India-Israel Relations
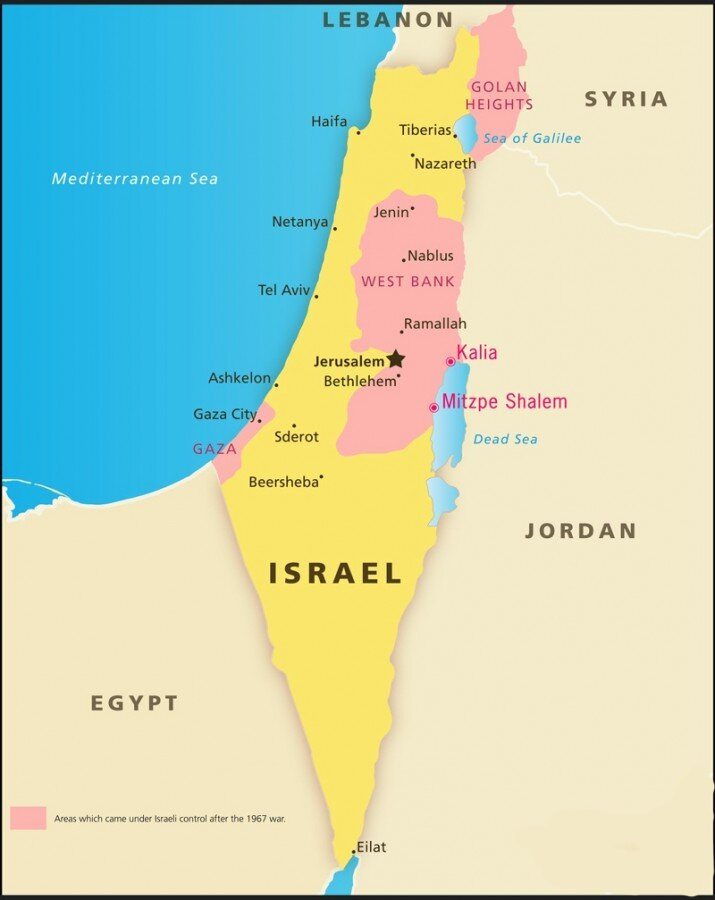
For Prelims: Location of Israel
For Mains: India and Israel Relations, related issues and way ahead
Why in News?
Recently, Israel’s Deputy Prime Minister and Defence Minister visited India and held bilateral Meetings and agreed to deepen defence ties.
What are the Key Highlights of the Visit?
- Joint Declaration:
- The two Ministers presented a joint declaration marking 30 years of Israel-India relations.
- The declaration reiterated the commitment of both the countries to deepen defence ties.
- India-Israel Vision on Defense Cooperation:
- Both sides adopted the India-Israel Vision on Defense Cooperation to further strengthen the existing framework of the Indo-Israeli defense cooperation architecture.
- A Letter of Intent was Exchanged:
- A Letter of Intent on enhancing cooperation in the field of futuristic defence technologies was exchanged.
- Bilateral Cooperation will be in line with Prime Minister Modi’s Make in India vision.
- Military-To-Military Activities:
- Both countries reviewed the existing military-to-military activities which have increased despite the challenges due to Covid-19 pandemic.
- They discussed ways to increase cooperation in all domains with a focus on Research & Development in future technologies and defence co-production.
- Acknowledgement of Mutual Security Challenges:
- Both the Ministers acknowledged mutual security challenges and their convergences on a number of strategic and defence issues.
- They expressed commitment to work together to enhance cooperation in all forums.
How has the India-Israel Relations been So Far?
- Diplomatic Ties:
- Though India officially recognised Israel in 1950, the two countries established full diplomatic ties only on 29th January 1992. As of December 2020, India was among 164 United Nations (UN) member states to have diplomatic ties with Israel.
- Economic and Commercial Relations:
- From USD 200 million in 1992, bilateral merchandise trade stood at USD 4.14 billion (excluding defence) during the period April 2020 – February 2021 with the balance of trade being in India’s favour.
- Trade in diamonds constitutes about 50% of bilateral trade..
- India is Israel's third-largest trade partner in Asia and seventh largest globally.
- Israeli companies have invested in India in energy, renewable energy, telecom, real estate, water technologies, and are focusing on setting up R&D centers or production units in India.
- India is also in dialogue with Israel for concluding a Free Trade Agreement (FTA).
- From USD 200 million in 1992, bilateral merchandise trade stood at USD 4.14 billion (excluding defence) during the period April 2020 – February 2021 with the balance of trade being in India’s favour.
- Defence:
- India is the largest buyer of military equipment from Israel, which, in turn, is the second-largest defence supplier to India, after Russia.
- The Indian armed forces have inducted a wide array of Israeli weapon systems over the years, which range from Phalcon AWACS (Airborne Warning And Control Systems) and Heron, Searcher-II and Harop drones to Barak anti-missile defence systems and Spyder quick-reaction anti-aircraft missile systems.
