Centre brings Crypto under PMLA
Prelims: Crypto Currency, PMLA, ED, Virtual Digital Assets.
Mains: Crypto under Money Laundering Act.
Why in News?
The Union Ministry of Finance, through a gazette notification, has brought Virtual Digital Assets (VDA) or the Crypto Currency under the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA).
What are the Key Points of the Move?
- Need:
- Cryptocurrency transactions continue to lack transparency and the trail is difficult to establish.
- This moves pushes responsibility on the cryptocurrency markets to bring transparency to cryptocurrency trading.
- In the digital era of finance, compliance is a must not just to safeguard interest of investors but also of the country and in this aspect the crypto industry is becoming increasingly important, governments and regulators around the world are paying closer attention to this rapidly evolving space.
- The measure is also expected to aid investigative agencies in carrying out action against crypto firms.
- Cryptocurrency transactions continue to lack transparency and the trail is difficult to establish.
- Norms:
- VDA service providers / businesses have now become the ‘Reporting Entities’ under PMLA Act, and they have to follow similar reporting standards and KYC norms as the other regulated entities like banks, securities intermediaries, payment system operators, etc.
- Activities covered under PMLA:
- Exchange between virtual digital assets (VDA) and Fiat Currencies.
- Exchange between one or more forms of VDAs
- Transfer of VDAs
- Safekeeping or administration of VDAs or instruments enabling control over VDAs.
- Participation in and provision of financial services related to an issuer’s offer and sale of a VDA.
What are the Related Concerns?
- The notification does not offer entities time to adhere to the fresh norms. The Crypto industry is also concerned that in the absence of a central regulator, crypto entities could end up dealing directly with enforcement agencies like the Directorate of Enforcement (ED).
- 17 lakh users Indian VDA users have switched from domestic centralized VDA exchanges to foreign counterparts since the announcement of the tax regime in the Union Budget in February 2022
- Indian crypto traders have moved over USD 3.8 billion in trading volume from local exchanges to international crypto platforms.
- This is likely to lead to a large negative impact on tax revenues, as well as a decrease in transaction traceability— which defeats the two central goals of the extant policy architecture.
- The downside impact of the VDA tax architecture is likely to further accentuate capital outflow and deter international investors.
What is the Legal Status of Crypto in India?
- In the Union Budget 2022-23, even though the government brought in a tax for cryptocurrencies, it did not proceed with framing regulations.
- Earlier, the Reserve Bank (RBI) of India had proposed a ban that was set aside by Supreme Court order.
- In July 2022, flagging the RBI’s concerns, the finance minister told Parliament that “international collaboration” would be needed for any effective regulation or ban on cryptocurrency.
- From April 2022, India introduced a 30% income tax on gains made from cryptocurrencies.
- In July 2022, rules regarding 1% tax deducted at source on cryptocurrency came into effect.
Way Forward
- If there are laws and guidelines against crypto laundering, investors will have the fear of being penalized. To make things more streamlined, exchanges in India must track transfers made by investors within a tax year exceeding a certain amount and report the same to the tax authorities.
- To overcome the impact of VDA tax architecture, the Government should adopt a progressive tax structure with differentiated rates for short-term and long-term gains, in line with international best practices.
- A new tax regime pertaining to VDA was announced in 2022, switching users from domestic to international counterparts, which furthered the capital outflow.
IBSA and Digital Governance Reform
For Prelims: IBSA Forum, United Nations (UN) Office for South-South Cooperation (UNOSSC), India’s Aadhaar biometric ID system, India’s G-20 presidency.
For Mains: Major Issues Related to Global Digital Governance, Initiatives of IBSA Grouping.
Why in News?
According to the Geneva-based DiploFoundation, India, Brazil, and South Africa, which have together formed the tripartite IBSA Forum, may play a prominent role in the process of reforming digital governance.
What is IBSA?
- About:
- The IBSA is a trilateral, developmental initiative between India, Brazil and South Africa to promote South-South cooperation and exchange.
- Formation:
- The grouping was formalised and named the IBSA Dialogue Forum when the Foreign Ministers of the three countries met in Brasilia (Brazil) on 6th June 2003 and issued the Brasilia Declaration.
