Indian Polity
Right to Strike
Prelims: Article 19, Industrial Dispute Act, 1947, Fundamental Rights.
Mains: Right to Strike.
Why in News?
The Kerala High Court has reiterated that government employees who participate in general strikes, affecting the normal life of the public and Public Exchequer, are not entitled to be protected under Article 19(1)(c) of the Constitution and are also a violation of the provisions of the Kerala Government Servants’ Conduct Rules, 1960.
What is Right to Strike?
- About:
- Strike is the collective refusal by employees to work under the conditions required by employers. Strikes arise for a number of reasons, though principally in response to economic conditions (defined as an economic strike and meant to improve wages and benefits) or labour practices (intended to improve work conditions).
- In each country whether it is democratic, capitalist, socialist, give the right to strike to the workers. But this right must be the weapon of last resort because if this right is misused, it will create a problem in the production and financial profit of the industry.
- This would ultimately affect the economy of the country.
- In India, the right to protest is a fundamental right under Article 19 of the Constitution of India.
- But right to strike is not a fundamental right but a legal right and with this right statutory restriction is attached in the Industrial Dispute Act, 1947.
- The Industrial Dispute Act, 1947 is subsumed under The Industrial Relations Code, 2020.
- Position in India:
- In India, unlike America, the right to strike is not expressly recognized by the law.
- The trade union Act, 1926 for the first time provided limited right to strike by legalizing certain activities of a registered trade union in furtherance of a trade dispute which otherwise breach of common economic law.
- Nowadays a right to strike is recognized only to a limited extent permissible under the limits laid down by the law itself, as a legitimate weapon of Trade Unions.
- The right to strike in the Indian constitution set up is not an absolute right but it flows from the fundamental right to form a union.
- As every other fundamental right is subject to reasonable restrictions, the same is also the case to form trade unions to give a call to the workers to go on strike and the state can impose reasonable restrictions.
- Right to strike under International Convention:
- Right to strike has also been recognised by the conventions of the International Labour Organization (ILO).
- India is a founder member of the ILO.
- Right to strike has also been recognised by the conventions of the International Labour Organization (ILO).
What are the Important Supreme Court Judgements related to Right to Strike?
- The Supreme Court in Delhi Police v. Union of India (1986) upheld the restrictions to form association by the members of the non-gazetted police force after the Police Forces (Restriction of Rights) Act, 1966, and the Rules as amended by Amendment Rules, 1970, came into effect.
- In T.K. Rangarajan v. Government of Tamil Nadu (2003), the Supreme Court held that the employees have no fundamental right to resort to strike. Further, there is prohibition to go on strike under the Tamil Nadu Government Servants’ Conduct Rules, 1973.
Internal Security
Unmanned Combat Systems and Concerns
Prelims: Indian Navy Indian Ocean Region, Littorals, Artificial Intelligence.
Mains: Unmanned Combat Systems and Concerns. AI in Warfare.
Why in News?
India is on a drive to induct Unmanned Combat Systems (UCS) into the military. In August, 2022 it inducted “Swarm Drones” into its mechanized forces, reiterating the importance of autonomous systems in creating a “future-proof” Indian Navy (IN).
- Despite their growing usage in armed conflict, artificially intelligent unmanned combat systems raise questions of law, ethics and accountability.
What are Unmanned Combat Systems?
- About:
- Unmanned Combat Systems (UCS) are going to be the new age weapons overturning the rules of future war and have been the focus of research and development of military powers.
- There are no generally accepted definitions for these so-called boasted core weapons of the 21st century.
- UCS from the research heading, is an integrated combat system comprising unmanned combat platforms, task payloads, command and control (C2) systems and network systems.
- For field applications, they can be categorized into,
- Deep space unmanned systems
- Unmanned aerial vehicle systems
- Ground unmanned systems
- Surface unmanned systems
- Underwater unmanned systems
- Significance:
- Faced with the increasingly complex international situation and brutal military wars, the lives and safety of combat soldiers are greatly threatened.
- At this time, the unmanned combat System is becoming increasingly important and has gradually become an important attack and defense force on the information battlefield.
- The biggest feature of the ground unmanned combat platform is that it can carry certain weapons and equipment under the premise of unmanned participation, and be remotely controlled through the configured wireless communication equipment to conduct reconnaissance, surveillance, electronic interference, and direct combat.
- UCS has a higher degree of automation, good remote control, strong digital communication ability and anti-interference, excellent target detection and recognition ability, good concealment, and strong adaptability to the ground environment.
