POCSO Act
For Prelims: POCSO Act, UN Convention on the Rights of the Child in 1992, Indian Penal Code, Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, POCSO Court,
For Mains: POCSO Act, Issues in Implementation and Way Forward.
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Women and Child Development has informed the Lok Sabha that the Protection of Children from Sexual Offenses (POCSO) Act, 2012, is one of the crucial legislations enacted by the Government to protect children from Sexual Abuse.
What is the POCSO Act?
- About:
- POCSO Act came into effect on 14th November 2012 which was enacted in consequence to India’s ratification of the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child in 1992.
- The aim of this special law is to address offences of sexual exploitation and sexual abuse of children, which were either not specifically defined or in adequately penalised.
- The Act defines a child as any person below the age of 18 years. The Act provides punishment as per the gravity of offence.
- The Act was further reviewed and amended in 2019 to Introduce more stringent punishment including the death penalty for Committing sexual crimes on children, with a view to deter the perpetrators & prevent such crimes against children.
- The Government of India has also notified the POCSO Rules, 2020.
- Features:
- Gender-Neutral Nature:
- The Act recognizes that both girls and boys can be victims of sexual abuse and that such abuse is a crime regardless of the gender of the victim.
- This is in line with the principle that all children have the right to protection from sexual abuse and exploitation, and that laws should not discriminate based on gender.
- The Act recognizes that both girls and boys can be victims of sexual abuse and that such abuse is a crime regardless of the gender of the victim.
- Ease in Reporting Cases:
- There is sufficient general awareness now to report cases of sexual exploitation of children not only by individuals but also by institutions as non-reporting has been made a specific offence under the POCSO Act. This has made it comparatively difficult to hide offences against children.
- Explicit Definition of Terms:
- The storage of child pornography material has been made a new offence.
- Further, the offence of ‘sexual assault’ has been defined in explicit terms (with increased minimum punishment) unlike an abstract definition of ‘outraging modesty of a woman’ in the Indian Penal Code.
- Gender-Neutral Nature:
- POCSO Rules 2020:
- Interim Compensation and Special Relief
- Rule-9 of the POCSO Rules allows the Special Court to order interim compensation for the child's needs related to relief or rehabilitation after the FIR's registration. This compensation is adjusted against the final compensation, if any.
- Immediate Payment of Special Relief:
- Under the POCSO Rules, the Child Welfare Committee (CWC) may recommend immediate payment for essential needs like food, clothes, and transportation, using funds from the District Legal Services Authority (DLSA), the District Child Protection Unit (DCPU), or funds maintained under the Juvenile Justice Act 2015.
- The payment must be made within a week of receiving the CWC's recommendation.
- Support Person for the Child:
- The POCSO Rules empower the CWC to provide a support person to assist the child throughout the investigation and trial process.
- The support person is responsible for ensuring the child's best interests, including physical, emotional, and mental well-being, access to medical care, counseling, and education. They also inform the child and their parents or guardians about court proceedings and developments related to the case.
- Interim Compensation and Special Relief
Note: In furtherance to the Criminal law (Amendment) Act, 2018, Department of Justice has started a Centrally Sponsored Scheme in October, 2019 for setting up of a total of 1023 Fast Track Special Courts (FTSCs) (including 389 exclusive POCSO Courts) Across the country.
- As on May 31, 2023, a total of 758 FTSCs including 412 Exclusive POCSO (e-POCSO) Courts are functional in 29 States/UTs across the country.
What are the Issues and Challenges with the POCSO Act?
- Issue with the Investigation:
- Low Representation of Women in the Police Force:
- The POCSO Act provides for recording the statement of the affected child by a woman sub-inspector at the child’s residence or place of choice.
- But it is practically impossible to comply with this provision when the number of women in the police force is just 10%, and many police stations hardly have women staff.
- Lapses in the Investigation:
- Though there is a provision to record statements using audio-video means, however, there are still reports of lapses in the investigation and preservation of crime scenes in some cases,
- In Shafhi Mohammad vs The State of Himachal Pradesh (2018), the Supreme Court held in cases of heinous crimes, it is the duty of the investigating officer to photograph and videograph the scene of crime and to preserve the same as evidence.
- Though there is a provision to record statements using audio-video means, however, there are still reports of lapses in the investigation and preservation of crime scenes in some cases,
- No Examination by Judicial Magistrates:
- Another provision of the act mandates the recording of the statement of the prosecutrix by a judicial magistrate.
- Though such statements are recorded in most cases, judicial magistrates are neither called for cross-examination during trial nor are those who retract their statement punished. In such a scenario, such statements get nullified.
- Low Representation of Women in the Police Force:
- Issue of Age Determination:
- Though age determination of a juvenile delinquent is guided by the Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act 2015 no such provision exists under the POCSO Act for juvenile victims.
- In Jarnail Singh vs State of Haryana (2013) case, the SC held that the given statutory provision should also be the basis to help determine age even for a child who is a victim of crime.
- However, in absence of any change in the law or even specific directions, the investigating officers (IOs) continue to rely on the date of birth recorded in school admission-withdrawal registers.
