 ULBs are ODF+ with functional and hygienic community and public toilets, and 1,191 ULBs are ODF++ with complete faecal sludge management.
- 14 cities are certified Water+, which entails treatment of wastewater and its optimum reuse.
- Waste Processing:
- Waste Processing in India has gone up by over 4 times from 17% in 2014 to 75% in 2023, aided through 100% door-to-door waste collection in 97% wards and source segregation of waste being practised by citizens across almost 90% wards in all ULBs in the country.
- Garbage Free Cities:
- The Garbage Free Cities(GFC)-Star rating protocol launched in January 2018 has increased from only 56 cities in the first year to 445 cities till date, with an ambitious target of having at least 1,000 3-star GFC by October 2024.
- The 2023-24 budget has reinforced India's commitment to building a circular economy through an enhanced focus on scientific management of dry and wet waste.
- The Garbage Free Cities(GFC)-Star rating protocol launched in January 2018 has increased from only 56 cities in the first year to 445 cities till date, with an ambitious target of having at least 1,000 3-star GFC by October 2024.
- Open Defecation Free (ODF):
What is Open Defecation Free Status?
- ODF: An area can be notified or declared as ODF if at any point of the day, not even a single person is found defecating in the open.
- ODF+: This status is given if at any point of the day, not a single person is found defecating and/or urinating in the open, and all community and public toilets are functional and well maintained.
- ODF++: This status is given if the area is already ODF+ and the faecal sludge/septage and sewage are safely managed and treated, with no discharging or dumping of untreated faecal sludge and sewage into the open drains, water bodies or areas.
What are the Key Highlights of the JMP Report?
- Open Defecation Rate:
- The report reveals that 17% of the rural population in India still practices open defecation.
- Access to Basic Sanitation Facilities:
- A quarter of the rural population in India lacks access to "at least basic" sanitation facilities.
- Basic services are defined as improved sanitation facilities that households do not share with others.
- A quarter of the rural population in India lacks access to "at least basic" sanitation facilities.
- Progress since 2015:
- The report tracks progress since 2015 when the goals for sanitation were set.
- In 2015, approximately 41% of the rural population practiced open defecation, which was reduced to 17% in 2022.
- In terms of sanitation facilities, 51% of households had at least basic sanitation in 2015, increasing to 75% in 2022.
- Rate of Decline in Open Defecation:
- India has registered an annual average decline of 3.39% in open defecation.
- If this decline rate continues, it would take around four to five years to achieve open defecation-free status.
- Recommendations:
- Emphasize the importance of behavioral change to promote toilet usage over open defecation.
- Quantify and measure the behavioral shift towards using toilets to accurately ascertain ODF status.
- Address the public health implications of open defecation by working towards its elimination.
- Maintain continuous monitoring and evaluation of sanitation practices to identify areas for improvement and ensure sustained progress.
- Reassess the ODF milestone in India based on the findings of the JMP report and take comprehensive measures to address open defecation and improve sanitation facilities.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. “To ensure effective implementation of policies addressing the water, sanitation and hygiene needs the identification of the beneficiary segments is to be synchronized with anticipated outcomes.” Examine the statement in the context of the WASH scheme. (2017)
Q. How could social influence and persuasion contribute to the success of Swachh Bharat Abhiyan? (2016)


Indian Economy
India Emerges as Most Attractive Emerging Market for Investment
For Prelims: foreign direct investment, emerging market, ease of doing business,
For Mains: Growth of India as Emerging Market for Investment, Challenges and Risks associated with investing in emerging markets
Why in News?
According to Invesco Global Sovereign Asset Management Study by Invesco (an independent global investment management firm), India has surpassed China to become the most attractive emerging market for investment in 2023.
- The report emphasizes India's attractiveness to sovereign wealth funds due to its strong demographics, political stability, and proactive regulation.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- India is ranked as the most attractive emerging market for investing in emerging market debt.
- India offers attractive yields, a favorable currency outlook, and strong macroeconomic fundamentals for debt investors.
