Infographics
Science & Technology
Large Hadron Collider
For Prelims: Large Hadron Collider, CERN, Quarks and gluons, Protons, Big Bang, Supersymmetry and Extra Dimensions.
For Mains: Large Hadron Collider.
Why in News?
The LHC (Large Hadron Collider) has recently undergone upgrades to make it more accurate and sensitive and will start collecting data in May 2023.
- The LHC has undergone upgrades to increase its sensitivity and accuracy, allowing scientists to study particles with even higher energy.
What is Hadron?
- Hadron is any member of a class of subatomic particles that are built from quarks and thus react through the agency of the strong force. The hadrons embrace mesons, baryons (e.g., protons, neutrons, and sigma particles), and their many resonances.
What is LHC?
- About:
- The LHC is a huge experiment that collides two beams of particles to study physics at very high energies. It's the largest science experiment in the world and is operated by CERN (European Organisation for Nuclear Research)
- The LHC is a circular pipe that is 27 km long and is located on the Franco-Swiss border near Geneva, Switzerland.
- It consists of two D-shaped magnetic fields created by almost 9,600 magnets.
- Working Mechanism:
- Protons, which are subatomic particles made up of quarks and gluons, are accelerated inside the LHC using these magnets.
- Quarks and gluons are subatomic particles that make up protons and neutrons. Quarks come in six different "flavors": up, down, charm, strange, top, and bottom. Gluons are particles that "glue" quarks together inside protons and neutrons through the strong nuclear force.
- Protons are not the only particles accelerated in the LHC.
- By switching the direction of the magnetic field rapidly, protons can be accelerated through the beam pipe.
- Other components help to focus the particles and keep them from hitting the pipe's walls.
- The protons eventually move at 99.999999% of the speed of light.
- Protons, which are subatomic particles made up of quarks and gluons, are accelerated inside the LHC using these magnets.
- Significance:
- At such high energies, the LHC can create conditions that existed only fractions of a second after the Big Bang.
- Scientists use detectors placed along the beam pipe to observe the interactions of the accelerated particles, which can reveal new insights into the nature of matter and the universe.
- The LHC has already discovered the Higgs boson in 2012 and confirmed their findings in 2013, which is a particle that gives other particles mass.
- The LHC also helps to test theories in particle physics, such as supersymmetry and extra dimensions.
What are Supersymmetry and Extra Dimensions?
- Supersymmetry:
- It proposes that every known particle in the universe has a yet-to-be-discovered "superpartner" particle, which would have opposite spin and different quantum numbers.
- This would mean that every particle in the universe would have a partner that has not yet been observed, and it could help to solve some of the problems with the current standard model of particle physics, such as the hierarchy problem.
- Extra Dimensions:
- Extra dimensions propose that the universe has more than the three dimensions of space and one dimension of time that we are familiar with.
- The idea is that there may be additional dimensions that are "curled up" or compactified and are too small to be detected by our current experiments.
- The concept of extra dimensions arises in certain theories of gravity, such as string theory, which suggest that gravity is stronger than expected at small distances because it "feels" extra dimensions.
What are the Related Challenges?
- The LHC faces many technical challenges, such as maintaining the stability of the magnets and avoiding collisions between particles and the pipe's walls.
- The LHC generates enormous amounts of data. Handling and processing this data is a challenge that requires advanced computing and storage systems.
- The LHC is an international collaboration that involves thousands of scientists from different countries and institutions. Coordinating this collaboration and ensuring that all participants have access to the data and facilities they need is a challenge.
Way Forward
- The LHC is a remarkable scientific achievement, but operating it requires a coordinated effort from many people and institutions. Addressing the challenges associated with the LHC is crucial to advancing our understanding of the universe.
- The LHC has tested and disproved some theories that aim to explain the limitations of the Standard Model, causing uncertainty in the physics community. To move forward, two ideas have emerged: upgrading the LHC to increase its luminosity and building a bigger and more expensive version in the hopes of finding new physics.
- While CERN and China have proposed such a machine, some physicists question whether the money would be better spent on less-expensive experiments with guaranteed results.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. The efforts to detect the existence of Higgs boson particle have become frequent news in the recent past. What is/are the importance of discovering this particle?
- It will enable us to understand as to why elementary particles have mass.
- It will enable us in the near future to develop the technology of transferring matter from one point to another without traversing the physical space between them.
- It will enable us to create better fuels for nuclear fission.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)


Indian Polity
Role of Parliamentary Committees in Indian Democracy
For Prelims: Types of Parliamentary Committees, Speaker, Rajya Sabha, Lok Sabha
For Mains: Parliament Committees and its Significance
Why in News?