- Though age determination of a juvenile delinquent is guided by the Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act 2015 no such provision exists under the POCSO Act for juvenile victims.
- Delays in the Filing of Charges:
- As per the POCSO Act, the investigation of a case under the act is to be completed within a period of one month from the date of the commission of the offence, or from the date of the reporting of the offence.
- However, in practice, the completion of investigation often takes longer than one month due to various reasons such as lack of adequate resources, delays in obtaining forensic evidence, or the complexity of the case.
- No Conditions to Prove Recent Intercourse:
- Courts are required to presume that the accused committed the offence under the POCSO Act.
- The POCSO Act does not impose any conditions on the prosecution, contrary to the Indian Evidence Act , which clearly requires the prosecution to establish recent intercourse, as well as the consent of the prosecutrix.
- However, it has been observed that even after the minor age of the victim is proved, no such presumption is taken up by the court during trial.
- Under such circumstances, the expected increase in the conviction rate is unlikely to be achieved.
What are the Initiatives to Curb Child Abuse?
Way Forward
- The government should provide adequate resources such as funding and personnel to investigating agencies handling POCSO cases. This will help to ensure that investigations are conducted in a timely and efficient manner.
- Investigating officers should be provided with proper training on the handling of POCSO cases. This can include training on the proper techniques for collecting and preserving evidence, interviewing child victims and witnesses, and the legal requirements of the POCSO Act.
- Setting up special courts for POCSO cases can help to ensure that cases are handled promptly and efficiently. This will also help to speed up the trial process, which can be important for the victim and their family.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Examine the main provisions of the National Child Policy and throw light on the status of its implementation. (2016)
Carbon Capture and Storage
For Prelims: Global Energy & Carbon Dioxide Emissions, Carbon Storage, Global warming, Climate change, National Centre of Excellence in Carbon Capture and Utilization Mumbai, Afforestation, Paris Agreement.
For Mains: Approaches to Carbon Capture and Storage and Related Challenges.
Why in News?
The UK government has reasserted its commitment to advancing projects aimed at capturing and storing carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions as a crucial component of its strategy to achieve net-zero emissions.
What is Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)?
- About:
- It is a process designed to mitigate the emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2) generated from industrial processes and the burning of fossil fuels, particularly in power plants.
- The goal of CCS is to prevent a significant amount of CO2 from entering the atmosphere and contributing to global warming and climate change.
- Approaches: Carbon capture and storage (CCS) encompasses two primary approaches:
- The first method is known as point-source CCS, which involves capturing CO2 directly at the site of its production, such as industrial smokestacks.
- The second method, direct air capture (DAC), focuses on removing CO2 that has already been emitted into the atmosphere.
- The recent UK initiatives specifically target point-source CCS.
- Mechanisms of Point Source- CCS: The process of carbon capture and storage encompasses several distinct steps, each contributing to the effective containment of CO2 emissions:
- Capture: CO2 is isolated from other gases generated during industrial processes or power generation.
- Compression and Transportation: Once captured, CO2 is compressed and transported to designated storage sites, frequently through pipelines.
- Injection: The CO2 is then injected into subterranean rock formations, often situated at depths of one kilometer or more, where it remains stored for extended periods, sometimes lasting decades.
- Applications:
- Mineralization: Captured carbon can be reacted with certain minerals to form stable carbonates, which can be stored safely underground or used in construction materials.
- This process, known as mineral carbonation, offers a long-term and secure method of carbon storage.
- Synthetic Fuels: Captured CO2 can be combined with hydrogen (often produced via electrolysis using renewable energy) to produce synthetic fuels such as synthetic natural gas, synthetic diesel, or even synthetic jet fuel.
- Greenhouses and Indoor Agriculture: Captured carbon dioxide can be supplied to greenhouses and indoor farming facilities to enhance plant growth.
- Dry Ice Production: Captured carbon dioxide can be used to produce dry ice, which is solid carbon dioxide at extremely low temperatures.
- Dry ice has various applications, including shipping and transportation of perishable goods, medical and scientific purposes, and special effects in the entertainment industry.
- Mineralization: Captured carbon can be reacted with certain minerals to form stable carbonates, which can be stored safely underground or used in construction materials.
Note:
- In India, two National Centres of Excellence in Carbon Capture and Utilization are being established.
- National Centre of Excellence in Carbon Capture and Utilization (NCoE-CCU) at Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Bombay, Mumbai
- National Centre in Carbon Capture and Utilization (NCCCU) at Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research (JNCASR), Bengaluru.
- Challenges:
- Cost and Economics: CCS involves high initial capital costs for building capture, transportation, and storage infrastructure.
- The cost of capturing CO2 from flue gases or industrial processes can be significant, affecting the overall viability of CCS projects.
- Geological Storage Suitability: Identifying and securing suitable geological formations for long-term CO2 storage is a challenge.
- Not all geological formations are appropriate for CO2 storage due to potential risks of leakage or seismic activity.
- Extended Lifespan of Fossil Fuel Companies: Certain environmental organizations raise concerns regarding the effectiveness of CSS, suggesting that its implementation might unintentionally prolong the operational viability of fossil fuel companies.
