India’s Earthquake Preparedness
For Prelims: Turkey Syria Earthquake, Richter Scale, Himalayan Plate, Tectonic Plates.
For Mains: Causes of Earthquake, Earthquakes In/Around India, Steps for Earthquake Preparedness in India.
Why in News?
A severe earthquake followed by an almost equal magnitude aftershock hit southeastern Turkey and Syria on February 6, 2023, causing widespread destruction and loss of life.
- The Turkey-Syria earthquake should motivate a review of India’s earthquake preparedness, as poor enforcement of zoning and construction rules is prevalent in the country.
What Makes India Susceptible to Earthquakes?
- About:
- India’s terrain is prone to great earthquakes, particularly in the Himalayan plate boundary, which has the potential for large quakes (magnitude 7 and above).
- In India, earthquakes are primarily caused by the collision of the Indian Plate with the Eurasian Plate.
- This collision has resulted in the formation of the Himalayas, as well as frequent earthquakes in the region.
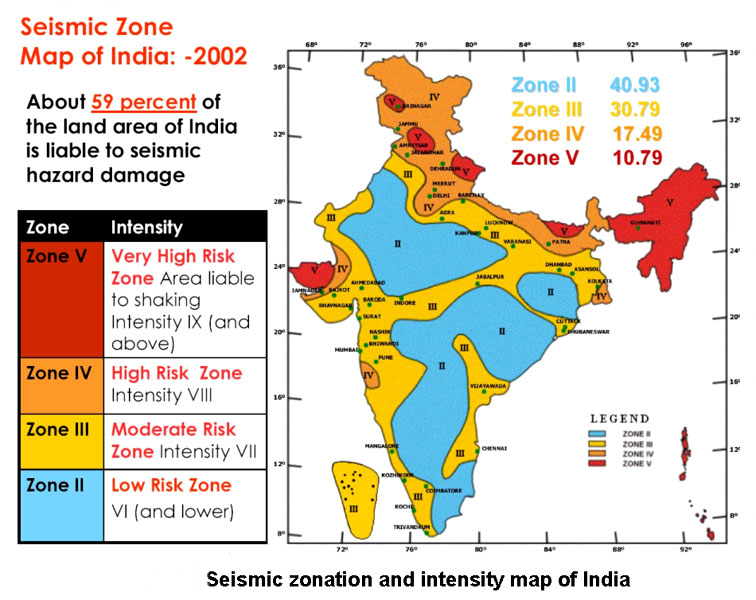
- Seismic Zones:
- Susceptibility of Major Earthquakes:
- Scientists are aware of identifiable seismic gaps along the Himalayan axis where the historical release of geological tension doesn’t fully account for the strain that has built up.
- For instance, the Central Himalaya has been historically deficient in earthquakes compared to other areas. So, it’s one region that can reasonably be expected to generate a large earthquake in the future.
- Scientists are aware of identifiable seismic gaps along the Himalayan axis where the historical release of geological tension doesn’t fully account for the strain that has built up.
Note: Seismic Gap is the part of an active fault that has experienced little or no seismic activity for a long period, indicating the buildup of stresses that are useful in predicting earthquakes.
- Earthquakes In/Around India:
- India has experienced several significant earthquakes over the years, here are some examples:
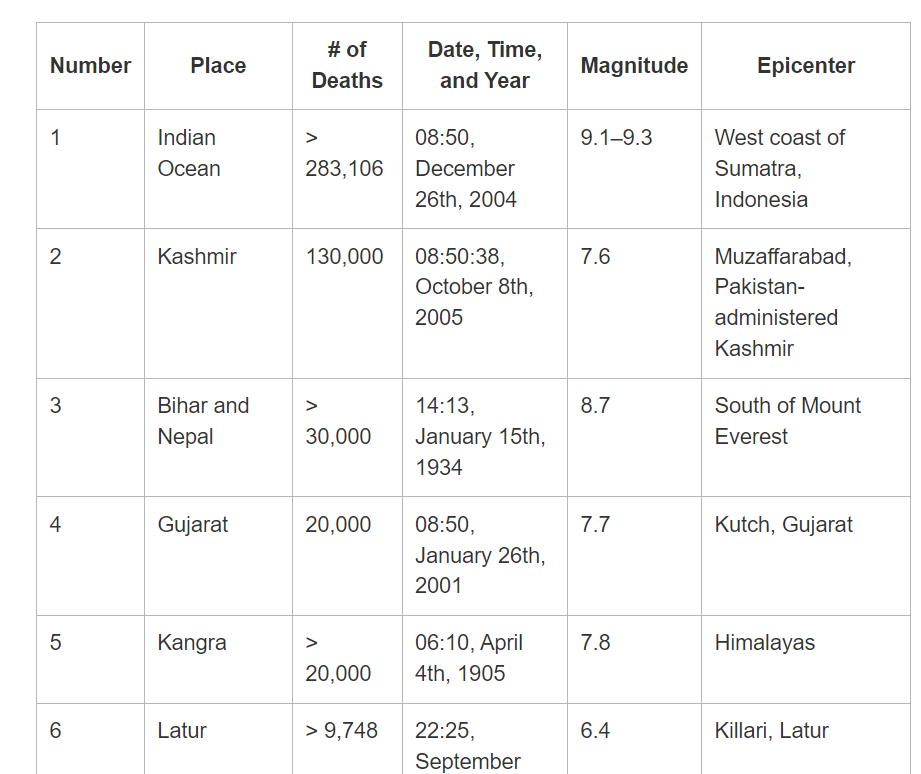
- Nepal Earthquake 2015: On April 25, 2015, a magnitude 7.8 earthquake struck Nepal. The earthquake also had a significant impact in northern India.
- Imphal Earthquake 2016: On January 4, 2016, a magnitude 6.7 earthquake struck the northeastern Indian state of Manipur, causing widespread damage.
- Uttarakhand Earthquake 2017: On February 6, 2017, a magnitude 6.7 earthquake struck the northern Indian state of Uttarakhand.
- India has experienced several significant earthquakes over the years, here are some examples:
What Steps can be Taken for Earthquake Preparedness in India?