- The acquisitions also include a host of Israeli missiles and precision-guided munitions, from Python and Derby air-to-air missiles to Crystal Maze and Spice-2000 bombs.
- At the 15th Joint Working Group (JWG 2021) meeting on Bilateral Defence Cooperation, countries agreed to form a Task Force to formulate a comprehensive Ten-Year Roadmap to identify new areas of cooperation.
- Cooperation in Agriculture:
- In May 2021, “a three-year work program agreement” for development in agriculture cooperation, was signed.
- The programme aims to grow existing Centres of Excellence (CoE), establish new centers, increase CoE’s value chain, bring the Centres of Excellence into the self-sufficient mode, and encourage private sector companies and collaboration.
- Science & Technology:
- Recently, experts from India and Israel deliberated on widening the scope of India-Israel Industrial R&D and Technological Innovation Fund (I4F) at its 8th Governing Body meeting.
- They approved 3 joint R&D projects worth 5.5 million USD and suggested measures to create a broader India-Israel collaborative ecosystem.
- I4F is a cooperation between the two countries to promote, facilitate and support joint industrial R&D projects between companies from India and Israel to address the challenges in the agreed ‘Focus Sectors’.
- Others:
- Israel is also joining the India-led International Solar Alliance (ISA), which aligns very well with the objectives of both countries to scale up their cooperation in renewable energy and partner in clean energy.
Way Forward
- The ties between the two nations have flourished since 1992, primarily due to common strategic interests and security threats.
- Indians are sympathetic towards Israel and the government is balancing and recalibrating its West Asia policy on the premise of its own national interest.
- India and Israel need to overcome the vulnerability of their religious extremist neighbours and work productively on global issues like climate change, water scarcity, population explosion and food scarcity.
- A more aggressive and proactive Middle Eastern policy is the need of the hour for India to reap the maximum benefit of the geopolitical realignments gradually being brought in by the Abraham Accords.
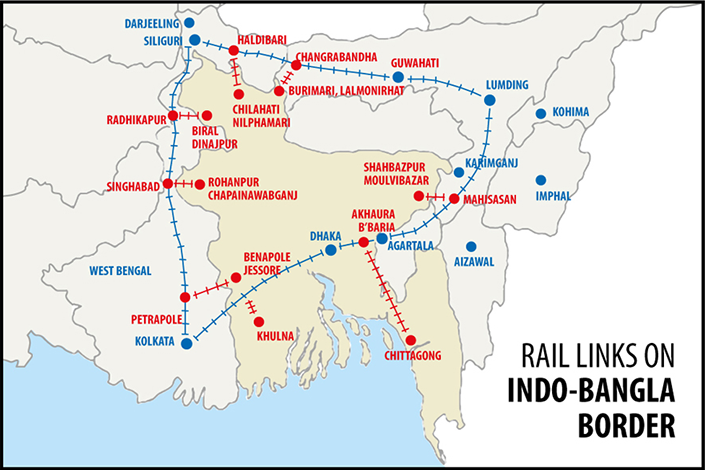
India-Bangladesh Railway Links Restored
For Prelims: Mitali Express, Maitree Express, Maitri Setu Bridge, Sampriti Exercise, Exercise Bongosagar
For Mains: Different trends in Indo-Bangladesh relations, issue of connectivity in south Asia
Why in News?
Two years after train services were stopped due to the onset of the Covid-19 pandemic, passenger train services between India and Bangladesh resumed recently.
- The following trains have been flagged off after the resumption of train services:
- Bandhan Express from Kolkata to Khulna
- Maitree Express from Dhaka to Kolkata
- Mitali Express from New Jalpaiguri to Dhaka
What are other Important Rail Links Between India and Bangladesh?
- Petrapole (India)-Benapole (Bangladesh),
- Gede (India)-Darshana (Bangladesh),
- Singhabad (India)-Rohanpur (Bangladesh),
- Radhikapur (India)-Birol (Bangladesh),
- Haldibari (India)-Chilahati (Bangladesh),
- Agartala (India)- Akahaura(Bangladesh),
Indo-Bangladesh ties
- Historical Ties:
- Fifty years ago, the Bangladesh Liberation War in 1971 had added the colours of victory for India as it led the charge towards the formation of the new nation of Bangladesh.
- Defence Cooperation:
- Joint exercises:
- SAMPRITI (Army)
- TABLE TOP (Air)
- IN-BN CORPAT (Navy)
- Exercise Bongosagar (Navy)
- SAMVEDNA (Multinational Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) Exercise with Bangladesh, Nepal, Sri Lanka and UAE).
- Border Management: India and Bangladesh share 4096.7 km. of border, which is the longest land boundary that India shares with any of its neighbours.
- Joint exercises:
- Economic Relations:
- Bangladesh is India’s largest trading partner in the sub-continent with the total bilateral trade between the two nations standing at USD 9.5 billion (2019-20), down compared to the previous fiscal (2018-19), having crossed USD10 billion.
