Social Justice
International Women’s Day: Women in Armed Forces
For Prelims: India’s Female Labour Force Participation, Women in Informal Economy, ILO, Global gender gap index.
For Mains: Status of Women in Armed Forces, India’s Female Labour Force Participation.
Why in News?
Recently, on the occasion of International Women's Day, Group Captain Shaliza Dhami has been selected to take over the command of a frontline combat unit in the Western sector (facing Pakistan).
- She will be the first woman officer in the IAF to command a missile squadron in the Western sector.
What are the Key Points about International Women’s Day?
- About: It is celebrated annually on 8th March. It includes:
- Celebration of women's achievements,
- raising awareness about women's equality,
- lobbying for accelerated gender parity,
- fundraising for female-focused charities, etc.
- Brief History:
- Women’s Day was first celebrated back in 1911 by Clara Zetkin, who was a German. The roots of the celebration had been in the labour movement across Europe and North America.
- However, it was only in 1913 that the celebrations were shifted to 8th March, and it has remained that way ever since.
- International Women's Day was celebrated for the first time by the United Nations in 1975.
- In December 1977, the UN General Assembly adopted a resolution proclaiming a United Nations Day for Women’s Rights and International Peace to be observed on any day of the year by Member States, in accordance with their historical and national traditions.
- Women’s Day was first celebrated back in 1911 by Clara Zetkin, who was a German. The roots of the celebration had been in the labour movement across Europe and North America.
- Theme:
- The theme for International Women's Day, 2023, according to the United Nations is “DigitALL: Innovation and technology for gender equality” and it aims to emphasize the importance of technology in bringing gender issues to light.
What is the Status of Women in Armed Forces?
- Background:
- The Indian Air Force started inducting women fighter pilots in 2016. The first batch had three women fighter pilots who currently fly the MiG-21, Su-30MKI and Rafale.
- Women officers have started taking command of various Army units in arms and services including Engineers, Signals, Army Air Defence, Intelligence Corps, Army Service Corps, Army Ordnance Corps and Electronics and Mechanical Engineers.
- Current Statistics:
- There are 10,493 women officers serving in the armed forces, the majority in the medical services.
- The Indian Army, being the largest of the three services, has the largest number of women officers at 1,705, followed by 1,640 women officers in the Indian Air Force, and 559 in the Indian Navy.
- In January 2023, the army deployed a woman officer, Captain Shiva Chouhan, on the Siachen glacier for the first time.
- In February 2023, the army began assigning women officers to command roles outside of the medical stream for the first time.
- Around 50 of them are set to head units in operational areas under the Northern and Eastern Commands responsible for guarding India's borders with China.
- The Navy has also started inducting women officers on frontline ships, earlier a no-go zone for women officers.
- Many of them have been posted in the sensitive northern and eastern commands of the Army.
What are the Concerns Related to Gender Equality?
- Global:
- UN Secretary General stated that Gender equality is growing more distant. On the current track, UN Women puts it 300 years away.
- According to the UN, legal restrictions have kept 2.7 billion women from accessing the same choice of jobs as men.
- As of 2019, less than 25% of parliamentarians were women.
- One in three women experience gender-based violence.
- India Specific:
- According to CMIE data, as of December 2021, while the male LFPR was 67.4%, the female LFPR was as low as 9.4%.
- Even if one sources data from the World Bank, India’s female labor force participation rate is around 25% when the global average is 47%.
- In the Global gender gap index (which measures progress towards gender parity), India slipped to 135th place in 2022.
- However, recently the WEF has agreed to make changes in criteria for Global Gender Gap Reports by taking into account the participation of women at panchayat level to rank countries in its future reports. It will better India’s position at the global level.
- As per the data compiled by the Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU), of which India is a member, women represent just 14.44% of the total members of the Lok Sabha.
- According to a 2018 study by the International Labour Organization (ILO), more than 95% of India’s working women are informal workers who work in labour-intensive, low-paying, highly precarious jobs/conditions, and with no social protection.
What are the Challenges for Women in Armed Forces?
- Societal Issues:
- Composition of male officers, predominantly drawn from a rural background, with prevailing societal norms, troops are not yet mentally schooled to accept women officers in command of units.
- Society has low acceptance for the women officer who had been caught as a prisoner of war by an enemy country.