- India is ranked among the top destinations for increasing exposure in both public and private markets.
- India and South Korea are the most preferred markets for increasing exposure in public equities.
- India and Brazil are the most favored markets for increasing exposure in private equity.
- India, along with Mexico and Brazil, is benefiting from increased foreign direct investment, supporting currencies, and domestic assets while funding current account deficits.
- The report acknowledged the challenges and risks of investing in emerging markets and advised sovereign investors to carefully assess and manage them.
What Makes India Attractive to Investors?
- Business and Political Stability: India is considered a stable destination for sovereign investors due to improved business and political stability.
- Ease of Doing Business: India has implemented reforms to enhance the ease of doing business, including lowering corporate tax rates and liberalizing foreign direct investment norms.
- Production-Linked Incentive Schemes: India has introduced production-linked incentive schemes to attract foreign investment in various sectors.
- Fast-growing Demographics: India's large and young consumer market, skilled labor force, and potential for innovation and entrepreneurship make it an attractive destination for investors.
- Proactive Regulation: India has taken steps to address challenges faced by sovereign investors, such as taxation, currency volatility, and legal disputes.
- Friendly Investment Environment: India is known for its openness and willingness to engage with sovereign investors, offering various opportunities for collaboration and investment.
What are the Challenges and Risks of Investing in India?
- Inflation: Rising inflationary pressures pose a short-term risk, leading to tighter monetary policy, higher interest rates, lower asset prices, and currency depreciation in emerging markets like India.
- Geopolitical Risk: Increasing geopolitical tensions can result in trade wars, sanctions, conflicts, or cyberattacks, affecting trade flows, supply chains, energy security, and market sentiment.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: The Covid-19 pandemic has highlighted the vulnerabilities of global supply chains, impacting the availability and cost of raw materials, intermediate goods, and final products, which can affect economic activity and inflation.
- Climate Change: Climate change presents physical risks to infrastructure, agriculture, health, and biodiversity, as well as transition risks to energy sources, industries, regulations, and policies. These risks can have implications for investments in India.
Way Forward
- Strengthen diplomatic relations and engage in bilateral and multilateral partnerships to promote trade, investment, and technology transfer, further enhancing India's global attractiveness as an investment destination.
- Continue implementing reforms to improve the ease of doing business, reducing bureaucratic hurdles, simplifying procedures, and enhancing transparency to facilitate foreign investments.
- Embrace sustainable practices and invest in renewable energy, clean technologies, and climate resilience measures to mitigate environmental risks and attract socially responsible sovereign investors.
- Invest in skill development programs and education to nurture a highly skilled workforce and foster innovation, thereby enhancing India's competitive advantage and attracting long-term investments.
- Continue proactive regulation to address challenges faced by sovereign investors, including tax reforms, currency volatility management, and efficient dispute resolution mechanisms.
UPSC Civil Services, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. Consider the following actions which the Government can take: (2011)
- Devaluing the domestic currency.
- Reduction in the export subsidy.
- Adopting suitable policies which attract greater FDI and more funds from FIIs.
Which of the above action/actions can help in reducing the current account deficit?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 3 only
(d) 1 and 3
Ans: (d)


Important Facts For Prelims
SAGAR SAMPARK
Why in News?
The Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways of India has inaugurated 'SAGAR SAMPARK’, that marks a significant step towards digital transformation in the maritime industry.
What is SAGAR SAMPARK?
- About:
- It is an indigenous Differential Global Navigation Satellite System (DGNSS).
- DGNSS is a terrestrial based enhancement system which corrects the errors and inaccuracies in the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) allowing for more accurate positioning information.
- The introduction of the DGNSS system will have a profound impact on maritime navigation, enabling safer and more efficient movement of vessels in port and harbor areas.
- It is an indigenous Differential Global Navigation Satellite System (DGNSS).
- Features:
- Enhanced Safety: The DGNSS service will assist mariners in safe navigation, reducing the risk of collisions, groundings, and accidents at sea.