- This potential consequence could inadvertently hinder the speed of transitioning to more sustainable and cleaner energy sources.
- Cost and Economics: CCS involves high initial capital costs for building capture, transportation, and storage infrastructure.
Way Forward
- Natural Climate Solutions Integration: Combining CCS with natural climate solutions can enhance its effectiveness.
- Embracing initiatives like reforestation, afforestation, and sustainable land management can complement CCS efforts by sequestering carbon naturally, promoting biodiversity, and enhancing ecosystem resilience.
- International Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing: To address global climate challenges, countries must collaborate and share knowledge and expertise in CCS.
- Establishing international forums, research partnerships, and technology-sharing initiatives can accelerate the development and adoption of innovative carbon capture solutions.
- Balancing CCS and Emission Reduction for Climate Action: The United Nations report underscores CCS's potential to align with the Paris Agreement’s market-based mechanisms like carbon trading through carbon credits.
- However, it emphasizes that emission prevention remains paramount. An inclusive climate strategy mandates both carbon capture technology adoption and proactive emission reduction to effectively address climate change.
- In line, in terms of Nationally Determined Contribution, India now stands committed to reduce Emissions Intensity of its GDP by 45% by 2030.
- However, it emphasizes that emission prevention remains paramount. An inclusive climate strategy mandates both carbon capture technology adoption and proactive emission reduction to effectively address climate change.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q1. Consider the following agricultural practices: (2012)
- Contour bunding
- Relay cropping
- Zero tillage
In the context of global climate change, which of the above helps/help in carbon sequestration/storage in the soil?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) None of them
Ans: (b)
Q2. In the context of mitigating the impending global warming due to anthropogenic emissions of carbon dioxide, which of the following can be the potential sites for carbon sequestration? (2017)
- Abandoned and uneconomic coal seams
- Depleted oil and gas reservoirs
- Subterranean deep saline formations
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q3. What is/are the advantage/advantages of zero tillage in agriculture? (2020)
- Sowing of wheat is possible without burning the residue of previous crop.
- Without the need for nursery of rice saplings, direct planting of paddy seeds in the wet soil is possible.
- Carbon sequestration in the soil is possible.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
National Initiative for Developing and Harnessing Innovations
For Prelims: NIDHI, Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, Technology Incubation and Development of Entrepreneurs (TIDE 2.0)
For Mains: Significance of NIDHI, Major Challenges Related to Startups in India, Recent Government Initiatives Related to Startups.
Why in News?
Recently, in a written reply in the Rajya Sabha, the Union Minister of State for Science and Technology highlighted achievement in India's innovation landscape through the NIDHI (National Initiative for Developing and Harnessing Innovations).
- The Department of Science & Technology (DST) launched the NIDHI program in 2016. NIDHI also involves collaboration with other key entities to encourage startups.
What is the National Initiative for Developing and Harnessing Innovations (NIDHI)?
- About:
- The NIDHI is a groundbreaking initiative designed to drive innovation, support startups, and create a thriving entrepreneurial ecosystem in India.
- NIDHI comprises various components that provide a comprehensive framework for promoting and accelerating innovation-driven enterprises across the nation.
- Components of NIDHI Program:
- NIDHI-PRAYAS (Promoting and Accelerating Young and Aspiring Innovators and Startups):
- Focuses on converting innovative ideas into tangible prototypes.
- Offers mentoring and financial support at the Proof-of-Concept level.
- NIDHI Entrepreneurs-In-Residence (EIR) Program:
- Provides fellowships to students pursuing entrepreneurship.
- Aims to nurture and encourage young entrepreneurs.
- NIDHI Seed Support Program:
- Offers early-stage seed funding to startups.
- Enables startups to embark on their innovation journey.
- NIDHI Accelerator Program:
- Speeds up the investment readiness of startups.
- Equips startups with the resources needed for growth and scaling.
- Technology Business Incubators (TBIs) and Centres of Excellence (CoE):
- Establishes state-of-the-art infrastructure for incubating startups.
- Fosters innovation in technology sectors.
- NIDHI-Inclusive Technology Business Incubators (iTBI) program:
- Strengthens the innovation and startup incubation ecosystem in Tier II and Tier III cities.
- The iTBI program has helped increase entrepreneurial inclusiveness in terms of geographies, gender and persons with special abilities.
- NIDHI-PRAYAS (Promoting and Accelerating Young and Aspiring Innovators and Startups):
- Key Players and Collaborators:
- Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR):
- NIDHI collaborates closely with CSIR to shape and develop cutting-edge incubation facilities.
- Plays an active role in conceptualizing and developing advanced incubation facilities.
- Supports translating technology and products, benefiting society, industry, and the country.
- NIDHI collaborates closely with CSIR to shape and develop cutting-edge incubation facilities.
- Department of Biotechnology (DBT) through Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC):
- NIDHI joins hands with DBT and BIRAC to encourage startups, entrepreneurs, and innovators in the biotechnology domain.
- Through strategic collaboration, they drive translational research and facilitate the creation of affordable biotech solutions.
- Supports startups, entrepreneurs, and innovators in developing affordable products and technologies.