Parliamentary committees are constituted to delve deeper into matters of public concern and develop expert opinions.
What are Parliamentary Committees?
- Evolution of Committees:
- The structured committee system was established in 1993, but individual committees have been formed since independence.
- For instance, five of the many crucial committees of the Constituent Assembly are
- The Ad Hoc Committee on the Citizenship Clause was formed to discuss the nature and scope of Indian citizenship.
- The Northeast Frontier (Assam) Tribal and Excluded Areas Sub-Committee and the Excluded and Partially Excluded Areas (Other than Assam) Sub-Committee were significant committees during independence.
- The Expert Committee on Financial Provisions of the Union Constitution and the Advisory Committee on the Subject of Political Safeguards for Minorities were formed to give recommendations on taxation and abolition of reservations for religious minorities, respectively.
- About:
- A parliamentary committee means a committee that:
- Is appointed or elected by the House or nominated by the Speaker / Chairman.
- Works under the direction of the Speaker / Chairman.
- Presents its report to the House or to the Speaker /Chairman.
- Has a secretariat provided by the Lok Sabha / Rajya Sabha.
- The consultative committees, which also consist of members of Parliament, are not parliamentary committees as they do not fulfill the above four conditions.
- A parliamentary committee means a committee that:
- Types:
- Standing Committees: Permanent (constituted every year or periodically) and work on a continuous basis.
- Standing Committees can be classified into the following six categories:
- Financial Committees
- Departmental Standing Committees
- Committees to Enquire
- Committees to Scrutinise and Control
- Committees Relating to the Day-to-Day Business of the House
- House-Keeping Committees or Service Committees
- Standing Committees can be classified into the following six categories:
- Ad Hoc Committees:
- Temporary and cease to exist on completion of the task assigned to them. E.g. Joint Parliamentary Committee.
- Standing Committees: Permanent (constituted every year or periodically) and work on a continuous basis.
- Constitutional Provisions:
- Parliamentary committees draw their authority from Article 105 (on privileges of Parliament members) and Article 118 (on Parliament’s authority to make rules for regulating its procedure and conduct of business).
What is the Role of Parliamentary Committees?
- Provides Legislative Expertise:
- Most MPs are not subject matter experts on the topics being discussed. Parliamentary committees are meant to help MPs seek expertise and give them time to think about issues in detail.
- Acting as a Mini-Parliament:
- These committees act as a mini parliament, as they have MPs representing different parties are elected into them through a system of the single transferable vote, in roughly the same proportion as their strength in Parliament.
- Instrument for Detailed Scrutiny:
- When bills are referred to these committees, they are examined closely and inputs are sought from various external stakeholders, including the public.
- Provides a Check on the Government:
- Although committee recommendations are not binding on the government, their reports create a public record of the consultations that took place and put pressure on the government to reconsider its stand on debatable provisions.
- By virtue of being closed-door and away from the public eye, discussions in committee meetings are also more collaborative, with MPs feeling less pressured to posture for media galleries.
How has the Role of Parliamentary Committees Declined Recently?
- During the course of the 17th Lok Sabha, only 14 Bills have been referred for further examination so far.
- As per data from PRS, as little as 25% of the Bills introduced were referred to committees in the 16th Lok Sabha, as compared to 71% and 60% in the 15th and 14th Lok Sabha, respectively.
Way Forward
- Strengthen the role of parliamentary committees by giving them more resources, powers, and authority to hold the executive accountable.
- Encourage greater participation from civil society, experts, and stakeholders in the committee proceedings to ensure diverse perspectives and informed decision-making.
- Ensure transparency and accountability in committee proceedings by live streaming and recording meetings and making reports and recommendations publicly available.
- Develop a culture of bipartisan consensus-building within committees to ensure that the interests of all stakeholders are represented and to promote a more productive and efficient legislative process.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. In India, which of the following review the independent regulator in sectors like telecommunications, insurance, electricity, etc.? (2019)
- Ad Hoc Committees set up by the Parliament
- Parliamentary Department Related Standing Committees
- Finance Commission
- Financial Sector Legislative Reforms Commission
- NITI Aayog
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 1, 3 and 4
(c) 3, 4 and 5
(d) 2 and 5
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- Parliamentary Committees are of two kinds Standing Committees and Ad Hoc Committees.
- The Former are elected or appointed every year or periodically and their work goes on, more or less, on a continuous basis.
- The latter are appointed on an ad hoc basis as the need arises and they cease to exist as soon as they complete the task assigned to them. Hence option a is correct.