- Accuracy Improvement: The DGNSS significantly improves the accuracy of GPS positioning, reducing errors caused by atmospheric inferences, satellite clock drift and other factors.
- Redundancy and Availability: The DGNSS incorporates multiple satellite constellations like GPS and Global Navigation Satellite System (GLONASS), ensuring increased availability and redundancy as per international standards.
- Precise Positioning: Mariners can now improve their positioning within 5 meters using the latest DGNSS system, enabling better navigation and reducing the margin of error.
- Meeting International Obligations: The DGNSS fulfills the international obligations of the International Maritime Organization (IMO), Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS), and the International Association of Marine Aids to Navigation and Lighthouse Authorities (IALA).
Note:
- Safety of Life at Sea: The International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS), is an important international treaty concerning the safety of merchant ships.
- It ensures that ships comply with minimum safety standards in construction, equipment and operation of ships.
- International Association of Marine Aids to Navigation and Lighthouse Authorities: IALA is a non-profit, international technical association.
- Established in 1957, IALA encourages its members to work together in a common effort to harmonise Marine Aids to Navigation worldwide and to ensure that the movements of vessels are safe, expeditious and cost-effective while protecting the environment.
What are the Other Government Initiatives Related to Maritime Security?
- NavIC: NavIC or Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) is designed with a constellation of 7 satellites and a network of ground stations operating 24×7.
- NavIC coverage area includes India and a region up to 1500 km beyond Indian boundary.