- The progress made through BIRACs incubation program include setting up of 75 Incubation Centers supported through BIRAC’s BioNEST and E-YUVA (Empowering Youth for Undertaking Value Added Innovative Translational Research) schemes of BIRAC across the country, around 900 innovative projects supported under Biotech Ignition Grant (BIG).
- Ministry of Defence (MoD):
- Collaborating with MoD's Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX), NIDHI contributes to a dynamic ecosystem for innovation.
- This partnership engages industries, startups, and R&D institutes to drive advancements in defence and aerospace technologies.
- Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY):
- NIDHI's partnership with MeitY in the Technology Incubation and Development of Entrepreneurs (TIDE 2.0) Scheme empowers tech-driven startups.
- Together, they provide financial and technical support to foster technology-based entrepreneurship.
- Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR):
- Collaborating with ICAR's National Agriculture Innovation Fund, NIDHI empowers agri-tech startups.
- Their joint efforts establish Agri-business Incubator (ABIs) centres, driving innovative solutions in agriculture.
- Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR):
Department of Science and Technology:
- The foundation of DST was laid on 3rd May 1971 along the model of National Science Foundation (NSF), USA.
- It provides funding and also makes policies and co-ordinates scientific work with other countries.
- It empowers scientists and scientific institutions and also works with a highly distributed system permeating stakeholders ranging from school college, PhD, Postdoc students, young scientists, startups and NGOs working in Science & Technology.
What is the Status of India’s Innovation and Startup Ecosystem?
- India is ranked 40th out of 132 among the top innovative economies globally as per the Global Innovation Index (GII) 2022.
- India has emerged as the 3rd largest ecosystem for startups globally as of 31st May 2023.
- As of June 2023, India is home to 108 Unicorns with a total valuation of USD 340.80 Bn.
- Out of the total number of unicorns, 44 unicorns were born in 2021 and 21 unicorns were born in 2022.
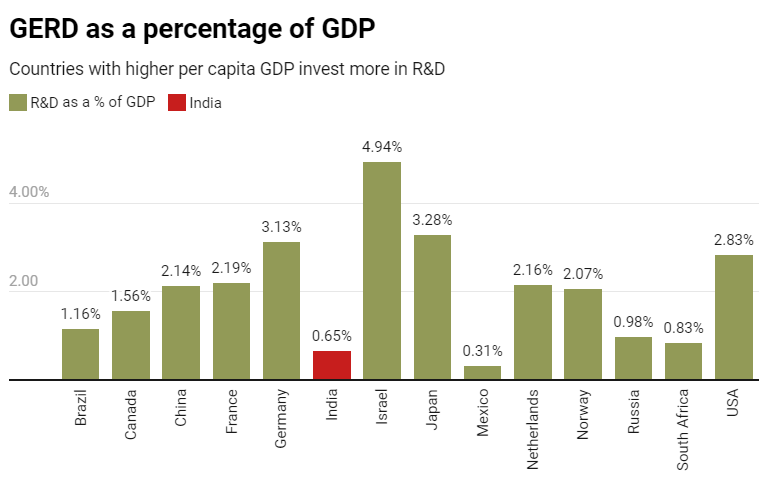
- India’s Gross Domestic Expenditure on R&D (GERD) as a percentage of GDP was 0.65% in 2017-18, which is lower than the global average of 2.2% and much lower than the leading innovators such as Israel (4.9%), South Korea (4.5%), and Japan (3.2%).
- India faces issues such as funding, revenue generation, and supportive infrastructure in its innovation and startup journey.
- India’s public sector accounts for about three-fourths of the total R&D expenditure in the country, while the private sector contributes only about one-fourth. This is in contrast to the global trend, where the private sector plays a dominant role in R&D spending.
What are the Other Initiatives Related to Encourage Startup and Innovation in India?
- Fund of Funds for Startups (FFS) Scheme.
- Credit Guarantee Scheme for Startups (CGSS).
- Startup India Hub.
- Startup India Seed Fund Scheme (SISFS).
- Centres of Excellence.
- Startup India Action Plan (SIAP).
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. What does venture capital mean? (2014)
(a) A short-term capital provided to industries
(b) A long-term start-up capital provided to new entrepreneurs
(c) Funds provided to industries at times of incurring losses
(d) Funds provided for replacement and renovation of industries
Ans: (b)
Explanation:
- Venture capital is a form of fund for a new or growing business. It usually comes from venture capital firms that specialize in building high risk financial portfolios.
- With venture capital, the venture capital firm gives funding to the startup company in exchange for equity in the startup.
- The people who invest this money are called venture capitalists (VCs). Venture capital investment is also referred to as risk capital or patient risk capital, as it includes the risk of losing the money if the venture does not succeed and takes a medium to long-term period for the investments to fructify.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Excess Cane Payments
For Prelims: Sugarcane, Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP)
For Mains: Agricultural Pricing, Sugar production in the Indian Economy, Challenges faced by sugarcane industry.
Why in News?
In a significant move, the Government of India has taken a step to provide relief to cooperative sugar mills by allowing them to claim excess cane price payments made to farmers as "business expenditure."
What is the Issue of Excess Cane Payments?