- Collaboration:
- Joint Naval Exercise:
- IBSAMAR (IBSA Maritime Exercise) is an important part of IBSA trilateral defence cooperation.
- IBSA Fund:
- Established in 2004, IBSA Fund (India, Brazil and South Africa Facility for Poverty and Hunger Alleviation) is a unique Fund through which development projects are executed with IBSA funding in fellow developing countries.
- The fund is managed by the United Nations (UN) Office for South-South Cooperation (UNOSSC).
- Joint Naval Exercise:
How can IBSA Contribute to Global Digital Governance?
- Potential of IBSA:
- Digital inclusion:
- Digitalisation is driving growth in the IBSA economies.
- The three countries have spearheaded digital inclusion by prioritising affordable access to citizens, supporting training for digital skills, and creating a legal framework for the growth of small digital enterprises. India leads the way, with a vibrant digital economy.
- Data Governance:
- India’s G-20 presidency aims to take strategic leadership with practical initiatives, such as a self-evaluation of nations’ data governance architecture, modernisation of national data systems to regularly incorporate citizen voices and preferences, and transparency principles for governing data.
- With a big population, IBSA countries also see data as a national resource.
- Digital inclusion:
- Issues:
- Geopolitical Rivalry:
- Satellite collisions, cyber-resilience and security of space services, exploration of space resources has increased competition between countries with a potential of weaponization of outer space.
- Also, semiconductors are at the centre of the geopolitical battle between the US and China.
- Satellite collisions, cyber-resilience and security of space services, exploration of space resources has increased competition between countries with a potential of weaponization of outer space.
- Sovereignty vs Integration:
- The Foundation observes that many countries will have to balance data sovereignty and integration in the global economy.
- Free flow of data will be essential for small and export-oriented economies.
- Geopolitical Rivalry:
What is India's Progress in Digital Governance?
- Aadhar: India’s Aadhaar biometric ID system is seen by many as a leading digital identity initiative, inspiring similar systems in other countries.
- MyGov Platform: It has laid the robust foundation for citizen engagement and participatory governance in the country by providing a common digital platform, where citizens can share their views on government programmes and schemes.
- Unified Payments Interface (UPI): Launched in 2016, UPI is a real-time payment system that enables instant money transfers between bank accounts using a mobile device.
- UPI has transformed the way payments are made in India, making it faster, more convenient, and more secure. UPI's success has inspired other countries to tie up with India and adopt similar payment systems.
- Digital India Act: Government of India has proposed to come up with Digital India Act 2023 that envisages to act as catalysts for Indian economy by enabling more innovation, more startups, and at the same time protecting the citizens of India in terms of safety, trust, and accountability.
Way Forward
- Collaborate with Other Countries & Organizations: IBSA countries should work together and with other nations and international organizations to develop global standards for digital governance, data protection, and cybersecurity.
- Develop a Common Strategy: IBSA countries should develop a common strategy on digital governance and work towards a shared vision of a global digital economy that prioritizes digital inclusion, data privacy, and security.
- This strategy should be based on their shared values and principles, such as respect for human rights, democracy, and the rule of law.
