Women, Business and the Law 2024
For Prelims: Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), Gender Gap, Women, Business and the Law 2024, World Bank (WB).
For Mains: Women, Business and the Law 2024, Issues Related to Women in India and world and its effect on development of Human Resource.
Why in News?
Recently, the World Bank (WB) Group has released a report titled-Women, Business and the Law 2024, presenting in-depth analysis of the challenges obstructing women’s entry into the global workforce, hindering their ability to contribute to prosperity for themselves, their families and their communities.
What is Women Business and Law 2024 Report?
- Its indexes align areas of the law and public policy instruments with the economic decisions that women make throughout their lives and careers, identifying where and in what areas women continue to face hurdles.
- Indicators: It has 10 indicators- Safety, Mobility, Workplace, Pay, Child Care, Marriage, Parenthood, Entrepreneurship, Assets, and Pension.
- Safety from violence and access to childcare services are very crucial indicators.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- Legal Frameworks Index:
- Among the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) high-income economies, 11 scored 90 or above, with Italy leading at 95, followed by New Zealand and Portugal with 92.5.
- By contrast, more than 37 economies provide women with less than half of the legal rights enjoyed by men, affecting approximately half a billion women. Notably, high-income economies have an average score of 75.4.
- Upper-middle-income economies follow closely, with an average score of 66.8. The gap in scores between the highest- and lowest scoring economies is most pronounced in high-income economies, with a substantial difference of 75 points.
- Women Enjoy Fewer Legal Rights than Men:
- Women around the world enjoy only 64% of the legal protections that men do, when legal differences involving violence and childcare are taken into account. This is even lower than the previous estimate of 77%.
- Gap Between Legal Reforms and Actual Outcomes for Women:
- Even though many countries have enacted laws promoting gender equality, there is a significant gap between these laws and the actual experiences of women.
- 98 economies have enacted legislation mandating equal pay for women for work of equal value.
- Yet only 35 economies, fewer than one out of every five, have adopted pay-transparency measures to address the pay gap.
- Poor Performances by the Countries:
- Togo has been a standout among Sub-Saharan economies, enacting laws that give women roughly 77% of the rights available to men, more than any other country in the continent.
- Yet Togo, so far, has established only 27% of systems necessary for full implementation.
- This rate is average for Sub-Saharan economies.
- In 2023, governments were assertive in advancing three categories of legal equal-opportunity reforms, Pay, Parental Rights, and workplace protections.
- Still, nearly all countries performed poorly in the two categories being tracked for the first time—access to childcare and women’s safety.
- Togo has been a standout among Sub-Saharan economies, enacting laws that give women roughly 77% of the rights available to men, more than any other country in the continent.
- Women’s Safety:
- The greatest weakness is in women's safety, with the global average score being just 36. Women have barely a third of the necessary legal protections against domestic violence, sexual harassment, child marriage, and femicide.
- Although 151 economies have laws in place prohibiting sexual harassment in the workplace, just 39 have laws prohibiting it in public spaces. This often prevents women from using public transportation to get to work.
- Childcare:
- Women spend an average of 2.4 more hours a day on unpaid care work than men, much of it on the care of children.
- Only 78 economies,fewer than half, provide some financial or tax support for parents with young children.
- Only 62 economies—fewer than a third—have quality standards governing childcare services, without which women might think twice about going to work while they have children in their care.
- Significant Obstacles for Women:
- Women face significant obstacles in other areas. In the area of entrepreneurship, for example, just one in every five economies mandates gender-sensitive criteria for public procurement processes, meaning women are largely cut out of a USD 10-trillion-a-year economic opportunity.
- In the area of pay, women earn just 77 cents for every USD 1 paid to men. The rights gap extends all the way to retirement. In 62 economies, the ages at which men and women can retire are not the same.
- Women tend to live longer than men, but because they receive lower pay while they work, take time off when they have children, and retire earlier, they end up with smaller pension benefits and greater financial insecurity in old age.
How did India Perform in Women, Business and the Law 2024 Report?
- India’s rank has marginally improved to 113, with a score of 74.4%. While the country’s score has remained constant since 2021, its ranking witnessed a decline from 122 in 2021 to 125 in 2022 and further to 126 in the 2023 index.
- Indian women have just 60% of the legal rights compared to men, slightly below the global average of 64.2%.
- However, India outperformed its South Asian counterparts, where women have only 45.9% of the legal protections enjoyed by men.
- When it comes to constraints on freedom of movement and constraints related to marriage, India got a full score.
- India receives one of its lowest scores in the indicator evaluating laws impacting women’s pay.
- To enhance this aspect India could explore measures such as mandating equal pay for equivalent work, permitting women to work at night on par with men and enabling women to engage in industrial jobs on an equal footing with men.
- When it comes to supportive frameworks, India scored higher than both the global and South Asian averages.
What are the Recommendations of the Report?
- Eliminating discriminatory laws and practices hindering women from working or initiating businesses could result in a more than 20% increase in global gross domestic product.
- It has the potential to double the rate of global growth in the upcoming decade.
- Effective implementation of equal-opportunity laws depends on an adequate supporting framework, including strong enforcement mechanisms, a system for tracking gender-related pay disparities, and the availability of healthcare services for women who survive violence.
- It is more urgent than ever to accelerate efforts to reform laws and enact public policies that empower women to work and start and grow businesses.
- Increasing women's economic participation is the key to amplifying their voices and shaping decisions that affect them directly.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q.1 India’s ranking in the ‘Ease of Doing Business Index’ is sometimes seen in the news. Which of the following has declared that ranking? (2016)
(a) Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)
(b) World Economic Forum
(c) World Bank
(d) World Trade Organization (WTO)
Ans: (c)
Q.2 Which one of the following issues the ‘Global Economic Prospects’ report periodically? (2015)
(a) The Asian Development Bank
(b) The European Bank for Reconstruction and Development
(c) The US Federal Reserve Bank
(d) The World Bank
Ans: (d)
Q.3 Which of the following organizations brings out the publication known as ‘World Economic Outlook’? (2014)
(a) The International Monetary Fund
(b) The United Nations Development Programme
(c) The World Economic Forum
(d) The World Bank
Ans: (a)
Q.4 ‘BioCarbon Fund Initiative for Sustainable Forest Landscapes’ is managed by the (2015)
(a) Asian Development Bank
(b) International Monetary Fund
(c) United Nations Environment Program
(d) World Bank
Ans: (d)
Mains:
Q.1 We are witnessing increasing instances of sexual violence against women in the country. Despite existing legal provisions against it, the number ofsuch incidencesis on the rise. Suggestsome innovative measures to tackle this menace. (2014)
Q.2 What are the continued challenges for Women in India against time and space? (2019)
Amul a Pillar of India's Dairy Sector
For Prelims: Anand Pattern, White Revolution, National Dairy Development Board (NDDB), World Food Programme, Rashtriya Gokul Mission, National Livestock Mission
For Mains: Role of dairy and livestock sector in Indian economy, Related issues and Initiatives taken to promote the sector.