- India’s exports to Bangladesh account for more than 85% of the total bilateral trade.
- In December 2020, to further boost the bilateral trade cooperation, an India-Bangladesh CEO’s Forum was launched.
- Bangladesh has appreciated the Duty-Free and Quota Free access given to Bangladeshi exports to India under South Asian Free Trade Area (SAFTA) since 2011.
- Cooperation in Connectivity:
- In March 2021, Maitri Setu–a 1.9 km bridge built over Feni River joining Sabroom in India and Ramgarh in Bangladesh was inaugurated.
- Protocol on Inland Water Transit and Trade (PIWTT).
- Bangladesh-Bhutan-India-Nepal (BBIN) Motor Vehicles Agreement is in pipeline.
- Partnership on Multilateral forums:
- Other Developments:
- Line of Credit:
- India has extended 3 Lines of Credits (LOC) to Bangladesh in the last 8 years amounting to USD 8 billion for development of infrastructure in sectors including roads, railways, shipping and ports.
- Covid-19 Support:
- Bangladesh is the biggest recipient of Made-in-India Covid-19 vaccine doses, accounting for 16% of the total supplies.
- India also offered collaboration in therapeutics and partnership in vaccine production.
- Line of Credit:
- Emerging Disputes:
- Bangladesh has already raised concerns over roll out of the National Register of Citizens (NRC) in Assam, an exercise carried out to identify genuine Indian citizens living in Assam and weed out illegal Bangladeshis.
- Currently, Bangladesh is an active partner of the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) that Delhi has not signed up to.
- In the security sector, Bangladesh is also a major recipient of Chinese military inventory, including submarines.
Way Forward
- There should be efforts to resolve pending issues concerning sharing of waters, resolving continental shelf issues in the Bay of Bengal, bringing down border incidents to zero, and managing the media.
- Regular exchanges between younger entrepreneurs and civil society based on areas such as culture, music, sports, films, and sharing of best practices in sustainable development, human capital development, gender equitable growth, amongst others, needs to be pursued.
- Increasing tourist footfall at select border locations from both sides and facilitating a mechanism of exchange through the creation of a common entertainment zone at the border can help strengthen the camaraderie.
- There is a need to jointly work towards a new paradigm of security at the shared borders. A paradigm that enables borders to be not merely thick lines which demarcate national boundaries but act as “connector zones” for inclusive growth and prosperity.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question
Q. Consider the following statements: (2020)
- The value of Indo-Sri Lanka trade has consistently increased in the last decade.
- “Textile and textile articles” constitute an important item of trade between India and Bangladesh.
- In the last five years, Nepal has been the largest trading partner of India in South Asia.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- As per data from the Department of Commerce, Indo-Sri Lanka bilateral trade value for a decade (2007 to 2016) was 3.0, 3.4, 2.1, 3.8, 5.2, 4.5, 5.3, 7.0, 6.3, 4.8 (in billion USD). It reflects continuous fluctuation in the trend of trade value. There has been an overall increase but the same cannot be said as a consistent rise in trade value. Hence statement 1 is not correct.
- Bangladesh has been a major textile trading partner for India, with a share of more than 5% in exports and over 7% in imports. While annual textile exports to Bangladesh averages $2,000 million, imports are worth $400 (Year: 2016-17).
- The major items of exports are fibre and yarn of cotton, man-made staple fibres and man-made filaments while major import items include apparel and clothing, fabric and other made-up textile articles. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- According to the data, in 2016-17, Bangladesh isIndia’s largest trading partner in South Asia, followed by Nepal, Sri Lanka, Pakistan, Bhutan, Afghanistan and Maldives. The level of Indian exports also follows the same order. Hence, statement 3 is not correct.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Etalin Hydro Power Project
For Prelims: Etalin hydro power project, Dibang valley, Forest Advisory committee
For Mains: Preference to Growth and development, Growth and development over environment
Why in news?
Wildlife scientists and conservationists in Arunachal Pradesh flagged threats to local biodiversity from the proposed Etalin hydroelectric (3,097 MW) project in Dibang Valley. To raise the issue,they approached the Forest Advisory Committee (FAC) under the Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC).
- WildLIfe Institute of India (WII) and the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) have suggested taking cognizance of certain safeguards and mitigation measures while considering project approval.
- FAC ordered the formation of a four-member committee to address apprehensions concerning wildlife as well as endemic flora and fauna of the area in a holistic manner.
What is the Significance of Dibang River?
- The Project is based on the river Dibang and is proposed to be completed in 7 years.
- Dibang is a tributary of the Brahmaputra River which flows through the states of Arunachal Pradesh and Assam.
- It envisages construction of two dams over the tributaries of Dibang: Dir and Tangon.
