Maps
Governance
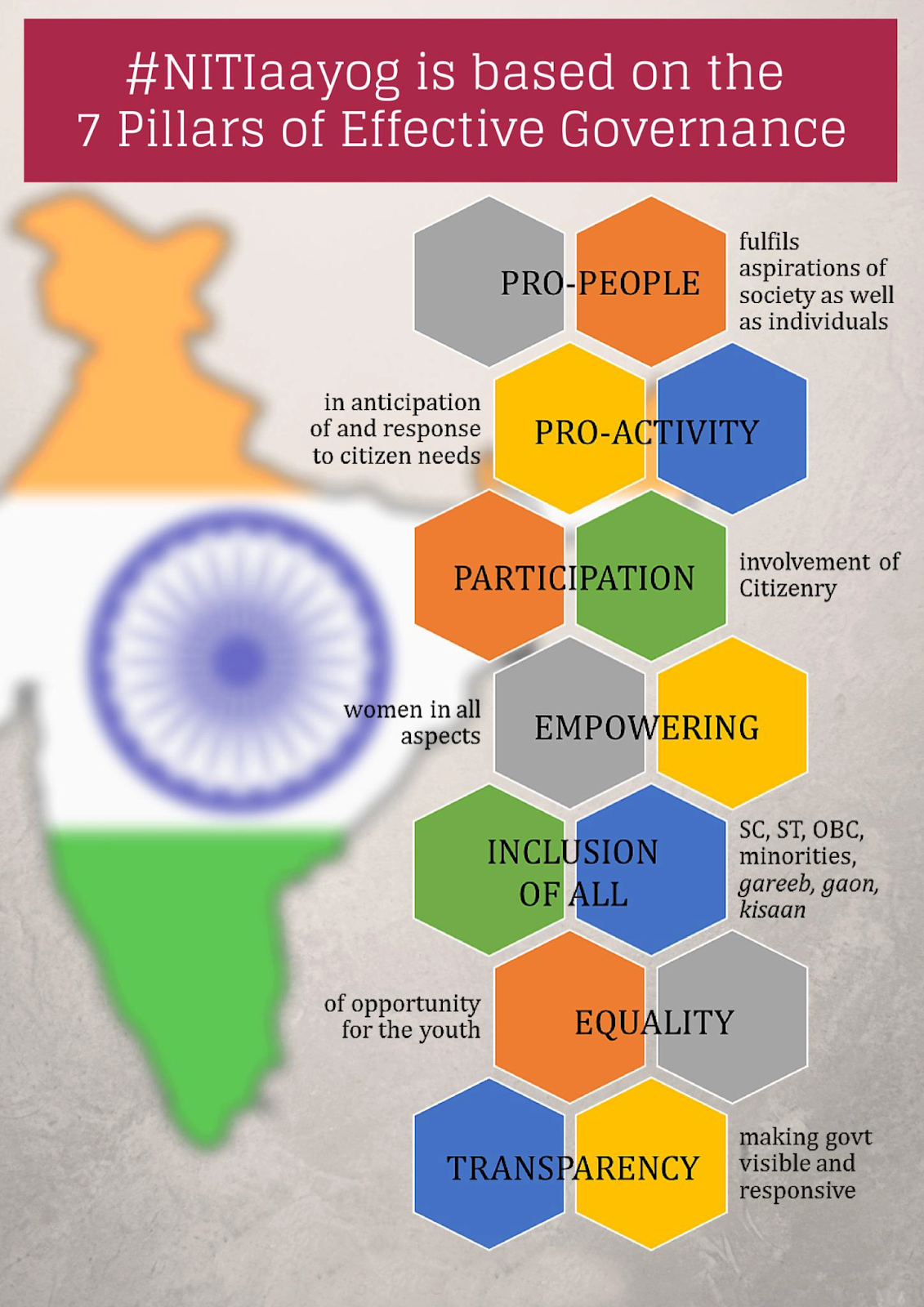
NITI Aayog-like Bodies in States
For Prelims: NITI Aayog, Cooperative Federalism.
For Mains: The Need and the Plan for Setting-Up NITI Aayog-like Bodies in States.
Why in News?
The National Institution for Transforming India (NITI) Aayog will assist each state to set up similar bodies, replacing their planning boards for faster and inclusive economic growth along with the vision of becoming a developed nation by 2047.
What is NITI Aayog?
- NITI Aayog is the apex public policy think tank of the Government of India.
- It replaced the Planning Commission on 1st January, 2015 with emphasis on ‘Bottom –Up’ approach to envisage the vision of Maximum Governance, Minimum Government, echoing the spirit of ‘Cooperative Federalism’.
- It has two Hubs.
- Team India Hub acts as interface between States and Centre.
- Knowledge and Innovation Hub builds the think-tank acumen of NITI Aayog.
What is the Need for Setting up NITI Aayog-like Bodies in States?
- States are the Indian economy’s growth drivers. The national gross domestic product (GDP) growth is an aggregation of states’ rates of growth except for sectors like defence, railways and highways.
- Health, education and skilling are primarily with the state government.
- State governments’ role is critical to improving ease of doing business, land reforms, infrastructure development, credit flows and urbanisation, all of which are vital for sustained economic growth.
- Most states so far have done little to rejuvenate their planning departments/boards, which earlier dealt with the Planning Commission and prepared parallel state five year-plans with the Centre.
- Most states’ planning departments, with huge manpower, are almost defunct and have no clarity what work they will do.
What is the Agenda for Implementation?
- Initially, it aims for 8-10 states to set up such bodies, before reaching out to all by March 2023.
- Four states i.e., Karnataka, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh and Assam have already begun work in this regard.
- Maharashtra, Odisha, Andhra Pradesh and Gujarat will likely begin work soon.
- A plan has been chalked out by NITI Aayog to:
- Help in the creation of teams that will examine the existing structure of state planning boards.