Why in News?
The Prime Minister participated in the Golden Jubilee celebration of the Gujarat Cooperative Milk Marketing Federation (GCMMF) and highlighted the success of Anand Milk Union Limited (Amul) which comes from GCMMF.
What is the History of Amul?
- Amul was established in 1946 as the Kaira District Co-operative Milk Producers’ Union Limited in Anand, Gujarat.
- It was founded by Tribhuvandas Patel, with the support of Morarji Desai and Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel.
- In 1950, Amul (Anand Milk Union Limited) was formed as a brand for the dairy products produced by the cooperative.
- Amul is managed by the GCMMF, which is jointly owned by more than 3.6 million milk producers in Gujarat.
- Amul pioneered the adoption of the Anand Pattern, an economic organisational model designed to empower small producers through collective action.
- This approach fosters integration among producers, enabling economies of scale while preserving individual autonomy in decision-making.
- Amul's success story garnered international attention, becoming a case study in cooperative economics and rural development.
- Amul played a pivotal role in India's White Revolution, which aimed to increase milk production and make India self-sufficient in milk.
- Amul spearheaded the White Revolution in India, starting with the introduction of milk powder manufacturing in 1955.
- Amul products are now exported to over 50 countries, with a network of over 18,000 milk cooperative committees and over 36,000 farmers. Processing over 3.5 crore litres of milk daily, Amul also facilitates online payments exceeding Rs 200 crores to livestock breeders.
What is India's White Revolution or Operation Flood?
- Background:
- The National Dairy Development Board (NDDB), chaired by Verghese Kurien ('Father of White Revolution in India'), was established in 1965 to revolutionize India's dairy industry. Inspired by the successful "Anand Pattern", NDDB launched the White Revolution, also known as Operation Flood in 1970, connecting rural milk producers with urban consumers through dairy cooperatives.
- This initiative transformed India into the world's largest milk producer, significantly boosting milk production and improving its management efficiency.
- Operation Flood transformed the dairy-deficient nation into the global leader in milk production.
- The nationwide Operation Flood unfolded in three phases over three decades.
- The National Dairy Development Board (NDDB), chaired by Verghese Kurien ('Father of White Revolution in India'), was established in 1965 to revolutionize India's dairy industry. Inspired by the successful "Anand Pattern", NDDB launched the White Revolution, also known as Operation Flood in 1970, connecting rural milk producers with urban consumers through dairy cooperatives.
- Phases of Operation Flood:
- Phase I (1970-1980):
- Financed by the sale of skimmed milk powder and butter oil gifted by the European Union (then European Economic Community) through the World Food Programme.
- Operation Flood linked 18 milksheds with consumers in major metropolitan cities.
- Initiated the foundation of a self-sustaining system of village cooperatives.
- Phase II (1981-1985):
- Increased milksheds from 18 to 136 and expanded outlets to 290 urban markets.
- Established a self-sustaining system of 43,000 village cooperatives, covering 4.25 million milk producers.
- Significantly increased domestic milk powder production, promoting self-reliance.
- Phase III (1985-1996):
- Enabled dairy cooperatives to expand and strengthen infrastructure for procuring and marketing milk.
- Emphasised veterinary healthcare services, feed, and artificial insemination.
- Added 30,000 new dairy cooperatives and peaked milksheds to 173 in 1988-89.
- Phase I (1970-1980):
- Post-Operation Flood:
- In 1991, India underwent liberalisation, privatisation and globalisation reforms, allowing for private participation in various sectors, including dairy.
- Foreign equity of up to 51% was allowed in milk products, except for malted products.
- The initial phase saw the proliferation of unregulated dairies, leading to concerns of adulterated and contaminated milk.
- The Milk and Milk Products Order (MMPO) was instituted in 1992 to regulate the sector and introduce oversight.
- MMPO is a regulatory order of the Government of India that regulates the production, supply, and distribution of milk and milk products. The MMPO was promulgated under the provisions of the Essential Commodities Act, 1955.
- The order's objective is to maintain and increase the supply of milk and milk products.
- MMPO is a regulatory order of the Government of India that regulates the production, supply, and distribution of milk and milk products. The MMPO was promulgated under the provisions of the Essential Commodities Act, 1955.
- The industry witnessed significant growth in processing capacity, primarily driven by large private players.
- In 1991, India underwent liberalisation, privatisation and globalisation reforms, allowing for private participation in various sectors, including dairy.
- Current Milk Production:
- India is the highest milk producer i.e., ranks first position in the world contributing twenty-four percent of global milk production in the year 2021-22.
- In the last 10 years, milk production increased by almost 60% and per capita milk availability has increased by about 40%.
- The top 5 milk-producing states are Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat and Andhra Pradesh.
- The Indian dairy sector is growing by 6% per year as compared to the global average of 2%.
- India's Export of Dairy products was 67,572.99 Metric Ton (MT) to the world worth USD 284.65 Mn during the year 2022-23.
What are the Initiatives Related to the Dairy Sector?
- Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF).
- National Programme for Dairy Development.
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Sampada Yojana
- Kisan Credit Cards (KCC) to Livestock Farmers
- Rashtriya Gokul Mission
- National Livestock Mission
What are the Challenges Faced by the Indian Dairy Sector?
- Low Milk Yield:
- Milk yield per animal in India is significantly lower than the global average. This can be attributed to factors like poor quality feed and fodder, traditional cattle breeds, and lack of proper veterinary care.
- Issues in Milk Collection and Processing:
- Challenges in collection, pasteurization, and transportation of milk pose significant hurdles, particularly in ensuring safe milk handling in informal dairy setups.
- Adulteration Concerns:
- Adulteration of milk remains a persistent issue due to difficulties in quality control.
- Profit Disparities:
- Milk producers often receive low purchase prices compared to market rates, leading to disparities in profit distribution within the value chain.
- Cattle Health Challenges:
- Frequent outbreaks of diseases like Foot and Mouth Disease, Black Quarter infection, and Influenza significantly impact livestock health and lower productivity.