- IMO has recognized NavIC as a component of the World-Wide Radio Navigation System (WWRNS).
- SAGAR Vision: In 2015, India unveiled it's strategic vision for the Indian Ocean i.e. Security and Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR) to improve relations with its maritime neighbours on the economic and security fronts.
- Indian Ocean Naval Symposium: The IONS is a voluntary and inclusive initiative that brings together navies of Indian Ocean Region (IOR) littoral states to increase maritime co-operation and enhance regional security.
- Maritime India Vision 2030: It aims to accelerate the growth of the maritime sector over the next decade by enhancing infrastructure, efficiency, services and capacity across ports, shipping and waterways.


Important Facts For Prelims
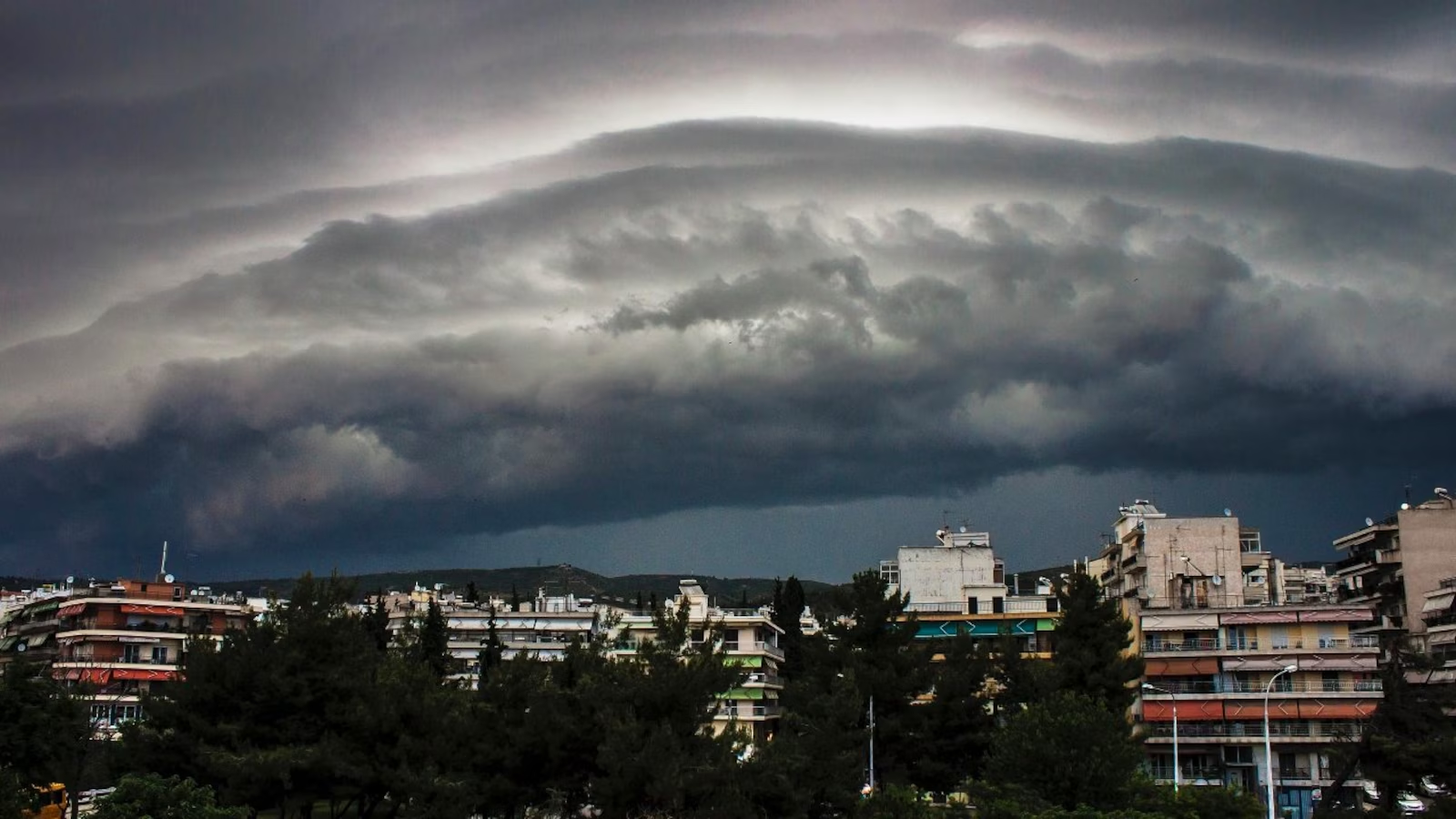
Massive Shelf Clouds Formation
Why in News?
Recently, a massive Shelf Cloud formation has been spotted in Haridwar, Uttarakhand.
What are Shelf Clouds?
- About:
- Shelf clouds - also known as Arcus clouds - are often associated with powerful storm systems, and many times they are reported as wall clouds, funnel clouds, or rotation.
- These clouds are sometimes seen beneath cumulonimbus clouds, the dense, towering vertical cloud that causes intense rain.
- They often appear ahead of powerful Thunderstorms with heavy rain, strong winds, and occasionally hail or tornadoes.
- Formation:
- When a cold downdraft from a cumulonimbus cloud reaches the ground, the cold air may spread rapidly along the ground, pushing existing warm moist air upwards.
- As the cold air descends, it pushes warm air upward, causing condensation and cloud formation. This process creates the distinct horizontal shape and appearance of a shelf cloud.
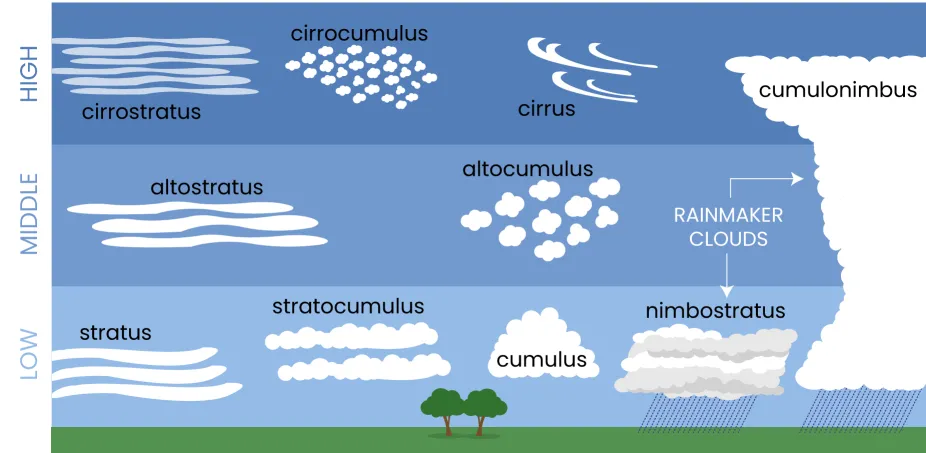
What are the Types of Clouds?