- Physiological Challenges:
- Motherhood, childcare, psychological limitations are vital factors, which have a bearing on the employment of women officers in the Army.
- It is a challenge for women to meet these hazards of service owing to prolonged absence during pregnancy, motherhood and domestic obligations towards their children and families especially when both husband and wife happen to be service officers.
- Family Issues:
- Armed forces require sacrifices and commitment beyond the call of duty by the entire family of service personnel involving separation and frequent transfers, affecting the education of children and career prospects of the spouse.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following gives ‘Global Gender Gap Index’ ranking to the countries of the world? (2017)
(a) World Economic Forum
(b) UN Human Rights Council
(c) UN Women
(d) World Health Organization
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. What are the continued challenges for Women in India against time and space? (2019)
Q. Discuss the desirability of greater representation to women in the higher judiciary to ensure diversity, equity and inclusiveness. (2021)
International Relations
India-Central Asia Joint Working Group (JWG) on Afghanistan
For Prelims: India-Central Asia Joint Working Group (JWG) on Afghanistan, United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime, India-Central Asia summit
For Mains: Global Groupings, India and its Neighbourhood, Significance of Central Asia for India, Geo-political Dynamics of the Region.
Why in News?
India will send its next consignment of wheat as aid to Afghanistan under the Taliban regime via Chabahar port. The decision, that was announced at the first meeting of the India-Central Asia Joint Working Group (JWG) on Afghanistan in Delhi.
- This comes after the agreement with Pakistan to extend for sending the wheat over the land route expired and talks on extension have failed.
What are the Key Points about the JWG?
- The JWG meeting comes a year after the India-Central Asia summit in January 2022, where the decision to hold a special contact group on Afghanistan was announced.
- The issues of drugs, the export of terrorism and radicalism, and refugees has been at the top of concerns for neighbouring countries in Central Asia.
- According to UNODC reports, opium production is up by nearly a third in the past year, after the Taliban took control of Kabul.
- More than 80% of the world’s opium and heroin is smuggled out of Afghanistan, which is a part of Golden crescent.
- An estimated 3 million people, or nearly one tenth of the population of Afghanistan is addicted to opium.
- According to UNODC reports, opium production is up by nearly a third in the past year, after the Taliban took control of Kabul.
- The JWG also emphasised the “importance of formation of a truly inclusive and representative political structure that extends the equal rights for all Afghans including minorities, women, girls.
What are the Key Outcomes of JWG Meeting?
- The joint statement said that no terror organizations including UN designated terrorists should be provided sanctuary or allowed to use the territory of Afghanistan.
- India also agreed to offer:
- Customised capacity building courses for UNODC (United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime) Officials and stakeholders; and
- Cooperation on initiatives to counter drug trafficking and rehabilitation efforts for Afghan drug users, especially women.
What is India’s Previous Assistance Measures to Afghanistan?
- Food Grains:
- In 2022, India signed an agreement with the United Nations World Food Programme (WFP) for the distribution of 50,000 MT of wheat that it has committed to sending to Afghanistan as part of a humanitarian assistance.
- India committed to delivering 75,000 MT of wheat to Afghanistan in 2020 to combat the global pandemic of COVID-19 and related issues of food security.
- India distributed 2000 tonnes of pulses to Afghanistan in 2018 to promote food security, particularly for children during times of drought.
- Medical Supplies:
- India supplied 5 lakh tablets of Hydroxy-chloroquinine, 1 Lakh tablets of Paracetamol, and 50,000 pairs of surgical gloves to the Government of Afghanistan in 2020.
- India established a Medical Diagnostic Centre in Kabul in 2015, providing the latest diagnostic facilities to Afghan children and generating goodwill for India.
- Infrastructure:
- Since 2001, India has committed USD 3 billion towards rebuilding and reconstruction of Afghanistan.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. What is the importance of developing Chabahar Port by India? (2017)
(a) India’s trade with African countries will enormously increase.
(b) India’s relations with oil-producing Arab countries will be strengthened.
(c) India will not depend on Pakistan for access to Afghanistan and Central Asia.
(d) Pakistan will facilitate and protect the installation of a gas pipeline between Iraq and India.
Ans: (c)
- A commercial contract for the development and operations of Chabahar Port was signed between India and Iran in 2016. The contract is for a period of 10 years.