- Limited Crossbreeding Success:
- Crossbreeding indigenous species with exotic stocks to improve genetic potential has achieved limited success.
Way Forward
- Strengthening veterinary care, promoting quality feed and fodder, and implementing robust quality control measures are essential to address productivity and health challenges.
- Enhancing infrastructure for milk collection, processing, and transportation will help streamline operations and ensure safe milk handling.
- Emphasizing research and development in genetics, nutrition, and disease management will be crucial for enhancing milk yield and animal health.
- Promoting farmer cooperatives and incentivizing sustainable practices can empower small-scale producers and ensure equitable growth across the dairy value chain.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 Consider the following crops of India: (2012)
- Cowpea
- Green gram
- Pigeon pea
Which of the above is/are used as pulse, fodder and green manure?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q.1 Livestock rearing has a big potential for providing non-farm employment and income in rural areas. Discuss suggesting suitable measures to promote this sector in India. (2015)
Q.2 The concept of cooperative federalism has been increasingly emphasized in recent years. Highlight the drawbacks in the existing structure and the extent to which cooperative federalism would answer the shortcomings. (2015)
The Unjust Climate: FAO
For Prelims: The Unjust Climate: FAO, Food and Agriculture Organization, Climate Change, Extreme Precipitation, Heat Stress.
For Mains: The Unjust Climate: FAO, Impact of Climate Change on Agriculture and Food Security.
Why in News?
Recently, the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), has released a report titled- The Unjust Climate, shows how the effects of Climate Change on income and adaptation in rural areas vary with gender, wealth and age.
- FAO analyzed socioeconomic data from over 100,000 rural households representing more than 950 million people across 24 LMICs (Lower Middle Income Countries).
- The study integrated this information with 70 years of georeferenced daily precipitation and temperature data to examine the impacts of climate stressors on incomes, labour, and adaptation strategies, differentiating based on wealth, gender, and age.
What are the Key Findings of the Report?
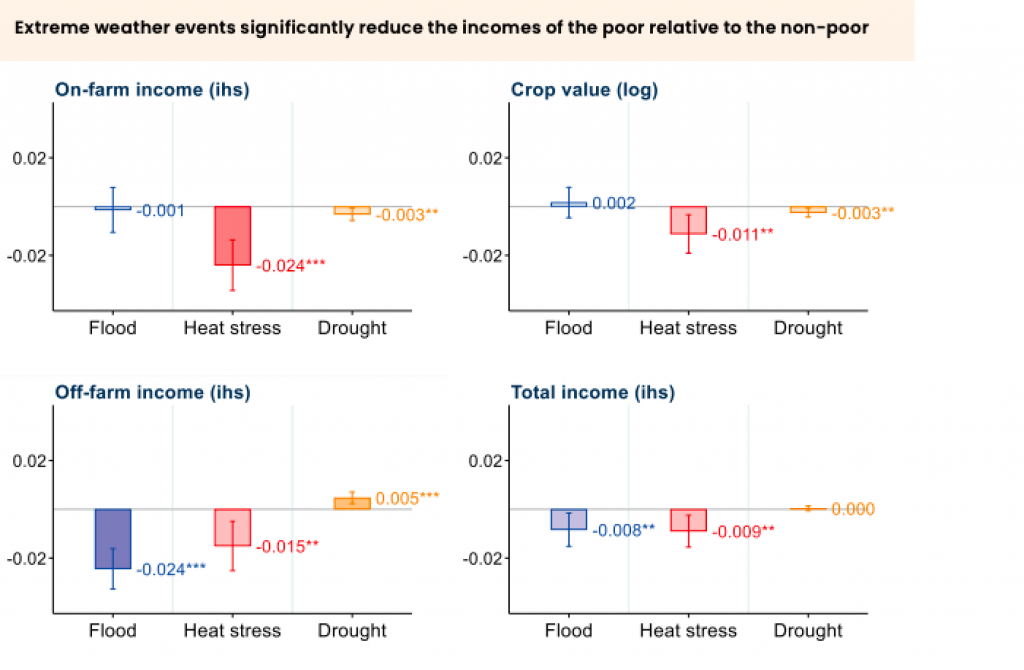
- Impact of Extreme Weather on Poor Rural Households:
- Every day of extreme heat results in poor rural households losing 2.4% of on-farm incomes, 1.1% of crop value, and 1.5% of off-farm income compared to non-poor households across India and 23 other LMICs (Lower Middle Income Countries).
- A 1°C increase in long-term temperatures would push rural poor households to rely more on climate-dependent agriculture, leading to a 33% decrease in off-farm incomes.
- Similarly, every day of extreme Precipitation causes poor households to lose 0.8% of their incomes relative to non-poor households, mainly driven by losses in off-farm incomes.
- Income Inequality Widening Due to Climate Stressors:
- In an average year, poor households lose 5% of their total income due to Heat Stress and 4.4% due to floods compared to better-off households.
- Floods and heat stress widen the income gap between poor and non-poor households in rural areas by approximately USD 21 billion and USD 20 billion a year, respectively.
- Maladaptive Coping Strategies:
- Extreme weather events push poor rural households to adopt maladaptive coping strategies, including distress sale of livestock and redirecting expenditures away from their farms.
- Poor households reduce their investments in agriculture relative to non-poor households when faced with floods and droughts, as they redirect their scarce resources away from agricultural production towards immediate consumption needs.
- These maladaptive coping strategies are likely to make them more vulnerable to future climate stressors than non-poor rural households.
- Inadequate Inclusion in National Climate Policies:
- Rural people and their climate vulnerabilities are largely absent in national climate policies.
- Less than 1% of Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC) and national adaptation plans (NAP) of the 24 analysed countries mention poor people, and only about 6% refer to farmers in rural communities.
- Only 7.5% of tracked climate finance in 2017-18 went towards climate change adaptation, with less than 3% allocated to agriculture, forestry, and other land uses.
- Agricultural policies also miss the opportunity to address gender equality and women's empowerment and intersecting vulnerabilities such as climate change.
- An analysis of agricultural policies from 68 low- and middle-income countries done by FAO in 2023 showed that about 80% of policies did not consider women and climate change.
What are the Recommendations of the Report?
- It is suggested that addressing these challenges requires targeted interventions to empower various rural populations to engage in climate-adaptive measures.
- It is imperative to invest in policies and programmes that address the multidimensional climate vulnerabilities of rural people and their specific constraints, including their limited access to productive resources.