- Conceptualise the State Institution for Transformation (SIT) in the next 4-6 months.
- Lateral entry of professionals will be encouraged in SITs to undertake high-quality analytical work and policy recommendations.
- Besides reorienting state planning boards as SITs, a blueprint will be made on:
- Guiding states in policy formulation.
- Monitoring and evaluation of government policies and programmes.
- Suggesting better technology or models for delivery of schemes.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Atal Innovation Mission is set up under the (2019)
(a) Department of Science and Technology
(b) Ministry of Labour and Employment
(c) NITI Aayog
(d) Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- The Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) is a flagship initiative set up by the NITI Aayog to promote innovation and entrepreneurship based on a detailed study and deliberations on innovation and entrepreneurial needs of the country.
- AIM is envisaged as an umbrella innovation organization that would play an instrumental role in alignment of innovation policies between Central, State and sectoral innovation schemes incentivizing the establishment and promotion of an ecosystem of innovation and entrepreneurship at various levels – higher secondary schools; science, engineering and higher academic institutions; SME/MSME industry,corporate and NGO levels.
- Hence, option C is the correct answer.


Governance
Deemed University Status
For Prelims: National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT), University Grants Commission (UGC), Institute of National Importance.
For Mains: Significance of Higher Education.
Why in News?
Recently, the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) has applied to the University Grants Commission (UGC) for the deemed university status.
Why did NCERT apply for Deemed University Tag?
- Lack of Government Decision: The government’s proposal to make the NCERT an institute of national importance is on hold.
- Benefits: The status would allow NCERT to offer its own graduate, postgraduate and doctoral degrees and have autonomy in terms of introduction of programmes, course structure, conducting examinations and management, among others.
- Present Status: The graduate and post-graduate programmes offered by NCERT’s Regional Institute of Education (RIE) are affiliated with local universities like Barkatullah University, Bhopal, M D S University, Ajmer, University of Mysuru, Utkal University, Bhubaneshwar and North-Eastern Hill University, Shillong.
- Need: Despite offering innovative teacher education courses through RIEs for decades, the NCERT is still dependent on the approval of local universities to introduce programmes.
What is the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT)?
- About:
- The NCERT is an autonomous organization set up in 1961 by the Government of India to assist and advise the Central and State Governments on policies and programmes for qualitative improvement in school education.
- The Executive Committee (EC) is the highest decision-making body of NCERT and is chaired by the Education Minister.
- Objectives:
- To undertake, promote and coordinate research in areas related to school education, prepare and publish model textbooks, supplementary material, newsletters, journals and develop educational kits, multimedia digital materials, etc.
What is a Deemed University?
- About:
- Deemed University is a type of higher education institute, it has been recognized by the status of “deemed to be university” under Section 3 of the University Grants Commission (UGC) Act, 1956.
- In broad terms, it means that the institution has been granted permission to offer its own degree programs, which are equivalent to those provided by regular universities.
- Deemed University is a type of higher education institute, it has been recognized by the status of “deemed to be university” under Section 3 of the University Grants Commission (UGC) Act, 1956.
- Benefits:
- There are many benefits of being a Deemed University, such as increased funding opportunities and attracting better faculty. Additionally, these institutions often have more flexible admissions policies.
- The authority to revise the curriculum.
- The right to conduct examinations and evaluations.
- There are many benefits of being a Deemed University, such as increased funding opportunities and attracting better faculty. Additionally, these institutions often have more flexible admissions policies.
What are the other Different types of Universities in India?
- Central University:
- A university established or incorporated by a Central Act. The establishment and operation are funded by the Union Government.
- State University:
- A university established or incorporated by a Provincial Act or by a State Act.
- Private University:
- A university established through a State/Central Act by a sponsoring body viz. A Society registered under the Societies Registration Act 1860, or any other corresponding law for the time being in force in a State or a Public Trust or a Company registered under Section 25 of the Companies Act, 1956.
- Institution of National Importance:
- An Institution established by Act of Parliament and declared as Institution of National Importance. They are funded by the Government of India and include all the IITs, NITs and AIIMs institutes.
- Institution under State Legislature Act:
- An Institution established or incorporated by a State Legislature Act.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Regarding Wood’s Dispatch, which of the following statements are true? (2018)
- Grants-in-Aid system was introduced.
- Establishment of universities was recommended.
- English as a medium of instruction at all levels of education was recommended.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- Charles Wood was a British Liberal politician and a Member of Parliament. In 1854, he sent the “Wood’s Dispatch” to the Governor General Lord Dalhousie which is called the Magna Carta of English Education in India.
- As per the Dispatch, an education department was to be set up in every Province, universities on the model of the London University were to be established in big cities such as Bombay, Calcutta and Madras, at least one government school was to be opened in every district, affiliated private schools were to be given grants-in-aid, and the Indian natives were to be given training in their mother tongue also. Hence, statements 1 and 2 are true.
- The Wood’s Dispatch gave importance to the teaching of English, but at the same time, it also stressed on the teaching of Indian languages at primary level. Hence, statement 3 is not true. Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer


Indian Economy
Rise in Retail Inflation & Contract in Index of Industrial Production
For Prelims: Inflation, Index of Industrial Production (IIP), National Statistical Office (NSO), GDP (Gross Domestic Product)
For Mains: Causes and Consequences of Inflation and Measures
Why in News?
According to the recent National Statistical Office (NSO) data, the retail inflation rose to 7% in July, 2022 and the Index of Industrial Production (IIP) declined to a four-month low of 2.4% in July,2022 as against a growth of 11.5% in 2021.
- Nine of the 22 manufacturing sub-sectors reported a contraction in output, including food products, tobacco products, leather products and electrical equipment.
What is Inflation?
- Inflation refers to the rise in the prices of most goods and services of daily or common use, such as food, clothing, housing, recreation, transport, consumer staples, etc.