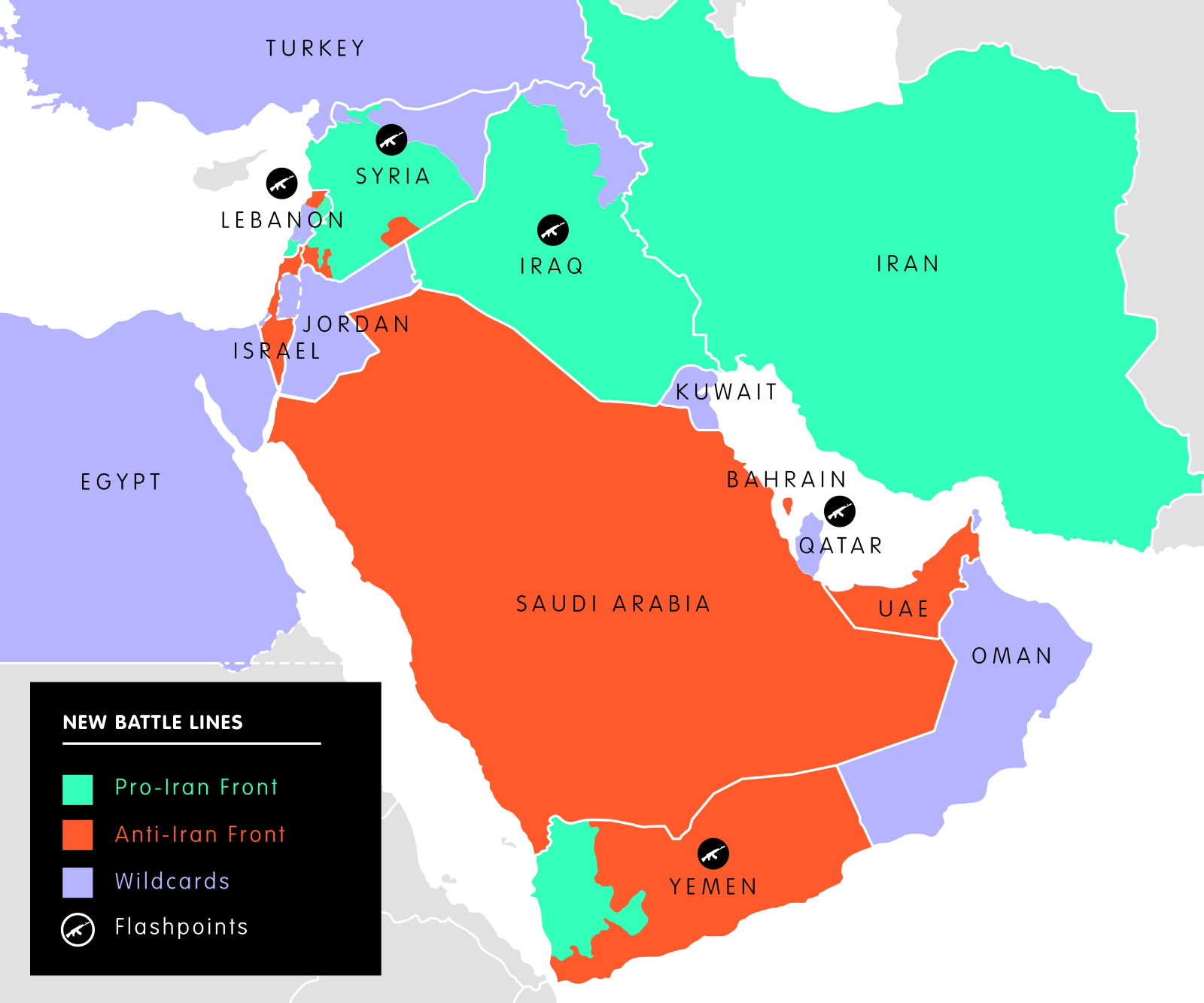
Saudi, Iran agree to Restore Diplomatic Ties
For Prelims: Houthi rebels in Yemen, Geographic Location of Middle Eastern Countries, West Asia.
For Mains: Role of India in Saudi-Iran Relations, Effect of Policies & Politics of Countries on India's Interests.
Why in News?
Recently, Saudi and Iranian officials held bilateral talks that concluded with an agreement to restore diplomatic ties which have been severed since 2016. The major diplomatic breakthrough negotiated by China in Beijing.
- It comes as diplomats have been trying to end a long war in Yemen, a conflict in which both Iran and Saudi Arabia are deeply entrenched.
What are the Key Outcomes of the Talks?
- The two countries plan to reopen their respective embassies in Tehran and Riyadh.
- They also vowed to respect countries’ sovereignty and not interfere in internal affairs.
- They also agreed to activate a 2001 security cooperation agreement, as well as a general economy, trade and investment agreement signed in 1998.
What is the Conflict between Iran and Saudi Arabia?
- Religious Factor:
- Saudi Arabia broke off ties with Iran in 2016 after protesters invaded Saudi diplomatic posts after Saudi Arabia had executed a prominent Shiite cleric days earlier.