- It is recommended to link social protection programmes to advisory services that can encourage adaptation and compensate farmers for losers, such as cash-based social assistance programs.
- Gender-transformative methodologies that directly challenge discriminatory gender norms, could also tackle the entrenched discrimination that often prevents women from exercising full agency over economic decisions that impact their lives.
What are the FAO’s Initiatives to Tackle the Impact of Climate Change?
- Inclusive climate actions are embedded in FAO’s Strategy and Action Plan on Climate Change and in the FAO Strategic Framework 2022–2031, where tackling the impact of climate change is mainstreamed in efforts to achieve the four betters: better production, better nutrition, better environment and better life for all.
- FAO’s Global Roadmap for Achieving SDG (Sustainable Development Goal) 2 without breaching the 1.5 °C threshold, establishes that gender inequalities, climate actions and nutrition are simultaneous considerations, and actions must encompass these dimensions and promote inclusivity for women, youth and Indigenous Peoples.
What is the Food and Agriculture Organization?
- About:
- FAO is a specialised agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger.
- World Food Day is celebrated every year around the world on 16th October. The day is celebrated to mark the anniversary of the founding of the FAO in 1945.
- It is one of the UN food aid organisations based in Rome (Italy). Its sister bodies are the World Food Programme and the International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD).
- FAO is a specialised agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger.
- Initiatives Taken:
- Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS).
- Monitors the Desert Locust situation throughout the world.
- The Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC) is the body responsible for all matters regarding the implementation of the Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Programme.
- The International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture was adopted by the Thirty-First Session of the Conference of the FAO in 2001.
- Flagship Publications:
- The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture (SOFIA).
- The State of the World's Forests (SOFO).
- The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World (SOFI).
- The State of Food and Agriculture (SOFA).
- The State of Agricultural Commodity Markets (SOCO).
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. The FAO accords the status of ‘Globally Important Agricultural Heritage System (GIAHS)’ to traditional agricultural systems. What is the overall goal of this initiative? (2016)
- To provide modern technology, training in modern farming methods and financial support to local communities of identified GIAHS so as to greatly enhance their agricultural productivity.
- To identify and safeguard eco-friendly traditional farm practices and their associated landscapes, agricultural biodiversity and knowledge systems of the local communities.
- To provide Geographical Indication status to all the varieties of agricultural produce in such identified GIAHS.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains:
Q.1 The effective management of land and water resources will drastically reduce the human miseries. Explain. (2016)
Market Monopoly and Anti-Competitive Practices
For Prelims: Market Monopoly and Anti-Competitive Practices, Google Play Store, Competition Commission of India (CCI), Competition Act, 2002.
For Mains: Market Monopoly and Anti-Competitive Practices, Market Monopoly and Laws in India, Inclusive growth and issues arising from it.
Why in News?
Recently, a dispute has emerged between Google and app developers, where Google removed almost a dozen firms out of its marketplace for Android apps.
- The dispute incorporate concerns over Market Monopoly and Anti-Competitive practices, with Google's firm grip over the Android app ecosystem serving as a focal point of contention.
What is the Issue Between Google and App Developers?
- Background and Context:
- Google's Android platform and its app marketplace, Google Play, dominate the Indian smartphone ecosystem.
- Indian app developers rely heavily on Google Play for distribution and monetization of their apps, making them susceptible to Google's policies and fees.
- The dispute stems from Google's imposition of fees ranging from 11% to 30% on in-app purchases of digital services, which developers consider excessive and harmful to innovation and competition.
- Issues and Concerns:
- Indian app developers, including major players like Bharat Matrimony and Disney+ Hotstar, have challenged Google's fees in court, citing economic burden and lack of choice.
- The Competition Commission of India (CCI) has fined Google for anticompetitive practices, indicating regulatory scrutiny over its market dominance and pricing policies.
- The conflict underscores broader concerns about platform monopolies and their impact on small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), innovation, and consumer welfare.
- Indian app developers, including major players like Bharat Matrimony and Disney+ Hotstar, have challenged Google's fees in court, citing economic burden and lack of choice.
- International Comparisons:
- Similar disputes between tech giants and app developers have occurred globally, with Apple facing scrutiny over its App Store fees and practices.
- Legal and regulatory actions in jurisdictions like the European Union and the United States serve as precedents for addressing antitrust concerns and enforcing fair competition in digital markets.
How Does the Play Store Work?
- Google’s operating system Android runs on Samsung, OnePlus, Motorola and Oppo among other smartphones.
- Some of the Google apps and Play Store come pre-installed in the phones that a user buys.
- But in order to add a new app, the user has to visit the Play Store and download it.
- Apps on Google have three options to accept payments for digital services, Google’s billing system, alternative payment where the company charges the commission and consumption mode where the developer redirects the user to an external website to accept payments.
What is Market Monopoly?
- About:
- Market monopoly refers to a situation in which a single company or a group of companies dominates and controls a significant share of a particular market or industry.
- In a monopoly, there is only one seller or producer that provides a specific product or service, and there are no close substitutes available to consumers.
- This gives the monopolistic entity substantial market power, allowing it to influence the market conditions, set prices, and control the supply of goods or services.
- Features of Market Monopoly:
- Single Seller or Producer:
- In a monopoly, there is only one entity that dominates the entire market. This company is the exclusive provider of a particular product or service.
- High Barriers to Entry:
- Monopolies often arise when there are significant barriers preventing new competitors from entering the market. Barriers may include high startup costs, exclusive access to resources, government regulations, or strong brand loyalty.
- No Substitutes:
- Consumers have limited or no alternative options for the product or service offered by the monopolistic company. There are no close substitutes available in the market.
- Market Power and Pricing Control:
- The monopoly has considerable market power, allowing it to control prices without significant fear of competition. This can lead to higher prices for consumers and potentially reduced output.
- Influence Over Supply:
- The monopoly has control over the supply of the product or service. It can determine the quantity produced and adjust supply to impact market conditions.
- Lack of Competition:
- Due to the absence of competitors, monopolies operate in an environment where there is no direct competition for their specific product or service. This lack of competition can result in reduced incentives for innovation and efficiency.
- Single Seller or Producer:
What are the Key Terms Related to Anti-Competitive Practices?
- Predatory Pricing:
- Predatory pricing occurs when a company intentionally sets its prices below cost in order to drive competitors out of the market. Once competitors are eliminated, the company can raise prices to recoup losses and enjoy a monopolistic position.
- Cartels:
- Cartels are associations of independent businesses or countries formed to regulate production, pricing, and marketing of goods or services.