- Chabahar Port will provide India with an alternative and reliable access route into Afghanistan and also a reliable and more direct sea-route access into the Central Asian region.
- It will eliminate dependency on Pakistan for access to Afghanistan and Central Asia. Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. India’s proximity to the two of the world’s biggest illicit opium-growing states has enhanced her internal security concerns. Explain the linkages between drug trafficking and other illicit activities such as gunrunning, money laundering and human trafficking. What countermeasures should be taken to prevent the same? (2018)
Governance
National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC)
For Prelims: National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC), University Grants Commission (UGC), Paramarsh, All India Survey on Higher Education (AISHE), 2020-2021.
For Mains: Current Accreditation Criteria in India, Challenges Related to India’s Higher Education System.
Why in News?
Recently, the National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC) has been facing allegations of irregularities in its functioning.
What is NAAC?
- About:
- Established in 1994, it is an autonomous body under the University Grants Commission (UGC) responsible for assessing the quality of higher educational institutions in India.
- Functions of NAAC:
- Through a multi-layered assessment process, it awards grades ranging from A++ to C based on parameters such as curriculum, faculty, infrastructure, research and financial well-being.
- Allegations:
- The former chairperson of NAAC's executive committee resigned after alleging that malpractices were leading to questionable grades being awarded to some institutions.
- An inquiry commissioned found irregularities in the IT system and allocation of assessors.
- The inquiry also highlighted that nearly 70% of experts from the pool of around 4,000 assessors have not received any opportunity to make site visits.
- As of January 2023, out of the 1,113 universities and 43,796 colleges in the All India Survey on Higher Education (AISHE), 2020-2021, only 418 universities and 9,062 colleges were NAAC-accredited.
What are the Current Accreditation Criteria in India?
- Criteria:
- Currently, only institutes that are at least 6 years old or from where at least two batches of students have graduated can apply for accreditation, which is valid for 5 years.
- Accreditation Mandate:
- Accreditation by NAAC is voluntary, though many circulars have been issued by the UGC urging institutions to undergo assessment.
- Efforts to Expedite Accreditation:
- The UGC launched a scheme named 'Paramarsh' in 2019 to mentor institutes aspiring to get accredited.
- NAAC explored the possibility of issuing Provisional Accreditation for Colleges (PAC) to one-year-old institutes.
- The National Education Policy (2020) has set an ambitious target of getting all higher educational institutes to obtain the highest level of accreditation over the next 15 years.
What are the Other Challenges in India’s Higher Education System?
- Limited Access: Despite efforts to increase access to higher education, many students from marginalised communities still face barriers to entry, including financial constraints and lack of educational opportunities.
- Especially, the number of students in the Persons with Disabilities category dropped in 2020-21 to 79,035 from 92,831 in 2019-20.
- Gender Inequality: Women continue to face significant barriers to accessing higher education in India, including social and cultural biases and a lack of support systems.
- According to All India Survey on Higher Education (AISHE), 2020-2021, the female enrolment in higher education programmes was 49% of total enrolments in 2020-21.
- Employability Issues: Despite having a large number of graduates, many students in India struggle to find employment due to a lack of practical skills and industry-relevant education.
- Also, India lags behind many other countries in terms of research output, and there is a lack of a research culture in many higher education institutions.
Way Forward
- Promote Digital Learning: The use of digital technology can help make education more accessible, cost-effective, and efficient.
- Institutions should invest in digital infrastructure and provide training to students and faculty to adapt to new technologies.
- Increase Accreditation: The accreditation process should be made more transparent and accessible to encourage more institutions to seek accreditation.
- The government should also ensure that the accreditation process is fair and free from corruption.
- Promote International Collaborations: International collaborations can help improve the quality of education and research in India.
- Institutions should partner with foreign institutions to exchange knowledge, expertise, and resources.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. What is the aim of the programme ‘Unnat Bharat Abhiyan’? (2017)
(a) Achieving 100% literacy by promoting collaboration between voluntary organisations and the government's education system and local communities.
(b) Connecting institutions of higher education with local communities to address development challenges through appropriate technologies.
(c) Strengthening India’s scientific research institutions in order to make India a scientific and technological power.
(d) Developing human capital by allocating special funds for health care and education of rural and urban poor, and organising skill development programmes and vocational training for them.