- Sugarcane is a major crop in India, especially in states like Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu.
- The Centre fixes a fair and remunerative price (FRP) for sugarcane every year, which is the minimum amount that sugar mills have to pay to farmers for procuring their cane.
- However, some cooperative sugar mills, especially in Maharashtra, pay more than the FRP to farmers as an incentive or bonus. This is called excess cane payment.
- The excess cane payment has resulted in tax disputes between the cooperative sugar mills and the Income Tax Department.
- The mills claim the excess payment as business expenditure, while the department treats it as a distribution of profits and disallows it as a deduction.
How has the Government of India Resolved the Issue of Excess Cane Payments?
- In the 2015-16 Union Budget, the Government of India introduced an amendment to the Finance Act that allowed cooperative sugar mills to claim excess cane payment as deduction for computing their business income. However, this was applicable only from the 2016-17 assessment year onwards.
- In the 2023-24 Union Budget, the Government of India extended the benefit of deduction to all financial years prior to 2015-16. This was done by amending Section 155 of the Income Tax Act .
- The move is expected to provide relief of almost Rs 10,000 crore to cooperative sugar mills, against pending tax demands and litigation in respect of payments made before the 2015-16 financial year.
What is the FRP?
- About:
- FRP is the price set by the government that sugar mills are obligated to pay to farmers for the sugarcane procured from them.
- Payment and Agreement:
- Mills are legally required to pay the FRP to farmers for their cane.
- Mills can choose to sign agreements with farmers, allowing them to pay the FRP in installments.
- Delayed payments can attract interest charges of up to 15% per annum, and the sugar commissioner can recover unpaid FRP by attaching properties of the mills.
- Governing Regulations:
- The pricing of sugarcane is governed by the statutory provisions of the Sugarcane (Control) Order, 1966 issued under the Essential Commodities Act (ECA), 1955.
- According to the regulations, the FRP must be paid within 14 days of cane delivery.
- Determination and Announcement:
- The FRP is determined based on the recommendations of the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP).
- The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) announces the FRP.
- Factors Considered:
- The FRP takes into account various factors, including the cost of sugarcane production, returns from alternative crops, trends in agricultural commodity prices, availability of sugar to consumers, selling price of sugar, sugar recovery from cane, and income margins for cane growers.
What is Sugarcane?
- Temperature: Between 21-27°C with hot and humid climate.
- Rainfall: Around 75-100 cm.
- Soil Type: Deep rich loamy soil.
- Top Sugarcane Producing States: Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Bihar.
- India is the second largest producer of sugarcane after Brazil.
- It can be grown on all varieties of soils ranging from sandy loam to clay loam given these soils should be well drained.
- It needs manual labour from sowing to harvesting.
- It is the main source of sugar, gur (jaggery), khandsari and molasses.
- Scheme for Extending Financial Assistance to Sugar Undertakings (SEFASU) and National Policy on Biofuels are two of the government initiatives to support sugarcane production and the sugar industry.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. With reference to the current trends in the cultivation of sugarcane in India, consider the following statements: (2020)
- A substantial saving in seed material is made when ‘bud chip settlings’ are raised in a nurse, and transplanted in the main field.
- When direct planting of setts is done, the germination percentage is better with single budded setts as compared to setts with many buds.
- If bad weather conditions prevail when setts are directly planted, single-budded setts have better survival as compared to large setts
- Sugarcane can be cultivated using settlings prepared from tissue culture.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 2, 3 and 4 only
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- Tissue Culture Technology
- Tissue culture is a technique in which fragments of plants are cultured and grown in a laboratory.
- It provides a new way to rapidly produce and supply disease-free seed cane of existing commercial varieties.
- It uses meristem to clone the mother plant.
- It also preserves genetic identity.
- The tissue culture technique, owing to its cumbersome outfit and physical limitation, is turning out to be uneconomical.
- Bud Chip Technology
- As a viable alternative of tissue culture, it reduces the mass and enables quick multiplication of seeds.
- This method has proved to be more economical and convenient than the traditional method of planting two to three bud setts.
- The returns are relatively better, with substantial savings on the seed material used for planting. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- The researchers have found that the setts having two buds are giving germination about 65 to 70% with better yield. Hence, statement 2 is not correct.
- Large setts have better survival under bad weather but single budded setts also give 70% germination if protected with chemical treatment. Hence, statement 3 is not correct.
- Tissue culture can be used to germinate and grow sugarcane settlings which can be transplanted later in the field. Hence, statement 4 is correct. Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
World Breastfeeding Week 2023
Why in News?
On the occasion of World Breastfeeding Week 2023, the United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) and the World Health Organization (WHO) lauded the progress made by several countries in increasing exclusive breastfeeding rates, while also highlighting the potential for further advancements if breastfeeding is protected and supported, particularly in the workplace.
What is World Breastfeeding Week?
- World Breastfeeding Week, observed annually during the first week of August in commemoration of the 1990 Innocenti Declaration.
- In 1990, the Innocenti Declaration was signed by government policymakers, UN health agencies, and other organisations to protect, promote, and support breastfeeding.