- Saudi Arabia has long portrayed itself as the world’s leading Sunni nation while Iran views itself as the protector of the Islam’s Shiite minority.
- Attacks on Saudi Arabia:
- Since US’s withdrawal from Iran’s Nuclear deal, Iran was blamed for a series of attacks including one targeting the heart of Saudi Arabia’s oil industry in 2019.
- Western nations and experts have blamed the attack on Iran though the latter has denied launching the attack.
- Since US’s withdrawal from Iran’s Nuclear deal, Iran was blamed for a series of attacks including one targeting the heart of Saudi Arabia’s oil industry in 2019.
- Regional Cold War: Saudi Arabia and Iran - two powerful neighbours - are locked in a fierce struggle for regional dominance.
- Uprisings across the Arab world (after the Arab Spring in 2011) caused political instability throughout the region.
- Iran and Saudi Arabia exploited these upheavals to expand their influence, notably in Syria, Bahrain and Yemen, further heightening mutual suspicions.
- Moreover, external powers like the US and Israel have a major role in exacerbating conflict between Saudi Arabia and Iran.
- Proxy Wars: Iran and Saudi Arabia are not directly fighting but they are engaged in a variety of proxy wars (conflicts where they support rival sides and militias) around the region.
- For Example, Houthi rebels in Yemen. These groups can acquire greater capabilities which can cause further instability in the region. Saudi Arabia accuses Iran of supporting them.
- Leader of Islamic World: Historically, Saudi Arabia, a monarchy and home to the birthplace of Islam, saw itself as the leader of the Muslim world.
- However, this was challenged in 1979 by the Islamic revolution in Iran which created a new type of state in the region - a kind of revolutionary theocracy - that had an explicit goal of exporting this model beyond its own borders.
What can be the Global Implications?
- The deal may have implications for a US-led effort to isolate Iran economically through sanctions as the deal may facilitate possible Saudi investment inside Iran.
- In Yemen, the Saudis have been backing the internationally recognised government in an eight-year civil war against Iranian-backed Houthi rebels but have been looking for a way to end the war by conducting private talks in Oman with the Houthis.
- Saudi Arabia will hope that Iran will halt Houthi drone and missile strikes on the kingdom, and that Iran will help with Saudi talks with the Houthis.
- The deal will cause concern among many Israeli politicians who have sought global isolation for its arch-enemy Iran. Israel described the pact as a “serious and dangerous” development.
What can be the Implications for India?
- Energy Security:
- Iran and Saudi Arabia are two major oil producers in the world, and any conflict between them can lead to oil price spikes that can have a significant impact on India's energy security.
- Normalizing ties between these two countries could help stabilize global oil prices and ensure a consistent supply of oil to India.
- Trade:
- Both Iran and Saudi Arabia are important trading partners for India. Normalizing ties between them could open up new avenues for trade and investment, leading to increased economic opportunities for India.
- Regional Stability:
- India has strong economic and strategic interests in the Middle East including International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC).
- Iran is part of India’s extended neighbourhood. Any instability in the region can have far-reaching consequences for India. Normalizing ties between Iran and Saudi Arabia could contribute to greater stability in the region, reducing the risk of conflict and terrorism.
- Geopolitics:
- India maintains cordial relations with both Iran and Saudi Arabia and plays a role in maintaining peace and stability in the region. Normalizing ties between these two countries could help India in its efforts to promote peace and security in the region.
- However, Chinese mediation between Iran and Saudi will create challenges for India as it will contribute to increasing Chinese influence in the region.
Way Forward
- India can play a constructive role in promoting dialogue and cooperation between these two countries, which can help in achieving regional stability.
- India needs to be vigilant about the increasing Chinese influence in the region and work towards securing its strategic interests in the Middle East.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs):
Q.1 Which one of the following countries of South-West Asia does not open out to the Mediterranean Sea? (2015)
(a) Syria
(b) Jordan
(c) Lebanon
(d) Israel
Ans: (b)
Q.2 Which of the following is not a member of ‘Gulf Cooperation Council’? (2016)
(a) Iran
(b) Saudi Arabia
(c) Oman
(d) Kuwait
Ans: (a)
Q.3 What is the importance of developing Chabahar Port by India? (2017)
(a) India’s trade with African countries will enormously increase.