- High Clouds:
- Cirrus Clouds: Cirrus clouds are high-altitude clouds that appear wispy, feathery, and white. They are composed of ice crystals and are often associated with fair weather.
- Cirrus clouds can cause halo, a ring around the sun or the moon.
- Cirrocumulus Clouds: High-altitude clouds that appear as small, white, and fluffy cloud patches. They often have a wavy or honeycomb-like pattern.
- Cirrostratus Clouds: High-altitude clouds that form a thin, whitish veil covering the sky. They can produce halos around the sun or moon.
- Cirrus Clouds: Cirrus clouds are high-altitude clouds that appear wispy, feathery, and white. They are composed of ice crystals and are often associated with fair weather.
- Middle Clouds:
- Altocumulus Clouds: Mid-level clouds that form white or gray patches or layers. They often have a wavy or lumpy appearance.
- Altostratus Clouds: Mid-level clouds that create a uniform, gray or bluish-gray layer covering the sky. They are thicker and denser than cirrostratus clouds and can lead to light precipitation.
- Low Clouds:
- Cumulus Clouds: Cumulus clouds are fluffy, white clouds with a flat base and a rounded top. They are typically formed by rising warm air currents and are often seen on sunny days. Cumulus clouds can develop into cumulonimbus clouds, which are associated with thunderstorms.
- Stratus Clouds: Stratus clouds are low-level clouds that appear as a uniform grayish layer covering the sky. They often bring drizzle or light precipitation and can create a dull, overcast appearance.
- Stratocumulus Clouds: Low-level clouds with a patchy appearance, often appearing as rounded masses. They can be white or gray and cover a significant portion of the sky.
- Nimbostratus Clouds: Thick, dark, and featureless clouds that cover the sky. They bring continuous precipitation, often lasting for an extended period.
- Clouds that exhibit Significant Vertical Development:
- Cumulonimbus Clouds: Large, towering clouds associated with thunderstorms. They have a dark base and can reach high altitudes, producing heavy rain, lightning, and strong winds.
UPSC Civil Services, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following statements:
- High clouds primarily reflect solar radiation and cool the surface of the Earth.
- Low clouds have a high absorption of infrared radiation emanating from the Earth's surface and thus cause warming effect.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Explanation:
- The study of clouds, where they occur, and their characteristics, play a key role in the understanding of climate change. Low, thick clouds primarily reflect solar radiation and cool the surface of the Earth. High, thin clouds primarily transmit incoming solar radiation; at the same time, they trap some of the outgoing infrared radiation emitted by the Earth and radiate it back downward, thereby warming the surface of the Earth. Hence, both statements are not correct.


Important Facts For Prelims
Quality Control Orders
Why in News?
The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce & Industry has recently notified two new Quality Control Orders (QCOs) on 'Potable Water Bottles' and 'Flame-Producing Lighters'.
- These QCOs aim to strengthen the quality ecosystem in India and ensure the public health and safety of consumers.
What are the Key Points Related to the QCOs?
- The QCO for ‘Potable water bottles’ mandates compulsory certification under the appropriate IS Standard for the production and import of potable water bottles made of copper, stainless steel, or aluminum.
- The QCO for ‘Flame-Producing Lighter’ mandates compulsory certification under IS Standards for ‘Safety Specification for Lighters’, and ‘Safety Specifications for Utility Lighters’, for the Flame lighters manufactured for domestic market or imported into India.
What are Quality Control Orders?
- QCOs are regulatory measures introduced by the government to establish quality standards for specific products or product categories. These orders are designed to ensure that products meet certain prescribed quality, safety, and performance requirements before they can be manufactured, imported, stored, or sold in the country.