Governance
National Credit Framework
For Prelims: University Grants Commission, National Credit Framework (NCrF), National School Education Qualification Framework, National Education Policy (NEP).
For Mains: Provisions of National Education Policy (NEP) and National Credit Framework (NCrF).
Why in News?
The University Grants Commission has announced the implementation of the National Credit Framework (NCrF) for all regulatory organisations and universities in India.
- This framework is designed to integrate the credits earned through school education, higher education, vocational, and skill education, and provide lifelong learning opportunities.
What is National Credit Framework?
- About:
- According to the framework, an academic year will be defined by the number of hours a student puts in and credits will be provided to them accordingly at the end of each academic year.
- NCrF is a meta-framework that consists of three verticals:
- National School Education Qualification Framework (NSEQF)
- National Higher Education Qualification Framework (NHEQF), and
- National Skills Qualification Framework (NSQF).
- NCrF is a meta-framework that consists of three verticals:
- According to the framework, an academic year will be defined by the number of hours a student puts in and credits will be provided to them accordingly at the end of each academic year.
- Provisions:
- Integration of Academic and Vocational Education:
- The integration of academic and vocational education is emphasised by the National Education Policy (NEP) and is provided by the NCrF.
- This mechanism ensures equivalence within and between the two education streams.
- Credit System:
- The total 'Notional Learning hours in a year' for assignment of Credits will be 1200 hours. A minimum of 40 credits may be earned for 1200 hours of learning every year with 20 credits per semester of six months
- Notional hours refer to the time that the average student would need to attend all classes, study for tests and do assignments and homework.
- The total credits earned by a student during the entire schooling period will be 160 credits.
- By the end of a three-year bachelor's degree course, the student will have earned 120 credits.
- When a student completes a Ph.D., the earned credits would be 320.
- Students will also get credits for participating in Olympiads, science quizzes, internships, and taking up jobs while they are studying in college.
- The total 'Notional Learning hours in a year' for assignment of Credits will be 1200 hours. A minimum of 40 credits may be earned for 1200 hours of learning every year with 20 credits per semester of six months
- Credit Levels:
- The NCrF has proposed several levels within this framework ranging from level 1 to level 8.
- The credit level that can be attained after completion of school education, i.e., grade 5th will be level 1, grade 8th will be level 2, grade 10th will be level 3, and grade 12th will be level 4.
- Higher education shall be from credit levels of 4.5 to level 8.
- The NCrF credit levels for school education are upto level 4, while for higher education
- For vocational education & training level 1 to level 8.
- The NCrF has proposed several levels within this framework ranging from level 1 to level 8.
- Aadhaar-Enabled Student Registration:
- An Aadhaar-enabled student registration will take place. After student registration, an Academic Bank of Credit (ABC) account will be opened.
- The deposit of degree and credits will take place in those accounts. There will be a knowledge locker along the lines of DigiLocker.
- Integration of Academic and Vocational Education:
- Challenges:
- Standardisation: The NCrF consists of different verticals such as NSEQF, NHEQF, and NSQF. Ensuring standardisation across these verticals while catering to the unique needs of each stream might be a challenge.
- Data Security and Privacy: The use of Aadhaar-enabled student registration and an academic bank of credit (ABC) account to store student data may pose security and privacy risks.
- Ensuring the security and confidentiality of the data will be crucial for the successful implementation of the NCrF.
Conclusion
- NCrF aims to provide seamless horizontal and vertical mobility between different education streams in India. However, the successful implementation of the NCrF may face several challenges such as implementation, standardisation, acceptance and adoption. Addressing these challenges will require a collaborative effort from various stakeholders to ensure that the framework is up-to-date, relevant, and effective in addressing the changing needs of the education system in India.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. National Education Policy 2020 is in conformity with the Sustainable Development Goal-4 (2030). It intends to restructure and reorient the education system in India. Critically examine the statement. (2020)
Indian Economy
Retail Inflation Slides Below 6%
For Prelims: RBI, CPI, WPI, Core Inflation, MPC.
For Mains: Retail Inflation Slides Below 6%.
Why in News?
Recently, India's retail inflation rate declined to 5.66%, below the Reserve Bank of India's (RBI) upper target of 6% in March 2023, primarily due to a decrease in food prices, especially for vegetables.
- Core inflation, which excludes food and fuel prices, was at 5.95% in March, down from 6.12% in February.
What is the Significance of the Decline?
- The decrease in retail inflation is a positive development for the economy.
- It provides some relief to consumers who have been dealing with rising prices for essential goods and services. Moreover, it could give the RBI more flexibility in its monetary policy decisions going forward.