- In 1991, the World Alliance for Breastfeeding Action (WABA) was formed as a global network, and since 1992, the world has marked Breastfeeding Week, annually.
- Since 2016, WBW has been aligned with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Breastfeeding can help achieve many of the 17 SDGs, including goals on poverty, hunger, health, education, gender equality, and sustainable consumption.
- Since 2016, WBW has been aligned with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Theme 2023: "Let's make breastfeeding at work, work”.
- UNICEF and WHO called on governments, donors, civil society and the private sector to step up efforts to help eliminate barriers women and families face to achieving their breastfeeding goals and reach the global 2030 target of 70%.
What is the Progress in Exclusive Breastfeeding Rates?
- Exclusive breastfeeding involves feeding babies only breast milk and excluding all other foods, liquids, infant formula, or water, except for necessary medications or vitamin and mineral supplements.
- The practice of exclusive breastfeeding offers vital health benefits to infants, including protection against common infectious diseases and bolstering their immune systems, ensuring they receive essential nutrients for optimal growth and development.
- Over the past decade, the global rate of exclusive breastfeeding has risen by an impressive 10% points, reaching 48%.
What are the Indian Government Initiatives Relates to Breastfeeding?
- MAA - "Mothers Absolute Affection"
- MAA is a nationwide programme of the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare to promote breastfeeding.
- Vatsalya – Maatri Amrit Kosh
- Vatsalya, a National Human Milk Bank and Lactation Counselling Centre has been established in collaboration with the Norwegian government
Himalayan Vulture: Gyps Himalayensis
Why in News?
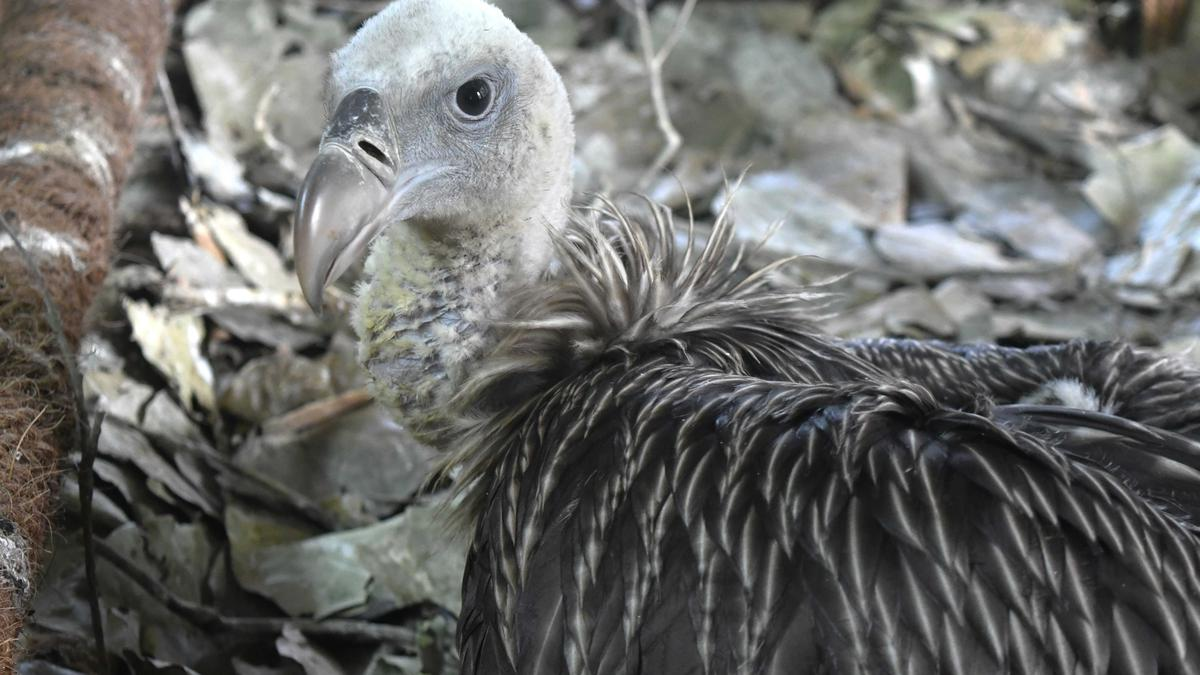
Recently, the Assam State Zoo in Guwahati has achieved a groundbreaking feat by successfully breeding the elusive Himalayan vulture (Gyps himalayensis) in captivity for the first time in India.
- Additionally, the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare's decision to prohibit the manufacture, sale, and distribution of ketoprofen and aceclofenac has sparked optimism among vulture conservationists and experts.
What are the Key Highlights of the Himalayan Vulture ?
- Conservation Status:
- Distinctive Characteristics:
- The Himalayan vulture is one of the largest Old World vulture species, boasting an impressive wingspan and formidable presence.
- Its plumage is dominated by shades of black and brown, which aid in its camouflage against the rugged mountain terrain.
- The vulture's powerful hooked beak and keen eyesight make it a proficient scavenger, playing a crucial role in the ecosystem by cleaning up carrion.
- Habitat and Range:
- The Himalayan vulture is aptly named, as it primarily inhabits the towering peaks and valleys of the Himalayan mountain range.