What are the Ethical Concerns Raised by AI Warfare?
- Risk of Shared Liability:
- AI Warfare enhances the risk of shared liability between networked systems, particularly when weapon algorithms are sourced from abroad, and when the satellite and link systems that enable combat solutions are not under the control of the user.
- Confidence Undermining:
- AI is characterized by a predisposition to certain kinds of data. Biases in the collection of data, in the set of instructions for data analysis, and in the selection of probabilistic outcomes muddle rational decision-making, undermining confidence in automated combat solutions.
- Inconsistent with Laws of War:
- AI may automate weapon systems in ways that are inconsistent with the laws of war.
- Cannot Make Informed Decision:
- A system of targeting human beings based on probabilistic assessments by computers that act merely on machine-learned experiences, they contend, is problematic because the computer neither has access to all relevant data to make an informed decision nor recognises that it needs more information to come up with an optimal solution.
- If it erroneously used force in a theater of conflict, there is no one to be held accountable, as blame can’t be pinned on a machine.
What are Swarn Drones?
- About:
- Swarm Drones are a collection of small and lightweight aerial vehicles that can be controlled from the same station.
- These drones are equipped with advanced communication systems which enables them to be controlled as a collective.
- Furthermore, through communication systems, swarm drones can also communicate with each other to create different flying formations for surveillance and attack modes.
- Such drones can also carry a variety of payloads in a single mission and organize a collaborative attack against an enemy unit.
- Backed by swarming algorithms and Artificial Intelligence software, Swarm Drones can operate autonomously with minimum human intervention
- The AI software can also be used to identify targets and expedite response in case of a surprise operation.
- Advantages:
- All Weather Operations: Swarm Drone System can be deployed at high altitudes, rough-weather conditions
- High Speed and Agility: Drones are powered by advanced motors and can fly at a speed of 100 km per hour giving it high speed and agility for military operations.
- Employed for Different Missions: Drones can be deployed by the armed forces for different types of offensive and defensive operations as they can carry out strikes against tanks, infantry combat vehicles, ammunition holding areas, fuel dumps and terror launch pads.
- ATR Feature: Swarm Drones are backed by Artificial Intelligence and are equipped with the Automatic Target Recognition (ATR) feature, which can enable them to automatically recognise targets. ATR is capable of identifying tanks, guns, vehicles and humans and displaying them on the operators’ screen to minimize the chances of a miss hit.
Way Forward
- All parties to an armed conflict that any use of armed drones during the conduct of hostilities must comply with relevant IHL (International humanitarian law). principles.
- Hence, before deploying any armed drones, parties to the conflict must ensure that the armed drone is and can be directed against a military objective and will not cause excessive civilian harm.
- In order to foster transparency and accountability for drone strikes, parties need to properly articulate their policies governing the use of drones, including how the likelihood for civilian harm is assessed, and provide for remedies for victims.
- All parties to the armed conflict that beyond compliance with IHL, parties need to consider the humanitarian impact of their use of armed drones for the civilian population, including the disruption of civilian infrastructure and mental health trauma.
- It is worth acknowledging that AI in warfare is not just a matter of combat effectiveness but also of warfighting ethics. AI-infused unmanned systems on the maritime battlefront pose a degree of danger, making it incumbent upon the military to deploy its assets in ways that are consistent with national and international law.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following activities: (2020)
- Spraying pesticides on a crop field
- Inspecting the craters of active volcanoes
- Collecting breath samples from spouting whales for DNA analysis
At the present level of technology, which of the above activities can be successfully carried out by using drones?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Governance
The Indian Telegraph (Infrastructure Safety) Rules 2022
For Prelims: Department of Telecommunications formulates the Indian Telegraph (Infrastructure Safety) Rules 2022, PM Gati Shakti NMP platform.
For Mains: Significance of Indian Telegraph (Infrastructure Safety) Rules, 2022.
Why in News?
Recently, the Department of Telecommunications under the Ministry of Communications has formulated the Indian Telegraph (Infrastructure Safety) Rules, 2022.
- The Central government has envisioned fulfilling the communication needs of the citizens and enterprises through establishment of a resilient, secure, accessible and affordable Digital Communications Infrastructure and Services.
What is the Indian Telegraph (Infrastructure Safety) Rules, 2022?
- Under the Rules, any person who wishes to exercise a legal right to dig or excavate any property which is likely to cause damage to a telegraph infrastructure must give notice to the licensee.
- The person digging or excavating shall take appropriate action on precautionary measures provided by the licensee.