(b) India’s relations with oil-producing Arab countries will be strengthened.
(c) India will not depend on Pakistan for access to Afghanistan and Central Asia.
(d) Pakistan will facilitate and protect the installation of a gas pipeline between Iraq and India.
Ans: (c)
MSME Competitive (LEAN) Scheme
For Prelims: Lean Manufacturing, UDYAM Platform, Raising and Accelerating MSME Performance (RAMP) Scheme, Credit Guarantee Trust Fund for Micro & Small Enterprises (CGTMSE), Interest Subsidy Eligibility Certificate (ISEC), A Scheme for Promoting Innovation, Rural Industry & Entrepreneurship (ASPIRE), Zero Defect & Zero Effect (ZED).
For Mains: Significance of MSME Sector for India, Current Challenges Related to MSME Sector, Recent Government Initiatives Related to MSMEs.
Why in News?
- Recently, Ministry of MSMEs launched the MSME Competitive (LEAN) Scheme to provide a roadmap to global competitiveness for the MSMEs of India.
- The idea is to improve quality, productivity, performance and capability to change the mind-sets of manufacturers and transform them into world class manufacturers.
What is Lean Manufacturing?
- About: Lean Manufacturing or Lean Production, known simply as LEAN, is a production practice that considers the expenditure of resources for any goal, other than the creation of value for the end customer, to be wasteful and hence should be eliminated.
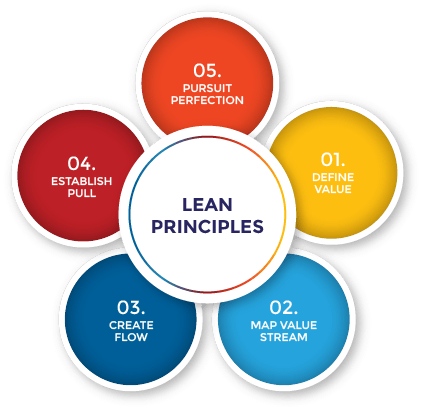
- Lean Principles: Lean manufacturing includes a set of principles that lean thinkers use to achieve improvements in productivity, quality, and lead-time by eliminating waste through kaizen. Principles of Lean Manufacturing are:
- Identify Value: Determine what value means from the customer's perspective. This includes understanding what the customer wants, needs, and is willing to pay for.
- Map the Value Stream: Create a map of the value stream, which is the sequence of steps required to produce a product or service. This helps identify areas of waste and inefficiency.
- Create Flow: Create a smooth, uninterrupted flow of work through the value stream. This involves eliminating bottlenecks and interruptions that slow down the process.
- Implement Pull: Implement a pull system that produces products only as they are needed, based on customer demand. This helps to reduce inventory and waste.
- Strive for Perfection: Continuously strive for perfection by identifying and eliminating waste, improving processes, and ensuring quality.
Note:
- Kaizen is a Japanese word that essentially means "change for the better" or "good change."
- The goal is to provide the customer with a defect free product or service when it is needed and, in quantity, it is needed.
What are the Key Points of the Scheme?
- Objective:
- Through the LEAN journey, MSMEs can reduce wastage substantially, increase productivity, improve quality, work safely, expand their markets, and finally become competitive and profitable.
- Tools:
- Under the scheme, MSMEs will implement LEAN manufacturing tools like 5S, Kaizen, KANBAN, Visual workplace, Poka Yoka etc under the able guidance of trained and competent LEAN Consultants to attain LEAN levels like Basic, Intermediate and Advanced.
- Government Support:
- The government will contribute 90% of implementation cost for handholding and consultancy fees.
- There will be an additional contribution of 5% for the MSMEs which are part of SFURTI clusters, owned by Women/SC/ST and located in Northeast region.
- There will be an additional contribution of 5% for MSMEs which are registering through Industry Associations/ Overall Equipment Manufacturing (OEM) organizations after completing all levels.
- This is a unique feature to encourage Industry Associations and OEMs for motivating their supply chain vendors to participate in this scheme.