- Building Codes and Standards: India has established building codes and standards for earthquake-resistant construction.
- It is important to strictly enforce these codes and standards to ensure that new buildings are built to withstand earthquakes. This will also require regular inspections and enforcement of existing building codes.
- Retrofitting and Reinforcement: Older buildings may not meet current earthquake-resistant standards, and many of them can be retrofitted or reinforced to improve their seismic performance.
- Emergency Response Planning: Planning for emergency response is critical for minimising the impact of earthquakes. This includes developing evacuation plans, establishing emergency shelters, and training personnel on how to respond to earthquakes.
- Research and Monitoring: Investing in research and monitoring can help improve our understanding of earthquakes and their causes, and can also help to develop better methods for predicting and mitigating their impact.
- Land-Use Planning: It is important to consider the potential impacts of earthquakes when planning and developing land-use policies. This includes limiting development in areas that are prone to earthquakes and ensuring that new development is designed and constructed in a way that minimises the risk of damage.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. The frequency of earthquakes appears to have increased in the Indian subcontinent. However, India’s preparedness for mitigating their impact has significant gaps. Discuss various aspects. (2015)
Q. Discuss about the vulnerability of India to earthquake related hazards. Give examples including the salient features of major disasters caused by earthquakes in different parts of India during the last three decades. (2021)
3rd ASEAN Digital Ministers Meeting
For Prelims: Artificial Intelligence, India-ASEAN Digital Work Plan 2023, ASEAN Declaration, Look East Policy, ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA), Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement, ASEAN India Friendship Year, ASEAN-India Green Fund.
For Mains: India-ASEAN Relations, Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement.
Why in News?
The 3rd ASEAN Digital Ministers (ADGMIN) meeting was held recently .
- The theme of the meeting was "Synergy Towards a Sustainable Digital Future”.
What are the Major Highlights of the Meeting?
- The meeting focused on enhancing the relationship between India and ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations) in the area of Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs) .
- India emphasised its reforms to promote fair competition, and increase broadband and telecom connectivity.
- The significance of digital transformation was also highlighted as a means of creating an inclusive and equitable society, promoting sustainable development, and empowering citizens through digital means.
- India-ASEAN Digital Work Plan 2023 was approved, which includes initiatives for capacity building and knowledge sharing in areas such as Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity, IoT and AI in Next Generation Smart Cities, and the role of ICTs in implementing digital health and security.
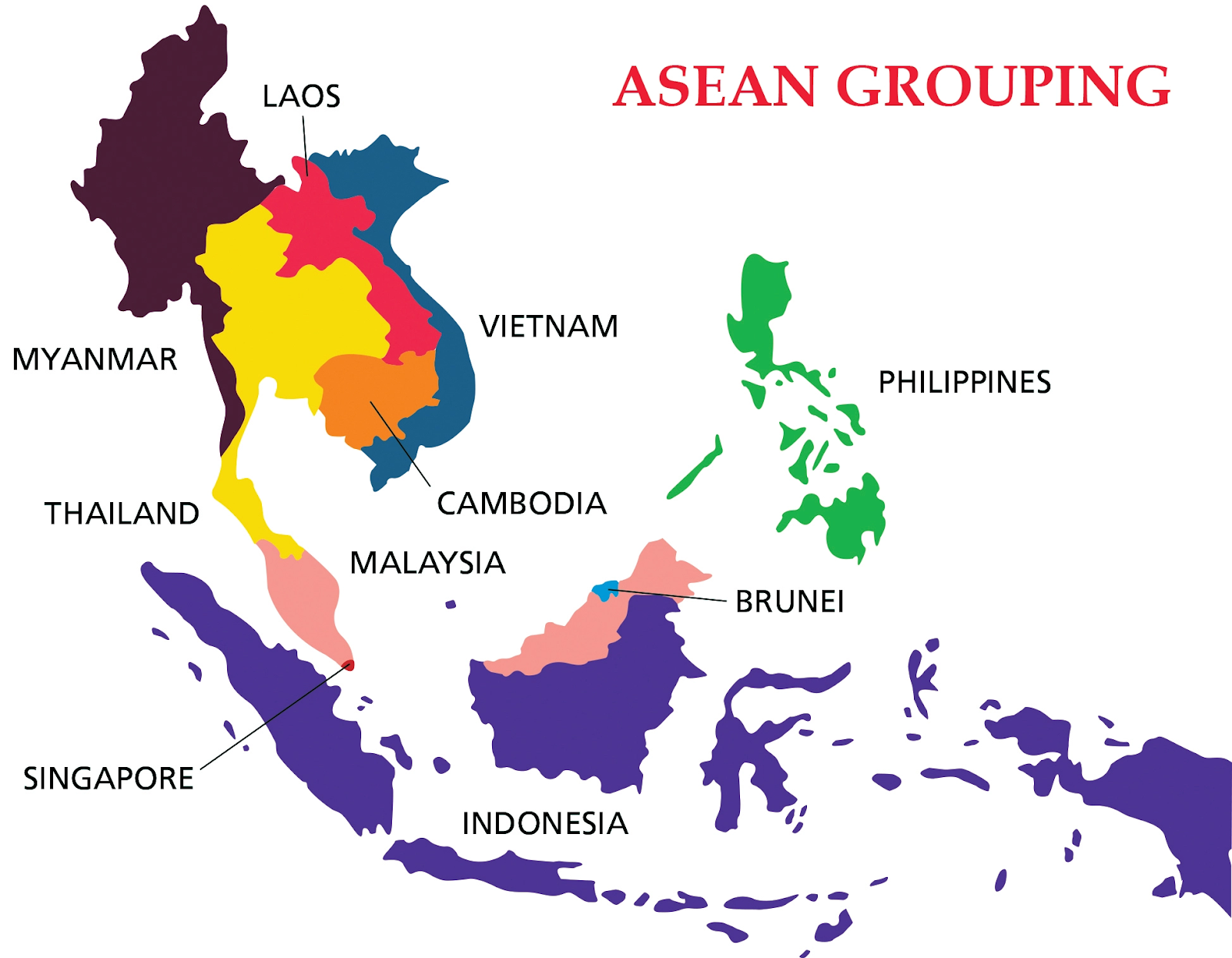
What is ASEAN Grouping?