- However, it remains to be seen if this trend will continue, and if the RBI will adjust interest rates accordingly.
What is Retail Inflation?
- Retail Inflation:
- Retail inflation, also known as Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation, is the rate at which the prices of goods and services that consumers buy for personal use increase over time.
- It measures the change in the cost of a basket of goods and services that are typically purchased by households, including food, clothing, housing, transportation, and medical care.
- Four types of CPI are as follows:
- CPI for Industrial Workers (IW).
- CPI for Agricultural Labourer (AL).
- CPI for Rural Labourer (RL).
- CPI for Urban Non-Manual Employees (UNME).
- Of these, the first three are compiled by the Labour Bureau in the Ministry of Labour and Employment. Fourth is compiled by the NSO in the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation.
- Base Year for CPI is 2012.
- In 2020, the Ministry of Labour and Employment released the new series of Consumer Price Index for Industrial Worker (CPI-IW) with base year 2016.
- The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) uses CPI data to control inflation. In April 2014, the RBI adopted the CPI as its key measure of inflation.
What is the Need for Monitoring Inflation in the Economy?
- Price Stability:
- Inflation erodes the value of money, which makes it harder for people to plan their finances and can lead to economic instability.
- By monitoring inflation, policymakers can take steps to maintain price stability, which promotes economic growth and stability.
- Consumer and Business Confidence:
- When inflation is low and stable, it provides consumers and businesses with confidence in the economy, encouraging them to spend and invest.
- Interest Rates:
- Inflation affects interest rates, which in turn affects borrowing and lending decisions, investment decisions, and overall economic growth.
- By monitoring inflation, policymakers can adjust interest rates to ensure that the economy is growing sustainably.
- International Competitiveness:
- High inflation rates can make a country's exports more expensive, which can reduce its international competitiveness.
- Monitoring inflation can help policymakers keep inflation in check, which can support a country's economic competitiveness.
What is the Wholesale Price Index?
- It measures the changes in the prices of goods sold and traded in bulk by wholesale businesses to other businesses.
- Published by the Office of Economic Adviser, Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- It is the most widely used inflation indicator in India.
- Major criticism for this index is that the general public does not buy products at wholesale price.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q.1 With reference to Indian economy, demand-pull inflation can be caused/increased by which of the following?
- Expansionary policies
- Fiscal stimulus
- Inflation-indexing of wages
- Higher purchasing power
- Rising interest rates
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 4 only
(b) 3, 4 and 5 only
(c) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (a)
Q.2 Consider the following statements: (2020)
- The weightage of food in Consumer Price Index (CPI) is higher than that in Wholesale Price Index (WPI).
- The WPI does not capture changes in the prices of services, which CPI does.
- Reserve Bank of India has now adopted WPI as its key measure of inflation and to decide on changing the key policy rates.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)


Indian Economy
Dabba Trading: An Unregulated and Illegal Practice
For Prelims: National Stock Exchange (NSE), Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act (SCRA) 1956.
For Mains: Issues Related to the Banking Sector in India.
Why in News?
Recently, National Stock Exchange (NSE) issued a string of notices naming entities involved in “dabba trading”.
What is Dabba Trading?
- About:
- Dabba trading is a form of informal trading that takes place outside the purview of the stock exchanges.
- In this practice, traders bet on stock price movements without incurring a real transaction to take physical ownership of a particular stock as is done in an exchange.
- This results in gambling centred around stock price movements, which is illegal and unregulated.
- For example, an investor places a bet on a stock at a price point, say ₹1,000. If the price point rose to ₹1,500, he/she would make a gain of ₹500. However, if the price point falls to ₹900, the investor would have to pay the difference to the dabba broker.
- Thus, it could be concluded that the broker’s profit equates the investor’s loss and vice-versa. The equations are particularly consequential during bull runs or bear market.
- Legality:
- It is recognised as an offence under Section 23(1) of the Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act (SCRA), 1956 and upon conviction, can invite imprisonment for a term extending up to 10 years or a fine up to ₹25 crore, or both.
- Issues Associated:
- Cash Transactions: Transactions are facilitated using cash and the mechanism is operated using unrecognised software terminals, which helps dabba traders escape taxation.
- The use of cash means that they are outside the purview of the formal banking system. It results in a loss to the government exchequer.
- Lack of Security to Investors: Being outside the regulatory purview implies that investors are without formal provisions for investor protection, dispute resolution mechanisms and grievance redressal mechanisms that are available within an exchange.
- The primary risk entails the possibility that the broker defaults in paying the investor or the entity becomes insolvent or bankrupt.
- Black Money: It could potentially encourage the growth of ‘black money’ alongside perpetuating a parallel economy, which could lead to risks entailing money laundering and criminal activities.
- Cash Transactions: Transactions are facilitated using cash and the mechanism is operated using unrecognised software terminals, which helps dabba traders escape taxation.
How can Dabba Trading be Prevented?
- Strict Enforcement of Laws: The Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act, 1956, already prohibits 'dabba trading' and provides for severe penalties upon conviction. However, these laws need to be more strictly enforced, and culprits should be punished to deter others from engaging in such activities.
- Increasing Awareness: Retail investors need to be educated and made aware of the dangers of 'dabba trading'. Financial regulators can conduct awareness campaigns and disseminate information about the risks associated with such trades.
- Monitoring Social Media and Mobile Apps: 'Dabba trading' is often facilitated through mobile apps and social media. Regulators can monitor these platforms and take action against those who promote or engage in it.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. In the parlance of financial investments, the term ‘bear’ denotes (2010)
(a) An investor who feels that the price of a particular security is going to fall
(b) An investor who expects the price of particular shares to rise
(c) A shareholder or a bondholder who has an interest in a company, financial or otherwise
(d) Any lender whether by making a loan or buying a bond
Ans: (a)
- A ‘bear’ is an investor who believes that a particular security or market is headed downward and attempts to profit from a decline in stock prices. ‘Bears’ are typically pessimistic about the state of a given market.
- Whereas, a ‘bull’ is an investor who thinks the market, a specific security or an industry is poised to rise. Investors who adopt a ‘bull’ approach purchase securities under the assumption that they can sell them later at a higher price. ‘Bulls’ are optimistic investors who are attempting to profit from the upward movement of stocks.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.


Governance
Indian DefSpace Symposium
For Prelims: Positive Indigenization List, Initiatives in the Defence Sector, Indian DefSpace Symposium
For Mains: Mission DefSpace, Government Policies & Interventions, Indigenization of Technology, Significance of Indigenisation of Defence and associated challenges.
Why in News?
Recently, the Indian Space Association (ISpA) in association with the Defence Research and Development Organization (DRDO) organized the Indian DefSpace Symposium which focuses on the growing government and military focus on the space domain and explores ways to enhance India's space capabilities.
- The event was held as part of the deliberations under ‘Mission Def-Space,’ an ambitious effort launched by Prime Minister of India to develop innovative solutions in the space domain through the Indian industry and start-ups.
What is the Need for Transformation of Warfare?
- The nature of warfare is on the fold of major transformation, and space is being used to enhance combat capabilities in land, sea, and cyber domains.
- The symposium discusses the need for developing dual-use platforms with cutting-edge technology and increasing offensive and defensive capabilities in the space domain. and to explore the field of miniaturization of satellites and reusable launch platforms to mitigate costs and challenges.
- DRDO emphasized the need to enhance space situational awareness capability, safeguard space assets with counter space capabilities, and build resilience and redundancy in a space-based infrastructure.
- It also explores ways to expand the Navic constellation, provide agile space-based intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR), and ensure secure satellite-assisted communications.
- The symposium also discussed the need to factor in the presence of trans-domain weapons, targeting from air or from inner to outer space, and integrate future space-based surveillance networks.
What is India’s Stand on Militarisation of Space?
- Changing Polarity in Current Scenarios: In India, historically, space has remained the sole jurisdiction of its civilian space agency, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). India has always maintained a pacifist approach towards space security, opposing the weaponization and militarisation of space.
- For the last decade, India’s approach to outer space has been shifting and is now increasingly driven by national security concerns. Rather than opting for a morally driven policy, India is focusing on peaceful uses of outer space.
- Though India has still not abandoned its policy of non-weaponization, it has felt that its inaction and ignoring of contemporary developments in outer space could leave it vulnerable to a range of threats to its space assets.
- For the last decade, India’s approach to outer space has been shifting and is now increasingly driven by national security concerns. Rather than opting for a morally driven policy, India is focusing on peaceful uses of outer space.
- Recent Developments: In 2019, India conducted its first ever simulated space warfare exercise (IndSpaceX) with an eye on Chinese threats and successfully tested an anti-satellite weapon (Mission Shakti) in the same year.
- Also, the launch of the tri-service Defence Space Agency (DSA) has permanently taken the military away from the shadows of civil space.
- India has also set up the Defence Space Research Agency (DSRA) to help develop space-based weapons for the DSA. Space is as much recognised as a military domain as land, water, air and cyber.