Ans: (b)
Important Facts For Prelims
Coronary Heart Disease
Why in News?
Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death worldwide, with coronary heart disease being a major concern among researchers.
What is Coronary Heart Disease?
- About:
- Coronary heart disease (CHD) is a condition in which the blood vessels that supply the heart with oxygen-rich blood become narrow due to the buildup of fatty deposits (plaques) inside the arteries.
- Over time, these deposits can harden and narrow the arteries, reducing the flow of blood to the heart.
- Causes:
- Unhealthy lifestyles, poor diets, physical inactivity, tobacco use, and harmful levels of alcohol consumption are the major contributors to coronary heart disease.
- Damaged heart tissue cannot be regrown in humans, and the only option is to undergo heart transplant, which comes with its own complications.
- Unhealthy lifestyles, poor diets, physical inactivity, tobacco use, and harmful levels of alcohol consumption are the major contributors to coronary heart disease.
- Recent Studies:
- A group of scientists has come up with a solution where healthy skin cells from an adult can be converted into heart cells using special proteins.
- Converting cells from one form to another, known as cellular reprogramming, involves specific proteins called transcription factors, which alter the expression of genes within a cell and direct it to take on a new cellular identity.
- The researchers established a recombinant protein toolbox consisting of six potential cardiac transcription factors: GATA4, MEF2C, TBX5, ETS2, MESP1, and HAND2.
- Each of these proteins plays a significant role in reprogramming fibroblasts.
- The advantage of using recombinant proteins is that they work their miracle inside the nucleus and eventually disappear over time without leaving behind their toxic waste, unlike their generic counterparts.
- A group of scientists has come up with a solution where healthy skin cells from an adult can be converted into heart cells using special proteins.
What are the Initiatives to Promote Awareness About Cardiovascular Diseases?
Conclusion
This study offers a safer approach for direct cardiac reprogramming using recombinant proteins, which can then be used to reprogram cardiac fibroblasts and provides hope for those suffering from heart disease and the possibility of developing a personalised treatment option that is both safe and efficient.
Science & Technology
Megha-Tropiques-1 Satellite
Prelims: Megha-Tropiques-1 Satellite, ISRO, Re-entry of Satellite, CNES, Earth Observation Satellite.
Mains: Megha-Tropiques-1 Satellite.
Why in News?
Recently, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has successfully carried out the controlled Re-Entry experiment for the decommissioned Megha-Tropiques-1 (MT-1) Satellite.
- An uninhabited area in the Pacific Ocean between 5°S to 14°S latitude and 119°W to 100°W longitude was identified as the targeted re-entry zone for MT1.
What is Controlled Re-entry?
- Controlled re-entries involve de-orbiting to very low altitudes to ensure the impact occurs within a targeted safe zone.
- Usually, large satellites or rocket bodies, which are likely to survive aero-thermal fragmentation upon re-entry, are made to undergo controlled re-entry to limit ground casualty risk.
- Aero-Thermal Fragmentation is a process in which an object traveling through the Earth's atmosphere at high-speed experiences extreme heat and pressure, causing it to break apart or fragment.
- However, all such satellites are specifically designed to undergo controlled re-entry at end-of-life.
What are the Key points of the MT-1 Satellite?
- About:
- It is an Indo-French Earth Observation Satellite, which was launched in October 2011 for carrying out tropical weather and climate studies
- The main objective of this mission is to understand the life cycle of convective systems that influence the tropical weather and climate and their role in the associated energy and moisture budget of the atmosphere in tropical regions.
- With its circular orbit inclined 20° to the equator, it is a unique satellite for climate research that aided scientists seeking to refine prediction models.
- Payloads:
- Microwave Analysis and Detection of Rain and Atmospheric Structures (MADRAS), an Imaging Radiometer developed jointly by CNES (Centre National d'études Spatiales), France and ISRO;
- Sounder for Probing Vertical Profiles of Humidity (SAPHIR), from CNES;
- Scanner for Radiation Budget (ScaRaB), from CNES;
- Radio Occultation Sensor for Vertical Profiling of Temperature and Humidity (ROSA), procured from Italy.
Important Facts For Prelims
CEA Regulations for Great Indian Bustard Area
Why in News?