- About:
- It is a regional grouping that promotes economic, political, and security cooperation.
- It was established in August 1967 in Bangkok, Thailand with the signing of the ASEAN Declaration (Bangkok Declaration) by the founding fathers of ASEAN, namely Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore and Thailand.
- Its chairmanship rotates annually, based on the alphabetical order of the English names of Member States.
- Members:
How is India’s Relations with ASEAN?
- About:
- India and ASEAN have a long-standing and multi-faceted relationship that encompasses political, economic, cultural, and security dimensions.
- Evolution of Bilateral Relations:
- India-ASEAN bilateral relationship started evolving since India introduced 'Look East Policy' in 1990s.
- This initiative was further transformed to ‘Act East Policy’ in 2014 mainly to develop economic and strategic relations with the nations of Southeast Asian countries.
- In 1992, India emerged as a Sectoral Partner of ASEAN followed by Dialogue Partner in 1996 and a Summit-level Partner in 2002.
- In 2009, The ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) was signed and entered into force on 1 January 2010.
- Also, India has a Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA) with various countries of the ASEAN region (Singapore, Malaysia and Thailand) which has resulted in concessional trade and a rise in investments.
- In 2015, India also set up a separate Mission to ASEAN and the East Asia Summit in Jakarta in 2015 to strengthen engagement with ASEAN countries.
- In 2022, the ASEAN India Friendship Year was observed to commemorate the 30-year milestone of the establishment of dialogue relations between ASEAN and India, leading to the elevation of their Strategic Partnership to a Comprehensive Strategic Partnership (CSP).
- India-ASEAN bilateral relationship started evolving since India introduced 'Look East Policy' in 1990s.
- Other Areas of Engagement:
- Financial Assistance:
- India offers financial support to ASEAN countries through various channels such as the ASEAN-India Cooperation Fund, the ASEAN-India Science and Technology Development Fund, and the ASEAN-India Green Fund.
- Connectivity:
- India has been implementing several connectivity initiatives, such as the India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway and the Kaladan Multimodal Project.
- Additionally, India is working towards establishing a Maritime Transportation Agreement with ASEAN and has plans for a railway connection between New Delhi, India and Hanoi, Vietnam.
- Financial Assistance:
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. Consider the following countries: (2018)
- Australia
- Canada
- China
- India
- Japan
- USA
Which of the above are among the ‘free-trade partners’ of ASEAN?
(a) 1, 2, 4 and 5
(b) 3, 4, 5 and 6
(c) 1, 3, 4 and 5
(d) 2, 3, 4 and 6
Ans: (c)
Q2. The term ‘Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership’ often appears in the news in the context of the affairs of a group of countries known as (2016)
(a) G20
(b) ASEAN
(c) SCO
(d) SAARC
Ans: (b)
Q3. In the Mekong-Ganga Cooperation, an initiative of six countries, which of the following is/are not a participant/ participants? (2015)
- Bangladesh
- Cambodia
- China
- Myanmar
- Thailand
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1, 2 and 5
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. Evaluate the economic and strategic dimensions of India’s Look East Policy in the context of the post-Cold War international scenario. (2016)
India-Mongolia Relations
Prelims: India-Mongolia Relations, Covid-19 Pandemic, Buddhism, Act East Policy.
Mains: India-Mongolia Relations.
Why in News?
Recently, the 11th meeting of the India-Mongolia Joint Working Group was held in India.
- While acknowledging the growing ties between both the countries, they expressed satisfaction at the ongoing defense cooperation despite the limitations imposed by Covid-19 pandemic.
How have been the India-Mongolia Relations?
- Historical Relations:
- India and Mongolia have interacted through Buddhism throughout history.
- Mongolia regards India as its “third” neighbor along with US, Japan, and Germany and a “spiritual neighbour”.
- Diplomatic Relations:
- India established diplomatic relations with Mongolia in 1955 and it was the first country outside the Soviet bloc to open diplomatic relations with Mongolia.
- The Indian Resident Mission in Ulaanbaatar was opened in 1971.
- This relationship was upgraded to “strategic partnership” in 2015 when the Indian Prime Minister visited Mongolia and declared it as an essential component of ‘Act East Policy’.
- International Cooperation:
- Mongolia has publicly reiterated its support for India’s membership to the permanent seat of the expanded United Nations Security Council (UNSC).
- India has played an important role in getting Mongolia membership to key international forums, including the United Nations (UN), despite strong opposition from China and Taiwan.
- India also championed the inclusion of Mongolia in the Non-Aligned Movement.
- In a reciprocal gesture, Mongolia co-sponsored a 1972 UN resolution with India and Bhutan for the recognition of the newly liberated Bangladesh.
- Economic Cooperation:
- In 2022, an India-built oil refinery at the cost of more than USD 1 billion and with a capacity of 1.5 million metric tonnes was opened near Sainshand in southern Dornogovi province of Mongolia.
- This refinery will take care of 75 % of Mongolia’s oil refining needs.
- India - Mongolia bilateral trade was USD 35.3 million in 2020, down from USD 38.3 million in 2019.
- In 2022, an India-built oil refinery at the cost of more than USD 1 billion and with a capacity of 1.5 million metric tonnes was opened near Sainshand in southern Dornogovi province of Mongolia.
- Cultural Cooperation:
- The India-Mongolian Agreement on Cultural Cooperation, signed in 1961, has governed the Cultural Exchange Programme (CEP) between the two countries.
- The Agreement envisages co-operation in the fields of education by way of scholarships, exchange of experts, participation in conferences, etc.
- Defence Cooperation:
- Joint defence exercises code-named Nomadic Elephant.
- India is also an active participant in an annual week-long joint training exercise called the Khaan Quest, hosted by Mongolia.
- Cooperation over Environmental Issues:
- Part of the Bishkek Declaration (snow leopard).