- Inflation is indicative of the decrease in the purchasing power of a unit of a country’s currency. This could ultimately lead to a deceleration in economic growth.
- However, a moderate level of inflation is required in the economy to ensure that production is promoted.
- In India, the NSO under the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation measures inflation.
- In India, inflation is primarily measured by two main indices — WPI (Wholesale Price Index) and CPI (Consumer Price Index) which measure wholesale and retail-level price changes, respectively.
- Consumer Price Index
- It measures price changes from the perspective of a retail buyer.
- The CPI calculates the difference in the price of commodities and services such as food, medical care, education, electronics etc, which Indian consumers buy for use.
- Four types of CPI are as follows:
- CPI for Industrial Workers (IW).
- CPI for Agricultural Labourer (AL).
- CPI for Rural Labourer (RL).
- CPI (Rural/Urban/Combined).
- Of these, the first three are compiled by the Labour Bureau in the Ministry of Labour and Employment. Fourth is compiled by the National Statistical Office (NSO) in the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation.
- Base Year for CPI is 2012.
- Consumer Price Index
- The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) uses CPI data to control inflation.
- Headline and Core Inflation:
- The food and fuel inflation form one of the components of headline inflation in India.
- Headline Inflation is the total inflation for the period, comprising a basket of commodities.
- Core Inflation excludes volatile goods from the basket of commodities tracking Headline Inflation. These volatile commodities mainly comprise food and beverages (including vegetables) and fuel and light (crude oil).
- Core inflation = Headline inflation – (Food and Fuel) inflation
What are the Causes of Recent Inflation in India?
- Food Inflation: The uptick in inflation was largely driven by ‘a broad-based rise across the food segment’, with a higher inflation in cereals, pulses, milk, fruits.
- The price rise in cereals rose further from 6.9% in July to 9.6% in August (2022).
- Rural inflation saw a sharper rise than urban inflation.
- Low Kharif output: Due to erratic monsoon, the Kharif crop sowing is unlikely to touch last year’s levels of production, therefore food inflation could remain a problem in the near future.
- Base Effect: The rise in inflation is attributable both to an adverse base effect and an increase in food and fuel prices.
- Core inflation — headline inflation excluding food and fuel — was at 5.9% in August, remaining below the tolerance limit of 6% for the fourth consecutive month.
- Other reasons: Global inflation pressures, Inflationary expectations, Weakness in Indian currency, etc.
What is the Index of Industrial Production?
- IIP is an indicator that measures the changes in the volume of production of industrial products during a given period.
- It is compiled and published monthly by the National Statistical Office (NSO), Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation.
- It is a composite indicator that measures the growth rate of industry groups classified under:
- Broad sectors, namely, Mining, Manufacturing, and Electricity.
- Use-based sectors, namely Basic Goods, Capital Goods, and Intermediate Goods.
- The base year for IIP is 2011-2012.
- Significance of IIP:
- It is used by government agencies including the Ministry of Finance, the Reserve Bank of India, etc, for policy-making purposes.
- IIP remains highly relevant to calculating the quarterly and advance GDP (Gross Domestic Product) estimates.
- About Eight Core Sectors:
- These comprise 40.27% of the weight of items included in the Index of Industrial Production (IIP).
- The eight core sector industries in decreasing order of their weightage: Refinery Products> Electricity> Steel> Coal> Crude Oil> Natural Gas> Cement> Fertilizers.
What are the Reasons for Recent IIP Contraction?
- Mining sector output contracted 3.3 per cent in July,2022. Non-durables contracted 2.0% in July, 2022.
- The sharp YoY contraction in mining output in July 2022 was a surprise, given the double-digit growth in coal output, and is likely to have been led by the excess rainfall seen during the month.
- The IIP growth plunged to a four-month low due to the shift in discretionary consumption to contact-intensive services also.
- Industrial output was only 2.1% higher than pre-Covid levels of July 2019, with the consumer durables and non-durables segment lagging their pre-Covid levels by 6.8% and 2.5 %.
- Supply disruptions, the weakening global growth outlook also impact the industrial output.
What can be the Way Forward?
- There should be consistency in import policy as that sends appropriate market signals in advance. Intervening through import tariffs is better than quotas, which leads to greater welfare loss. Recently, Government has prohibited exports of food products like wheat flour/atta, rice, maida, etc. to keep domestic supplies steady and curb rise in prices.
- There is a need for more accurate crop forecasts using satellite remote sensing and GIS techniques to indicate shortfall/surplus in a crop year much in advance.
- Moreover, a decade old CPI base year of 2011-12 that gives nearly half of the weight to food items needs to be revised and updated to reflect the change in food habits and lifestyle of the population. With the rising middle-class, spending on non-food items has increased and this needs to be better reflected in the CPI, thereby enabling RBI to better target the non-volatile segment (core inflation).
- Strong recovery in domestic demand will remain a key source of support for India’s industrial output.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. In the ‘Index of Eight Core Industries’, which one of the following is given the highest weight? (2015)
(a) Coal production
(b) Electricity generation
(c) Fertilizer production
(d) Steel production
Ans: (b)
- In 2015, Electricity was having the highest weightage in the index of 8 core industries.
- The Eight Core Industries comprise 40.27% of the weight of items included in the Index of Industrial Production (IIP).
- The current weight (April 2021), of eight core industries is given below:
- Petroleum Refinery production (28.04%),
- Electricity (19.85%),
- Steel(17.92%),
- Coal production (10.33%),
- Crude Oil (8.98%),
- Natural Gas production (6.88%),
- Cement production (5.37%),
- Fertilizer production (2.63%).
- Index of Industrial Production
- The Index of Industrial Production (IIP) is an index which details out the growth of various sectors in an economy such as mineral mining, electricity, manufacturing, etc.