- It is a common winter migrant to the Indian plains.
- Its range extends across several countries, including India, Nepal, Bhutan, and China, where it thrives in challenging high-altitude environments.
- The Himalayan vulture is aptly named, as it primarily inhabits the towering peaks and valleys of the Himalayan mountain range.
- Ecological Significance:
- As a top predator and scavenger, the Himalayan vulture plays a vital role in maintaining the health of its habitat by efficiently disposing of animal remains.
- Its scavenging behavior helps prevent the spread of diseases that could arise from decaying carcasses, thus contributing to the overall balance of the ecosystem.
- Challenges and Conservation Efforts:
- Breeding the Himalayan vulture in captivity posed challenges due to its natural breeding habits in snow-clad mountains.
- Successful breeding at the zoo was made possible through long-term captivity and acclimatization to the tropical environment.
- Factors such as habitat loss, food scarcity, and accidental poisoning from veterinary drugs have contributed to its vulnerable status.
- Conservation breeding centers, such as the Vulture Conservation Breeding Centre (VCBC) at Rani, Assam, are instrumental in safeguarding vulture species.
What are Ketoprofen and Aceclofenac, and How Do They Impact Vultures?
- Ketoprofen and aceclofenac are two types of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) that are used to treat pain and inflammation in animals, especially cattle.
- Prescribed for arthritis, injuries, and post-surgery pain.
- However, these drugs have been found to be harmful to vultures, as they cause kidney failure and death when the vultures feed on the carcasses of animals treated with these drugs.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Vultures which used to be very common in Indian countryside some years ago are rarely seen nowadays. This is attributed to (2012)
(a) the destruction of their nesting sites by new invasive species
(b) a drug used by cattle owners for treating their diseased cattle
(c) scarcity of food available to them
(d) a widespread, persistent and fatal disease among them.
Ans: (b)
LK-99: The Quest for a Room-Temperature Superconductor
Why in News?
A group of South Korean scientists have recently claimed the discovery of a material they named LK-99. According to their reports, LK-99 is a superconductor at room temperature and pressure.
- This groundbreaking claim has piqued the interest of the scientific community and could potentially revolutionize the world of electrical conductivity and technology.
What does the Claim on Discovery of LK-99 Suggest?
- Exploring Apatite Materials: The South Korean group's discovery involved a rather unexpected material called apatite.
- Apatites are minerals with a phosphate scaffold in a tetrahedral or pyramidal motif(one phosphorus atom is surrounded by four oxygen atoms).
- The scientists started with lead apatite and substituted some of the lead atoms with copper, resulting in copper-substituted lead apatite, which they named LK-99.
- Evidence of Superconductivity: The group reported that at 10% copper substitution, LK-99 exhibited the characteristics of a superconductor.
- The material also maintained superconductivity in the presence of an external magnetic field, up to a certain critical threshold, a behavior consistent with known superconductors.
- The Implications of LK-99: If the claims of LK-99 being a room-temperature superconductor are confirmed, it could usher in a new era for electrical conductivity and technology.
- The widespread application of superconductors in everyday devices could lead to increased energy efficiency, reduced power losses, and the development of revolutionary technologies.
What are Superconductors?
- About:
- Superconductors are materials that exhibit zero electrical resistance when cooled to extremely low temperatures. This property allows them to conduct electricity with no loss of energy.
- Example: Lanthanum-Barium-Copper Oxide, Yttrium-Barium-Copper Oxide, Niobium-Tin etc.
- Superconductors are materials that exhibit zero electrical resistance when cooled to extremely low temperatures. This property allows them to conduct electricity with no loss of energy.
- Discovery:
- In 1911 Kamerlingh Onnes discovered that the electrical resistance of mercury completely disappeared at temperatures a few degrees above absolute zero.
- The phenomenon became known as superconductivity.
- In 1911 Kamerlingh Onnes discovered that the electrical resistance of mercury completely disappeared at temperatures a few degrees above absolute zero.
- Applications of Superconductors:
- Energy Transmission: Superconducting cables can transmit electricity without losses, making them ideal for long-distance power transmission.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Superconducting magnets are used in MRI machines to create strong and stable magnetic fields, enabling detailed medical imaging.
- Particle Accelerators: Superconducting magnets are crucial components in particle accelerators like the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), allowing particles to reach high velocities.
- Electric Motors and Generators: Superconducting materials can enhance the efficiency and power density of electric motors and generators.
- Maglev Trains: Superconducting magnets enable magnetic levitation (maglev) trains to float above tracks, reducing friction and enabling high-speed travel.
- Quantum Computing: Some superconducting materials are being explored for their potential in quantum computing due to their ability to exhibit quantum states.
505-Million Year Old Jellyfish Fossils
Why in News?
Recently, researchers have unveiled a collection of jellyfish fossils from the Cambrian period, providing a unique glimpse into their distant past.
- These preserved fossils, found in the Burgess Shale- a renowned fossil-rich site in the Canadian Rockies, offer an improbable pathway to preservation.
What are the Major Findings of the Research?
