Artificial Intelligence Safety Summit 2023
For Prelims: Artificial Intelligence, Frontier AI, Ethical AI, Bletchley Park, Bletchley Park Declaration
For Mains: Science and Technology- Developments and their Applications and Effects in Everyday Life, Awareness in the fields of IT , Disadvantages of AI, Applications of AI
Why in News?
The Artificial Intelligence (AI) Safety Summit 2023 held at Bletchley Park, England has marked a significant turning point in the global approach to tackling the challenges posed by frontier AI technologies.
- To tackle these challenges, 28 major countries, including the United States, China, India, and the European Union, signed the Bletchley Park Declaration at this first-ever AI Safety Summit.
- This landmark declaration seeks to create a collective understanding and coordinated approach to address the potential risks and benefits of advanced AI systems, known as frontier AI.
Note
- Frontier AI is defined as highly capable foundation generative AI models that can produce realistic and convincing outputs, such as text, images, audio, or video, on demand.
What are the Key Highlights of Artificial Intelligence Safety Summit 2023?
- Bletchley Park Declaration:
- The Bletchley Park Declaration is the first global pact on tackling frontier AI risks, and it reflects a high-level political consensus and commitment among the major AI players in the world.
- It acknowledges the potential of AI to enhance human well-being but also recognizes the risks posed by AI, especially frontier AI, which may cause serious harm, either deliberate or unintentional, particularly in domains like cybersecurity, biotechnology, and disinformation.
- It emphasizes the need for international cooperation to address AI-related risks, as they are inherently global, and calls for collaboration among all actors, including companies, civil society, and academia.
- The declaration also announces the establishment of a regular AI Safety Summit, which will provide a platform for dialogue and collaboration on frontier AI safety.
- The next summit will be hosted by France within a year, and South Korea will co-host a mini virtual AI summit in the next six months.
- India's Stance at the Summit:
- India has shifted from a stance of not considering AI regulation to actively formulating regulations based on a risk-based, user-harm approach.
- India called for a global framework for the expansion of "ethical" AI tools, signaling a commitment to responsible AI usage.
- India has shown interest in establishing regulatory bodies at both domestic and international levels to ensure the responsible use of AI.
- Digital India Act, 2023 which is yet to Implement , is expected to introduce issue-specific regulations for online intermediaries, including AI-based platforms.
- India has shifted from a stance of not considering AI regulation to actively formulating regulations based on a risk-based, user-harm approach.
Key Facts About Bletchley Park
- Bletchley Park is located approximately 80 km north of London in Buckinghamshire, England.
- During World War II, it served as the main site for the British Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS).
- Bletchley Park during the war, worked on deciphering enemy messages.
- The Turing Bombe, developed at Bletchley Park, is renowned for its pivotal role in breaking the supposedly unbreakable German Enigma code.
- This electro-mechanical device significantly accelerated the code breaking process, contributing to the Allies' success during World War II.
- Bletchley Park also developed the Colossus machine, often regarded as the world's first programmable electronic digital computer.
- The principles and innovations developed at Bletchley Park continue to influence modern computing and artificial intelligence.
- Bletchley Park is now a museum and a historic site, attracting visitors interested in its wartime history and contributions.
- During World War II, it served as the main site for the British Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS).
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Q. Consider the following pairs: (2018)
| Terms sometimes seen in news | Context/Topic | |
| 1. | Belle II experiment | Artificial Intelligence |
| 2. | Blockchain technology | Digital/ Cryptocurrency |
| 3. | CRISPR – Cas9 | Particle Physics |
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains:
Q. What are the main socio-economic implications arising out of the development of IT industries in major cities of India? (2021)
Extension of Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana
For Prelims: Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana, National Food Security Act, 2013, Antyodaya Anna Yojana , Targeted Public Distribution System, e-Rupi.
For Mains: Issues Arising out of Design and Implementation of Government Policies, Beneficiaries under NFSA.
Why in News?
Recently, the Indian Prime Minister has announced an extension of the Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana (PMGKAY) for an additional five years.
What is PMGKAY?
- The PMGKAY was first introduced in 2020 during the Covid-19 pandemic, and was designed to provide 5kg free foodgrains to eligible ration card holders under the National Food Security Act, 2013 (NFSA).
- Initially set to expire in December 2022, the scheme was extended till December 2023 and now, it has been extended for an additional five years.
- Since its inception, the government has allocated 1,118 lakh metric tonnes of foodgrains from its central procurement pool at a cost of Rs 3.9 lakh crore.
What is the National Food Security Act, 2013?
- About:
- National Food Security Act, (NFSA) 2013 marks a paradigm shift in the approach to food security from welfare to rights based approach.
- Beneficiaries:
- The Act legally entitled upto 75% of the rural population and 50% of the urban population to receive subsidized food grains under Targeted Public Distribution System.
- About two thirds of the population therefore is covered under the Act to receive highly subsidized foodgrains.
- It encompasses two categories of ration card holders: Antyodaya Anna Yojana (AAY) and Priority Households (PHH).
- As a step towards women empowerment, the eldest woman of the household of age 18 years or above is mandated to be the head of the household for the purpose of issuing ration cards under the Act.
- The Act legally entitled upto 75% of the rural population and 50% of the urban population to receive subsidized food grains under Targeted Public Distribution System.
- Provision:
- Under this program, AAY households are entitled to receive 35 kg of foodgrains every month, regardless of the number of family members.
- Priority Households receive food grains based on family size, with each member getting 5 kg per month.
- Merger of PMGKAY and NFSA:
- In January 2023, the PMGKAY was integrated with the NFSA, resulting in the provision of all rations for AAY and PHH families at no cost.