- It is compiled and published monthly by the Central Statistical Organisation (CSO), Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation six weeks after the reference month ends, i.e., a lag of six weeks.
- The Base Year of the Index of Eight Core Industries has been revised from the year 2004-05 to 2011-12 from April, 2017. Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.


International Relations
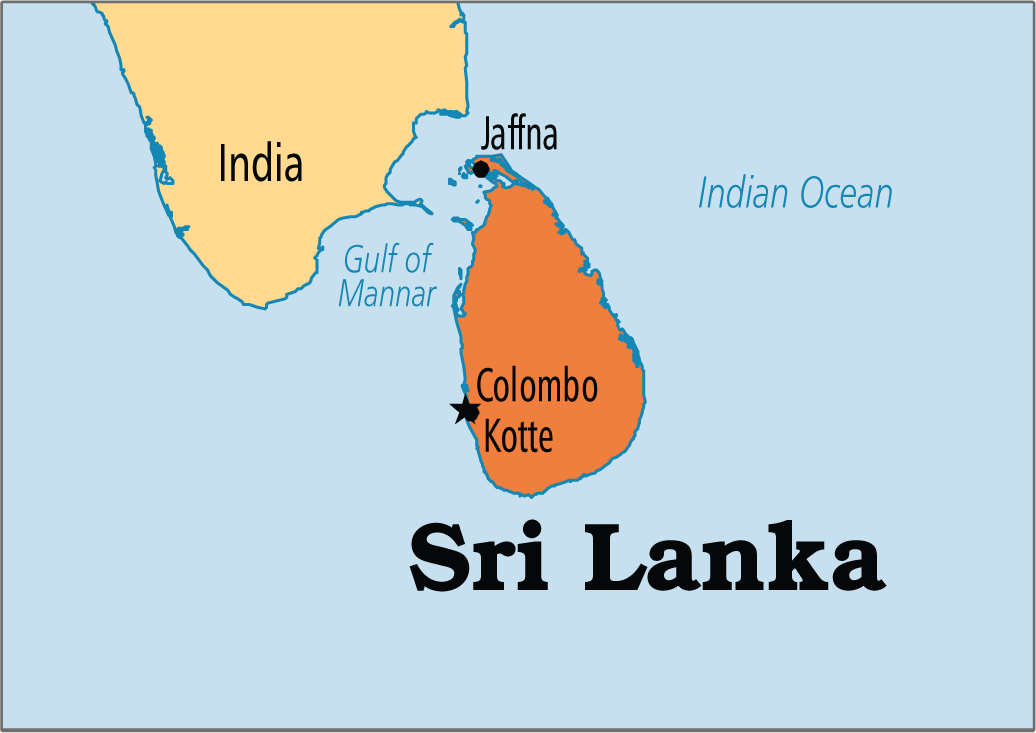
Issue of Tamilians in Sri Lanka
For Prelims: Issue of Tamilians in Sri Lanka, UNHRC, UN Charter, LTTE.
For Mains: Effect of Policies & Politics of Countries on India's Interests, India and its Neighbourhood, India-Sri Lanka Relations.
Why in News?
Recently, India has expressed concern over the lack of any measurable progress by Sri Lanka on its commitment towards reaching a political solution on the Tamil issue.
- India, in its statement at the 51st session of the United Nations Human Rights Council in Geneva said it has “always believed in the responsibility of States for promotion and protection of human rights and constructive international dialogue and cooperation” guided by the U.N. Charter.
What Concerns were Raised by India?
- The current crisis in Sri Lanka has demonstrated the limitations of a debt-driven economy and the impact it has on the standard of living.
- It is in the best interests of Sri Lanka to build the capacity of its citizens and work towards their empowerment.
- Over 13 years since the end of Sri Lanka’s civil war in 2009, when tens of thousands of civilians were killed and disappeared, survivors continue demanding justice and accountability for war-time crimes.
- In the post-war years, Sri Lanka’s human rights defenders have frequently flagged concerns over persisting militarisation, especially in the Tamil-majority north and east, repression, and the shrinking space for dissent.
What is the Tamil Issue and its History?
- Background:
- Sri Lanka is 74.9 % Sinhalese and 11.2 % Sri Lankan Tamil. Within these two groups, Sinhalese tend to be Buddhist and Tamils tend to be Hindu, displaying significant linguistic and religious divisions.
- It is believed that the Tamils arrived in Srilanka both as invaders and traders from India’s Chola Kingdom.
- Some origin stories suggest that the Sinhalese and Tamil communities have experienced tension from the very beginning—not out of cultural incompatibility, but rather out of power disputes.
- Pre-Civil War:
- During British Rule the pattern of Tamil favoritism left Sinhalese people feeling isolated and oppressed. Soon after British occupiers left the island in 1948, these patterns of Tamil dominance changed dramatically.
- After British independence, many Sinhalese gained power and went on to gradually pass acts effectively disenfranchising their Tamil counterparts, which led to the creation of Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE) in 1976.
- LTTE was an uncompromising group inspired by Che Guevarra and his guerilla warfare tactics.
- The conflict then escalated into civil war in 1983, leading to riots targeting Tamils in Colombo.
- The fighting lasted just under three decades and ended in May 2009, when the Sri Lankan government announced that they killed the LTTE leader.
- Post-Civil War:
- Although the Civil War ended in 2009, the current situation in Sri Lanka has only partially improved.
- A large portion of the Tamil population remains displaced. While there are fewer political and civil rights issues, instances of torture and enforced disappearances persist even in recent years.
- The government’s Prevention of Terrorism Act (PTA) targets mostly Tamils. In a more subtle sense, the Sri Lankan government continues to disenfranchise the Tamil community.
- Through the process of “Sinhalization,” for instance, Sinhalese culture has slowly replaced that of the Tamil population.
- Sinahlese monuments, road signs, street and village names, as well as Buddhist places of worship became more common in predominantly Tamil areas.