- The Project falls under the richest bio-geographical province of the Himalayan zone and would be located at the junction of major biogeographic zones like Palearctic Zone and Indo-Malayan Zone.
- It is expected to be one of the biggest hydropower projects in India in terms of installed capacity.
What are the Concerns Raised by the Environmentalists?
- Conservationists highlighted that the FAC sub-committee ignored established tenets of forest conservation and related legal issues while recommending the proposal.
- FAC ignored the threat of forest fragmentation.
- Forest fragmentation results from ill-planned intrusion of developmental projects into contiguous landscapes with natural forests and threatens rare floral and faunal species in a biodiversity hotspot.
- FAC’s site inspection report was also questioned for leaving out key details like number of grids across an altitudinal range inspected and the status of vegetation there, direct and indirect signs of wild animals listed in the various schedules of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 and overall appreciation of the ecological value of the area.
- The inadequacy of the Environment Impact Assessment report on Etalin was also highlighted.
- Wildlife officials ignored observations which include the threat to 25 globally endangered mammal and bird species in the area to be affected.
- The proposed mitigation measures like setting up butterfly and reptile parks are inadequate and insufficient.
What is the Forest Advisory Committee?
- It is a statutory body which was constituted by the Forest (Conservation) Act 1980.
- It comes under the Ministry of Environment, Forests & Climate Change (MoEF&CC).
- It considers questions on the diversion of forest land for non-forest uses such as mining, industrial projects, townships and advises the government on the issue of granting forest clearances. However, its role is advisory.
Way Forward
- Community-led approach: The local population of the region should be consulted and should have participation in the decision making to ensure that the final decision making should reflect their concerns.
- Demarcation of ecological sensitive areas: The areas which are at risk of loss of biodiversity should be properly delineated to ensure that they remain undisturbed.
- Environment Impact assessment (EIA): A proper and complete assessment of the impact of the project on the local environment should be studied comprehensively.
- Extension of Protected Areas: The greater number of national parks and sanctuaries should be established to protect the endangered animals and plants.
Maharashtra Re-emerges as Top Sugar Producer
For Prelims: Sugarcane crop, Red rot fungal disease, South-West Monsoon, Ethanol Blending
For Mains: Environmental and Meteorological factors affecting agricultural productivity, Ethanol blending as challenges for food security
Why in News?
Maharashtra has once again the top sugar producer state in India after five years. It has overtaken Uttar Pradesh in sugar production.
- The overall production of sugar by Maharashtra accounts for 138 lakh tonnes for the year 2021-22.
- The total sugar produced by the Uttar Pradesh in the year 2021-22 accounts for 105 lakh tonnes.
What are the Reasons for the Huge Production of Sugar in Maharashtra?
- Abundant Supply of Water:
- Sugarcane is a water intensive crop which needs a huge water supply which farmers from Maharashtra were getting properly through rainfall, water reservoirs, network of canals and from groundwater.
- Maharashtra has been receiving more than sufficient rainwater since 2019 during the south-west monsoon season.
- Groundwater aquifers and other reservoirs were filled by water due to sufficient rainfall. These sources of water play a key role in agricultural production.
- Underreporting of Cane Production:
- Data regarding actual production of the sugarcane in the state of Maharashtra was not quite accurate.
- Keeping this in mind the concerned administration tried to make corrections in the recorded data of the sugarcane production.
- This ultimately resulted in increased acreage under the sugarcane production from 11.42 lakh hectare to 12.4 lakh hectares.
- Thus, Maharashtra harnessed the benefits from increased acreage under sugarcane in 2021-22.
Why did Sugar Production in Uttar Pradesh Decline?
- Uttar Pradesh has become the largest ethanol producer because a large amount of sugarcane production in Uttar Pradesh diverted toward the production of ethanol.
- It has been estimated that 12.60 lakh tonnes equivalent of sugar from cane have been diverted for making ethanol in the year 2021-22 compared to 7.19 lakh tonnes in 2020-21 and 4.81 lakh tonnes in 2019-20 and 0.31 lakh tonnes in 2018-19.
- Uttar Pradesh also has achieved the highest blending of ethanol in petrol ratio among all states.
- It has been estimated that 12.60 lakh tonnes equivalent of sugar from cane have been diverted for making ethanol in the year 2021-22 compared to 7.19 lakh tonnes in 2020-21 and 4.81 lakh tonnes in 2019-20 and 0.31 lakh tonnes in 2018-19.
- Excess rain with water logging problems are associated with the state of Uttar Pradesh which incurred heavy loss of sugarcane crops.
- Majority of the land in sugarcane area in Uttar Pradesh(87%) is planted under a single variety of sugarcane (Co-0238). This variety is not a high yield variety of the sugarcane.
- Adverse impact of red rot fungal disease on sugarcane crop is a severe cause for the decline of sugarcane production in Uttar Pradesh.
- Co-0238 variety of the sugarcane is highly susceptible to the red rot fungal diseases.