- This merger eliminated the extra provisions that were introduced during the Covid-19 pandemic by incorporating the free component of the PMGKAY into the NFSA.
What are the Impacts of the Extension of PMGKAY?
- Positive Impacts:
- Addressing Immediate Food Security Needs: The extension provides relief to lower-income households, ensuring continued access to essential food supplies, addressing immediate food security concerns.
- In times of economic distress or natural disasters, the program provides a safety net, offering immediate relief to those facing sudden hardships, ensuring basic sustenance during crises.
- Boosting Rural Economy: The procurement of foodgrains for the scheme provides support to local farmers and agricultural communities, contributing to rural economic growth and stability.
- Social Cohesion: The program fosters a sense of community welfare, where government initiatives ensure no one goes hungry, promoting social cohesion and a sense of collective responsibility towards those in need.
- Addressing Immediate Food Security Needs: The extension provides relief to lower-income households, ensuring continued access to essential food supplies, addressing immediate food security concerns.
- Negative Impacts:
- Long-term Fiscal and Economic Concerns: The program's extension incurs significant fiscal costs.
- Over time, the cost may escalate due to rising procurement expenses, leading to a burden on the government's budget.
- There is a risk of straining the fiscal deficit, especially if accompanied by lack of corresponding revenue increases.
- Distortion in Market Dynamics: The extended scheme, by providing free or highly subsidized foodgrains, might disrupt market dynamics, impacting the agricultural sector and distorting prices.
- Dependency and Sustainability Issues: The perpetuation of free foodgrains could create dependency among beneficiaries, reducing the drive for self-sufficiency or alternative livelihood efforts.
- Depending on government handouts may not be a sustainable, long-term solution for addressing poverty and hunger.
- Competitive Populism and Policy Consistency: This extension might lead to competitive populist measures among political parties, which may drive unsustainable policies and put pressure on public finances.
- Long-term Fiscal and Economic Concerns: The program's extension incurs significant fiscal costs.
Way Forward
- Short Term:
- Digital Vouchers for Food Access: Utilizing e-Rupi as digital vouchers specifically for purchasing essential food items.
- The government can allocate E-Rupi vouchers to targeted beneficiaries, ensuring that the funds are utilized solely for purchasing nutritious food.
- Crowdsourced Distribution Networks: Developing technology platforms or apps that facilitate the distribution of excess food from individuals, restaurants, and supermarkets to those in need.
- This would involve community participation in identifying surplus food and efficiently distributing it to those who require it.
- Digital Vouchers for Food Access: Utilizing e-Rupi as digital vouchers specifically for purchasing essential food items.
- Long Term:
- Economic Empowerment Programs: Instead of perpetual handouts, there is a need to invest in programs that empower individuals economically.
- This could include skill development, job training, and entrepreneurial opportunities to help people become self-sufficient.
- Gradual Reduction of Subsidies: Instead of abruptly stopping the free ration program, gradually phase it out while simultaneously implementing other support systems. This can help avoid sudden shocks to vulnerable populations and the economy.
- Economic Empowerment Programs: Instead of perpetual handouts, there is a need to invest in programs that empower individuals economically.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to the provisions made under the National Food Security Act, 2013, consider the following statements: (2018)
- The families coming under the category of ‘below poverty line (BPL)’ only are eligible to receive subsidised food grains.
- The eldest woman in a household, of age 18 years or above, shall be the head of the household for the purpose of issuance of a ration card.
- Pregnant women and lactating mothers are entitled to a ‘take-home ration’ of 1600 calories per day during pregnancy and for six months thereafter.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 3 only
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q.1 In what way could replacement of price subsidy with Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) change the scenario of subsidies in India? Discuss. (2015)
Q.2 What are the salient features of the National Food Security Act, 2013? How has the Food Security Bill helped in eliminating hunger and malnutrition in India? (2021)
India-Bhutan Relations
For Prelims: India-Bhutan Relations, 13th Five-Year Plan, G20 Summit, Global South, Renewable energy, Doklam standoff in 2017, Trade Deficit.
For Mains: India-Bhutan Relations, India and its neighborhood- relations, Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
Why in News?
Recently, India and Bhutan agreed to discuss new routes of Regional Connectivity, and upgrade border and immigration posts, in order to enhance trade and Partnership during Bhutan King’s India visit.
What are the Key Highlights of the Discussion?
- Regional Connectivity:
- India and Bhutan have agreed to discuss new routes of regional connectivity, which includes the development of a cross-border rail link between Gelephu in Bhutan and Kokrajhar in Assam, spanning 58 km.
- Additionally, there is a plan to explore a second rail link of approximately 18 km between Samtse in Bhutan and Banarhat in the tea gardens area of West Bengal.
- Both sides discussed upgrading border and immigration posts to support this project, and it could be a significant development in the border area.
- Trade and Connectivity:
- The two countries agreed to facilitate trade by allowing Bhutanese trade items to be carried further from Haldibari in West Bengal to Chilahati in Bangladesh, aiming to enhance trade opportunities and ease the movement of goods between Bhutan and Bangladesh through Indian territory.
- Immigration Check Post:
- The Darranga-Samdrup Jongkhar border crossing between Assam and Bhutan's SouthEastern district will be designated as an immigration check post.
- This will allow not only Indian and Bhutanese nationals but also third country nationals to enter and exit the area, promoting tourism and enhancing connectivity.
- Support for Bhutanese SEZ Project:
- The two sides agreed to strengthen trade infrastructure with the upgradation of an existing land customs station at Dadgiri (Assam) to a modernised “Integrated Check Post” (ICP) along with “development of facilities on the Bhutanese side at Gelephu”, indicating India’s support to the Bhutanese SEZ project.