- These efforts have infringed upon, and in some cases even erased, the Tamil perspective on Sri Lankan history, as well as Tamil and Hindu elements of the country’s culture.
What are the Concerns for India?
- Rehabilitation of Refugees: A lot of Srilankan Tamils who evaded from Srilankan civil war (2009) are seeking refuge in Tamil Nadu. They are not returning in fear of being targeted again. It is a challenge for India to rehabilitate them.
- Sentiments of Indian Tamils: A number of protests and criticism is drawn at the end of the Indian Government for overlooking the plight of Srilankan Tamils to maintain good relationship with Srilanka.
- Strategic interests vs Tamil question: Often India has to trade off on the question of Tamilian minority rights over strategic issues to protect its economic interests in its neighborhood and to counter Chinese influence in the Indian Ocean.
What are the Other Issues in India-Sri Lanka Relations?
- Killing of Fisherman:
- Killing of Indian fishermen by the Sri Lankan Navy is a lingering issue between these two nations.
- In 2019 and 2020, a total of 284 Indian fishermen were arrested and a total of 53 Indian boats were confiscated by the Sri Lankan authorities.
- East Coast Terminal project:
- In 2021 Sri Lanka canceled an MoU signed with India and Japan for the East Coast Terminal project.
- Influence of China:
- China’s rapidly growing economic footprint (and political clout as a corollary) in Sri Lanka is straining India-Sri Lanka relations.
- China is already the largest investor in Sri Lanka, accounting for 23.6% of the total Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) during 2010-2019 as against 10.4% from India.
- 13th Amendment of the Sri Lankan Constitution:
- It envisages devolution of necessary powers to the provincial councils to address the just demand of the Tamil people for equality, justice, peace, and respect within a united Sri Lanka.
Way Forward
- It is in Sri Lanka’s best interests to build the capacity of its citizens and work towards their empowerment, for which devolution of power to the grassroots level is a pre-requisite.
- Nurturing the Neighbourhood First policy with Sri Lanka is important for India to preserve its strategic interests in the Indian Ocean region.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2020)
- The value of Indo-Sri Lanka trade has consistently increased in the last decade.
- “Textile and textile articles” constitute an important item of trade between India and Bangladesh.
- In the last five years, Nepal has been the largest trading partner of India in South Asia.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
- As per data from the Department of Commerce, Indo- Sri Lanka bilateral trade value for a decade (2007 to 2016) was 3.0, 3.4, 2.1, 3.8, 5.2, 4.5, 5.3, 7.0, 6.3, 4.8 (in billion USD). It reflects continuous fluctuation in the trend of trade value. There has been an overall increase but the same cannot be said as consistent rise in trade value. Hence statement 1 is not correct.
- Bangladesh has been a major textile trading partner for India, with a share of more than 5% in exports and over 7% in imports. While annual textile exports to Bangladesh averages $2,000 million, imports are worth $400 (Year: 2016-17).
- The major items of exports are fibre and yarn of cotton, man-made staple fibres and man-made filaments while major import items include apparel and clothing, fabric and other made up textile articles. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- According to the data, in 2016-17, Bangladesh is India’s largest trading partner in South Asia, followed by Nepal, Sri Lanka, Pakistan, Bhutan, Afghanistan and Maldives. The level of Indian exports also follows the same order. Hence, statement 3 is not correct.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. In respect of India-Sri Lanka relations, discuss how domestic factors influence foreign policy. (2013)


International Relations
India Qatar GI Products Meet
For Prelims: Geographical Indication, India Qatar Trade, APEDA
For Mains: India Qatar Relations, Geographical Indication, APEDA
Why in News?
Recently, the government of India organized a Virtual Networking Meet for Agri and Food Geographical Indication (GI) products in association with the Embassy of India, Doha and Indian Business and Professionals Council (IBPC) Qatar.
- This Meet provided a platform for interaction between the India exporters and importers of Qatar on the strength of India in export of agri and food products of Indian origin and distinct attributes.
What is a Geographical Indication (GI) Tag?
- About:
- Geographical Indication (GI) is an indication used to identify goods having special characteristics originating from a definite geographical territory.
- The Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999 seeks to provide for the registration and better protection of geographical indications relating to goods in India.
- It is governed and directed by the WTO Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS).
- It was decided and also stated under Articles 1 (2) and 10 of the Paris Convention that the “protection of industrial Property and Geographical Indication are elements of Intellectual Property”.
- It is primarily an agricultural, natural or a manufactured product (handicrafts and industrial goods).
- Validity:
- This tag is valid for a period of 10 years following which it can be renewed.
- Significance:
- Once a product gets this tag, any person or company cannot sell a similar item under that name.
- GI registration of a product provides it legal protection and prevention against unauthorised use by others.
- GI tag helps in promoting the exports of the product.
- It also provides comfort to customers about the authenticity of that product.
- Agri GI Products:
- Presently, there are more than 400 registered Geographical Indications in India of which around 150 are agricultural and food products GI.
- More than 100 registered GI products fall under the category of Agriculture and Processed Food Export Development Authority (APEDA) scheduled products (fresh fruits and vegetables, processed foods, animal products and cereals).
How has India’s Relations with Qatar been?
- Developments during Indian Vice President visit June 2022:
- India-Qatar Start Up bridge:
- The Vice President launched the “India-Qatar Start Up bridge” that aims to link the start-up ecosystems of the two countries.
- India has emerged as the 3rd largest ecosystem for startups globally, with over 70,000 registered Startups.
- India is home to 100 unicorns with a total valuation of over USD 300 billion.
- The Vice President launched the “India-Qatar Start Up bridge” that aims to link the start-up ecosystems of the two countries.
- Environment and Climate Change:
- The Vice President invited Qatar, as India’s trusted partner in its energy security, to be a partner in this journey for sustainability and join the International Solar Alliance (ISA).