- It should be replaced by the new varieties, such as Co-0118 and Co-15023 because both of them are resistant to red rot fungal disease.
Sugarcane
- Temperature: Between 21-27°C with hot and humid climate.
- Rainfall: Around 100-150 cm.
- Soil Type: Deep rich loamy soil.
- Top Sugarcane Producing States: Uttar Pradesh > Maharashtra > Karnataka > Tamil Nadu > Bihar.
- India is the second largest producer of sugarcane after Brazil.
- It can be grown on all varieties of soils ranging from sandy loam to clay loam given these soils should be well drained.
- It needs manual labour from sowing to harvesting.
- It is the main source of sugar, gur (jaggery), khandsari and molasses.
- Scheme for Extending Financial Assistance to Sugar Undertakings (SEFASU) and National Policy on Biofuels are two of the government initiatives to support sugarcane production and sugar industry.
Ethanol Blending:
- Ethanol: It is one of the principal biofuels, which is naturally produced by the fermentation of sugars by yeasts or via petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration.
- Ethanol Blending Programme (EBP): It is aimed at reducing the country’s dependence on crude oil imports, cutting carbon emissions and boosting farmers’ incomes.
- Blending Target: The Government of India has advanced the target for 20% ethanol blending in petrol (also called E20) to 2025 from 2030.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question
Q. With reference to the current trends in the cultivation of sugarcane in India, consider the following statements: (2020)
- A substantial saving in seed material is made when ‘bud chip settlings’ are raised in a nurse, and transplanted in the main field.
- When direct planting of setts is done, the germination percentage is better with singlebudded setts as compared to setts with many buds.
- If bad weather conditions prevail when setts are directly planted, single-budded setts have better survival as compared to large setts.
- Sugarcane can be cultivated using settlings prepared from tissue culture.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 2, 3 and 4 only
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- Tissue Culture Technology
- Tissue culture is a technique in which fragments of plants are cultured and grown in a laboratory.
- It provides a new way to rapidly produce and supply disease-free seed cane of existing commercial varieties.
- It uses meristem to clone the mother plant.
- It also preserves genetic identity.
- The tissue culture technique, owing to its cumbersome outfit and physical limitation, is turning out to be uneconomical.
- Bud Chip Technology
- As a viable alternative of tissue culture, it reduces the mass and enables quick multiplication of seeds.
- This method has proved to be more economical and convenient than the traditional method of planting two to three bud setts.
- The returns are relatively better, with substantial savings on the seed material used for planting. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- The researchers have found that the setts having two buds are giving germination about 65 to 70% with better yield. Hence, statement 2 is not correct.
- Large setts have better survival under bad weather but single budded setts also give 70% germination if protected with chemical treatment. Hence, statement 3 is not correct.
- Tissue culture can be used to germinate and grow sugarcane settlings which can be transplanted later in the field. Hence, statement 4 is correct. Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer
Information Technology Rules, 2021
For Prelims: over-the-top (OTT) platforms, social media intermediaries, Section 69A of the IT Act
For Mains: Information Technology Rules 2021, freedom of speech and expression, Issues Arising Out of Design & Implementation of Policies, Government Policies & Interventions
Why in News?
The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) issued a draft proposal for public comment on a set of proposed amendments to the Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021.
- The draft document was however withdrawn the same day.
- The Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021 (IT Rules, 2021) was notified in February 2021.
What is the Law?
- Mandates Social Media to Exercise Greater Diligence:
- Broadly, the IT Rules (2021) mandate social media platforms to exercise greater diligence with respect to the content on their platforms.
- Establish a Grievance Officer:
- They are required to establish a grievance redressal mechanism and remove unlawful and unfitting content within stipulated time frames.
- The grievance officer of the platform’s redressal mechanism is responsible for receiving and resolving complaints of the users.
- She/he is expected to acknowledge receipt of the complaint within 24 hours and dispose of the same in an appropriate manner within 15 days.
- Its access and spread by any other means on the platform should also be disabled.
- The privacy policies of the social media platforms must ensure that users are educated about not circulating copyrighted material and anything that can be construed as defamatory, racially or ethnically objectionable, paedophilic, threatening the unity, integrity, defence, security or sovereignty of India or friendly relations with foreign states, or violative of any contemporary law.
- They are required to establish a grievance redressal mechanism and remove unlawful and unfitting content within stipulated time frames.
What were the Changes Proposed in the Withdrawn Draft?
- Grievance Appellate Committee:
- It proposed an additional level of oversight, namely, the ‘Grievance Appellate Committee’, functioning over and above the intermediary’s grievance redressal officer.
- Broadly, in case a user is not satisfied with the resolution provided by the intermediary, she/he can appeal against the decision at the appellate rather than going directly to court.
- However, this did not take away the user’s right to appeal in any other court.
- All Orders of the Appellate must be Compiled:
- The draft stipulated that all orders of this appellate must be complied with.