- Development Assistance:
- India has committed to continue its support for Bhutan's socio-economic development, with a particular focus on the 13th Five-Year Plan. This underscores the enduring commitment to their strong bilateral ties.
- For the 12th Five Year Plan, India’s contribution of Rs 4,500 crore constituted 73% of Bhutan’s total external grant component.
- India has committed to continue its support for Bhutan's socio-economic development, with a particular focus on the 13th Five-Year Plan. This underscores the enduring commitment to their strong bilateral ties.
- Lauds India’s Support for Global South:
- Bhutan lauded India’s successful organization of the recent G20 Summit, praising India for fostering consensus and constructive decisions outlined in the Delhi Declaration.
- Bhutan commended India’s dedication to integrating the interests and priorities of Global South countries in G20 deliberations.
- India-Bhutan Energy Partnership:
- Progress on the construction of the 1020 MW Punatsangchhu-II hydropower project was noted with satisfaction, with its early commissioning expected in 2024.
- An agreement was reached to expand the existing India-Bhutan energy Partnership from hydro to non-hydro renewables, including solar energy, as well as green initiatives related to hydrogen and e-mobility.
- India assured essential technical and financial support for projects in these areas.
- Recalling Operation All Clear:
- Bhutan King recalled Operation All Clear which was a military operation conducted by the Royal Bhutan Army in 2003 against Assam separatist insurgent groups in the southern regions of Bhutan.
What is the Significance of Bhutan for India?
- Strategic Importance:
- Bhutan shares its borders with India and China, and its strategic location makes it an important buffer state for India's security interests.
- India has provided Bhutan with assistance in areas such as defense, infrastructure, and communication, which has helped to maintain Bhutan's sovereignty and territorial integrity.
- India has helped Bhutan build and maintain its border infrastructure, such as roads and bridges, to strengthen its defense capabilities and ensure its territorial integrity.
- In 2017, during the Doklam standoff between India and China, Bhutan played a crucial role in allowing Indian troops to enter its territory to resist Chinese incursions.
- Economic Importance:
- India is Bhutan's largest trading partner, and Bhutan's major export destination.
- Bhutan's hydropower potential is a significant source of revenue for the country, and India has been instrumental in assisting Bhutan in developing its hydropower projects.
- India also provides Bhutan with financial assistance for its development projects.
- Cultural Importance:
- Bhutan and India share strong cultural ties, as both countries are predominantly Buddhist.
- India has provided assistance to Bhutan in preserving its cultural heritage, and many Bhutanese students come to India for higher education.
- Environmental Importance:
- Bhutan is one of the few countries in the world that has pledged to remain carbon-neutral, and India has been a key partner in helping Bhutan achieve this goal.
- India has provided assistance to Bhutan in areas such as Renewable energy, forest conservation, and sustainable tourism.
What are the Challenges in the India-Bhutan Relations?
- China's Growing Influence:
- China's increasing presence in Bhutan, particularly along the disputed border between Bhutan and China, has raised concerns in India. India has been Bhutan's closest ally and has played a key role in protecting Bhutan's sovereignty and security.
- However, China's growing economic and military influence in the region poses a challenge to India's strategic interests in Bhutan.
- Border Disputes:
- India and Bhutan share a 699 km long border, which has been largely peaceful.
- However, there have been some incidents of border incursions by Chinese forces in recent years.
- The Doklam standoff in 2017 was a major flashpoint in the India-China-Bhutan tri-junction. Any escalation of such disputes could strain India-Bhutan relations.
- Hydropower Projects:
- Bhutan's hydropower sector is a key pillar of its economy, and India has been a major partner in its development.
- However, there have been concerns in Bhutan over the terms of some of the hydropower projects, which have been seen as too favorable to India.
- This has led to some public opposition in Bhutan to Indian involvement in the sector.
- Bhutan's hydropower sector is a key pillar of its economy, and India has been a major partner in its development.
- Trade Issues:
- India is Bhutan's largest trading partner, accounting for over 80% of Bhutan's total imports and exports. However, there have been some concerns in Bhutan over the trade imbalance, with Bhutan importing more from India than it exports.
- Bhutan has been seeking greater access to the Indian market for its products, which could help to reduce the Trade Deficit.
- India is Bhutan's largest trading partner, accounting for over 80% of Bhutan's total imports and exports. However, there have been some concerns in Bhutan over the trade imbalance, with Bhutan importing more from India than it exports.
What are the Key Facts Related to Bhutan?
- About:
- Bhutan is nestled between India and China and is a landlocked country. Mountains and valleys dominate the landscape of Bhutan.
- Thimphu is the Capital City of Butan.
- Bhutan became a democracy in 2008 after the first democratic elections were held in the country. The King of Bhutan is the Head of State.
- It is named 'Kingdom of Bhutan'. The Bhutanese name is Druk Gyal Khap, which means the 'Land of the Thunder Dragon'.
- Bhutan is nestled between India and China and is a landlocked country. Mountains and valleys dominate the landscape of Bhutan.
- River:
- The longest river in Bhutan is the Manas River with over 376 km in length.
- The Manas River is a transboundary river in the Himalayan foothills between southern Bhutan and India.
- The longest river in Bhutan is the Manas River with over 376 km in length.
- Government:
- Parliamentary monarchy.
- Border:
- Bhutan borders only two countries: India and Tibet, an autonomous region of China.
Way Forward
- India can help Bhutan to boost its economy by investing in infrastructure development, tourism, and other sectors. This will not only help Bhutan to become self-reliant but also create employment opportunities for its people.
- India and Bhutan can promote cultural exchange programs to foster greater understanding and appreciation of each other's culture, art, music, and literature.