- Cartels are typically illegal and are known for fostering anti-competitive behaviour.
- Mergers:
- Mergers involve the combination of two or more companies into a single entity. While not all mergers are anti-competitive, some may reduce competition in a particular market, leading to regulatory scrutiny.
- Price Discrimination:
- Price discrimination occurs when a seller charges different prices to different customers for the same product or service. While not always illegal, it can be considered anti-competitive if it harms competition.
- Price Fixing Agreements:
- Price fixing involves an agreement between competitors to set a specific price for their products or services. This eliminates competition and artificially inflates prices, violating antitrust laws.
What are the Indian and International Initiatives to Deal with Market Monopoly?
- Indian:
- Competition Act, 2002: The Competition Act, 2002, is the primary legislation in India addressing antitrust issues. It was enacted to promote and sustain competition in markets, prevent anti-competitive practices, and protect the interests of consumers.
- Competition Amendment Bill, 2022: The proposed amendment aims to further strengthen the regulatory framework, address emerging challenges, and enhance the effectiveness of competition law enforcement.
- Competition Commission of India (CCI): CCI is the regulator of competition under the Competition Act, 2002 in the Indian market. It is responsible for enforcing the provisions of the Competition Act 2002. It consists of a Chairperson and Members appointed by the Central Government.
- The CCI investigates and takes actions against anti-competitive practices, abuse of dominant position, and anti-competitive agreements.
- Competition Appellate Tribunal and NCLAT: The Competition Appellate Tribunal (COMPAT) was initially responsible for hearing appeals against CCI decisions.
- However, in 2017, the government replaced COMPAT with the National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (NCLAT), which now handles appeals related to competition matters.
- Competition Act, 2002: The Competition Act, 2002, is the primary legislation in India addressing antitrust issues. It was enacted to promote and sustain competition in markets, prevent anti-competitive practices, and protect the interests of consumers.
- International Initiatives:
- OECD Competition Committee: The OECD (Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development) addresses anti-competitive practices through various initiatives, including the OECD Competition Committee, which facilitates discussions and cooperation among member countries on competition-related issues.
- United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD): It provides guidance on competition policy and law through its Intergovernmental Group of Experts on Competition Law and Policy, supporting countries in implementing effective competition frameworks.
- It also deals with the policies to Protect consumers from abuse and Curb regulations that stifle competition.
- International Competition Network (ICN): The ICN is a network of competition authorities from around the world. It facilitates communication and cooperation among member jurisdictions to address global competition challenges.
- The ICN provides a platform for sharing best practices and developing guidelines on various aspects of competition law.
- World Trade Organization (WTO): While primarily focused on trade issues, the WTO addresses competition policy through its Working Group on the Interaction between Trade and Competition Policy.
- The aim is to ensure that competition policies do not create unnecessary barriers to trade.
Way Forward
- Advocates, such as public policy experts and industry representatives, propose regulatory reforms to enhance competition and mitigate the dominance of app store gatekeepers.
- It is important to include mandating transparency and fairness in app store policies, empowering developers with more payment options, and facilitating the emergence of alternative distribution channels.
- Balancing the interests of platform providers, developers, and consumers requires a nuanced approach that prioritises innovation, competition, and consumer welfare.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. With reference to ‘consumers’ rights/privileges under the provisions of law in India, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2012)
- Consumers are empowered to take samples for food testing.
- When a consumer files a complaint in any consumer forum, no fee is required to be paid.
- In case of death of consumer, his/her legal heir can file a complaint in the consumer forum on his/her behalf.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Mains:
Q. Has the Indian governmental system responded adequately to the demands of Liberalization, Privatization and Globalization started in 1991? What can the government do to be responsive to this important change? (2016)
INS Jatayu in the Lakshadweep Islands
Why in News?
The commissioning of INS Jatayu, an upgraded naval base in the Lakshadweep Islands, marks a significant development in India’s maritime security strategy, particularly in the context of growing Chinese influence in the Indian Ocean Region.
- Additionally, the Indian Navy commissioned its first MH-60R multi-role helicopter squadron Indian Naval Air Squadron (INAS) 334 at Kochi, a major capability boost for its rotary fleet and its anti-submarine warfare capabilities.
What are the Key Highlights of INS Jatayu?
- INS Jatayu, formerly Naval Detachment Minicoy, is commissioned as an upgraded naval base on Minicoy Island in the Lakshadweep archipelago.
- It will operate under the operational control of the Naval Officer in Charge (Lakshadweep), Southern Naval Command.
- The base enhances the operational reach of the Indian Navy in the Indian Ocean, bolstering its capabilities for anti-piracy, anti-narcotics, and surveillance operations.
- Situated in Minicoy, the southernmost atoll of the Lakshadweep archipelago, INS Jatayu strategically overlooks vital Sea Lines of Communications (SLOCs), strengthening India’s maritime presence in the region.
- In light of China's increasing presence in the Indian Ocean, INS Jatayu reinforces India's ability to counterbalance and deter any attempts to undermine its maritime dominance and territorial integrity.
- INS Jatayu will effectively be the country’s second naval base in Lakshadweep. The Navy’s first base on the islands, INS Dweeprakshak in Kavaratti, was commissioned in 2012.
- INS Jatayu will be equipped with additional infrastructure, including an airfield and personnel housing, to support naval operations and ensure comprehensive security coverage.
- Minicoy Island, where INS Jatayu is located, sits at the intersection of crucial Sea Lines of Communications (SLOCs) like the Eight Degree Channel and the Nine Degree Channel, making it susceptible to maritime pollution due to heavy maritime traffic.
- Eight Degree Channel separates Indian Minicoy island from Maldives.
- The Nine Degree Channel separates the island of Minicoy from the Lakshadweep archipelago.
The Lakshadweep Islands
- India's smallest Union Territory, Lakshadweep ( ‘a hundred thousand islands’ in Sanskrit and Malayalam) is an archipelago consisting of 36 islands located between 220 km and 440 km from Kochi.
- The islands, only 11 of which are inhabited, have a total area of only 32 sq km. It is directly under the control of the Centre through an administrator.
- The Lakshadweep is part of a chain of coralline islands in the Indian Ocean that includes the Maldives to the south, and the Chagos archipelago farther beyond, to the south of the equator.
What are the Key Highlights of the INAS 334 Squadron?
- The Indian Naval Air Squadron (INAS) 334 is the first squadron of the MH-60R helicopters, also known as the "Seahawks". The squadron was commissioned at INS Garuda, Kochi.