- The suggested question on ‘oversight’ stemmed from the fact that the appellate was to be constituted by the Central Govt empowered to appoint the Chairperson and other members.
What is the Issue with the IT Rules 2021?
- Made Government the Arbiter to Suppress Speech:
- This would have made the government the arbiter of permissible speech on the internet and incentivised social media platforms to suppress any speech that may not be palatable to the government.
- Obligation on Social Media to Resolve Complaints:
- The draft put forth the obligation that all social media intermediaries resolve all complaints within 72 hours of reporting.
- Intermediaries are known to invest sizable time in thoroughly scrutinising and determining the content and user accounts they are called to censor.
- The shortened timelines therefore invited fears of a hastier approach to get things done.
Have there been any Legal Challenges?
- The imposition of sub-clauses 1 and 3 of Rule 9 of the legislative guidelines were stayed in 2021.
- These sub-clauses dealt with the ‘Code of Ethics’ for online publishers dealing with news and current affairs content and/or curated content.
- The sub-clauses had stated that the entities subscribe to a three-tier mechanism in dealing with grievances (relevant to their platform) so as to adhere to their code.
- This entails self-regulation by the publishers (level I), by self-regulating bodies of the publishers (level II) and finally, an oversight mechanism by the Central Govt (level III).
- The Bombay High Court however ruled, “People would be starved of the liberty of thought and feel suffocated to exercise their right of freedom of speech and expression, if they are made to live in present times of content regulation on the internet with the Code of Ethics hanging over their head as the Sword of Damocles.”
Way Forward
- Making platforms share more information could prove counterproductive in a country where the citizens still do not have a data privacy law to guard themselves against excesses committed by any party.
- In this context, there is a need to expedite the passing of the personal data protection bill, 2019.
- After that, if regulation is still deemed to be necessary, then it must be implemented through legislation that is debated in Parliament instead of relying upon executive rule-making powers under Section 69A of the IT Act.
Single Nodal Agency (SNA) Dashboard of PFMS
For prelims: Public Financial Management System, Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav, Centrally Sponsored Schemes
For Mains: Government Policies & Interventions, Transparency & Accountability
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Minister for Finance & Corporate Affairs launched the Single Nodal Agency (SNA) Dashboard of PFMS (Public Financial Management System).
- It was launched as a part of the Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav (AKAM) celebrations by the Ministry of Finance.
- The Ministry of Finance is observing the ‘Iconic Week’ celebrations from 6th to 12th June 2022 to celebrate AKAM.
- Additionally, the training modules for the Department of Expenditure were launched as part of Mission Karmayogi.
What is Mission Karmayogi?
- It aims to prepare Indian civil servants for the future by making them more creative, constructive, imaginative, proactive, innovative, progressive, professional, energetic, transparent, and technology-enabled.
- Comprehensive reform of the capacity building apparatus at the individual, institutional and process levels for efficient public service delivery.
What is SNA Dashboard?
- About:
- It is a major reform initiated in 2021 with regards to the manner in which funds for Centrally Sponsored Schemes (CSS) are released, disbursed and monitored.
- This revised procedure, now referred to as the SNA model, requires each State to identify and designate a SNA for every scheme.
- All funds for that State in a particular scheme are now credited in this bank account, and all expenses by all other Implementing Agencies involved are affected from this account.
- Significance:
- Ensure Allocation of Funds:
- The SNA model ensures that allocation of funds to States for the CSS are made in a timely manner and after meeting various stipulations.
- Brought Greater Efficiency:
- Effective implementation of this Model has brought about greater efficiency in CSS fund utilization, tracking of funds, pragmatic and just-in-time release of funds to the States; ultimately all contributing to better Cash Management of the Government.
- Ensure Allocation of Funds:
- Need:
- In order to give the stakeholders of the SNA model the necessary feedback and monitoring tools in the operation of the schemes.
- The Dashboard depicts releases made to different States by Ministries, further releases made by State Treasuries to the SNA accounts, expenditure reported by the agencies, interest paid by banks to SNA accounts etc. in intelligible, informative and visually appealing graphics.
What is PFMS?
- About:
- PFMS, earlier known as Central Plan Schemes Monitoring System (CPSMS), is a web-based online software application developed and implemented by the Office of Controller General of Accounts (CGA), Ministry of Finance.
- PFMS was initially started during 2009 as a Central Sector Scheme of Planning Commission with the objective of tracking funds released under all Plan schemes of the Government of India, and real time reporting of expenditure at all levels of Programme implementation.
- Subsequently in the year 2013, the scope was enlarged to cover direct payment to beneficiaries under both Plan and non-Plan Schemes.
- In 2017, the Government scrapped the distinction between plan and non-plan expenditure.
- Objective:
- To facilitate a sound Public Financial Management System for the Government of India (GoI) by establishing an efficient fund flow system as well as a payment cum accounting network.