The Central Electricity Authority (CEA) has issued Draft Central Electricity Authority (Construction of Electric Lines in Great Indian Bustard Area) Regulations, 2023, making mandatory for electric lines to be underground or overhead through the ‘Great Indian Bustard (GIB) Area’.
- The regulations came in light of a case in the Supreme Court (SC) on the issue of threat to the endangered Great Indian Bustards.
- As per the regulations, all electric lines of 33 kV and below passing through the ‘Great Indian Bustard Area’ will be underground, while those above 33KV will be overhead lines installed with bird flight diverters.
- These diverters are aimed at improving power line visibility for birds and reducing the risk of collision.
What is GIB?
- About:
- The Great Indian Bustard (Ardeotis nigriceps), the State bird of Rajasthan, is considered India’s most critically endangered bird.
- It is considered the flagship grassland species, representing the health of the grassland ecology.
- Its population is confined mostly to Rajasthan and Gujarat. Small populations occur in Maharashtra, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh.
- Vulnerability:
- The bird is under constant threats due to collision/electrocution with power transmission lines, hunting (still prevalent in Pakistan), habitat loss and alteration as a result of widespread agricultural expansion, etc.
- Protection Status:
- IUCN red List: Critically Endangered
- Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES): Appendix1
- Convention on Migratory Species (CMS): Appendix I
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I
What are the Measures to Protect GIB?
- Species Recovery Programme:
- It is kept under the species recovery programme under the Integrated evelopment of Wildlife Habitats of the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- National Bustard Recovery Plans:
- It is currently being implemented by conservation agencies.
- Conservation Breeding Facility:
- MoEF&CC, Rajasthan government and Wildlife Institute of India (WII) have also established a conservation breeding facility in Desert National Park at Jaisalmer in June 2019.
- Project Great Indian Bustard:
- It has been launched by the Rajasthan government with an aim of constructing breeding enclosures for the species and developing infrastructure to reduce human pressure on its habitats.
- Eco-Friendly Measures:
- Task Force for suggesting eco-friendly measures to mitigate impacts of power transmission lines and other power transmission infrastructures on wildlife including the Great Indian Bustard.
Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Vision Screening for Drivers
Based on the observation by the Supreme Court-appointed Committee on Road Safety that 1.5 lakh people die every year as a result of road crashes, it has become imperative to provide vision screenings for drivers in the National Road Safety Plan (NRSP).
As per the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW), it has been established by traffic safety research groups that uncorrected vision issues are common among drivers, regular eye testing for vision prevents road accidents and should be included for road safety and drivers’ well-being.
While the MoHFW has endorsed the move, the next step is for the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) to include regular vision screening in its road safety activities. At present, eye check-up camps organised by the MoRTH are a one-time event.