- The squadron is a part of the 24-aircraft Foreign Military Sales (FMS) contract signed with the United States government in February 2020.
- The MH 60R Seahawk, a maritime variant of the Blackhawk helicopter, is designed for various roles including:
- Anti-submarine warfare, Anti-surface warfare, Search and rescue , Medical evacuation and Vertical replenishment.
- Deployment of Seahawks in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) strengthens the Indian Navy's maritime presence, dissuading potential threats and ensuring a secure environment in this strategically crucial region.
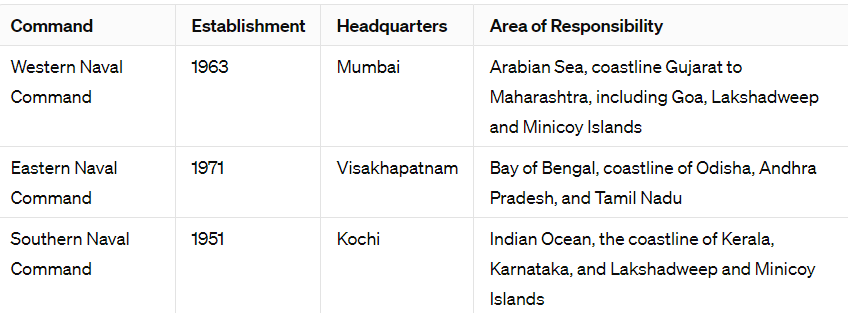
Commands of Indian Navy:
It has three operational and one theatre commands. Each command is headed by a Flag Officer Commanding-in-Chief holding the rank of Vice Admiral.
- Andaman and Nicobar Command, 2001: It is a unified tri-services theatre command based at Port Blair, A&N Islands.
- It includes the Indian Navy, Indian Army, Indian Air Force and Indian Coast Guard.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Which one of the following pairs of islands is separated from each other by the ‘Ten Degree Channel’? (2014)
(a) Andaman and Nicobar
(b) Nicobar and Sumatra
(c) Maldives and Lakshadweep
(d) Sumatra and Java
Ans: (a)
Q2. Which one of the following is the best description of ‘INS Astradharini’, that was in the news recently? (2016)
(a) Amphibious warfare ship
(b) Nuclear-powered submarine
(c) Torpedo launch and recovery vessel
(d) Nuclear-powered aircraft carrier
Ans: (c)
Q3. Consider the following in respect of Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS): (2017)
- Inaugural IONS was held in India in 2015 under the chairmanship of the Indian Navy.
- IONS is a voluntary initiative that seeks to increase maritime co-operation among navies of the littoral states of the Indian Ocean Region.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- The ‘Indian Ocean Naval Symposium’ (IONS) is a voluntary initiative that seeks to increase maritime cooperation among navies of the littoral States of the Indian Ocean Region by providing an open and inclusive forum for discussion of regionally relevant maritime issues. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- It provides a forum to increase maritime security cooperation, and promote friendly relationships among the member nations.
- The inaugural IONS-2008 was held in New Delhi, India in February, 2008. The Chief of the Naval Staff, Indian Navy was designated as the Chairman of IONS for the period 2008-10. Hence, statement 1 is not correct. Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. What do you understand by ‘The String of Pearls’? How does it impact India? Briefly outline the steps taken by India to counter this. (2013)
Q. Discuss the political developments in the Maldives in the last two years. Should they be of any cause for concern to India? (2013)
Amendments to the Electricity (Rights of Consumers) Rules, 2020
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Power has notified amendments to the Electricity (Rights of Consumers) Rules, 2020, to accelerate the installation of Rooftop Solar Projects and empower consumers – with provisions on connections in residential societies and solving complaints on meter readings.
What are the Major Amendments in Electricity Rules, 2020?
- Easier and Faster installation of Rooftop Solar Systems:
- Exemption has been given for the requirement of technical feasibility study, for systems up to a capacity of 10 kW.
- For systems of capacity higher than 10 kW, the timeline for completing the feasibility study has been reduced from 20 to 15 days.
- A technical feasibility study typically involves assessing factors such as site suitability, structural integrity of the building, available sunlight exposure, electrical infrastructure compatibility, and potential obstacles or challenges that may affect the installation and operation of the solar panels.
- It is mandated that the distribution system strengthening necessary for rooftop solar PV systems up to 5 kW capacity will be done by the distribution company at its own cost.
- Further, the timeline for the distribution licensee to commission Rooftop Solar PV systems has been reduced from 30 to 15 days.
- Separate Connections for Electric Vehicle Charging Stations:
- Consumers can obtain separate electricity connections for charging their Electric Vehicles (EVs).
- This aligns with India’s goal of reducing carbon emissions and reaching Net Zero by the year 2070.
- The time period for obtaining a new electricity connection has been reduced from 7 to 3 days in metropolitan areas, from 15 to 7 days in other municipal areas, and from 30 to 15 days in rural areas.
- However, in rural areas with hilly terrain, the time period for new connections or for modifications in existing connections will remain thirty days.
- Consumers can obtain separate electricity connections for charging their Electric Vehicles (EVs).
- Additional Rights for Consumers in Residential Colonies and Flats:
- Owners residing in co-operative group housing societies, multi-storied buildings, residential colonies, etc., will have the option to choose from the distribution licensee either individual connections for everyone or a single-point connection for the whole premises.
- The exercise of the option will be based on a transparent ballot to be conducted by the Distribution Company.
- Parity has also been brought in the tariff charged to consumers who get electricity supplied through single-point connection and to those who avail of individual connections.
- Metering, billing, and collection will be done separately for:
- Individual electricity consumption sourced from the distribution licensee
- Individual consumption of backup power supplied by the residential association
- Electricity consumption for common areas of such residential associations, which is sourced from the distribution licensee.
- Mandatory Additional Meter in cases of Complaints:
- In cases where consumers raise complaints about meter reading not aligning with their actual electricity consumption, the distribution licensee is now required to install an additional meter within five days from the date of receipt of the complaint.
- This additional meter will be used to verify the consumption for a minimum period of three months, thus reassuring consumers and ensuring accuracy in billing.
- In cases where consumers raise complaints about meter reading not aligning with their actual electricity consumption, the distribution licensee is now required to install an additional meter within five days from the date of receipt of the complaint.
What are the Other Government Initiatives for Solar Energy?
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Consider the following statements: (2016)
- The International Solar Alliance was launched at the United Nations Climate Change Conference in 2015.