- Coverage:
- At present, the ambit of PFMS coverage includes Central Sector and Centrally Sponsored Schemes as well as other expenditures including the Finance Commission Grants.
- PFMS provides various stakeholders with a real time, reliable and meaningful management information system and an effective decision support system, as part of the Digital India initiative of GoI.
- PFMS is integrated with the core banking system in the country.
Environment Performance Index
Why in News?
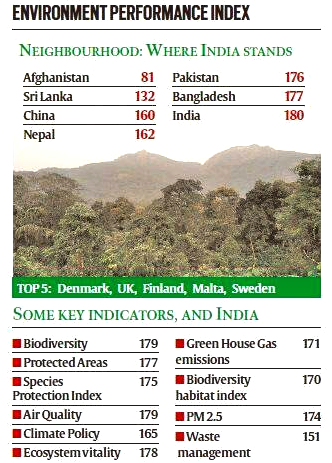
In the recently released Environment Performance Index-2022, India was at the bottom among 180.
What is the Environment Performance Index?
- About:
- The Environment Performance Index (EPI) is an international ranking system that measures environmental health and sustainability of countries.
- The EPI, a biennial index, was started in 2002 as Environmental Sustainability Index by the World Economic Forum in collaboration with the Yale Center for Environmental Law and Policy and the Columbia University Center for International Earth Science Information Network.
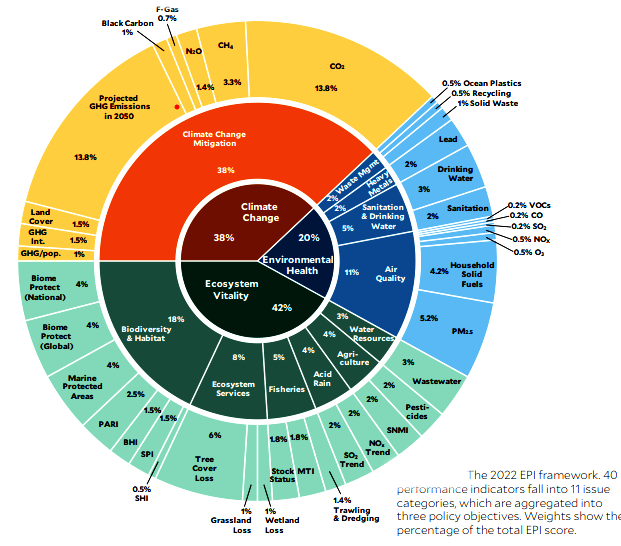
- Framework:
- The 2022 EPI leverages 40 performance indicators grouped into 11 issue categories.
- These issue categories are in turn aggregated into 3 policy objectives:
- Environmental Health
- Ecosystem Vitality
- Climate Change.
- These indicators provide a gauge at a national scale of how close countries are establishing environmental policy targets.
- The EPI team transforms the raw environmental data into indicators that place countries on a 0–100 scale from worst to best performance.
What are the Key Highlights?
- Denmark tops the 2022 rankings — an achievement rooted in strong performance across nearly all issues tracked by the EPI, with notable leadership in efforts to promote a clean energy future and sustainable agriculture.
- The United Kingdom and Finland place 2nd and 3rd, both earning high scores for slashing greenhouse gas emissions in recent years.
- The United States places 20th out of 22 wealthy democracies in the Global West and 43rd overall.
- With a paltry score of 18.9, India’s 180th ranking comes after Pakistan, Bangladesh, Vietnam and Myanmar.
- India has also scored low on rule of law, control of corruption and government effectiveness, according to EPI.
- India was ranked 168th in EPI-2020, with a score of 27.6.
- In EPI-2020, Denmark has been ranked first in environmental health and sustainability.
- Significance of EPI:
- EPI enables decision-makers to recognize the drivers of top-tier performance.
- Analysis of the EPI data demonstrates that financial resources, good governance, human development, and regulatory quality matter for elevating a country’s sustainability.
- Highlighting these connections, the EPI helps to promote sustainable development in support of a more environmentally secure and equitable future
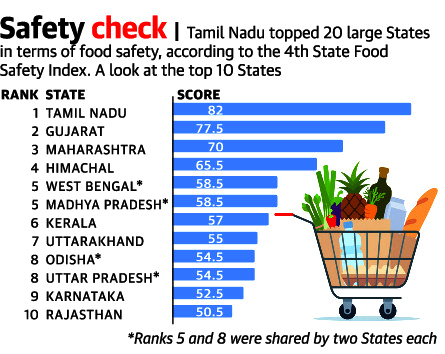
Food Safety Index: FSSAI
Why in News?
On the occasion of World Food Safety Day, the Union Health Minister released Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI)’s 4th State Food Safety Index (SFSI) to measure the performance of States across five parameters of food safety.
What is State Food Safety Index (SFSI)?
- About:
- SFSI was started from 2018-19 with the aim of creating a competitive and positive change in the food safety ecosystem in the country.