- A visa-free movement of peoples from both countries can strengthen sub-regional cooperation.
- India and Bhutan can strengthen their strategic cooperation to address shared security concerns. They can work together to combat terrorism, drug trafficking, and other transnational crimes.
India China Partnership for Global Harmony
For Prelims: A Global Community of Shared Future: China’s Proposals and Actions, Protectionism, G20 summit, BRICS, Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, New Development Bank, Conference on Disarmament, Sustainable Development Goals, Line of Actual Control, China's Belt and Road Initiative.
For Mains: Role of India and China in Building a Global Community of a Shared Future, Challenges and Obstacles in India-China Collaboration.
Why in News?
Recently, China released a white paper “A Global Community of Shared Future: China’s Proposals and Actions”, to address the common challenges and opportunities faced by humanity in the 21st century.
- Amidst global turmoil, with Russia- Ukraine crisis and issues in West Asia, attention turns to the historically linked civilizations of India and China. Their shared visions for the future could provide hope for global harmony.
What are the Key Vision Points for the Global Community of Shared Future?
- Economic Globalization and Inclusivity: Uphold the correct path of economic globalization. Jointly build an open world economy that represents the interests of developing nations, rejecting unilateralism, protectionism, and zero-sum games.
- Peace, Cooperation, and Development: Embrace peace, development, cooperation, and win-win results, steering clear of colonialism and hegemony, fostering joint efforts for global peace and contribution.
- Global Community of Shared Destiny: Construct a global community of shared destiny to evade conflict between emerging and established powers, emphasizing mutual respect, equity, and beneficial cooperation for deeper global partnerships.
- Genuine Multilateralism and Fair International System: Rejecting bloc politics and unilateral thinking, advocating for a fair, UN-centered international system. Upholding international law as the basis for global norms and order and promoting true multilateralism.
- Promotion of Common Human Values: Promoting equity, justice, democracy, and freedom without imposing a singular model of democracy.
- Embrace harmony amidst diversity, respecting each nation's right to choose its social systems and development paths.
How can India and China Cooperate in Building a Global Community of a Shared Future?
- About:
- As two ancient Asian civilizations that have been living side by side for thousands of years, China and India share common thoughts on the future and destiny of mankind.
- They have the responsibility, the ability and the opportunity to set an example for the rest of the world with their Oriental wisdom and civilizational heritage.
- The Chinese people have cherished the vision of “a world of fairness and justice for the common good” since ancient times.
- Ancient Indian literature also records the motto of “Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam”, which means “the world is one family” in Sanskrit.
- It was also used as the theme of the G20 summit held in New Delhi in September 2023.
- Ancient Indian literature also records the motto of “Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam”, which means “the world is one family” in Sanskrit.
- Also, in the 1950s, India and China jointly established the Five Principles of Peaceful Co-existence:
- Mutual respect for each other’s territorial integrity and sovereignty
- Mutual non-aggression
- Mutual non-interference
- Equality and mutual benefit
- Peaceful co-existence
- Areas and Platforms of Cooperation between India and China:
- Economic Cooperation: India and China are both members of the BRICS, the SCO, the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB), the New Development Bank (NDB).
- They can enhance their economic cooperation through these mechanisms and promote an open, inclusive, and balanced world economy that reflects the demands and interests of the developing countries.
- They can also expand their bilateral trade and investment, and explore new areas of cooperation such as digital economy, green economy, and innovation.
- Security Cooperation: Both India and China are members of the United Nations Conference on Disarmament (CD).
- They can cooperate in combating terrorism, extremism, and separatism, and maintain regional peace and stability.
- Cultural Cooperation: India and China are both ancient civilizations with rich and diverse cultures.
- They can enhance their cultural cooperation and mutual learning through increased people-to-people contact.
- They can also increase their exchanges and interactions in the fields of education, tourism, sports, youth, and media, and foster mutual understanding and friendship between the two peoples.
- Environmental Cooperation: India and China are both parties to the Paris Agreement on Climate change and the Convention on Biological Diversity.
- They can enhance their environmental cooperation and coordination on issues such as emission reduction, renewable energy, biodiversity conservation, and disaster management.
- They can also support each other in implementing Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Economic Cooperation: India and China are both members of the BRICS, the SCO, the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB), the New Development Bank (NDB).
- Benefits of India and China Cooperation
- Economic Growth and Trade Opportunities:
- Market Expansion: Both India and China possess massive consumer markets. Collaboration between the two could lead to greater trade opportunities, expanding markets for goods and services.
- Complementary Economies: China's manufacturing strength and infrastructure, coupled with India's services sector and skilled workforce, can create a symbiotic economic relationship.
- This collaboration can fill gaps and leverage the strengths of each other's economies.
- Technological Advancements and Innovation: Collaborative efforts in technology, research, and innovation can lead to breakthroughs in various sectors such as renewable energy, healthcare, and artificial intelligence.
- Pooling resources and expertise could accelerate advancements in areas like space exploration, cybersecurity, and climate change mitigation.
- Global Governance and Diplomacy: By aligning in global issues, both countries can act as a counterbalance to unilateral actions by other global powers, promoting a more multipolar world order.
- Together, India and China could influence international forums, speaking with a collective voice on global issues such as trade, security, and climate change.
- Working in tandem could strengthen their diplomatic outreach, potentially leading to more effective resolutions.
- Economic Growth and Trade Opportunities:
What are the Challenges and Obstacles in India-China Collaboration?