- The Alliance includes all the member countries of the United Nations.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (a)
Mains:
Q. India has immense potential of solar energy though there are regional variations in its developments. Elaborate. (2020)
Claude 3 AI Chatbot
Why in News?
Recently, the Artificial Intelligence (AI) start-up Anthropic announced its latest family of AI models called Claude 3, stating that it “sets new industry benchmarks across a wide range of cognitive tasks”.
- The family includes three state-of-the-art AI models in the ascending order of capabilities – Claude 3 Haiku, Claude 3 Sonnet, and Claude 3 Opus.
Note
- Anthropic is an OpenAI rival started by former leaders at the ChatGPT maker.
- While OpenAI has closely tied itself to its business partner Microsoft, Anthropic's primary cloud computing partner is Amazon.
What is Claude 3?
- About Claude:
- Claude is a group of Large Language Models (LLMs) developed by Anthropic.
- LLMs are a specific class of generative AI models that are trained to understand and generate human-like text.
- The chatbot is capable of handling text, voice messages, and documents.
- The chatbot is capable of generating faster, contextual responses compared to its peers.
- Claude is a group of Large Language Models (LLMs) developed by Anthropic.
- Training:
- Claude sources include the Internet and some licensed datasets using two methods, Supervised Learning (SL) and Reinforcement Learning (RL).
- In the SL phase, the LLM produces responses to prompts, and then self-assesses them based on a set of guiding principles.
- It later revises the responses — and according to its makers, this process is aimed at reducing the harmful effects of the AI’s outputs.
- RL phase involves training the model based on AI-generated feedback, in which the AI evaluates responses based on a set of constitutional principles.
- These methods, and the general approach, has been chosen with the aim of making Claude helpful and harmless.
- Claude 3:
- Among the new releases, Claude 3 Opus is the most powerful model, Claude 3 Sonnet is the middle model that is capable and price competitive, and Claude 3 Haiku is relevant for any use case that requires instant responses.
- Claude Sonnet powers the Claude.ai chatbot for free at present and users only need an email sign-in.
- However, Opus is only available through Anthropic’s web chat interface and if a user is subscribed to the Claude Pro service on the Anthropic website.
- Among the new releases, Claude 3 Opus is the most powerful model, Claude 3 Sonnet is the middle model that is capable and price competitive, and Claude 3 Haiku is relevant for any use case that requires instant responses.
- Limitations of Claude 3:
- Claude 3 performs well in tasks such as answering factual questions and optical character recognition (OCR), meaning the ability to extract text from images.
- Reportedly, the new model is good at following instructions and completing tasks like writing Shakespearean sonnets.
- However, it struggles with complex reasoning and mathematical problems at times. It also exhibited biases in its responses, such as favouring a certain racial group over others.
- Claude 3 performs well in tasks such as answering factual questions and optical character recognition (OCR), meaning the ability to extract text from images.
Read More: Large Language Models (LLMs), ChatGPT Chatbot, Ethical Implications of AI
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Chakshu and the Digital Intelligence Platform
The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) introduced two initiatives, Chakshu and the Digital Intelligence Platform (DIP), to combat spam and fraud calls through the Sanchar Saathi portal.
- Chakshu (meaning eyes) is accessible at sancharsaathi.gov.in/sfc, facilitating citizens to report suspicious communications.
- The platform allows users to report various types of fraud, including those related to bank accounts, payment wallets, SIM cards, gas and electricity connections, KYC updates, impersonation, and sextortion.
- The primary objective of Chakshu is to enable proactive reporting of suspicious activities, contributing to the prevention and mitigation of telecom-related fraud and spam calls.
- Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) is working on developing an app for the Chakshu platform, further streamlining the reporting process for users.
- The DIP is a secure and integrated platform created by the DoT for curbing the misuse of telecom resources and data through intelligence sharing and information exchange among the stakeholders covering a wide spectrum of telecom service providers, law enforcement agencies (LEAs), banks and financial institutions.
- It would be a non-public data-sharing resource for “Telecom Service Providers (TSPs), LEAs, banks and financial institutions, social media platforms, identity document issuing authorities etc.
Read more: World Telecom Day 2023
India's First Underwater Metro Service
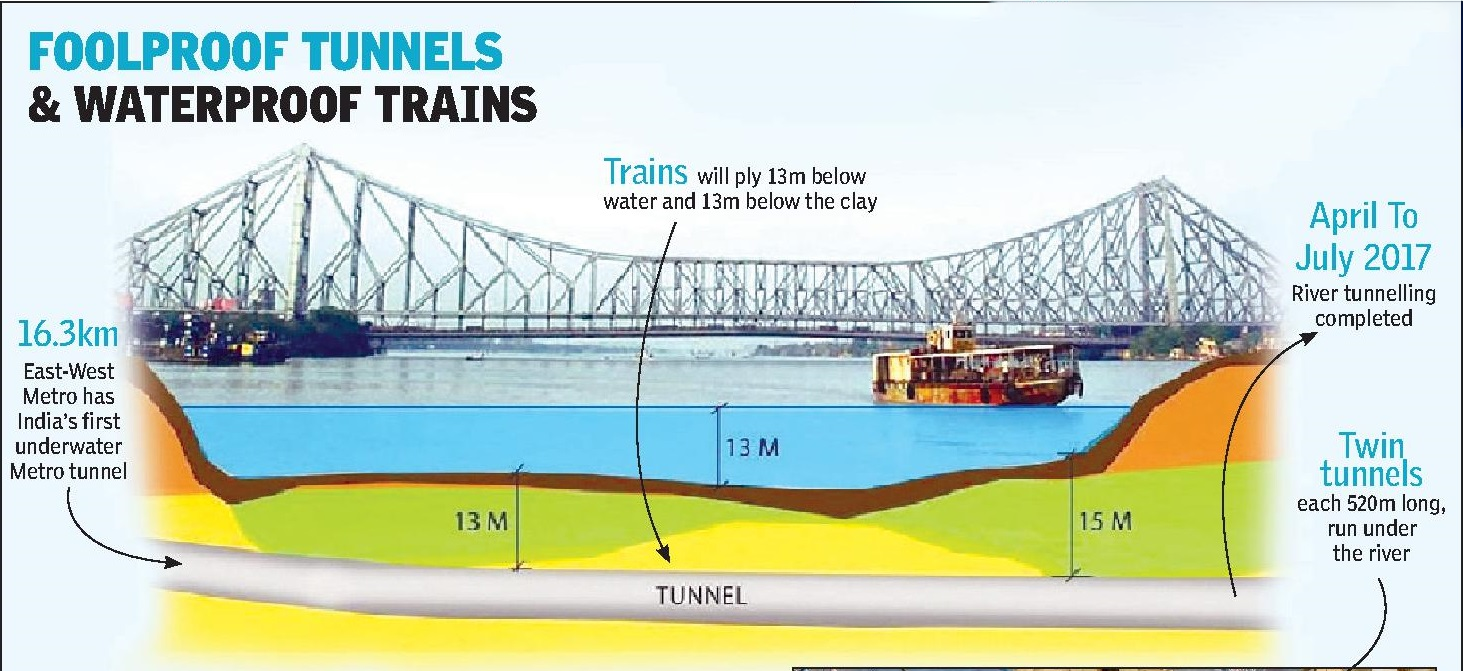
The Prime Minister inaugurated the Kolkata Metro's Esplanade-Howrah Maidan section, marking the inauguration of India’s first underwater transportation tunnel.