- The main objective of QCOs is to control the import of sub-standard and cheaper items into the domestic market and ensure that customers have access to quality products that meet the necessary standards.
- QCOs cannot be challenged at the World Trade Organization (WTO) if they are imposed on the grounds of health, safety, environment and deceptive trade practices, or national security.
- To ensure compliance with the quality standards set forth in the QCOs, the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) play a crucial role.
- BIS is responsible for certifying products that meet the prescribed standards, both for domestic and international manufacturers.
- With the QCOs, manufacturing, storing and sale of non-BIS certified products are prohibited as per the BIS Act, 2016."


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Official Mascot of Asian Athletics Championships 2023
The 2023 Asian Athletics Championships which began in Thailand recently have chosen revered Hindu god Hanuman as the official mascot for the 2023 year’s event. The event was held on the 50th anniversary of the establishment of the Asian Athletics Association (established in 1973).
The 25th Asian Athletics Championships 2023 logo indicates the athletes participating in the games, skills, teamwork of athletes, showcase of athleticism, dedication, and sportsmanship.
A total of nine countries (Japan; Hong Kong; Singapore; China; Indonesia; the Republic of Korea; Malaysia; and Philippines) participate in the Asian event including India.
Read More: Winter Olympics
Floating Gold
Recently, a massive chunk of floating gold has been found in the belly of a dead whale beached on the Spanish island of La Palma. The highly valuable substance is called ambergris.
Ambergris (grey amber), is generally referred to as whale vomit. It is a solid waxy substance originating in the intestine of the sperm whale. It is produced only by an estimated 1% of sperm whales. Chemically, ambergris contains alkaloids, acids, and a specific compound called ambrein, which is similar to cholesterol. It floats around the surface of the water body and at times settles on the coast. Because of its high value, it is referred to as floating gold. It is highly used in the perfume market.
The sperm whale, (Physeter macrocephalus), is dark blue-gray or brownish, with white patches on the belly. They are found in temperate and tropical waters throughout the world. They are listed as vulnerable in the IUCN Red List, mentioned in Appendix I of CITES and included in Schedule 1 of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
Read More: Ambergris & Sperm Whale
Railway Financial Code Modified to Prioritize Safety Projects
Following a tragic train accident in Balasore, Odisha, the Railway Board has taken swift action by modifying the Indian Railway Financial Code to prioritize safety-related projects, particularly those pertaining to signalling systems. The Indian Railway Financial Code sets the rules to financially evaluate the viability of projects.
The revised rules now exempt signalling works from the requirement of being financially remunerative, categorizing them under the 'Safety' category instead. This significant change ensures that projects aimed at improving the signalling infrastructure, such as the anti-collision system Kavach and Electronic Interlocking, do not need to pass the financial viability test.
Additionally, projects involving mobile train communications systems, Remote Diagnostic and Predictive Maintenance Systems, technology upgrades, and automatic Train Management Systems will also be exempt from the financial viability norms.
Read more: Kavach, Electronic Interlocking, Derailment
INS Sunayna Participates in Op Southern Readiness 2023
The recent participation of INS Sunayna in Op Southern Readiness 2023, conducted by the Combined Maritime Forces (CMF) in Seychelles from 10-12 Jul 23, marked a significant step towards strengthening multilateral ties and enhancing cooperation in the maritime domain.
The Combined Maritime Forces (CMF) is a multinational maritime partnership, which exists to uphold the Rules-Based International Order (RBIO) by countering illicit non-state actors on the high seas and promoting security, stability, and prosperity across approximately 3.2 million square miles of international waters, which encompass some of the world’s most important shipping lanes. It has 38 member nations ( including India).
INS Sunayna, the second of the NOPV (Naval Offshore Patrol Vessel) class of ship designed to undertake fleet support operations, coastal and offshore patrolling, ocean surveillance and monitoring of Sea Lines of Communications and offshore assets, and escort duties.
Read more: Combined Maritime Forces, Naval Offshore Patrol Vessel