- Special Features of the Fossils:
- The newly discovered jellyfish fossils retained remarkable features, such as over 90 fingerlike tentacles protruding from their bell-shaped bodies.
- Some specimens even contained stomach contents and gonads, providing invaluable insights into their anatomy and behavior.
- These things help scientists learn about how the jellyfish looked and acted.
- Link with Old Fossils from a Quarry:
- In the 1990s, scientists dug up over 170 jellyfish fossils in a place called Raymond Quarry in British Columbia. These fossils were kept for a long time.
- Researchers re-examined the specimens from the excavation and identified that the fossils actually belonged to a previously unknown species.
- This newly discovered species was named Burgessomedusa phasmiformis. The species falls under the medusozoans category.
What are Jellyfish?
- About:
- Jellyfish are members of the phylum Cnidaria, a group of animals that includes corals, sea anemones, hydroids, and siphonophores.
- Cnidarians are characterized by having radial symmetry, a central mouth surrounded by tentacles, and specialized stinging cells called cnidocytes that can inject venom into their prey or predators.
- Jellyfish tend to just follow the currents of the ocean, they can be found around the world in every type of ocean water.
- They are considered to be one of the earliest branches of the animal tree of life.
- Jellyfish are members of the phylum Cnidaria, a group of animals that includes corals, sea anemones, hydroids, and siphonophores.
- Characteristics:
- Despite their name, jellyfish do not have much characteristics of a fish, they are invertebrates, or animals with no backbones.
- Jellyfish are also among the simplest animals in terms of body organization and nervous system, lacking a brain, a heart, or a skeleton.
- However, some jellyfish have evolved remarkable adaptations, such as eyes, bioluminescence, and complex behaviors.
- Despite their name, jellyfish do not have much characteristics of a fish, they are invertebrates, or animals with no backbones.
- Prey:
- They dine on fish, shrimp, crabs and tiny plants. They have tiny stinging cells in their tentacles to stun or paralyze their prey before they eat them.
- Challenge of Jellyfish Fossilization:
- Jellyfish, composed of 95% water, pose a considerable challenge when it comes to fossilization. Their delicate structure makes them prone to rapid deterioration, leaving behind minimal traces in the fossil record.
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
India's first-ever Gold Medal at the World Archery Championship
Recently, the Prime Minister extended congratulations to the Indian women's compound team comprising Jyothi Surekha Vennam, Parneet Kaur, and Aditi Gopichand Swami, for securing India's inaugural Gold medal at the World Archery Championship in Berlin.
- Aditi Gopichand Swami became the youngest-ever senior world champion and the first Indian to win an individual compound gold medal at the World Archery Championships at the age of 17.
- World Archery is the international federation for the Olympic and Paralympic sport of archery.
- The organization was founded in 1931 and is responsible for regulating and promoting archery around the world.
- World Archery is based in the Olympic capital of Lausanne, Switzerland.
Ancient Giant Whale: Perucetus Colossus
The recent identification of Perucetus colossus (the colossal whale from Peru), an ancient whale species, has redefined the understanding of marine giants. A study published in Nature reveals this colossal creature's remarkable features, potentially reshaping the narrative of gigantism in marine mammals.
- The estimated skeletal mass of P. colossus exceeds that of any known mammal or aquatic vertebrate.
- The partial skeleton includes 13 vertebrae, 4 ribs, and 1 hip bone, found in Southern Peru and believed to be around 39 million years old.
- With an estimated body mass ranging between 85 and 340 tonnes and a length of 20 meters (66 feet), the newly discovered species challenges the blue whale's status as the heaviest animal. Although the blue whale remains longer, reaching over 100 feet (30 meters) in length.
- The species displays the highest degree of bone mass increase observed, associated with shallow diving.
- The trend towards gigantism in marine mammals might have originated earlier than previously believed.
Chandrayaan-3 Enters Lunar Orbit
Chandrayaan-3, India's ambitious lunar mission, has achieved a significant milestone by entering lunar orbit twenty-three days after its departure from Earth.
- Chandrayaan-3 is India's third lunar mission and second attempt at achieving a soft landing on the moon's surface.
- The mission took off from the Satish Dhawan Space Center (SDSC) in Sriharikota on July 14, 2023, at 2:35 pm.
- Orbits:
- Lunar orbit: The curved path followed by a spacecraft as it revolves around the Moon.
- Translunar: The trajectory that takes a spacecraft from Earth to a point beyond its orbit, en route to the Moon.
- Earth orbit: The elliptical or circular path that a satellite or spacecraft traces around the Earth due to gravitational forces.
Read more: Chandrayaan-3
9th National Handloom Day
National Handloom Day is observed across India on August 7 every year.
- The primary goal of celebrating Handloom Day is to promote the handloom and to recognise the efforts as well as skills of the community of weavers engaged in the sector.
- It was first celebrated on August 7, 2015. The date holds historical significance, paying homage to the Swadeshi Movement launched on August 7, 1905, which championed indigenous industries and, particularly, handloom weavers.
- Theme for National Handloom Day 2023: "Handlooms for Sustainable Fashion"
Read more: National Handloom Day, Swadeshi Movement