- The section, passing below the Hooghly River, showcasing the nation's engineering prowess hosts the deepest Metro station (the Howrah metro station at 30 metres) in India.
- The Hooghly River, also known as the Bhagirathi-Hoogly and Kati-Ganga Rivers, is one of the significant rivers in West Bengal. It is a distributary or arm of the Ganges River, about 260 km long. Formed in Murshidabad, where Ganga splits into two parts – while the part flowing through Bangladesh is called the Padma. The other part is the Hooghly.
Read more: Atal Setu Nhava Sheva Sea Link, Sudarshan Setu
Global Cervical Cancer Elimination Forum
The first ever Global Cervical Cancer Elimination Forum (GCF) in Cartagena de Indias, Colombia, secured nearly USD 600 million in funding from the World Bank, Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, and UNICEF.
- The funds will be utilised to enhance global access to vaccination, screening and treatment for cervical cancer.
- The Forum aims to catalyse governments, donors, civil society, and others to commit to cervical cancer elimination and galvanize the global community.
- Cervical cancer is a cancer that starts in the cervix, which is the lower end of the uterus that connects it to the vagina. It's caused by a long-lasting (human papillomavirus) HPV infection, which is a common virus transmitted through sexual contact.
- Cervical cancer is ranked as the fourth most prevalent cancer among women globally.
- Despite available tools for prevention and elimination, it claims a woman's life every 2 minutes globally, with over 90% of cervical cancer deaths in 2022 occurring in low- and middle-income nations.
- WHO's Global Strategy for Cervical Cancer Elimination, launched in November 2020, targets, by 2030:
- 90% of girls vaccinated against HPV by age 15
- 70% of women screened with a high-performance test by ages 35 and 45
- 90% of women with cervical disease receive treatment.
- Indian Government intends to initiate a three-phase vaccination drive against human papillomavirus (HPV) for girls aged 9-14, aiming to mitigate the risk of cervical cancer.
Read more: Expanding Cervical Cancer Prevention Initiatives, HPV Vaccine for Cervical Cancer
Arctic and Great Lakes Ice Trends
A recent study forecasts the Arctic's initial ice-free conditions by August or September of 2030, regardless of emission scenarios, with the possibility of recurring occurrences by mid-century (2035–2067).
- In recent years, the Arctic Ocean had around 3.3 million km2 of sea ice at its minimum in September 2023.
- Arctic sea ice reaches its minimum extent in September every year.
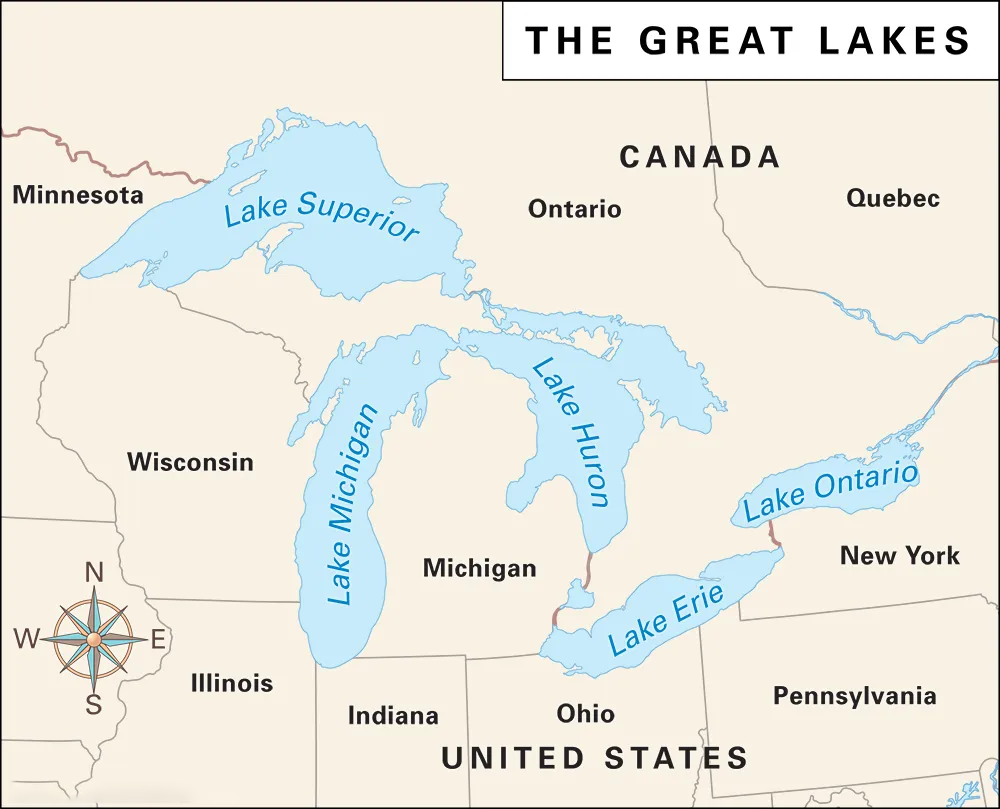
- Concurrently, the Great Lakes, comprising Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario have witnessed notably reduced ice cover for 2 consecutive years.
- They are renowned as Earth's 'freshwater tower,' and are now witnessing unprecedented declines in ice cover, attributed to global warming and the El Nino phenomenon.
- The year 2023 was designated as the hottest on record, largely influenced by El Nino.
- They are renowned as Earth's 'freshwater tower,' and are now witnessing unprecedented declines in ice cover, attributed to global warming and the El Nino phenomenon.
Read more: Arctic Region and Melting Aspirations, Great Lakes