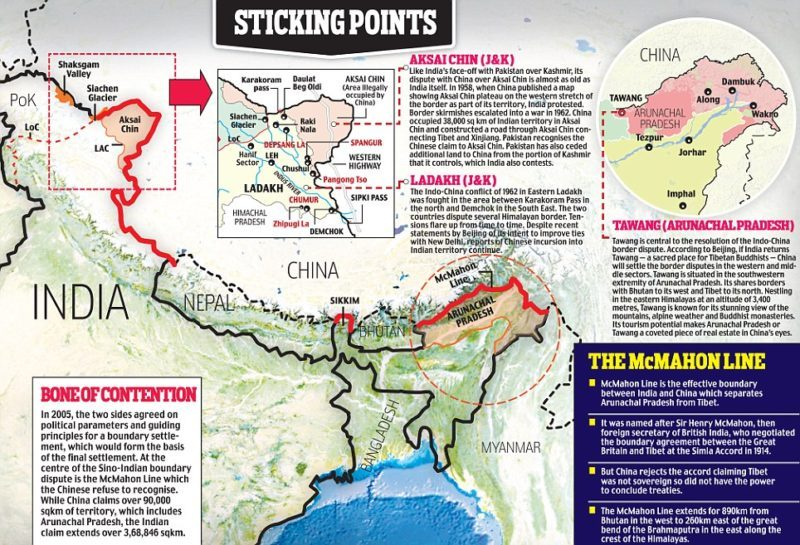
- Border Disputes: The long-standing border disputes, especially along the Line of Actual Control (LAC), have resulted in occasional military standoffs, creating mistrust and a potential for escalation.
- Also, India has criticized China's recent assertion regarding Arunachal Pradesh.
- Historical Conflicts and Layer of Suspicion: Historical conflicts and the 1962 Sino-Indian war have left deep-seated mistrust. Both nations view the other's intentions suspiciously, hindering efforts towards cooperation.
- Alongside China's use of its veto power against India in the UNSC and its close ties with Pakistan, India's abstention from China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) further contributes to the complexity of relations, adding layers of geopolitical tension and mutual suspicion.
- Strategic Competition and External Pressure: The strategic competition between China and India is a reality that cannot be ignored, as both countries have their own national interests and aspirations.
- The strategic competition is also influenced by external pressure, especially from the United States and its allies, who seek to contain China’s rise.
- Divergent Strategic Interests: Their strategic interests sometimes clash, especially in regions such as South Asia, where both countries seek influence.
- China's investments in countries surrounding India can be seen as encroaching on India's sphere of influence.
Way Forward
- Conflict Resolution Mechanisms: Establish robust conflict resolution mechanisms specifically tailored to address border disputes and other contentious issues, fostering a peaceful resolution through negotiations and mutual compromises.
- Implement confidence-building measures to reduce mistrust and promote transparency in military activities and intentions.
- Economic Collaboration: Encourage bilateral economic ties and cooperation by identifying sectors where both countries can mutually benefit. Focus on trade, investment, and joint ventures that promote shared prosperity.
- Respect for Sovereignty and Territorial Integrity: Affirm mutual respect for each other's sovereignty and territorial integrity, thereby maintaining stability and security in the region.
- Diplomatic Discretion and Sensitivity: Conduct diplomacy with a sense of discretion and sensitivity, acknowledging historical and geopolitical complexities without exacerbating existing tensions.
- Long-Term Vision: Strive for a long-term vision that prioritizes peace, stability, and mutual prosperity, setting aside short-term differences for the greater good of both nations and the region.
- Building trust, fostering understanding, and promoting common interests over differences is key to charting a positive path forward for India and China.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. “China is using its economic relations and positive trade surplus as tools to develop potential military power status in Asia”. In the light of this statement, discuss its impact on India as her neighbour. (2017)
The Indo-Pacific Maritime Domain Awareness
For Prelims: Indo-Pacific Maritime Domain Awareness (IPMDA), Indian Ocean Region (IOR), Goa Maritime Conclave (GMC), QUAD Grouping, Indian Navy’s Information Fusion Centre for Indian Ocean Region (IFC-IOR)
For Mains: Importance of institutions like QUAD in promoting and strengthening a rule-based world order.
Why in News?
Recently, the Chief of the Naval Staff Admiral addressed the fourth edition of the Goa Maritime Conclave (GMC) where he stressed that building networks and partnerships like the Indo-Pacific Maritime Domain Awareness (IPMDA) would be instrumental in ensuring the security and stability of the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
What is IPMDA?
- About:
- The IPMDA, introduced by the Quad group (consisting of India, Australia, Japan, and the US) at the Tokyo summit, 2022, aims to monitor "dark shipping" and create a more comprehensive and precise real-time maritime overview of partner nations' waters.
- It focuses on integrating the Pacific Islands, Southeast Asia, and the Indian Ocean region (IOR) in the Indo-Pacific.
- The IPMDA, introduced by the Quad group (consisting of India, Australia, Japan, and the US) at the Tokyo summit, 2022, aims to monitor "dark shipping" and create a more comprehensive and precise real-time maritime overview of partner nations' waters.
Dark Shipping
- Dark shipping is a term used to describe a vessel operating with its Automatic Identification System (AIS) turned off .
- AIS transponder systems transmit a ship’s position at sea, alongside identification data and other useful information that vessels and maritime authorities can reference.
- Objective:
- The initiative is a significant endeavour aimed at enhancing the security and stability of the Indo-Pacific region, which holds a central place in global geopolitics.
- It seeks to establish a comprehensive system for monitoring and securing maritime activities in the Indo-Pacific, ensuring the safety of critical sea lines of communication, and promoting cooperation among like-minded nations in the region.
- The initiative is a significant endeavour aimed at enhancing the security and stability of the Indo-Pacific region, which holds a central place in global geopolitics.