- Any person, who has dug or excavated any property causing damage to a telegraph infrastructure, will be liable to pay the damage charges to the telegraph authority.
- Once the asset owner agencies map their underlying assets with GIS coordinates on PM GatiShakti National Master Plan platform, it will also be possible to know the presence of underlying utility assets, at the point of interest, before start of excavation.
What are the Associated Advantages?
- Many utilities can be saved from unwanted cuts and wasteful costs towards restoration.
- Thus, saving thousands of crores for businesses and associated tax loss to Government.
- Inconvenience caused to citizens because of frequent breakdown may be reduced due to better synergy between the agencies.
What is PM Gati Shakti -National Master Plan for Multi-modal Connectivity?
- Aim:
- To ensure integrated planning and implementation of infrastructure projects in the next four years, with focus on expediting works on the ground, saving costs and creating jobs.
- Besides cutting logistics costs, the scheme is also aimed at increasing cargo handling capacity and reducing the turnaround time at ports to boost trade.
- It will help in fulfilling the ambitious targets set by the government for 2024-25, including expanding the length of the national highway network to 2 lakh kms, creation of more than 200 new airports, heliports and water aerodromes.
- PM Gati Shakti is based on Six Pillars:
- Comprehensiveness: It will include all the existing and planned initiatives of various Ministries and Departments with one centralized portal. Each and every Department will now have visibility of each other's activities providing critical data while planning & execution of projects in a comprehensive manner.
- Prioritization: Through this, different Departments will be able to prioritize their projects through cross-sectoral interactions.
- Optimization: The National Master Plan will assist different ministries in planning for projects after identification of critical gaps. For the transportation of the goods from one place to another, the plan will help in selecting the most optimum route in terms of time and cost.
- Synchronization: Individual Ministries and Departments often work in silos. There is lack of coordination in planning and implementation of the project resulting in delays. PM Gati Shakti will help in synchronizing the activities of each department, as well as of different layers of governance, in a holistic manner by ensuring coordination of work between them.
- Analytical: The plan will provide the entire data at one place with GIS based spatial planning and analytical tools having 200+ layers, enabling better visibility to the executing agency.
- Dynamic: All Ministries and Departments will now be able to visualize, review and monitor the progress of cross-sectoral projects, through the GIS platform, as the satellite imagery will give on-ground progress periodically and progress of the projects will be updated on a regular basis on the portal. It will help in identifying the vital interventions for enhancing and updating the master plan.
- Gati Shakti Digital Platform:
- It involves the creation of a common umbrella platform through which infrastructure projects can be planned and implemented in an efficacious manner by way of coordination between various ministries/departments on a real-time basis.
- It is essentially a digital platform to bring 16 Ministries including Railways and Roadways together.
 |
 |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. The Gati-Shakti Yojana needs meticulous co-ordination between the government and the private sector to achieve the goal of connectivity. Discuss. (2022)
Biodiversity & Environment
Global Glacier Change in the 21st Century
For Prelims: Paris Climate Agreement, Global Glacier Change, Climate Change
For Mains: Global Glacier Change in the 21st century, Climate Change, Natural Disasters
Why in News?
Recently, a report titled “Global glacier change in the 21st century: Every increase in temperature matters”, which states half the Earth’s glaciers may disappear by 2100.
- The researchers used two decades of satellite data to map the planet’s glaciers with greater precision than ever before.
- The United Nation’s (UN) Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change’s sixth assessment report released in 2022 also warned that we are running out of time to attain the 1.5°C target.
What are the Findings?
- Glaciers Melting at Unprecedented Rate:
- Glaciers are receding at unprecedented rates due to climate change and rising temperatures.
- The amount of ice lost by glaciers between 1994 and 2017 was around 30 trillion tones and they are now melting at a pace of 1.2 trillion tonnes each year.
- The glaciers in the Alps, Iceland and Alaska are some of those that are melting at the quickest rates.
- Half the Earth’s glaciers are destined to vanish by 2100, even if we adhere to the Paris Climate Agreement goal of limiting global temperature rise to 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels.
- A minimum of 50 % of the loss will occur within the next 30 years. 68% of glaciers will vanish if global warming continues at the current rate of 2.7°C.
- If this happens, by the end of the following century, there would be practically no glaciers left in central Europe, western Canada and the United States.
- Some of these glaciers can be saved from extinction by reducing global warming, the researchers noted.
- Glaciers, which hold 70 % of the Earth’s freshwater, currently encompass around 10 % of the planet’s land area.
- Glaciers are receding at unprecedented rates due to climate change and rising temperatures.