- Joint Business Council Between Business Chambers:
- A Joint Business Council between Business Chambers of India and Qatar has been established and that a Joint Task Force on Investments would take its work forward.
- Invest India and Qatar Investment Promotion Agency was appreciated for entering into a partnership of guiding and assisting businesses on both sides to tap new and emerging opportunities.
- Collaborations at Multilateral Forums:
- Greater collaboration between India and Qatar at multilateral forums like the Inter Parliamentary Union (IPU), Asian Parliamentary Assembly, and others was emphasized.
- India-Qatar Start Up bridge:
- Trade:
- India’s Exports to Qatar:
- In 2020, India exported USD 1.34 Billion to Qatar.
- The main products that India exported to Qatar are Rice, Jewellery and Gold.
- During the last 25 years the exports of India to Qatar have increased at an annualized rate of 16.5%, from USD 29.3 Million in 1995 to USD 1.34 Billion in 2020.
- In 2020, India exported USD 1.34 Billion to Qatar.
- India’s Imports from Qatar:
- In 2020, Qatar exported USD 7.25 Billion to India. The main products that Qatar exported to India were Petroleum Gas, Crude Petroleum and Halogenated Hydrocarbons.
- During the last 25 years the exports of Qatar to India have increased at an annualized rate of 19%, from USD 94.4Million in 1995 to USD 7.25 Billion in 2020.
- Qatar accounts for 41% of India’s total natural gas imports.
- India’s Exports to Qatar:
What is the Agriculture and Processed Food Export Development Authority (APEDA)?
- About:
- APEDA was established by the Government of India under the Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority Act passed by the Parliament in December, 1985.
- The Authority replaced the Processed Food Export Promotion Council (PFEPC).
- APEDA, which comes under the Ministry of Commerce & Industry has contributed significantly in promoting export of agriculture and processed food products with a share of around 50% (USD 24.77 bn) in overall agri exports during 2021-22.
- Functions:
- Development of industries relating to the scheduled products for export by way of providing financial assistance.
- Registration of persons as exporters of the scheduled products on payment of such fees as may be prescribed.
- Fixing of standards and specifications for the scheduled products for the purpose of exports.
- Improving packaging of the Scheduled products.
- Improving marketing of the Scheduled products outside India.
- Promotion of export-oriented production and development of the Scheduled products.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Which of the following has/have been accorded ‘Geographical Indication’ status? (2015)
- Banaras Brocades and Sarees
- Rajasthani Daal-Bati-Churma
- Tirupathi Laddu
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Explanation:
- A Geographical Indication (GI) is a sign used on products that have a specific geographical origin and possess qualities or a reputation that are due to that origin.
- India, as a member of the World Trade Organization (WTO), enacted the Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999, which came into force with effect from 15th September 2003.
- Darjeeling tea was the first product in India to get a GI tag.
- Banaras Brocades and Sarees and Tirupathi Laddu have got GI tag while Rajathan’s Daal-Baati-Churma does not. Hence, 1 and 3 are correct.
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Q. India enacted the Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999 in order to comply with the obligations to (2018)
(a) ILO
(b) IMF
(c) UNCTAD
(d) WTO
Ans: (d)
Explanation:
- Geographical indications (GIs) are a type of intellectual property (IP).
- The World Trade Organisation (WTO) recognises intellectual property rights under TRIPS (Trade- Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights) Agreement.
- Under Article 22(1) of the TRIPS Agreement, the GIs are defined as “indications which identify a good as originating in the territory of a Member, or a region or locality in that territory, where a given quality, reputation or other characteristic of the good is essentially attributable to its geographic origin”.
- The GIs act as source identifiers as well as quality indicators. GIs let consumers know that the goods come from an area where a given quality, reputation or other characteristic of the goods is essentially attributable to their geographic origin.
- Further, GIs as intellectual property rights enable relief from the acts of infringement and/or unfair competition.
- Following TRIPS Agreement, the Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999 was passed by the GoI. The Act aims to provide protection by granting GI tags to agricultural goods, natural goods or manufactured goods or any goods of handicraft or goods of industry including food stuff.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.


Economy
Agricultural and Processed Food Exports
For Prelims: Agriculture and Food Industry and Exports, Agriculture Export Policy 2018, B2B Exhibitions, GI Tag, APEDA
For Mains: Promotion of Agricultural and Processed Food Exports
Why in News?
Recently, the Directorate General of Commercial Intelligence and Statistics (DGCI&S) has released the data of India’s Agricultural and processed food products exports for the first quarter of current Fiscal (April-July 2022-23).
- DGCI&S, under the Ministry of Commerce, Government of India, is the pioneer official organization for collection, compilation and dissemination of India’s Trade Statistics and Commercial Information.
What are the Findings?
- India’s Agricultural and processed food products exports rose by 30 % to USD 9.6 billion during in the first four months of the current Financial Year 2022-23 in comparison to the corresponding period of FY 2021-22.
- For 2022-23, an export target of USD 23.56 billion has been fixed for the agricultural and processed food products basket.
- Exports of fruits and vegetables registered a 4 % growth during the period.
- Basmati Rice exports witnessed a growth of 29.13 %.
- Exports of non-Basmati rice rose by 9.24% during the period under review to USD 2.08 billion.
- The export of dairy products recorded a growth of 61.91% to USD 247.
What is the Scenario of Agriculture, Food Industry and Exports?
- About:
- The agriculture sector is the largest source of livelihood in India. India is one of the largest producers of agriculture and food products in the world.
- In 2021-22, India’s agriculture sector growth rate was estimated to be at 3.9% as compared to the 3.6% in the previous year.
- India produces many crops and food grains such as rice, wheat, pulses, oilseeds, coffee, jute, sugarcane, tea, tobacco, groundnuts, dairy products, fruits, etc.