- Importance of Navy:
- To secure the IOR and Indo Pacific, the importance of the Navy cannot be emphasized enough, where force modernisation is the need of the hour.
- The Navy currently has over 140 ships and submarines and is targeting a 170 to 180 Navy by 2028, and aim is for the Navy to be fully AtmaNirbhar by 2047.
- To secure the IOR and Indo Pacific, the importance of the Navy cannot be emphasized enough, where force modernisation is the need of the hour.
What Has Been the Progress and Achievements of GMC?
- Collaboration Among Navies:
- The Conclave has successfully brought together navies from the Indian Ocean region to collaborate on addressing common maritime challenges. This cooperation has led to coordinated efforts in responding to natural disasters, conducting joint exercises, and sharing critical maritime information.
- Effective Response to Piracy:
- Establishment of robust mechanisms for information sharing, such as through Information Fusion Centre for the Indian Ocean Region (IFC-IOR) at Gurugram, has greatly improved the situational awareness in the region. Navies have been able to respond more effectively to maritime threats, piracy, and other security concerns.
- Improving MDA:
- Sharing of intelligence and information has also contributed to enhanced MDA. This has not only improved maritime security but also allowed for better management of marine resources and environmental protection.
- Adopting Common Maritime Priorities:
- The last edition of GMC saw all Members unanimously adopt the ‘Common Maritime Priorities (CMPs)’, which signaled the common approach of all Members to find regional solutions to regional problems.
What are the Major Challenges Related to the Indian Ocean Region?
- Geopolitical Competition: The Indian Ocean region is a hotspot for geopolitical competition among major powers and regional actors. Its location allows for power projection and influence over regional affairs.
- The presence of key choke points such as the Strait of Hormuz, the Bab el-Mandeb Strait, and the Malacca Strait further enhances its strategic significance.
- China’s Militarization Move: China has been a challenge to India’s interests and stability in the Indian Ocean. India's neighbors are receiving military and infrastructural assistance from China, including submarines for Myanmar, and its overseas military base in Djibouti (Horn of Africa).
- Maritime Security Threats: The IOR is vulnerable to various maritime security threats, including piracy, smuggling, illegal fishing, and terrorism. Also, the vastness of the Indian Ocean makes it challenging to monitor and secure its maritime domain effectively.
- Environmental Challenges: Climate change, rising sea levels, coral reef degradation, and marine pollution are significant environmental challenges in the IOR. These issues affect coastal communities, marine ecosystems, and the livelihoods of millions of people.
Way Forward
- Driving Blue Economy Initiatives: The IOR is rich in marine resources, and leveraging the blue economy can drive sustainable economic growth. There is a need to include promoting renewable energy generation from ocean resources, supporting sustainable fisheries, developing marine biotechnology, and fostering eco-tourism.
- Maritime Security Collaboration: Given the strategic importance of the IOR, enhancing maritime security is crucial.
- There is a need to involve strengthening information-sharing mechanisms, leveraging technology for maritime domain awareness, promoting joint naval exercises and patrols, and fostering cooperation in countering maritime threats such as piracy, illegal fishing, and smuggling.
- Climate Change Resilience: The IOR is highly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, including rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and ocean acidification.
- Innovative strategies could focus on implementing climate-resilient infrastructure, developing early warning systems, promoting sustainable coastal management practices, and facilitating regional cooperation for climate change adaptation and mitigation.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q1. With reference to ‘Indian Ocean Rim Association for Regional Cooperation (IOR-ARC)’, consider the following statements: (2015)
- It was established very recently in response to incidents of piracy and accidents of oil spills.
- It is an alliance meant for maritime security only.
Which of the statements given above is/ are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. With respect to the South China sea, maritime territorial disputes and rising tension affirm the need for safeguarding maritime security to ensure freedom of navigation and overflight throughout the region. In this context, discuss the bilateral issues between India and China. (2014)
Ethical Perspectives on Online Gaming
For Prelims: GST on Online Gaming
For Mains: Online Gaming Market in India, Issues Related to Online Gaming.
Why in News?
The recent case of suspension of a Police Sub-Inspector (PSI) in Pune, Mahrastra highlights complex ethical concerns surrounding online gaming and the responsibilities of a law enforcement officer.
What are the Ethical Implications Surrounding the Officer's Participation in Online Gaming?
- Arguments In Favor of Officer's Involvement in Online Gaming
- Personal Freedom and Individual Rights: The officer, like any other citizen, has the right to engage in legal recreational activities during personal time.
- The officer's use of personal funds for legal recreational activities, including online gaming, falls under their discretionary spending and financial autonomy.
- Adherence to Legal Norms: If the online gaming activity is legally permissible and the officer complies with the law, their engagement is within the framework of legal norms and should be respected as part of individual autonomy.
- Mitigation of Stress: Online gaming, like any leisure activity, might serve as a stress-relieving tool, providing a mental escape and relaxation from the pressures of the job.
- Personal Freedom and Individual Rights: The officer, like any other citizen, has the right to engage in legal recreational activities during personal time.
- Ethics Issues Involved:
- Violation of Organizational Standards:
- Breach of Code of Conduct: Engaging in online gaming without permission from the unit commander breaches the established code of conduct within the Maharashtra State Police, indicating a disregard for institutional regulations.
- Conflict with Professional Norms: Ethically, the officer's participation in online gaming during duty hours conflicts with the expected professionalism and ethical standards required within law enforcement.
- Negative Public Image and Trust Implications:
- Public Perception and Trust Erosion: Media interviews discussing personal victories in uniform undermine public confidence in the officer's professional integrity and the broader image of law enforcement, potentially eroding trust in the police force.