- Increasing Risk of Disaster:
- Melting glaciers raise sea levels dramatically, jeopardizing up to two billion people’s access to water and increasing the risk of natural disasters and extreme weather events like floods.
- Global sea level rose by 21 % between 2000 and 2019. This was solely due to meltwater from melting glaciers and ice sheets.
- Recommendations:
- The rapidly increasing glacier mass losses as global temperature increases beyond 1.5C stresses the urgency of establishing more ambitious climate pledges to preserve the glaciers in these mountainous regions.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 In the context of India’s preparation for Climate-Smart Agriculture, consider the following statements: (2021)
- The ‘Climate-Smart Village’ approach in India is a part of a project led by the Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS), an international research programme.
- The project of CCAFS is carried out under Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research (CGIAR) headquartered in France.
- The International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) in India is one of the CGIAR’s research centres.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q.2 Which of the following best describes/describe the aim of ‘Green India Mission’ of the Government of India? (2016)
- Incorporating environmental benefits and costs into the Union and State Budgets thereby implementing the ‘green accounting’.
- Launching the second green revolution to enhance agricultural output so as to ensure food security to one and all in the future.
- Restoring and enhancing forest cover and responding to climate change by a combination of adaptation and mitigation measures.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Q.3 With reference to ‘Global Climate Change Alliance’, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2017)
- It is an initiative of the European Union.
- It provides technical and financial support to targeted developing countries to integrate climate change into their development policies and budgets.
- It is coordinated by World Resources Institute (WRI) and World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD).
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q.1 Describe the major outcomes of the 26th session of the Conference of the Parties (COP) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). What are the commitments made by India in this conference? (2021)
Q.2 ‘Climate Change’ is a global problem. How will India be affected by climate change? How Himalayan and coastal states of India will be affected by climate change? (2017)
Important Facts For Prelims
76th Foundation Day of BIS
Why in News?
Recently, the 76th Foundation Day of Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) was celebrated in New Delhi and various initiatives were launched by the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food & Public Distribution.
What are the Various Initiatives Launched?
- Portal for Mapping of Industrial Units and Laboratories:
- This is a centralized platform for information on industrial units and laboratories across the country.
- This will enable analysis of test facilities in the country and help entrepreneurs in accessing information about testing facilities.
- Standards National Action Plan (SNAP) 2022- 27:
- This is a document to serve as strong foundation for standardization to meet the emerging technologies and concerns of sustainability and climate change.
- SNAP 2022 - 27 will play an important role in steering the national standardization efforts which would lead to standards becoming a key enabler of India’s economic aspirations.
- The implementation of key recommendations and strategies of the document will be pivotal in enriching and strengthening “Quality Culture” in the Nation.
- Revision Exercise of National Building Code of India 2016 (NBC 2016):
- Published by the BIS, NBC is a “recommendatory document”, and state governments are expected to incorporate it into their local building by laws, making the recommendations a mandatory requirement.
- BIS is initiating the Exercise of Revision NBC 2016 to include:
- Sustainable City Planning Norms
- New and Sustainable Building Materials
- Design Concepts
- Construction Technologies
- Building and Plumbing Services
- BIS is initiating the Exercise of Revision NBC 2016 to include:
- Published by the BIS, NBC is a “recommendatory document”, and state governments are expected to incorporate it into their local building by laws, making the recommendations a mandatory requirement.
- Revised National Electrical Code of India 2023 (NEC 2023):
- NEC 2023, a comprehensive electrical installations Code prepared by BIS, is a national instrument providing guidelines for regulating the Electrical Installations practices across the country.
- India’s first National Electrical Code was formulated in the year 1985, which was subsequently revised in the year 2011.
- The current revision includes the requirements of electrical installation as per the latest International best practices.
- Some of the important new chapters added in the revised NEC are requirements related to Electrical installations at special locations like Hospitals, Community facilities, Hotels, Swimming Pools, Amusement Parks, Supplies for Electric vehicles, multi-storied buildings etc.
- NEC 2023, a comprehensive electrical installations Code prepared by BIS, is a national instrument providing guidelines for regulating the Electrical Installations practices across the country.
- Training Courses on National Building Code of India 2016 and National Electrical Code of India:
- BIS through its training arm, the National Institute of Training for Standardization (NITS) has designed training courses on NBC 2016 and NEC 2023 for national capacity building.
- Standards Clubs in Schools:
- Through Standards Clubs, BIS aims to expose science students of class 9th and above to the concepts of Quality and Standardization through student centric activities.