What are the Recent Government Initiatives Related to MSMEs?
- Raising and Accelerating MSME Performance (RAMP) Scheme
- Credit Guarantee Trust Fund for Micro & Small Enterprises (CGTMSE)
- Interest Subsidy Eligibility Certificate (ISEC)
- A Scheme for Promoting Innovation, Rural Industry & Entrepreneurship (ASPIRE)
- Credit Linked Capital Subsidy for Technology Upgradation (CLCSS)
- Zero Defect & Zero Effect (ZED)
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question:(PYQ)
Prelims:
Q.1 What is/are the recent policy initiative(s)of Government of India to promote the growth of the manufacturing sector? (2012)
- Setting up of National Investment and Manufacturing Zones
- Providing the benefit of ‘single window clearance’
- Establishing the Technology Acquisition and Development Fund
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q.2. Which of the following can aid in furthering the Government’s objective of inclusive growth? (2011)
- Promoting Self-Help Groups
- Promoting Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises
- Implementing the Right to Education Act
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Mains:
Q.1 Account for the failure of manufacturing sector in achieving the goal of labour-intensive exports. Suggest measures for more labour-intensive rather than capital-intensive exports.(2017)
Landslide Atlas of India
Prelims: Landslide, Kedarnath disaster in 2013, Land Subsidence and Joshi math Case, Rainfall variability, Western Ghats, Himalayas.
Mains: Key Highlights of Landslide Atlas of India, India’s Vulnerability to Landslides.
Why in News?
Recently, National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC) under the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has released the Landslide Atlas of India, a detailed guide identifying Landslide Hotspots in the country.
- NRSC has the mandate for remote sensing satellite data acquisition, processing, archiving, and dissemination to various users.
How was the Atlas Prepared?
- For the first time, scientists did a risk assessment on the basis of 80,000 landslides recorded between 1998 and 2022 in 147 districts in 17 states and two Union Territories to build a "Landslide Atlas" of the country.
- The atlas used satellite data of ISRO to map all seasonal and event-based landslides like the Kedarnath disaster in 2013 and landslides triggered due to the Sikkim earthquake in 2011.
- The pan-India landslide database classifies landslides into – seasonal (2014, 2017 monsoon seasons), event-based and route-based (2000 – 2017).
What are the Key Highlights?
- Uttarakhand, Kerala, Jammu and Kashmir, Mizoram, Tripura, Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh reported the highest number of landslides during 1998 – 2022.
- Mizoram topped the list, recording 12,385 landslide events in the past 25 years, of which 8,926 were recorded in 2017 alone.
- Mizoram is followed by Uttarakhand (11,219) and Kerala.
- Uttarakhand’s fragility was recently exposed during the land subsidence events reported from Joshimath.
- The number of districts with the maximum landslide exposure are in Arunachal Pradesh (16), Kerala (14), Uttarakhand and Jammu and Kashmir (13 each), Himachal Pradesh, Assam and Maharashtra (11 each), Mizoram (8) and Nagaland (7).
- Rudraprayag and Tehri Garhwal districts of Uttarakhand have the highest landslide density and landslide risk exposure in the country.
How Vulnerable India is to Landslides?
- India is considered among the top five landslide-prone countries globally, where at least one death per 100 sq km is reported in a year due to a landslide event.
- Rainfall variability pattern is the single biggest cause for landslides in the country, with the Himalayas and the Western Ghats remaining highly vulnerable.
- Excluding snow covered areas, approximately 12.6 % of the country’s geographical land area is prone to landslides. As many as 66.5 % of the landslides are reported from the North-western Himalayas, about 18.8 % from the North-eastern Himalayas, and about 14.7 % from the Western Ghats.
- In the Western Ghats, despite fewer events, landslides were found to be making inhabitants significantly vulnerable to fatalities, especially in Kerala.
What causes landslides?
- About:
- Landslides are natural disasters occurring mainly in mountainous terrains where there are conducive conditions of soil, rock, geology and slope.
- A sudden movement of rock, boulders, earth or debris down a slope is termed a landslide.
- Causes:
- Natural causes that trigger it include heavy rainfall, earthquakes, snow melting and undercutting of slopes due to flooding.