- In 2020, the Government of India approved the creation of IN-SPACe- an independent nodal agency under the Department of Space to encourage private participation in the space domain.
- Also, the launch of the tri-service Defence Space Agency (DSA) has permanently taken the military away from the shadows of civil space.
What is Mission Def-Space?
- It is an ambitious effort to develop innovative solutions for the three Services (Indian airforce, Navy, and Army) in the space domain through the Indian industry and start-ups.
- 75 challenges are being opened to get innovative solutions, based on the defence requirements in the space domain.
- Startups, innovators and the private sector will be invited to find solutions for the problems that will include both offensive and defensive capabilities.
- It aims to develop a range of military applications for space warfare and to enable the private industries to offer solutions to the armed forces for future offensive and defensive requirements.
- Defense applications in space will not only help the Indian armed forces but can also be extended to friendly foreign nations.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following in respect of Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS): (2017)
- Inaugural IONS was held in India in 2015 under the chairmanship of the Indian Navy.
- IONS is a voluntary initiative that seeks to increase maritime co-operation among navies of the littoral states of the Indian Ocean Region.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
- The ‘Indian Ocean Naval Symposium’ (IONS) is a voluntary initiative that seeks to increase maritime cooperation among navies of the littoral States of the Indian Ocean Region by providing an open and inclusive forum for discussion of regionally relevant maritime issues. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- It provides a forum to increase maritime security cooperation, and promote friendly relationships among the member nations.
- The inaugural IONS-2008 was held in New Delhi, India in Feburary, 2008. The Chief of the Naval Staff, Indian Navy was designated as the Chairman of IONS for the
- period 2008-10. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q1. Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in the defence sector is now set to be liberalized: What influence this is expected to have on Indian defence and economy in the short and long run? (2014)
Q2. What is the significance of Indo-US defence deals over Indo-Russian defence deals? Discuss with reference to stability in the Indo-Pacific region. (2020)


Important Facts For Prelims
Sunken Ocean Floor above Earth’s Core
Why in News?
Recently, Geologists have discovered a previously unknown layer between the core and the mantle of the Earth, likely to be a thin but dense sunken ocean floor.
- This layer is pencil-thin in geological terms, measuring tens of kilometers, which is minuscule when compared to the thickness of Earth's other layers.
What are the Key Highlights?
- The discovery of this ocean floor layer could play an important role in how heat escapes from the core.
- The material from ancient ocean floors can also get caught up in mantle plumes, traveling back to the surface through volcanic eruptions.
- There are mountains on the core, these underground "mountains" could be up to 5 times taller than Mt. Everest, and they could help explain the changes in physical properties between the outer core and the mantle, which are greater than those between the surface of the Earth and the air above it.
- The subducted oceanic material could collect along the core-mantle boundary where it can be pushed by the slowly flowing rock in the mantle over time. This suggests that Earth's history is more complex than previously thought, with the possibility of multiple sunken ocean floors adding to the complexity of the planet's geological makeup.
What are the Implications for Future Research?
- This new discovery opens up new avenues of research for geologists and could lead to a better understanding of Earth's geological processes.
- The detailed method used to probe a large portion of the southern hemisphere using sound wave echoes from the core-mantle boundary could be used in other parts of the world to uncover similar anomalies.
- It also highlights the importance of continued investment in high-resolution imaging technology for exploring the mysteries of our planet's interior.
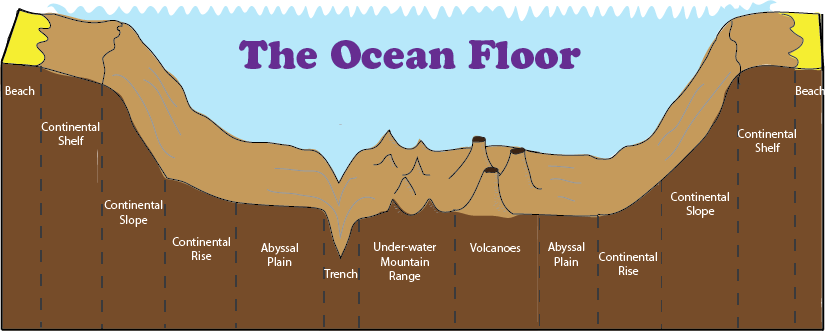
What is an Ocean Floor?
- The ocean floor is the bottom of the ocean that covers more than 70% of the Earth’s surface. It has different features and depths depending on the location and the movement of tectonic plates. The ocean floor can be divided into four main zones:
- Continental Shelf:
- The shallowest and widest part of the ocean floor.
- Extends from the coast to the edge of the continent, where it drops sharply into the continental slope.