- BIS has till date established over 4000 Standards Clubs across India and upon realizing the potential and success of the novel endeavor, the target is ambitiously enhanced to creating 10,000 clubs by the end of 2022-23.
What is BIS?
- It has been established for the harmonious development of the activities of standardization, marking and quality certification of goods and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.
- It was established by the BIS Act, 1986 which came into effect in December 1986. It works under the aegis of the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food & Public Distribution
- A new BIS Act 2016 has been brought into force with effect from October 2017.
- The Act establishes the BIS as the National Standards Body of India.
Important Facts For Prelims
Hockey World Cup
Why in News?
Ahead of Men’s Hockey World Cup 2023, Odisha Chief Minister has inaugurated Birsa Munda Hockey Stadium, one of the largest hockey stadiums in Rourkela.
- The 15th edition International Hockey Federation (FIH) Hockey World Cup 2023 will be held in Bhubaneswar and Rourkela from January 13 to 29.
What are the Key Points of the Hockey World Cup?
- Conceived jointly by India and Pakistan as the premier standalone competition for hockey outside of the Olympics and approved by the International Hockey Federation in 1969, it still took 13 long years and four editions of the event to be held in the Indian subcontinent for the first time.
- While the first edition in 1971 was allotted to Pakistan before being moved to Spain due to political and security issues, India was supposed to host in 1975 before governance issues forced it to be moved to Malaysia.
- While the initial editions were held every two years, since 1982 the tournament has been held every four years, bisecting the Olympic cycle.
- Pakistan was the inaugural world Cup winner, defeating Spain in 1971.
- The last world Cup hockey was played in 2018, where Belgium was the winner by defeating the Netherlands.
What is International Hockey Federation?
- FIH, founded in 1924, is responsible for field hockey’s major international tournaments, notably the World Cup.
- It is headquartered in Lausanne, Switzerland.
- The FIH is recognised by the International Olympic Committee as the sole ultimate governing body for the sport of Hockey throughout the world.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Years Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following statements in respect of the 32nd Summer Olympics: (2021)
- The official motto for this Olympics is ‘A New World’.
- Sport Climbing, Surfing, Skateboarding, Karate and Baseball are included in this Olympics.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
India and U.N. Peacekeeping Mission
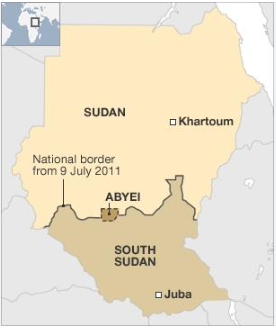
India will deploy an all-woman platoon of peacekeepers as part of a battalion to the United Nations Interim Security Force in Abyei (on the border between South Sudan and Sudan).
This will be India’s largest single unit of women peacekeepers in a U.N. mission since the deployment of the first-ever all-women’s contingent in Liberia in 2007.
India is one of the largest troop-contributing nations to the U.N. peacekeeping missions.
Read More: U.N. Peacekeeping Mission
Rajasthan’s ‘Tree Teacher’
A primary school teacher in Rajasthan’s Barmer district has achieved a record in the family forestry campaign by planting four lakh trees and connecting 1.2 lakh people with his drive during the last 24 years.
Fondly called a “tree teacher”, Bheraram Bhakhar works to prevent desertification in western Rajasthan through his diligent work. Harit Pranam (green salutation) introduced by the environmentalist-teacher has become popular among the people for greetings.
Read More: Desertification
Global South Summit
India will host a special virtual summit, the Voice of Global South summit, on January 12 and 13.
The summit under the theme ‘Unity of Voice, Unity of Purpose’ envisages bringing together countries of the Global South to share their perspectives and priorities on a common platform. More than 120 countries are being invited to participate in this Summit.
Global South refers to the developing and the less-developed countries of the world. India’s ongoing Presidency of the G20 provides a special and strong opportunity for those countries that are not part of the G20 process to share their ideas and expectations from the G20.
Read More: Global South
World's First Palm-leaf Manuscript Museum
Recently, Asia's first Palm leaf Manuscript Museum was inaugurated in Kerala.
The Museum is a repository of the administrative, socio-cultural and economic facets of the Travancore kingdom spanning a period of 650 years (till the end of 19th century). It has 187 manuscripts one of which accounts for the famous Battle of Colachel (1741) wherein the Travancore king defeated the Dutch East India Company at Colachel (TN).
The museum has eight galleries representing many segments: 'History of Writing', 'Land and people', 'Administration', 'War and peace', 'Education and Health', 'Economy', 'Art and culture' and 'Mathilakam Records'.