- The index is developed by FSSAI (Food Safety and Standards Authority of India) to measure the performance of states on five significant parameters of Food Safety.
- The parameters include Human Resources and Institutional Data, Compliance, Food Testing – Infrastructure and Surveillance, Training & Capacity Building and Consumer Empowerment.
- The Index is a dynamic quantitative and qualitative benchmarking model that provides an objective framework for evaluating food safety across all States/UTs.
- The first State Food Safety Index for the year 2018-19 was announced on the first-ever World Food Safety Day on 7th June 2019.
- Significance:
- The index will help in providing safe and nutritious food to our citizens.
How did the States Perform?
- Overall:
- Tamil Nadu topped the State Food Safety Index followed by Gujarat and Maharashtra.
- Among Smaller States:
- Goa stood first, followed by Manipur and Sikkim.
- Among UTs:
- Jammu and Kashmir, Delhi and Chandigarh secured first, second and third ranks.
What is Food Safety Day?
- About:
- The World Health Organization (WHO) and the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) jointly facilitate the observance of World Food Safety Day, in collaboration with Member States and other relevant organizations.
- It was first celebrated in 2019, to strengthen the commitment to scale up food safety made by the Addis Ababa Conference and the Geneva Forum in 2019 under the umbrella of “The Future of Food Safety”.
- The theme for 2022 was Safer Food, Better Health.
- Other Initiatives launched on the Occasion:
- Various innovative initiatives by the FSSAI, launched includes the Eat Right Research Awards and Grants – Phase II, Eat Right Creativity Challenge – Phase III, a school-level competition, and the logo for AyurvedaAahar.
- This logo contains the initials of Ayurveda and Aahar with five leaves symbolising the five elements of nature, would be beneficial in creating a unique identity for food products and in their easy identification.
- A guidance document on Food Borne Disease Outbreak Investigation and Microbiological Process Control, and Sampling and Testing of Fish and Fishery Products was released.
- Various innovative initiatives by the FSSAI, launched includes the Eat Right Research Awards and Grants – Phase II, Eat Right Creativity Challenge – Phase III, a school-level competition, and the logo for AyurvedaAahar.
National Air Sports Policy 2022
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Civil Aviation has launched National Air Sport Policy 2022 (NASP 2022).
- It has been drafted based on the inputs received from policy makers, air sports practitioners and public at large and will ensure establishment of good quality of infrastructure, equipment, instructors and services.
What is NASP 2022?
- About:
- NASP 2022 lays out the vision of making India as one of the top sports nations by 2030, by providing a safe, affordable, accessible, enjoyable and sustainable air sports ecosystem in India.
- Objectives:
- Promote an air sports culture in the country.
- Enable adoption of international good practices in safety including but not limited to, air sports infrastructure, equipment, operations, maintenance and training.
- Develop a simple, stakeholder-friendly and effective governance structure.
- Enhance participation and success of Indian sportspersons in global air sports events.
- Promote design, development and manufacturing of air sports equipment in India in line with the Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan.
- Governing Bodies: There will be four-tier governance structure for air sports in India namely:
- Air Sports Federation of India (ASFI) as the apex governing body.
- National associations for individual air sports or a set of air sports, as appropriate
- Regional (e.g. West/ South/ North East etc.) or State and Union Territory level units of the national air sports associations, as appropriate; and
- District-level air sports associations, as appropriate.
- Sports Covered:
- Aerobatics, Aero modeling and model rocketry, Amateur-built and experimental aircraft, Ballooning, Drones, Gliding and powered gliding, Hang gliding and powered hang gliding, Parachuting (including skydiving, BASE jumping and wing suits etc.), Paragliding and para motoring (including powered parachute trikes etc.), Powered aircraft (including ultra light, micro light and light sports aircraft etc.), Rotorcraft (including autogyro).
- Significance:
- India has the potential to be among the leading nations in the world of air sports. It has a large geographical expanse, diverse topography and fair weather conditions.
- It has a large population, especially the youth. It has a growing culture for adventure sports and aviation.
- Other than the direct revenue from air sports activities, the multiplier benefits in terms of growth of travel, tourism, infrastructure and local employment, especially in hilly areas of the country, are several times greater.
- Creation of air sports hubs across the country will also bring in air sports professionals and tourists from across the world.
- India has the potential to be among the leading nations in the world of air sports. It has a large geographical expanse, diverse topography and fair weather conditions.
What are the Government Initiatives for Sports Development?
- Khelo India Scheme.
- National Sports Development Fund.
- The National Sports Talent Contest (NSTC) Scheme.
- Sports Authority of India Training Centres Scheme (STC).
- Special Area Games (SAG) Scheme.
- Target Olympic Podium Scheme (TOPS)
- Khelo India Youth Games
Way Forward
- There is need to leverage the energy of Indian youth below the age of 35 which accounts for 70 % of India's population which is larger than the total population of Europe and three times that of USA.