- Rich in marine life and resources, such as fish, oil, and gas.
- Continental Slope:
- The steep slope that connects the continental shelf to the abyssal plain
- Cut by deep canyons and valleys that are formed by underwater landslides and rivers of sediment.
- Home to some deep-sea creatures, such as octopuses, squids, and anglerfish.
- Abyssal Plain:
- The flattest part of the ocean floor.
- Covers most of the ocean basin and lies between 4,000 and 6,000 meters below sea level.
- Covered by a thick layer of fine sediments that are carried by ocean currents and settle on the seafloor.
- Inhabited by some of the most bizarre and mysterious animals on Earth, such as giant tube worms, bioluminescent fish, and vampire squids.
- Oceanic Deeps or Trenches:
- These areas are the deepest parts of the oceans.
- The trenches are relatively steep sided, narrow basins. They are some 3-5 km deeper than the surrounding ocean floor.
- They occur at the bases of continental slopes and along island arcs and are associated with active volcanoes and strong earthquakes.
- That is why they are very significant in the study of plate movements. As many as 57 deeps have been explored so far; of which 32 are in the Pacific Ocean; 19 in the Atlantic Ocean and 6 in the Indian Ocean.
- Continental Shelf:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. In the structure of planet Earth, below the mantle, the core is mainly made up of which one of the following? (2009)
(a) Aluminium
(b) Chromium
(c) Iron
(d) Silicon
Ans: (c)


Important Facts For Prelims
Kurmis’ Push for ST Status
Why in News?
Recently, the Kurmi Community has called off the agitation in Bengal, asking for the inclusion in the ST (Scheduled Tribe) Status from Other Backward Class (OBC).
- They also want their Kurmali language to be included in the Eighth Schedule of the Constitution.
What is the Background?
- Kurmis were not included among the communities classified as STs in the 1931 Census and were excluded from the ST list in 1950.
- In 2004, the Jharkhand government recommended the community be added to the ST list rather than be categorized as OBCs.
- Following the recommendation, the matter went to the Tribal Research Institute (TRI), which held that Kurmis are a sub-caste of Kunbis and not tribals. Based on this, the Centre rejected the demand of Kurmis to be considered as ST.
- According to the Tribal Development Department of the state government, the state’s tribal population is almost 53 lakhs as per Census 2011, or about 5.8% of the state's total population.
What is the Process of Inclusion under ST?
- The process for including a community in the list of ST follows a set of modalities established in 1999.
- The respective State or Union Territory government must initiate the proposal for inclusion, which then goes to the Union Tribal Affairs Ministry and subsequently to the Office of the Registrar General of India (ORGI).
- If the ORGI approves the inclusion, the proposal is then sent to the National Commission for Scheduled Tribes, and if they concur, the proposal is forwarded to the Cabinet for amendment to the Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order, 1950.
Who are the Kurmis?
- About:
- Kurmis are a landowning farming community whose status varies from place to place.
- Kurmis are referred to as “progressive farmers” who “avail of maximum benefits of all the development schemes available in the area and region.
- Kurmis are distributed across several states — Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Odisha, Maharashtra, Gujarat, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, West Bengal, Jharkhand, Goa, and Karnataka.
- Caste Status:
- In most states, Kurmis belong to the OBC in both the central and state lists for reservations.
- In Gujarat, Patels, who are linked to Kurmis, are in the general category, and have been demanding OBC status.
- In West Bengal, Odisha, and Jharkhand — where Kurmi is written as ‘Kudmi’ — Kurmis want to be included among Scheduled Tribes.
- Kurmali Language:
- Kurmali language is a language spoken by the Kurmi community, primarily in the Indian states of Bihar, Jharkhand, and Odisha.
- The Kurmali language is a member of the Indo-Aryan language family and belongs to the Bihari language family. It shares some similarities with Maithili and Magahi. It has its own script called "Kurmi Kudali" which is a modified version of the Devanagari script.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. Every year, a month long ecologically important campaign/festival is held during which certain communities/tribes plant saplings of fruit-bearing trees. Which of the following are such communities/ tribes? (2014)
(a) Bhutia and Lepcha
(b) Gond and Korku
(c) Irula and Toda
(d) Sahariya and Agariya
Ans: (b)
Q2. The provisions in Fifth Schedule and Sixth Schedule in the Constitution of India are made in order to (2015)
(a) protect the interests of Scheduled Tribes
(b) determine the boundaries between States
(c) determine the powers, authority and responsibilities of Panchayats
(d) protect the interests of all the border States
Ans: (a)
Q3. Under which Schedule of the Constitution of India can the transfer of tribal land to private parties for mining be declared null and void? (2019)
(a) Third Schedule
(b) Fifth Schedule
(c) Ninth Schedule
(d) Twelfth Schedule
Ans: (b)
Q4. If a particular area is brought under the Fifth Schedule of the Constitution of India, which one of the following statements best reflects the consequence of it? (2022)
(a) This would prevent the transfer of land of tribal people to non-tribal people.