- India’s agriculture sector primarily exports agri & allied products, marine products, plantation, and textile & allied products.
- The agriculture sector is the largest source of livelihood in India. India is one of the largest producers of agriculture and food products in the world.
- Statistics:
- During 2021-22, India recorded USD 49.6 billion in total agriculture exports with a 20% increase from USD 41.3 billion in 2020-21.
- Agri & allied products exports were valued at US$ 37.3 billion, recording a growth of 17% over 2020-21.
- Rice is the largest exported agricultural product from India and contributed to more than 19% of the total agriculture export during the year 2021-22.
- Export Destinations:
- The largest importers of India’s agricultural products are USA, Bangladesh, China, UAE, Indonesia, Vietnam, Saudi Arabia, Iran, Nepal and Malaysia.
- The other importing countries are Korea, Japan, Italy, and the UK.
- During 2021-22, the USA was the largest importer of Indian agricultural products.
- Bangladesh is the major importer of Agri & allied products followed by UAE.
- USA and China are major importers of India’s marine products.
What are the Growth Drivers?
- B2B Exhibitions:
- Various initiatives have been taken for the export promotion of agricultural and processed food products such as organising B2B (Business to Business) exhibitions in different countries, exploring new potential markets through product-specific and general marketing campaigns by the active involvement of Indian Embassies.
- Agriculture Export Policy 2018:
- Key objectives of the AEP are to diversify export basket and destinations, to boost high value-added agricultural exports, to promote indigenous, organic, traditional and non-traditional Agri products exports.
- Financial Assistance Scheme:
- It is an export promotion scheme by (APEDA). The primary aim of this scheme is to assist businesses in export infrastructure development, quality development and market development.
- APEDA:
- In a bid to give a boost to the export of Indian wine, the APEDA (Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority) facilitated participation of 10 wine exporters in the London Wine Fair
- GI and Other Initiatives:
- Several initiatives have also been taken to promote products having registered Geographical Indications (GI) in India by organizing virtual Buyer Seller Meets on agricultural and food products with the United Arab Emirates and on GI products, including handicrafts with the USA.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Among the following, which one is the largest exporter of rice in the world in the last five years? (2019)
(a) China
(b) India
(c) Myanmar
(d) Vietnam
Ans: (b)
- India has been the world’s top rice exporter since the beginning of this decade primarily owing to the lift of ban on export of non-basmati varieties of rice by GoI in 2011.
- India replaced Thailand in 2011-12 to become the largest rice exporter of the world.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.


Agriculture
World Dairy Summit 2022
For Prelims: International Dairy Federation World Dairy Summit (IDF WDS) 2022, Rashtriya Gokul Mission, Goberdhan Yojna, Digitization of dairy sector and universal vaccination of cattle.Animal Husbandry infrastructure development fund,National Programme for Dairy development
For Mains: Significance of Dairy sector in India, Economics of Animal-Rearing
Why in News?
Recently, Prime Minister inaugurated the International Dairy Federation World Dairy Summit (IDF WDS) 2022 at India Expo Centre & Mart, Greater Noida.
- International Dairy Federation is the leading source of scientific and technical expertise for all stakeholders of the dairy chain.
- Since 1903, IDF's network of dairy experts has provided a mechanism for the dairy sector to reach a global consensus on how to help feed the world with safe and sustainable dairy products.
What are the Key Highlights of IDF World Dairy Summit?
- The IDF World Dairy Summit is an annual meeting of the global dairy sector, bringing together approximately 1500 participants from all over the world.
- The last such Summit was held in India about half a century ago in 1974.
- The theme for this year is Dairy for Nutrition and Livelihood.
- The IDF World Dairy Summit will provide a forum to industry experts to share knowledge and ideas on how the sector can contribute to nourish the world with safe and sustainable dairying.
- Participants will get an opportunity to acquire knowledge on latest research findings and experiences relevant to the global dairy sector in the broadest sense.
What is the status of Dairy sector in India?
- About:
- India is ranked first in milk production contributing 23% of global milk production followed by the United States of America, China, Pakistan and Brazil.
- The top 5 milk-producing states are: Uttar Pradesh (14.9%), Rajasthan (14.6%), Madhya Pradesh (8.6%,), Gujarat (7.6%,) and Andhra Pradesh (7.0%).
- Significance:
- The potential of the dairy sector not only gives impetus to the rural economy, but is also a major source of livelihood for crores of people across the world.
- This sector provides employment to more than 8 crore families in the country.
- There are more than a third of the members of dairy cooperatives in India are women.
What are the Challenges of this Sector?
- Shortage of fodder: There is an excessive number of unproductive animals which compete with productive dairy animals in the utilisation of available feeds and fodder.
- The grazing area is being reduced markedly every year due to industrial development resulting in shortage of supply of feeds and fodder to the total requirement.
- Health: Veterinary health care centres are located in far off places and the ratio between cattle population and veterinary institution is wider, resulting in inadequate health services to animals.
- Further, no regular and periodical vaccination schedule is followed, regular deworming programme is not done as per schedule, resulting in heavy mortality in calves, especially in buffalo.
- Hygiene Conditions: Many cattle owners do not provide proper shelter for their cattles leaving them exposed to extreme climatic conditions.
- Informal Nature of Dairy Sector: Unlike sugarcane, wheat, and rice-producing farmers, cattle raisers are unorganised and do not have the political clout to advocate for their rights.
- Lack of Remunerative Pricing: Though the value of milk produced outweighs the combined value of the output of wheat and rice in India, there is no official and periodical estimate of the cost of production and Minimum Support Price for milk.
What are the Initiatives taken by Government?
- Rise in Productivity: The government has taken multiple steps for the betterment of the dairy sector resulting in an increase of milk production by more than 44% in the last eight years.
- Further, as compared to the 2% production growth at the global level, India is clocking the milk production growth rate at more than 6%.