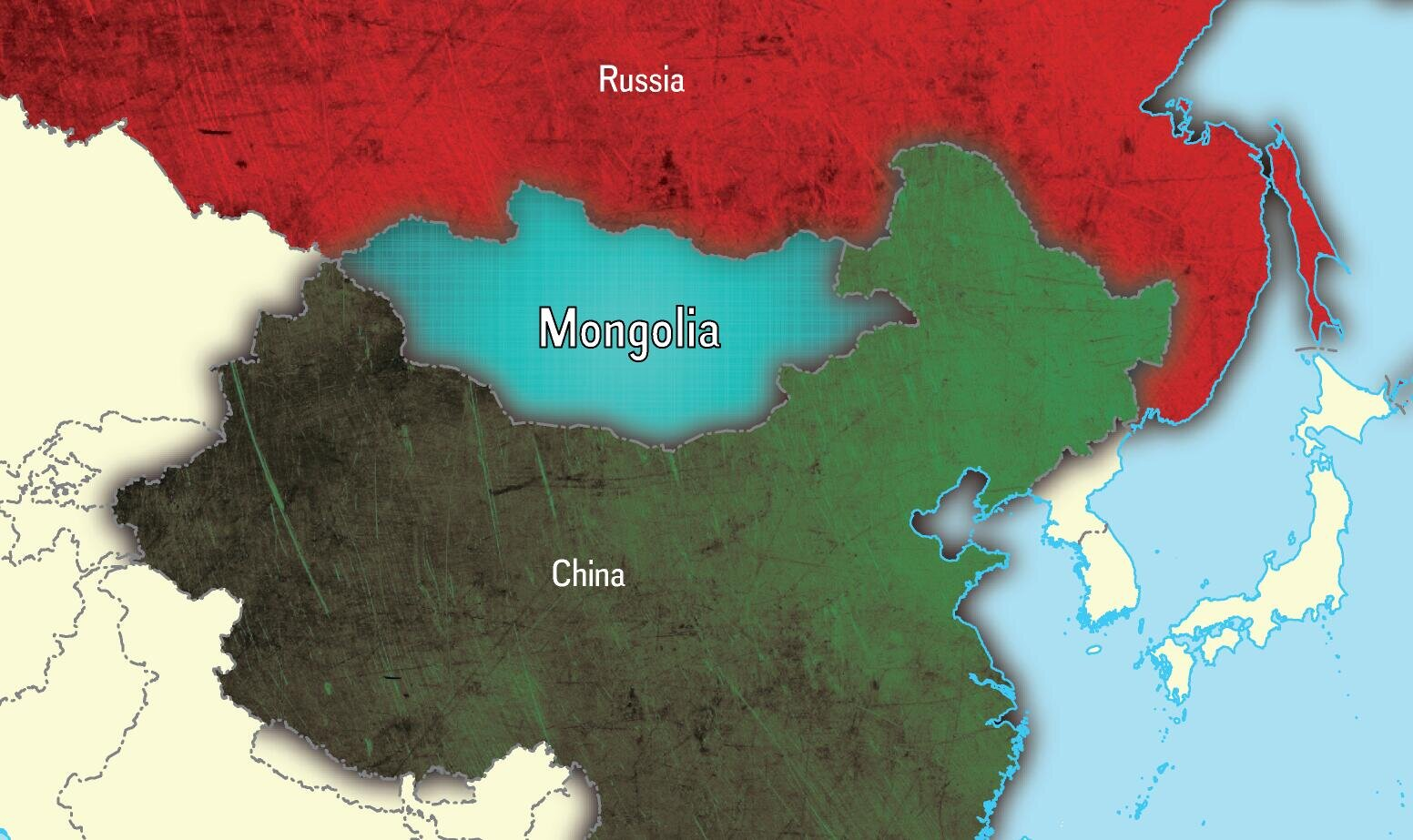
What are the Key Facts Related to Mongolia?
- Mongolia is a landlocked country located in East and Central Asia. It is bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south, east and west.
- It is the world's second-largest landlocked country and the most sparsely populated country in the world.
- The majority of the population still practices traditional nomadic herding, and Mongolia is home to a variety of ethnic groups, including Mongols, Kazakhs, and Tuvans.
- The country is known as the "Land of the Eternal Blue Sky" and as the "Land of the Horse".
- Mongolia's landscape is dominated by the Gobi Desert in the south and the towering Altai Mountains in the west.
- Despite its rapid modernization in recent years, Ulaanbaatar still retains a strong traditional Mongolian identity, with many historical temples, monasteries, and other cultural landmarks to explore.
- The country was once the center of the Mongol Empire, which was the largest contiguous empire in history, spanning from Europe to Asia.
Way Forward
- The way forward for India-Mongolia relations is to build on the existing foundation of historical and cultural ties, while also seeking to expand political, economic, and cultural cooperation.
- Mongolia’s strategic position at the cross junction of Central Asia, Northeast Asia, far East, China and Russia attract major powers towards it. India should consider Mongolia as a green zone of economic development that absorbs hi-tech features and production skills in a modernization process.
- With both countries facing common challenges in the region, there is tremendous potential for further strengthening the relationship in the coming years.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. “Climate is extreme, rainfall is scanty and the people used to be nomadic herders.” (2013)
The above statement best describes which of the following regions?
(a) African Savannah
(b) Central Asian Steppe
(c) North American Prairie
(d) Siberian Tundra
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- African Savannah: It is a tropical grassland and covers half the surface of Africa. Weather is typically warm with temperatures ranging from 20º to 30ºC. Rainfall in the savannas is moderate, up to 75 cm per year. The people living in this biome are mainly farmers who grow cereals and other plants that can resist long dry spells, such as millet, sorghum, barley and wheat, as well as peanuts, cotton, rice and sugarcane, while breeding prevails in drier Savannah areas.
- Temperate Grassland: Temperature varies much more in temperate grasslands than in the Savannas. Temperate grasslands have hot summers where temperatures can exceed 38ºC and cold winters that can drop below –40ºC.