(b) This would create a local self-governing body in that area.
(c) This would convert that area into a Union Territory.
(d) The State having such areas would be declared a Special Category State.
Ans: (a)


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Jallianwala Bagh Massacre
Jallianwala Bagh Massacre Day 2023 marks 104 years since the tragic incident that is seen as a turning point in Indian history. The Jallianwala Bagh massacre was a tragic incident that occurred on 13th April 1919 in Amritsar, India, where British Gurkha soldiers, on the orders of Brigadier-General Dyer, fired upon a large crowd of unarmed protestors who had gathered at Jallianwala Bagh to demonstrate against the Rowlatt Act 1919 peacefully. The event resulted in the death of over 1000 innocent men, women, and children and sparked widespread protests and unrest throughout the country.
The incident was a significant turning point in India's struggle for independence from British rule and galvanized the Indian people to unite and fight for their rights and freedom. The massacre led to widespread condemnation of British colonial policies, and it played a pivotal role in shaping the Indian independence movement. The incident also marked a significant turning point in Mahatma Gandhi's life as it led him to launch his first major nonviolent civil disobedience campaign, the Non-Cooperation Movement, which ultimately paved the way for India's independence in 1947. Today, Jallianwala Bagh serves as a powerful reminder of the sacrifices made by countless Indians in the fight for independence, and it continues to inspire people around the world to fight against oppression and injustice.
Read more: Jallianwala Bagh Massacre
Assam's Bihu Dance Sets Two Guinness World Records
Assam’s Bihu dance has made history by breaking two world records with 11,304 dancers and musicians performing at Sarusajai Stadium in Guwahati. The performers attempted to create world records in two categories - the largest Bihu dance performance and the largest performance by folk musicians. This marks a significant moment for the traditional folk dance of Bihu, which is popular across Assam and especially performed during Bohag Bihu or Rongali Bihu, the spring festival that heralds the Assamese New Year in mid-April.
The President of India has extended greetings on the occasion of various Traditional New Year Festivals celebrated across India, including Vaishakhi, Vishu (Kerala and other neighboring areas), Naba Barsha (West Bengal), Puthandu-Pirappu (Tamil Nadu), and Vaisakhadi. These festivals, observed during the spring season, signify the beginning of the new year according to different regional calendars in India. Vaishakhi is celebrated by Hindus and Sikhs and marks the formation of the Khalsa panth of warriors under Guru Gobind Singh. These festivals bring together people from various castes and religions across India and celebrate the rich cultural diversity of the country.
Read more: RONGALI BIHU, TRADITIONAL NEW YEAR FESTIVALS
IAF Joins Multinational Exercise Orion in France
The Indian Air Force (IAF) will be sending a contingent France to participate in Exercise Orion at Mont-de-Marsan, an Air Force base of the French Air and Space Force (FASF). from 17th April to 5th May 2023. This exercise would mark the first overseas participation for the IAF's Rafale aircraft. In addition to the IAF and FASF, Air Forces from Germany, Greece, Italy, Netherlands, the United Kingdom, Spain, and the United States of America will also take part in this multilateral exercise. This exercise will enable the IAF to learn the best practices of other Air Forces and enhance their employment philosophy, further enriching their capabilities.
Ghana Approves Oxford's Malaria Vaccine R21
Ghana has approved a new malaria vaccine from Oxford University, making it the first country in the world to do so, and a potential step forward in the fight against the disease. The vaccine, known as R21, has been approved domestically for children aged between 5 months and 36 months, who are at the highest risk of death from malaria. It is unclear when the vaccine may be rolled out in Ghana as other regulatory bodies, including the World Health Organization (WHO), are still assessing its safety and effectiveness. The Oxford vaccine is the second malaria vaccine to be approved for use and the first major vaccine to be approved in an African country ahead of rich nations. The approval is rare as it comes before the publication of final-stage trial data.
The Serum Institute of India has a deal with Oxford to produce up to 200 million doses of the vaccine annually. The WHO has said that in the areas where the Mosquirix vaccine has been given, all-cause child mortality has dropped by 10 percent, a sign of its impact.
Read more: World Malaria Day 2022