- Schemes:
- Rashtriya Gokul Mission
- Nationwide Artificial Insemination Programme
- Rashtriya Gokul Mission
- Goberdhan Yojna
- Digitization of dairy sector and universal vaccination of cattle.
- Animal Husbandry infrastructure development fund: It aims to help to increase meat processing capacity and product diversification thereby providing greater access for unorganized Dairy producers to organized the Dairy market.
- National Programme for Dairy development
- Upcoming Initiatives:
- Dairy Ecosystem: The government is working on developing a blanched dairy ecosystem where challenges of the sectors would be addressed along with a focus on increasing production.
- Further, extra income for the farmers, empowerment of the poor, swachhta, chemical-free farming, clean energy and care of the cattle is interlinked in this ecosystem.
- Pashu Aadhar: Government is building the largest database of dairy animals and every animal associated with the dairy sector is being tagged.
- By 2025, India will vaccinate 100% of animals against foot, mouth disease and brucellosis.
- Dairy Ecosystem: The government is working on developing a blanched dairy ecosystem where challenges of the sectors would be addressed along with a focus on increasing production.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Under the Kisan Credit Card scheme, short-term credit support is given to farmers for which of the following purposes? (2020)
- Working capital for maintenance of farm assets
- Purchase of combine harvesters, tractors and mini trucks
- Consumption requirements of farm households
- Post-harvest expenses
- Construction of family house and setting up of village cold storage facility
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 3, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- The Kisan Credit Card (KCC) scheme was introduced in 1998 for providing adequate and timely credit support from the banking system under a single window with flexible and simplified procedure to the farmers for their cultivation and other needs like purchase of agriculture inputs such as seeds, fertilizers, pesticides etc. and draw cash for their production needs.
- The scheme was further extended in the year 2004 for the investment credit requirement of farmers viz allied and non-farm activities.
- Kisan Credit Card is provided with the following objectives:
- The short term credit requirements for cultivation of crops,
- Post harvest expenses, hence 4 is correct.
- Produce marketing loan,
- Consumption requirements of farmer household, hence 3 is correct.
- Working capital for maintenance of farm assets and activities allied to agriculture, like dairy animals, inland fishery, etc., hence, 1 is correct.
- Investment credit requirement for agriculture and allied activities like pumpsets, sprayers, dairy animals, etc. However, this segment forms the long term credit limit portion.
- The Kisan Credit Card Scheme is implemented by Commercial Banks, RRBs, Small Finance Banks and Cooperatives.
- The short term credit support is not given to farmers for Purchase of combine harvesters, tractors and mini trucks and Construction of family house and setting up of village cold storage facility. Hence, 2 and 4 is not correct. Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.


Important Facts For Prelims
Project 17A and INS Taragiri
Why in News?
Recently, Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Ltd (MDL), which is under the Ministry of Defence, launched Taragiri, the third stealth frigate of Project 17A.
What is Project 17A?
- About:
- Project 17 Alpha frigates (P-17A) were launched by the Indian Navy in 2019 to construct a series of stealth guided-missile frigates.
- These are currently being constructed by two companies - Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders (MDL) and Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers (GRSE).
- These guided-missile frigates have been constructed with a specific stealth design, which has radar-absorbent coatings and is low-observable which can make its approach undetectable for the enemies.
- The new technology also reduces the infrared signals of the ship.
- The first stealth ship launched under Project 17A was the Nilgiri, which was launched in 2019.
- Udaygiri, the second ship, was launched in May 2022, and will likely be commissioned in 2024.
- Present Status: Further, seven P17A Frigates are under various stages of construction at MDL and GRSE.
- Benefits:
- It provides additional benefits such as economic development, and employment generation for Indian Shipyards, their sub-contractors and the ancillary industry.
- Around 75% of the orders of Project 17A have been placed on indigenous firms including MSMEs, thus reinforcing the country’s quest for Atma Nirbhar Bharat.
- Indigenous construction of complex frontline ships such as Stealth Frigates has catapulted the nation to a higher pedestal in the arena of shipbuilding.
What are the Key Highlights of Taragiri?
- Taragiri is named after a hill range in the Himalayas located at Garhwal.
- The ship has been built using an integrated construction methodology which involves hull block construction in different geographical locations.
- The ship will have state-of-the-art weapons, sensors, an advanced action information system, an integrated platform management system, world-class modular living spaces, a sophisticated power distribution system and a host of other advanced features.
- It will be fitted with a supersonic surface-to-surface missile system.
- The ship’s air defence capability, designed to counter the threat of enemy aircraft and anti-ship cruise missiles will revolve around the vertical launch and long-range surface-to-air missile system.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which one of the following is the best description of ‘INS Astradharini’, that was in the news recently? (2016)
(a) Amphibious warfare ship
(b) Nuclear-powered submarine
(c) Torpedo launch and recovery vessel
(d) Nuclear-powered aircraft carrier
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- INS Astradharini is an indigenously built Torpedo Launch and Recovery Vessel. It was commissioned on 6th October 2015.
- The design of the Astradharini was a collaborative effort of Naval Science and Technological Laboratory (NSTL), Shoft Shipyard and IIT Kharagpur.
- It is an advanced replacement for Astravahini which was decommissioned on 17th July 2015.
- It has a unique design of a catamaran hull form that significantly reduces its power requirement and is built with indigenous steel.
- It can operate at high sea states and has a large deck area with Torpedo Launchers for deploying and recovering various kinds of Torpedos during the trials.
- The ship also has modern power generation and distribution, navigation and communication systems.
- 95% of the systems of the ship are of indigenous design, thus demonstrating the Navy’s continued adherence to the ‘Make in India’ philosophy.
- INS Astradharini will be used to carry out the technical trials of underwater weapons and systems developed by NSTL, a naval systems laboratory of DRDO. Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.