- Central Asian Steppe: Grasslands (steppes) have temperate environments, with warm to hot summers and cool to very cold winters. Temperatures are often extreme in these mid continental areas. These are often located between deserts and temperate forests, and annual precipitation falls between the amounts characteristic of these zones. The grassland steppes of Eurasia spread from eastern China across Mongolia and Russia to Europe. People of this region used to be nomadic herders.
- North American Prairie: Prairies are the temperate grasslands of North America. The word ‘Prairie’ originated from the Latin word ‘Priata’ which means meadow. They are located in the heart of a continent. The climate is of the continental type with extreme temperatures. The summers are warm with temperatures of around 20ºC and winters are very cold with temperatures of around –20ºC. The people of this region are very industrious. They are successfully harnessing the technology to utilize its natural resources.
- Siberian Tundra: These are found in regions north of the Arctic Circle and south of the Antarctic Circle. The lowlands – coastal strip of Greenland, the barren grounds of northern Canada and Alaska and the Arctic seaboard of Eurasia, have tundra climate. The climate is characterized by a very low mean annual temperature. In mid-winter, temperatures are as low as 40-50°C below freezing point. Summers are relatively warmer. Normally not more than four months have temperatures above freezing-point. Precipitation is mainly in the form of snow and sleet. Convectional rainfall is generally absent. People live a semi-nomadic life. Human activities of the tundra are largely confined to the coast.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
India's Health Infrastructure
Prelims: PM-ABHIM, ADB, World Bank, National Health Mission, NITI Aayog.
Mains: India' Health Infrastructure.
Why in News?
Recently, the Indian government has signed loan agreements to borrow up to Rs 13,879 crore to strengthen health infrastructure from international agencies.
- The loan agreements have been signed to augment PM-ABHIM (Prime Minister-Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission) which was launched in October 2021 (till FY 2025-26).
What are the Key Points of the Agreement?
- Loan agreements have been signed with Asian Development Bank (ADB) for USD 300 million and with Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) for 50 billion Japanese Yen.
- The World Bank has approved USD 1 billion IBRD (International Bank for Reconstruction and Development) for PM-ABHIM.
- IBRD is the lending arm of the World Bank.
What is PM-ABHIM?
- About:
- It is one of the largest pan-India schemes for strengthening healthcare infrastructure across the country.
- It is in addition to the National Health Mission (NHM).
- It aims to provide support to 17,788 rural Health and Wellness Centres in 10 ‘high focus’ states and establish 11,024 urban Health and Wellness Centres across the country.
- Objectives:
- To ensure a robust public health infrastructure in both urban and rural areas.
- Establishing an IT-enabled disease surveillance system.
- All the public health labs will be connected through the Integrated Health Information Portal, which will be expanded to all states and UTs.
- Major Initiatives:
- It will help establish 602 critical care hospital blocks, critical care hospital blocks in 12 central hospitals to strengthen National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC), five new regional NCDCs, 10 Biosafety Levels (BSL) - III and one BSL-IV and 20 Metropolitan Surveillance Units (MSUs).
What is the Need for Improving Healthcare Infrastructure in India?
- Many primary healthcare centres (PHCs) lack basic infrastructural facilities like beds, rooms, toilets, and drinking water facilities, clean labour rooms to deliver babies, and electricity regularly.
- According to the Rural Health Statistics from MoHFW 2021, there are a total of 5439 PHCs in the urban areas and of 3966 PHCs in the tribal area.
- The NITI Aayog report 2021 titled ‘Reimagining Healthcare in India through Blended Finance’ highlighted that 50% of India’s population has access to 35% of hospital beds, thus indicating a strong need to strengthen healthcare infrastructure to ensure access to healthcare facilities for all.
What are the Recent Government Initiatives Related to Healthcare?
Way Forward
- In order to address the challenges related to healthcare, there is a need for better healthcare infrastructure in India, including increased investment in the construction of new healthcare facilities, the improvement of existing facilities, and the training and recruitment of more medical professionals.
- This will help to improve access to quality medical care and reduce the financial burden on patients.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following are the objectives of ‘National Nutrition Mission’? (2017)
- To create awareness relating to malnutrition among pregnant women and lactating mothers.
- To reduce the incidence of anaemia among young children, adolescent girls and women.
- To promote the consumption of millets, coarse cereals and unpolished rice.
- To promote the consumption of poultry eggs.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 4 only
(d) 3 and 4 only
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- National Nutrition Mission (POSHAN Abhiyaan) is a flagship programme of the Ministry of Women and Child Development, GoI, which ensures convergence with various programmes like Anganwadi services, National Health Mission, Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana, Swachh-Bharat Mission, etc.
- The goals of National Nutrition Mission (NNM) are to achieve improvement in nutritional status of children from 0-6 years, adolescent girls, pregnant women and lactating mothers in a time bound manner during the next three years beginning 2017- 18. Hence, 1 is correct.
- NNM targets to reduce stunting, under-nutrition, anaemia (among young children, women and adolescent girls) and reduce low birth weight of babies. Hence, 2 is correct.
- There is no such provision relating to consumption of millets, unpolished rice, coarse cereals and eggs under NNM. Hence, 3 and 4 are not correct.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. “Besides being a moral imperative of a Welfare State, primary health structure is a necessary precondition for sustainable development.” Analyse. (2021)
Ramping Up Border Infrastructure
Prelims: Border Infrastructure & Management, Border Area Development Programme
Mains: Significance of Border Infrastructure & Management in Securing Borders.
Why in News?
Recently, the Minister of External Affairs provided a briefing to the parliament regarding the government's projects on border infrastructure and connectivity.
- The report was released in the wake of an official Security Conference report that said Indian forces have lost access to 26 of 65 patrolling points along the LAC since 2020.
What are the Border Infrastructure Developments?
- Multi-Pronged Approach:
- Improving connectivity to the Line of Actual Control (LAC) through roads, bridges and tunnels.
- For instance, the length of roads constructed in the China border areas in the period from 2014 to 2022 (6,806 km) is almost double the length constructed from 2008-2014 (3,610 km).
- Improving cross-border connectivity to neighbouring countries via highways, bridges, inland waterways, railroads, electricity lines and fuel pipelines.
- Modernising and constructing Integrated Check Posts (ICPs) at all the border crossings to smooth trade, and funding and constructing infrastructure projects in neighbouring countries.
- Improving connectivity to the Line of Actual Control (LAC) through roads, bridges and tunnels.
- Neighbourhood Pojects:
- Nepal:
- South Asia’s first cross-border petroleum products pipeline Motihari - Amlekhgunj Pipeline .
- The Mahakali motorable bridge over the Mahakali River connecting Dharchula (India) with Darchula (Nepal), under Indian grant assistance.
- Bangladesh:
- Maitri Setu, High Speed Diesel pipeline with Bangladesh that will reduce petrol prices and road congestion.
- Myanmar:
- Bhutan:
- Dry port in Pasakha bordering West Bengal is being developed under an Indian government grant.
- Nepal:
What is the Importance of Border Infrastructure?
- India faces long-standing territorial and boundary disputes with China and Pakistan and porous borders along difficult terrain.
- For instance, successive skirmishes with the Chinese People’s Liberation Army in Chumar in 2014, Doklam in 2017.
- The ongoing standoff along the entire LAC since April 2020 when the Chinese army amassed troops along the border, which resulted in the Galwan clashes.
- Despite border wars and conflicts, the state of infrastructure at India's borders is inadequate and borders are manned by different military, para-military, and police forces, lacking in coordination.
- Smugglers, drug traffickers, and terrorists often take advantage of poor surveillance and infrastructure at borders.
What are the Other Initiatives to Secure Borders?
- Vibrant Villages Programme:
- Border villages with sparse population, limited connectivity and infrastructure will be covered under the new Vibrant Villages Programme, announced in the Budget 2022-23.
- The activities will include construction of village infrastructure, housing, tourist centers, road connectivity, provisioning of decentralized renewable energy, direct to home access for Doordarshan and educational channels, and support for livelihood generation.
- The move has been taken to counter the Chinese 'model villages' close to the LAC.
- The Border Area Development Programme (BADP):
- BADP was initiated in the border areas of the western region during the Seventh Five Year Plan (1985-90), for ensuring balanced development of border areas through development of infrastructure and promotion of a sense of security among the border population.
- The programme aims to meet the special development needs of the people living in remote and inaccessible areas situated near the international border.
- Smart Fencing in India (CIBMS):
- Two pilot projects covering about 71 Kms on Indo-Pakistan Border (10 Kms) and Indo-Bangladesh Border (61 Kms) of Comprehensive Integrated Border Management System (CIBMS) have been completed.
- CIBMS involves the deployment of advanced surveillance technologies such as thermal imagers, infra-red and laser alarms, aerostats, ground sensors, radars, sonar systems, fiber-optic sensors and a real-time command-and-control system to secure borders.
- BOLD-QIT (Border Electronically Dominated QRT Interception Technique) under CIBMS on the Indo- Bangladesh border in Dhubri district of Assam is also being used.
- Two pilot projects covering about 71 Kms on Indo-Pakistan Border (10 Kms) and Indo-Bangladesh Border (61 Kms) of Comprehensive Integrated Border Management System (CIBMS) have been completed.
- Border Road Organization:
- Founded in 1960, the organisation plays a major role in providing defence infrastructure including roads, bridges, highways, airports, tunnels, buildings and other such structures.
A Gist of Border Infrastructure Development |
|||
| Main Threat | What needs to be done? | What has been done? | |
| Pakistan | War, insurgency, smuggling. | C.I.B.M.S. monitoring with a well-trained and larger BOLD-QIT, more than one route connecting far flung areas, especially Jammu and Kashmir | C.I.B.M.S. in some stretches, 3rd route to Leh to be opened by 2023. |
| China | War | Armored vehicle capable infrastructure, high altitude airfields. | Daulet Beg Oldie airfield running, some bridges and tunnels armored vehicle capable. |
| Bangladesh | Smuggling, human trafficking | C.I.B.M.S. monitoring with BOLD-QIT throughout including riverine stretches | Brahmaputra river covered, rivulets still remaining. |
| Nepal | Smuggling, human trafficking | C.I.B.M.S. monitoring with BOLD-QIT | Planning stage. |
| Bhutan | Smuggling | Armored vehicle capable road connectivity till Bhutan-China border. | B.R.O. working on it. |
| Myanmar | Smuggling, insurgency, trafficking. | C.I.B.M.S. monitoring with bigger and more efficient BOLD-QIT to tackle insurgency, roads for swift troop movements | Some roads present. C.I.B.M.S. planning stage. |
Way Forward
- Continued investment in physical infrastructure such as roads, bridges, and other border infrastructure in regions along the border with China.
- Investment in telecommunications and transportation networks to improve connectivity with neighbouring countries.
- Enhancing the ability of border security forces to effectively patrol and monitor the border region through technology upgradation.
- Collaboration with neighbouring countries to develop mutually beneficial infrastructure projects and increasing economic and cultural exchange with neighbouring countries to strengthen relationships and build trust.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Department of Border Management is a Department of which one of the following Union Ministries? (2008)
(a) Ministry of Defence
(b) Ministry of Home Affairs
(c) Ministry of Shipping, Road Transport and Highways
(d) Ministry of Environment and Forests
Ans: (b)
- In January, 2004, the Department of Border Management was created under the Ministry of Home Affairs to pay focused attention to the issues relating to the management of international land and coastal borders.
- It is entrusted with strengthening of border policing and guarding, creation of infrastructure like roads, fencing and flood lighting on the borders and implementation of the Border Area Development Programme over Border Out Posts (BOPs) and Company Operating Bases (COBs) along the IndoPakistan, Indo-Bangladesh, Indo-China, Indo-Nepal and Indo-Bhutan borders.
- India has 15,106.7 km of land border and a coastline of 7,516.6 km including island territories. Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q1: Analyse the multidimensional challenges posed by external state and non-state actors, to the internal security of India. Also discuss measures required to be taken to combat these threats. (2021)
Q2: For effective border area management, discuss the steps required to be taken to deny local support to militants and also suggest ways to manage favourable perception among locals. (2020)
Q3: Analyse internal security threats and transborder crimes along Myanmar, Bangladesh and Pakistan borders including Line of Control (LoC). Also discuss the role played by various security forces in this regard. (2020)
Q4: Border management is a complex task due to difficult terrain and hostile relations with some countries. Elucidate the challenges and strategies for effective border management.(2016)
Sarojini Naidu- The Nightingale of India
Why in News?
13th February marks the birth anniversary of Sarojini Naidu. She was famously known as Bharatiya Kokila (The Nightingale of India).
- India celebrates Sarojini Naidu's birth anniversary as National Women's Day.
Who was Sarojini Naidu?
- About:
- Sarojini Naidu, was an Indian independence activist, poet, and politician.
- She was born on February 13, 1879, in Hyderabad, India.
- She joined the Indian national movement in the wake of partition of Bengal in 1905.
- The British government lauded Sarojini Naidu with the ‘Kaisar-i-Hind’ Medal for her service during the plague epidemic in India.
- Sarojini Naidu, was an Indian independence activist, poet, and politician.
- Contribution to Indian Freedom Movement:
- First Indian Woman President of INC: Naidu was elected as the first Indian woman president of the Indian National Congress(INC) in 1925(Kanpur Session) and continued to hold this position till 1928.
- Annie Besant was the first woman President of the INC who presided it in 1917.
- Participated in Non-Cooperation Movement: Naidu took part in the Non-Cooperation Movement launched by Gandhi in 1920 and was arrested several times for her involvement in various freedom activities.
- Lead Salt Satyagraha: In 1930, Naidu was selected by Gandhi to lead the Salt Satyagraha, a nonviolent protest against the British monopoly on salt production in India.
- On May 21, Sarojini Naidu led 2,500 marchers on the Dharasana Salt Works, some 150 miles north of Bombay.
- Quit India Movement: In 1942, Sarojini Naidu was arrested during the "Quit India" movement and was jailed for 21 months with Gandhiji.
- Traveled Abroad to Raise Awareness: Naidu traveled to different countries, including the United States and the United Kingdom, to raise awareness about India's struggle for independence and to mobilize international support.
- She also represented India at various international forums and spoke about the Indian independence movement and women's rights.
- First Indian Woman President of INC: Naidu was elected as the first Indian woman president of the Indian National Congress(INC) in 1925(Kanpur Session) and continued to hold this position till 1928.
- Contribution as a Politician:
- Second Round Table Conference: She accompanied Gandhiji to London for the inconclusive second session of the Round Table Conference for Indian–British cooperation (1931).
- Governor of Uttar Pradesh: After India gained independence, Naidu was appointed as the governor of Uttar Pradesh, becoming the first woman to hold a governor's office in India.
- Other Contributions:
- A Renowned Poetess: Naidu was a renowned poetess and wrote in both English and Urdu.
- Published in 1912, ‘In the Bazaars of Hyderabad’ remains one of her most popular poems.
- Her other works include "The Golden Threshold (1905)", "The Bird of Time (1912)", and "The Broken Wing (1912)".
- Worked for Women's Empowerment: Naidu was a strong advocate of women's rights and worked tirelessly to empower women in India.
- She was also a member of the All-India Women's Conference and worked to improve the status of women in India.
- A Renowned Poetess: Naidu was a renowned poetess and wrote in both English and Urdu.
- Death:
- She died on March 2, 1949, in Lucknow, India.
- Relevance of Sarojini Naidu in Present Times:
- Sarojini Naidu was a multifaceted personality and remains a role model for women in India and around the world. Her courage, dedication, and leadership inspired millions of Indians and continue to inspire generations to come.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. Who of the following is the author of a collection of poems called “Golden Threshold”? (2009)
(a) Aruna Asaf Ali
(b) Annie Besant
(c) Sarojini Naidu
(d) Vijayalakshmi Pandit
Ans: (c)
Q2. Consider the following statements: (2015)
- The first woman President of the Indian National Congress was Sarojini Naidu.
- The first Muslim President of the Indian National Congress was Badruddin Tyabji.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
India Energy Week
Why in News?
On February 6th, 2023, Indian Prime Minister (PM) inaugurated the India Energy Week (IEW) 2023 in Bengaluru, Karnataka.
- The PM also launched E20 fuel at 84 Retail Outlets of Oil Marketing Companies in 11 States/UTs and flagged off the Green Mobility Rally organised by Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Limited (HPCL)
What is the E-20 Ethanol Fuel and Green Mobility Rally?
- E-20 Ethanol Fuel:
- About:
- Ethanol Blending programme has been a key focus area of the Government to achieve Atma Nirbharta in the field of energy.
- E20 is a blend of 20% ethanol with petrol. The Government aims to achieve a complete 20% blending of ethanol by 2025, and HPCL and other oil marketing companies are setting up 2G-3G ethanol plants that will facilitate the progress.
- Achievement So Far:
- Due to the sustained efforts of the Government, Ethanol production capacity has seen six times increase since 2013-14.
- The achievements under Ethanol Blending Program & Biofuels Program have not only augmented India’s energy security but have also resulted in a host of other benefits including reduction of 318 Lakh Metric Tonnes of CO2 emissions and foreign exchange savings of around Rs 54,000 crore.
- About:
- Green Mobility Rally:
- The Green Mobility Rally's purpose was to raise public awareness for green fuels.
- Green mobility refers to the use of environmentally-friendly and sustainable transportation options to reduce carbon emissions and preserve natural resources.
- With proper policy support, industry action, market generation, increased investor interest and acceptance, India can position itself as a low-cost, zero-carbon manufacturing hub in green mobility, at the same time fulfilling its goal of economic development, job creation, and improved public health.
- Other Initiatives:
- The PM also launched the uniforms under the ‘Unbottled’ initiative of Indian Oil. These uniforms are made of recycled PET bottles.
- The PM also dedicated the twin-cooktop model of the Indian Oil’s Indoor Solar Cooking System and flagged off its commercial roll-out.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. In the context of proposals to the use of hydrogen enriched CNG (H-CNG) as fuel for buses in public transport, consider the following statements: (2019)
- The main advantage of the use of H-CNG is the elimination of carbon monoxide emissions.
- H-CNG as fuel reduces carbon dioxide and hydrocarbon emissions.
- Hydrogen up to one-fifth by volume can be blended with CNG as fuel for buses.
- H-CNG makes the fuel less expensive than CNG.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)
Q2. Given below are the names of four energy crops. Which one of them can be cultivated for ethanol? (2010)
(a) Jatropha
(b) Maize
(c) Pongamia
(d) Sunflower
Ans: (b)
Q3. According to India’s National Policy on Biofuels, which of the following can be used as raw materials for the production of biofuels? (2020)
- Cassava
- Damaged wheat grains
- Groundnut seeds
- Horse gram
- Rotten potatoes
- Sugar beet
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 5 and 6 only
(b) 1, 3, 4 and 6 only
(c) 2, 3, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. National urban transport policy emphasises on moving people instead of moving vehicles. Discuss critically the success of various strategies of the government in this regard. (2014)
Combating Filariasis
Why in News?
The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has launched a nationwide Mass Drug Administration (MDA) campaign aimed at ending filariasis disease.
- India aims to eliminate filariasis by 2027, three years ahead of the global target.
- High-burdened areas are Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, Karnataka, Odisha, Madhya Pradesh and Andhra Pradesh.
What is Filariasis?
- About:
- Filariasis is a parasitic infection caused by microscopic, thread-like worms known as filariae. It is spread by the bite of infected mosquitoes, and it affects millions of people in tropical and subtropical regions worldwide.
- Causes and Transmission:
- Lymphatic filariasis is caused by infection with parasites classified as nematodes (roundworms) of the family Filariodidea.
- There are 3 types of these thread-like filarial worms:
- Wuchereria bancrofti, which is responsible for 90% of the cases,
- Brugia malayi, which causes most of the remainder of the cases,
- Brugia timori, which also causes the disease.
- Symptoms:
- Lymphatic filariasis infection involves asymptomatic, acute, and chronic conditions.
- In chronic conditions, it leads to lymphoedema (tissue swelling) or elephantiasis (skin/tissue thickening) of limbs and hydrocele (scrotal swelling).
- Lymphatic filariasis infection involves asymptomatic, acute, and chronic conditions.
- Treatment:
- The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends three drug treatments to accelerate the global elimination of lymphatic filariasis. The treatment, known as IDA, involves a combination of ivermectin, diethylcarbamazine citrate and albendazole.
- The plan is to administer these drugs for two consecutive years. The life of the adult worm is hardly four years, so it would die a natural death without causing any harm to the person.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends three drug treatments to accelerate the global elimination of lymphatic filariasis. The treatment, known as IDA, involves a combination of ivermectin, diethylcarbamazine citrate and albendazole.
What are the Related Initiatives?
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Maharishi Dayanand Saraswati Jayanti
Recently, the Prime Minister of India inaugurated the year-long (two-year) celebrations commemorating the 200th birth anniversary of Maharishi Dayanand Saraswati. He also released a logo for commemoration.
Maharishi Dayanand Saraswati Jayanti is celebrated every year to mark the birth anniversary of the Maharishi Dayanand Saraswati.
He was born on 12th February 1824 in Tankara, Gujarat in a Brahmin family. Dayananda’s views were published in his famous work, Satyarth Prakash (The True Exposition).
He was an Indian philosopher, social leader and founder of the Arya Samaj. His vision of India included a classless and casteless society. He took inspiration from the Vedas and considered them to be ‘India’s Rock of Ages’. He also gave the slogan “Back to the Vedas”.
The DAV (Dayanand Anglo Vedic) schools came into existence in 1886 to realize the vision of Swami Dayanand Saraswati.
Read More: Arya Samaj
AMRITPEX 2023
Recently, the Minister for Communications, Electronics & Information Technology inaugurated AMRITPEX 2023 - National Philatelic Exhibition. This five-day Mahakumbh of Stamps (11th to 15th February 2023) in Pragati Maidan, New Delhi, is being organized as a part of Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav Celebrations.
The exhibition will feature stamps and photographic collections on the country’s history and culture. It is based on five themes – Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav and New India, Yuva Shakti, Nari Shakti, Nature and Wildlife, and India’s Culture and History.
For the first time in India, new Technology like Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality has been used to showcase the cultural heritage, history, nature and wildlife by narrating the stories of stamps.
Read More: Initiatives on 75th Independence Day, Virtual Reality
Deendayal Upadhyaya
The Prime Minister has paid tributes to Pandit Deendayal Upadhyaya Ji on his Punya Tithi (Death Anniversary).
He was born in 1916 in Nagla Chandrabhan village, now called Deendayal Dham in Uttar Pradesh. He joined the Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS) and dedicated himself to full-time work in RSS from 1942. He started a monthly magazine “Rashtra Dharma”, a weekly ‘Panchajanya’, and a daily ‘Swadesh’.
In 2019, Prime Minister unveiled a 63-feet tall statue of Pandit Upadhyaya while inaugurating the Pandit Deendayal Upadhyaya Memorial Centre in Padao on the Varanasi-Chandauli border.
Read More: Pandit Deendayal Upadhyay National Welfare Fund for Sportspersons (PDUNWFS)
NRIs and G-20 Countries to have Access to UPI
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) permitted all inbound travellers from the Group of Twenty (G-20) countries and Non-resident Indians (NRIs) to access Unified Payment Interface (UPI) for their merchant payments/ Person to Merchant (P2M) at select airports while they are in the country.
According to the RBI, banks and non-banks authorised to issue Prepaid Payment Instruments (PPIs) can issue rupee-denominated full-KYC PPIs to foreign nationals and NRIs visiting India. The conversion to the Indian rupee can be carried out only by entities authorised to deal in foreign exchange under Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (FEMA).
PPIs are payment instruments that facilitate purchase of goods and services against the value stored on such instruments. The value stored on such instruments represents the value paid for by the holder, by cash, by debit to a bank account, or by credit card