- Impact on Organizational Credibility: Ethically, such conduct damages the credibility and reputation of the entire police force, as the officer's actions are reflective of the institution, impacting its overall image and public trust.
- Role Model Expectations and Ethical Responsibilities:
- Role as a Public Figure: Ethically, as a law enforcement official, the officer is a public figure and is expected to serve as a role model, setting an example of ethical behavior and responsible conduct.
- Violation of Organizational Standards:
What are the Broader Ethical Issues Revolving Around Online Gaming?
- Addiction and Mental Health: Concerns arise from the addictive nature of certain online gaming activities, potentially leading to compulsive behavior, neglect of responsibilities, and adverse effects on mental health.
- Financial Risk and Vulnerability: Individuals, particularly vulnerable demographics, might face financial risks, leading to debt or economic hardship due to excessive spending on gaming, raising ethical questions about responsible consumer engagement and corporate duty of care.
- Exploitation of Vulnerable Users: Ethical concerns emerge about the potential exploitation of susceptible users who may be lured into spending beyond their means, highlighting the need for protective measures and corporate social responsibility.
- Regulatory Ambiguity and Legal Definitions: The distinction between skill-based gaming and gambling lacks clear definitions, leading to regulatory ambiguity, ethical debates, and varied interpretations about the nature of these gaming activities.
- Corporate Responsibility and User Well-being: Gaming companies have an ethical responsibility to ensure that their platforms do not exploit users or foster addictive behaviors, prioritizing user well-being over profit motives.
- Ethical considerations revolve around promoting responsible gaming practices, protecting users, and offering resources for addiction prevention and support.
- Impact on Social Norms: Ethical dilemmas emerge regarding the normalization of excessive gaming behavior in society, potentially altering social norms and behaviors, particularly among younger demographics.
Note
Recently, the Finance Ministry of India announced a 28% Goods and Services Tax (GST) on online money gaming, casinos, and horse racing.
Way Forward
- Regarding Conduct of Professionals:
- Clear Organizational Policies: Establish clear and unambiguous guidelines within law enforcement agencies regarding off-duty conduct, specifying permissible and non-permissible activities, especially related to online gaming.
- Ethical Training and Education: Provide ethical training and education to law enforcement officials, emphasizing the importance of upholding ethical conduct both on and off duty, ensuring they understand the impact of their actions on public perception.
- Strengthened Codes of Conduct: Review and strengthen existing codes of conduct to address modern-day challenges, including guidelines for engaging in recreational activities, maintaining professional image, and the use of social media in uniform.
- Support and Counseling Services: Provide support services and counseling for officers, addressing stress and promoting healthy coping mechanisms to mitigate stress, considering the challenging nature of their profession.
- Regarding Online Gaming:
- Clear Legal Definitions: Establishing clear distinctions between skill-based gaming and gambling, ensuring precise legal definitions to guide regulatory measures uniformly across states.
- Collaborative Governance and Oversight: Collaborate with gaming companies to promote responsible gaming practices, emphasizing user protection, addiction prevention, and measures to mitigate financial risks among users.
- Comprehensive Research and Analysis: Invest in extensive research on the psychological and socio-economic impacts of online gaming, facilitating evidence-based policymaking and the development of effective regulatory measures.
Subansiri Lower Hydroelectric Project
Why in News?
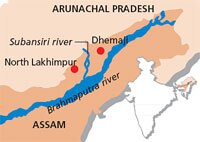
The Subansiri Lower Hydroelectric Project, India’s largest hydel project under construction, faced a setback when a landslide blocked the only functional diversion tunnel and stopped the flow of water downstream of the dam into the Subansiri River, a major tributary of the Brahmaputra.
- This resulted in the river bed drying up and endangering aquatic life. The incident also raised questions about the safety and viability of the project, which has faced multiple delays and opposition since its inception in 2005.
What is the Subansiri Lower Hydroelectric Project?
- The Subansiri Lower Hydroelectric Project is a run-of-river scheme that aims to generate 2,000 MW of power by harnessing the potential of the Subansiri River, which flows along the border of Arunachal Pradesh and Assam.
- A run-of-river dam is one in which the flow of water in the river downstream of the dam is the same as the flow of water upstream of the dam.
- The project is being executed by the National Hydroelectric Power Corporation (NHPC).
- The project involves the construction of a 116-metre-high concrete gravity dam, a 34.5-km-long reservoir, five diversion tunnels, eight spillways, and a powerhouse with eight 250-MW units.
- Gravity dam is constructed from concrete or cement, it is designed to hold back water by primarily utilizing the weight of the material alone to resist the horizontal pressure of water pushing against it.
- The project is expected to generate around 7,500 million units of power annually in a 90% dependable year.
- The project is also expected to provide flood moderation, irrigation, and drinking water benefits to the downstream areas.
- NHPC Limited commenced construction work of Subansiri Lower Hydroelectric Project in January 2005.
- However, due to agitations and protests by local stakeholders, the project construction work was stalled from December 2011 to October 2019. The project construction resumed from October 15, 2019, after the clearance by National Green Tribunal.
Subansiri River
- Subansiri, or “Gold River” is the largest tributary of the Upper Brahmaputra river.
- Emerging from the Tibetan Himalayas, the river flows into India through the Miri Hills of Arunachal Pradesh. The significant variation in its topography presents an opportunity for harnessing hydropower potential in the region.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following rivers: (2014)
- Barak
- Lohit
- Subansiri
Which of the above flows/flow through Arunachal Pradesh?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
FIDE Grand Swiss Open 2023
Why in News?
India celebrates as Vidit Santosh Gujrathi (FIDE Grand Swiss) and Vaishali Ramesh Babu (FIDE Women’s Grand Swiss) secure victories in the FIDE Grand Swiss Open, earning coveted spots in the 2024 Candidates Tournament for a chance to challenge the World Chess Champion.