- They can also be caused by anthropogenic activities such as excavation, cutting of hills and trees, excessive infrastructure development, and overgrazing by cattle.
- Some of the main factors that influence landslides are lithology, geological structures like faults, hill slopes, drainage, geomorphology, land use and land cover, soil texture and depth, and weathering of rocks.
- All these are factored in when a landslide susceptibility zone is earmarked for planning and making predictions.
Use of Antibiotics on Livestock
Why in News?
Recently, a team of Researchers in the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), has found that grazing by livestock leads to lower carbon storage in soil compared to grazing by wild herbivores.
- Livestock are the most abundant large mammals on earth. If the carbon stored in soil under livestock can be increased by even a small amount, then it can have a big impact on climate mitigation.
What are the Highlights of the Study?
- In a previous study, it was observed that herbivores play a key role in stabilizing the pool of soil carbon and the recent study showcases the difference as to how they affect the soil carbon stocks between livestock such as sheep and cattle compared to their wild herbivores such as the yak and ibex.
- Impact of Antibiotics: The use of veterinary antibiotics such as tetracycline on livestock is making carbon storage lower in soil as compared to other grazing herbivores.
- These antibiotics, when released into the soil through dung and urine, alter the microbial communities in soil in ways that are detrimental for sequestering carbon.
- Antibiotics such as tetracycline are long-lived and can linger in the soil for decades resulting in ecological imbalance.
- Difference in CUE: Although soils from the wild and livestock areas had many similarities, they differed in one key parameter called carbon use efficiency (CUE), which determines the ability of microbes to store carbon in the soil.
- CUE is defined as the ratio of net carbon gain to gross carbon assimilation during a period.
- The soil in the livestock areas had 19% lower CUE.
What are Antibiotics?
- Antibiotics are remarkable drugs capable of killing biological organisms in one’s body without harming the body.
- These are used for everything from preventing infections during surgeries to protecting cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy.
- India is the world’s largest consumer of antibiotics. India’s excessive antibiotic usage is leading to a powerful never before seen mutation within bacteria.
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
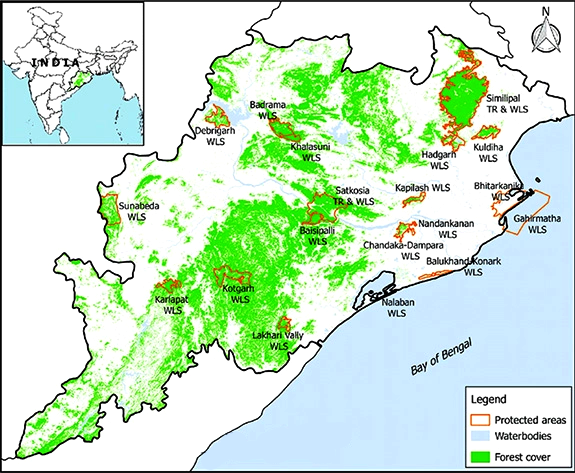
Country’s Worst Forest Fires in Odisha
According to the Forest Survey of India (FSI) data, forest fires continue to rage in Odisha after the state recorded 642 large fire incidents in March 2023 — the highest in the country during the period. A sudden jump in the incidents of fires across Odisha resulted in a massive loss of flora and fauna in the state’s forests.
Odisha has recorded 871 large forest fires since November 2022. This is also a national record for the season, official data showed. It was followed by Andhra Pradesh (754), Karnataka (642), Telangana (447) and Madhya Pradesh (316). In 2021, 51,968 forest fire incidents occurred in the state. Massive fires had broken out in Similipal National Park in the Mayurbhanj district, which is one of the major biospheres of Asia.
Forest fire is also called bush or vegetation fire or wildfire, it can be described as any uncontrolled and non-prescribed combustion or burning of plants in a natural setting such as a forest, grassland, brushland or tundra, which consumes the natural fuels and spreads based on environmental conditions (e.g., wind, topography).
Read More: Forest Fire: Causes, Classification, Incidents in India & Measures Taken
54th CISF Raising Day
March 10 is annually observed as the Raising Day when the Central Industrial Security Force (CISF) was set up under the Union ministry of Home Affairs.