Apart from participating in screening camps conducted by the MoRTH, Sightsavers India has been running a project called ‘RAAHI - National Truckers Eye Health Programme’ at major National Highways, over the last five years.
Read More: Road Accidents in India: Impacts & Way Forward
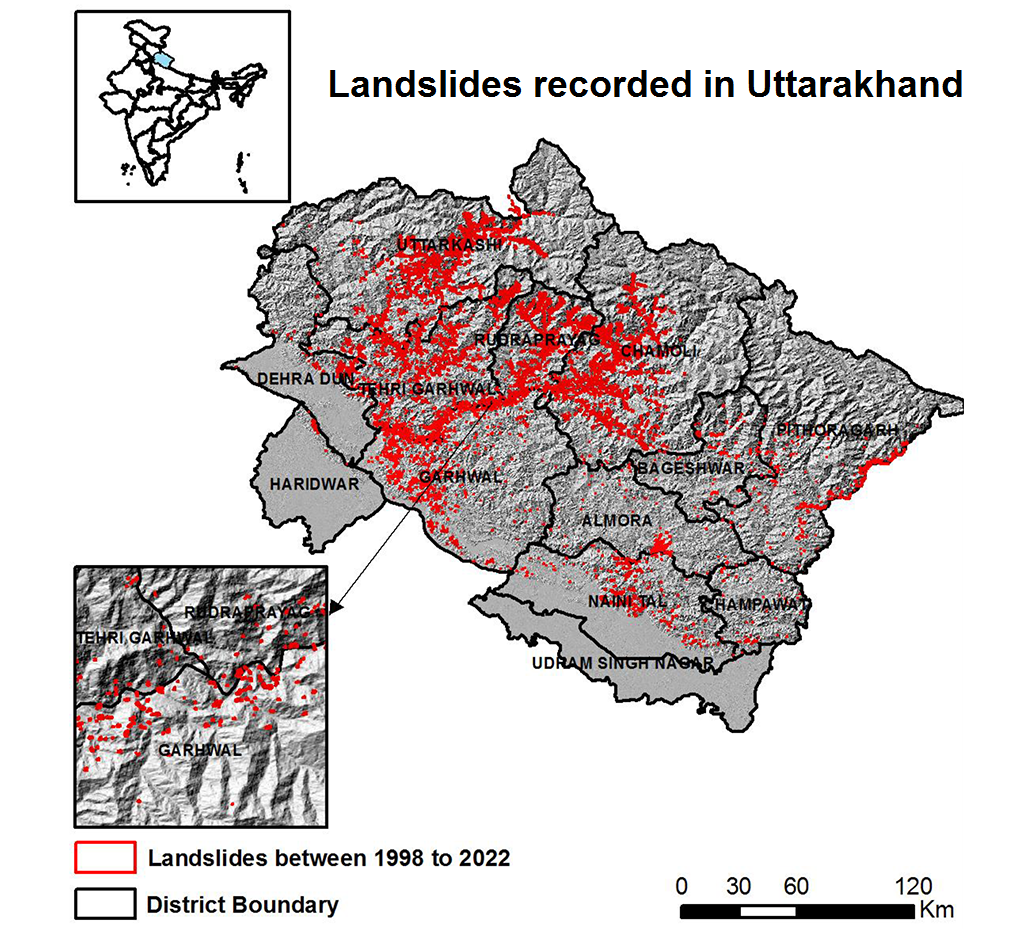
Most Landslide-prone Districts of India
According to satellite data by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), Rudraprayag and Tehri Garhwal in Uttarakhand are the most landslide-prone districts in the country. The recent case of Joshimath, Uttarakhand is also one of the major incidents that took place. Some of the other cases include the disaster in Kedarnath in 2013 and the landslides caused by the Sikkim earthquake in 2011.
Globally, landslides rank third in terms of deaths among natural disasters. India is among the four major countries where the risk of landslides is the highest. About 0.42 million square kilometres in the country are prone to landslides, which is 12.6% of the total land area of the country.
Read More: Landslide
H3N2 Outbreak
Across India, an outbreak of a respiratory illness with symptoms of cold, sore throat and fever accompanied by fatigue has been observed since December 2022 and January 2023.
The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) confirmed that Influenza Sub-type H3N2 has been causing this illness. It further warned that the virus appeared to lead to more hospitalisations than other Influenza subtypes.
There are four types of seasonal influenza viruses, types A, B, C and D. Influenza A and B viruses circulate and cause seasonal epidemics of disease. Influenza A viruses are the only influenza viruses known to cause flu pandemics (i.e., global epidemics of flu disease).
In June 2009, the WHO declared the H1N1 pandemic. This is also popularly referred to as the swine flu pandemic. Before the H1N1 pandemic in 2009, the influenza A (H1N1) virus had never been identified as a cause of infections in people. Genetic analyses of this virus have shown that it originated from animal influenza viruses and is unrelated to the human seasonal H1N1 viruses that have been in general circulation among people since 1977. In 2013, India saw a massive outbreak of swine flu.
Read More: 2009 Swine Flu Pandemic
Attukal Pongala
Considered one of the largest women's gatherings in the world, around 15 lakh women participated in the annual Attukal Pongala festival of Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala. The festival includes offering Pongala, a sweet delicacy made of rice to the deity of Attukal Bhagavathy Temple in Kerala's Thiruvananthapuram.
The highlight of the ten-day festival is the mass offering that takes place on the ninth day. Women from across the state make it to the capital in huge numbers.
In 2009, the ritual had made it to the Guinness Book of World Records for being the largest religious gathering of women on a single day when over 2.5 million people took part in it.
Attukal Temple is called the "Women's Sabarimala" as only women perform rituals, while it is predominantly men who undertake the pilgrimage to the hill shrine of Lord Ayyappa at Sabarimala.
Read More: Sabrimala Temple, Temples in India (Map)