- The World Chess Championship 2024 is scheduled to take place in Toronto, Canada in April 2024.
What is the FIDE Grand Swiss Open?
- The FIDE Grand Swiss Open is a chess tournament that is part of the qualification for the World Championship cycle.
- The FIDE Grand Swiss and FIDE Women’s Grand Swiss 2023 was held at the Villa Marina, Douglas, Isle of Man.
- The top two players in the open event will qualify for the 2024 Candidates Tournament, which will determine the challenger for the World Champion.
- The total prize fund is USD 600,000, with USD 460,000 for the Grand Swiss and USD 140,000 for the Women’s Grand Swiss.
- The first Grand Swiss was held in 2019 in the Isle of Man.
International Chess Federation (FIDE)
- It is the governing body of the sport of chess, and it regulates all international chess competitions.
- It's constituted as a non-governmental institution. It organizes the World Chess Championship.
- It was recognized by the International Olympic Committee as a Global Sporting Organization in 1999.
- FIDE currently has its headquarters in Lausanne (Switzerland), but it was initially founded in 1924 in Paris under the motto “Gens Una Sumus” (Latin for “We are one Family”).
- It was one of the very first International Sports Federations, alongside the governing bodies of the sports of Football, Cricket, Swimming, and Auto Racing. It is now one of the largest, encompassing 199 countries as affiliate members, in the form of National Chess Federations.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements in respect of the 44th Chess Olympiad, 2022:(2023)
- It was the first time that Chess Olympiad was held in India.
- The official mascot was named Thambi'.
- The trophy for the winning team in the open section is the Vera Menchik Cup.
- The trophy for the winning team in the women's section is the Hamilton-Russell Cup.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All four
Ans: b
Exp:
- The first official Olympiad held in London in 1927 at Westminster Central Hall was then known as the ‘Tournament of Nations’. This is the first time the Chess Olympiad was held in the place of origin of chess, India. It is coming to Asia for the first time in 3 decades. It has the highest ever number of countries participating. It has the highest ever number of teams participating. It has the highest number of entries in the women’s section. Hence, statement 1 is Correct.
- The Official Mascot of 44th Chess Olympiad is 'Thambi'. The word 'Thambi' in Tamil language means - little or younger brother. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- The trophy for the winning team in the open section is the Hamilton-Russell Cup, which was offered by the English magnate Frederick Hamilton-Russell as a prize for the 1st Olympiad (London 1927). Hence, statement 3 is NOT correct.
- The trophy for the winning women's team is known as the Vera Menchik Cup in honour of the first Women's World Chess Champion. Hence, statement 4 is NOT correct.
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
IREDA Launches CSR Portal
The Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency (IREDA) launched a Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) portal to improve transparency in CSR initiatives.
- The portal was launched during the valedictory function of “Vigilance Awareness Week 2023 (30th October to 5th November)”, held at the company's registered office in Delhi.
- The theme for the week was "Say No to Corruption; Commit to the Nation", aimed to raise public awareness about corruption and promote a corruption-free working environment.
- The portal is intended to facilitate transparency in the receipt and disposal of CSR requests from various organizations and institutions.
- IREDA is a Mini Ratna (Category – I) Government of India enterprise under the administrative control of the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy.
Read more: India's Renewable Energy Growth Praised by IRENA
Colour Spectrum of Fluorescent Lamps
Fluorescent lamps are commonly marked with values like 6500K, which represents the correlated colour temperature, indicating the spectral characteristics of the light emitted by the lamp.
- Correlated colour temperature reflects the light's spectral distribution, which is similar to that of a black body at the indicated temperature.
- When a black body is heated, it emits different colors at different temperatures. For example, at 6500K, it emits light that resembles cool daylight.
- Fluorescent tubes are categorized into three types based on their color appearance: daylight white (above 5,000K), neutral white (4,000K), and warm white (below 3,300K).
- The colour of light depends on the fluorescent coating inside the tube.
- Three types of coatings are generally given: tri-phosphor (emit yellow light similar to sunlight), standard phosphor (ordinary tube lights), and multi-phosphor.
Read more: UJALA Programme
The Legal Literacy and Legal Awareness Program (LLLAP)
As per the recent data, the Legal Literacy and legal Awareness Program (LLLAP) has reached more than 6 lakh people through 14 implementing agencies under the Designing Innovative Solutions for Holistic Access to Justice (DISHA) scheme.
- LLLAP is an initiative by the Department of Justice, Ministry of Law and Justice, Government of India aimed at increasing legal literacy and awareness among the masses.
- The program seeks to educate people about their legal rights, duties, and entitlements, as well as the various legal mechanisms available for seeking redressal of grievances.
- DISHA is launched for a period of five years 2021-2026 to advance the cause of access to justice. It aims to design and consolidate various initiatives to provide citizen- centric delivery of legal services.
- Under DISHA, the programmes being implemented at a pan India level are Tele-Law: Reaching the Unreached, Nyaya Bandhu (Pro Bono Legal Services) and Legal Literacy and Legal Awareness Programme.
Russia’s Withdrawal From Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty
Recently, Russia has withdrawn from the Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty (CTBT).
- CTBT bans all nuclear explosions, for both military and civilian purposes, in all environments.
- The treaty was negotiated at the Conference on Disarmament in Geneva in 1994 and adopted by the United Nations General Assembly.
- The CTBT was signed by 187 states, including Russia and the United States, but has not entered into force as eight countries, including the United States, have not ratified it.
- India has not yet signed the treaty.
Read more: Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty
.png)