CISF is one of the seven Central Armed Police Forces in India and is responsible for providing security to various public sector undertakings, airports, and other important installations. The CISF was set up under the act of the Parliament of India on March 10, 1969. Since then, CISF Raising Day is being celebrated on March 10 each year. However, in 2023, the date was revised (12th March).
Read More: Central Armed Police Force (CAPF)
Centers of Excellence Under MIDH
Under Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH), Centers of Excellence (CoEs) are being established in various States through Bilateral Cooperation or Research Institutes. These CoEs serve as demonstration and training centres for the latest technologies in the field of horticulture. 3 CoEs that have been approved include:
- CoE for Kamlam (Dragon Fruit) at Bengaluru, Karnataka
- CoE for Mango and Vegetables at Jajpur, Odisha
- CoE for Vegetables and Flowers at Ponda, Goa
MIDH is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme for the holistic growth of the horticulture sector covering fruits, vegetables and other areas. Under MIDH, the Government contributes 60% of the total outlay for developmental programmes in all the states (except Northeastern and Himalayan states where GOI contributes 90%) & 40% is contributed by State governments.
Read More: Status of the Horticulture Sector in India
First Woman to Lead Army Unit Near China border (Ladakh)
Recently, a woman officer, Colonel Geeta Rana has for the first time, taken over the command of an independent unit in the sensitive Ladakh sector where India and China have been locked in a lingering border row.
In January 2023, the army for the first time deployed a woman officer, Captain Shiva Chouhan, at Siachen, the world’s highest and coldest battleground. It also deployed its largest contingent of 27 women peacekeepers in Sudan’s disputed region of Abyei, where they are performing security-related tasks in a challenging mission as part of the United Nations Interim Security Force (UNISFA).
One of the turning points for women in the military came in 2015 when the Indian Air Force (IAF) decided to induct them into the fighter stream for the first time.
Read More: Representation of Women in Armed Forces
Dung Based Formulations for Farming
Why in News?
Recently, NITI Aayog has released a report titled- “Production and promotion of organic and bio fertilizers with special focus on improving economic viability of gaushalas”, recommending Capital Assistance to Cow Shelters to promote Dung-Based Fertilizers for Agriculture, thus promoting Natural Farming.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- Need to Promote Dung-based Formulations:
- Agriculture in India was based on an integrated approach of organic fertilizers. But after the Green Revolution, India could not maintain this balance and use of chemical fertilizers brought imbalance in the soil nutrients.
- Cow shelters can address the problem of stray cattle that damaged crops in many parts of the country.
- The number of stray and abandoned cattle had risen to a level beyond the resources available with existing gaushalas for their upkeep and sustenance and suggested channeling the potential of such cattle wealth for promoting natural and sustainable farming.
- Recommendations:
- The government can help gaushalas through capital assistance so that they could market cow dung and cow urine-based formulations for applications in agriculture.
- Gaushalas can be of great help in promoting natural farming and organic farming. Thus, complementarity can be built to promote gaushalas and natural farming.
- Significance:
- Cow dung-based organic fertilizers will have a huge impact in fulfilling the constitutional mandate under Article 48 that the State shall take steps for preserving and improving cattle breeds, and prohibiting the slaughter of cows and calves, and other milch and draught cattle.
What is Natural Farming?
- Natural farming is a method of agriculture that seeks to create a balanced and self-sustaining ecosystem in which crops can grow without the use of synthetic chemicals or genetically modified organisms.
- Instead of relying on artificial inputs like synthetic fertilisers and pesticides, natural farmers rely on techniques like crop rotation, intercropping, and composting to enhance soil health and support crop growth.
- Natural farming methods are often based on traditional knowledge and practices and may be adapted to local conditions and resources.
- The goal of natural farming is to produce healthy, nutritious food in a way that is sustainable and environmentally friendly.
What are the Initiatives Related to Sustainable Agriculture?
- Mission Organic Value Chain Development for Northeastern Region (MOVCDNER)
- National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture
- Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY)
- Sub-mission on AgroForestry (SMAF)
- Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana