Biodiversity & Environment
Converting Plastic Waste into Fuel
For Prelims: World Environment Day, Plastic, Plastic polymers, ICT-Poly Urja
For Mains: Environmental impact of plastic pollution, Solutions to Plastic-Waste Management, Recent Initiatives to combat Plastic waste
Why in News?
As the world observes the 50th anniversary of World Environment Day on June 5, this year's campaign, #BeatPlasticPollution, highlights the urgent need for global solutions to combat the pervasive issue of plastic pollution.
- The Department of Science and Technology (DST) is supporting a range of technologies aimed at addressing the global issue of plastic pollution. By focusing on reducing, reusing, and recycling plastic waste, they developed a Pilot scale mobile plant that converts plastic waste into fuel.
What is Plastic?
- About:
- The word plastic is derived from the Greek word plastikos, meaning “capable of being shaped or moulded.”
- It refers to a wide range of Synthetic or semi-synthetic materials derived from polymers, characterized by their plasticity and ability to undergo deformation.
- Modern plastics primarily originate from fossil fuel-based chemicals like natural gas or petroleum but can also be produced from renewable materials such as corn or cotton derivatives.
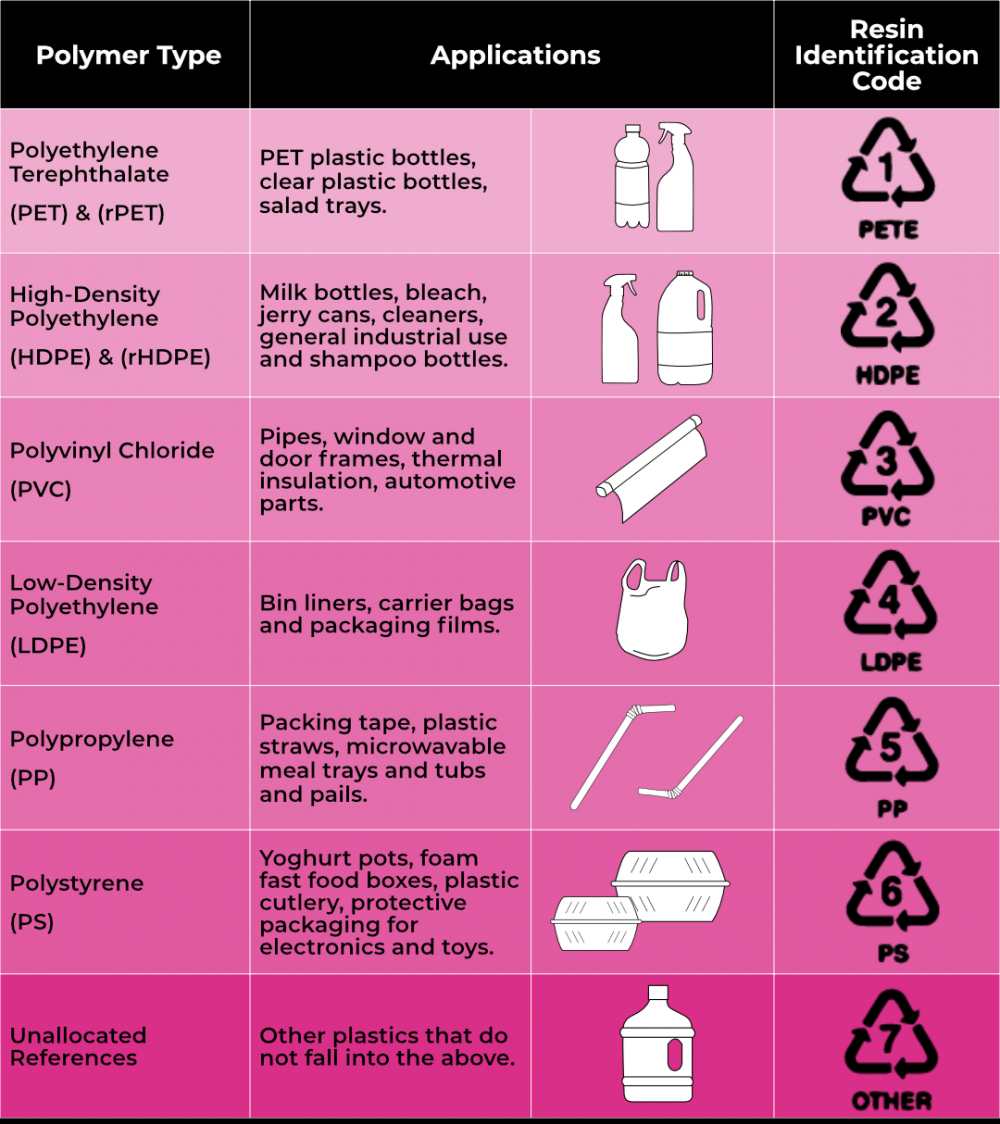
- Around 70% of global plastic production is concentrated in six major polymer types – referred to collectively as commodity plastics.
- These include
- Polyethylene terephthalate or PET,
- High-density polyethylene or HDPE,
- Polyvinyl chloride or PVC,
- Low-density polyethylene or LDPE,
- Polypropylene or PP,
- Polystyrene or PS,
- Other Plastics.
- Each of these has different properties and can be identified by their resin identification code (RIC) denoted by symbols found on plastic products.
- These include
- The word plastic is derived from the Greek word plastikos, meaning “capable of being shaped or moulded.”
What is Resin Identification Code?
- RIC was developed in 1988 by the Society of the Plastics Industry (SPI).
- Created to facilitate efficient sorting and recycling of plastics.
- Each RIC corresponds to a specific type of resin used in a plastic product.
- Proper recycling according to RIC preserves the value of the product.
- The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) an international organization took over the administration of RIC after 20 years.
- RIC specifically applies to plastic, not glass, paper, or other recyclable materials.
- Microplastics:
- Microplastics are plastic particles measuring less than five millimeters in diameter.
- Primary microplastics are tiny particles designed for commercial use, such as in cosmetics or textiles, while secondary microplastics result from the breakdown of larger plastic items.
- Microplastics persist in the environment, contaminating the food chain, water sources, and air, and posing health risks due to toxic chemicals they contain.
- Decomposition Rate and Impact:
- Plastics have a slow decomposition rate, leading to their accumulation in natural ecosystems.
- Instead of breaking down into harmless substances, plastics fragment into smaller particles, contributing to the presence of microplastics.
- According to the most recent global estimates, an average human consumes at least 50,000 microplastic particles annually due to contamination of the food chain, potable water, and air.
- Microplastics contain toxic chemicals, with the biggest health risk being associated with BPA (Bisphenol A).
- BPA, used to harden plastic, contaminates food and drinks, leading to liver function alterations, insulin resistance, adverse effects on foetal development, reproductive system issues, and impacts on brain function.
- Note:
- The Great Pacific Garbage Patch (GPGP) also known as the trash vortex, located in the North Pacific Ocean between California and Japan, is the largest accumulation of plastic waste, formed by converging ocean currents.
How Plastic is Converted into Fuel?
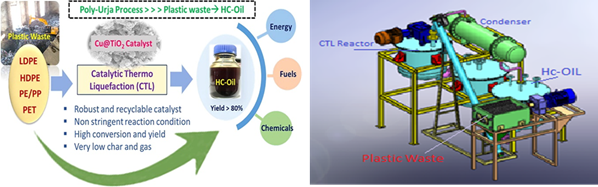
- Pilot Scale Mobile Plant:
- An indigenously designed process has led to the development of a vehicle-mounted mobile plant.
- The plant converts various types of plastic waste into carbon-densified HC-Oil (Hydrocarbon Oil) through a low-stringent process named ICT-Poly Urja.
- ICT Poly Urja is developed by the Institute of Chemical Technology (ICT) Mumbai.
- The presence of a selective, recyclable, reusable, and inexpensive catalyst enables low-cost conversion of plastic waste into fuel.
- ICT-Poly Urja Process:
- Different types of plastic waste, like bottles or packaging materials, are collected and sorted.
- A special substance called Cu@TiO2 catalyst is added to the plastic waste. This catalyst helps break down the plastic into smaller molecules.
- The mixture of plastic waste and catalyst is heated up under moderate conditions. This means it doesn't require extremely high temperatures.
- As the plastic waste is heated, it undergoes a chemical transformation called Catalytic Thermo Liquefaction (CTL). This process converts the plastic waste into a substance called Hydrocarbon Oil (HC-Oil).
- The resulting HC-Oil is a type of fuel that can be used for various purposes. It has a high energy content and can be burned to generate heat, steam, or even electricity.
- Efficient and Mobile:
- The CTL process requires less energy compared to traditional methods like pyrolysis and gasification.
- Moderate operating conditions contribute to energy efficiency.
- The mobile plant mounted on a vehicle offers operational benefits.
How is India Addressing the concerns regarding Plastic-Waste?
- National Dashboard on Elimination of Single Use Plastic and Plastic Waste Management.
- Plastic Waste Management Amendment Rules, 2022.
- India Plastics Pact.
- Project REPLAN.
UPSC Civil Services Exam, Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Q. Why is there a great concern about the ‘microbeads’ that are released into environment? (2019)
(a) They are considered harmful to marine ecosystems.
(b) They are considered to cause skin cancer in children.
(c) They are small enough to be absorbed by crop plants in irrigated fields.
(d) They are often found to be used as food adulterants.
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- Microbeads are small, solid, manufactured plastic particles that are less than 5mm and do not degrade or dissolve in water.
- Mainly made of polyethylene, microbeads can also be prepared from petrochemical plastics such as polystyrene and polypropylene. They may be added to a range of products, including rinse-off cosmetics, personal care and cleaning products.
- Microbeads, because of their small size pass unfiltered through the sewage treatment system and reach the water bodies. The untreated microbeads in the water bodies are taken up by the marine animals, thus producing toxicity and causing harm to the marine ecosystem.
- In 2014, Netherland became the first country to ban cosmetics microbeads.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Science & Technology
AI-Driven Discovery of Abaucin: A Powerful Antibiotic
For Prelims: Artificial Intelligence (AI), Antibiotic, Superbug, Acinetobacter baumannii, Abaucin
For Mains: Implications of antibiotic resistance on global health, Role of AI in accelerating drug discovery and its potential in addressing public health challenges
Why in News?
Recently, Scientists from the United States and Canada have achieved a remarkable feat in the field of medicine by using Artificial Intelligence (AI) to discover a powerful antibiotic called Abaucin capable of fighting Acinetobacter baumannii superbug.
- This breakthrough holds immense promise in the fight against drug-resistant bacteria.
What is Acinetobacter Baumannii?
- Acinetobacter baumannii is a dangerous bacterium resistant to antibiotics, as identified by the World Health Organization (WHO).
- It can cause severe infections like pneumonia, meningitis, and wound infections, leading to fatalities.
- Typically found in hospitals, Acinetobacter baumannii can survive on surfaces for long periods, making it difficult to eradicate.
- Due to its remarkable capacity to develop resistance to all currently available antibiotics, it was recognised as a "red alert" human pathogen.
How does Antibiotic Resistance Occur?
- Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria adapt and become resistant to the effects of antibiotics, rendering treatments ineffective.
- Antibiotics are medicines used to prevent and treat bacterial infections.
- Overuse and misuse of antibiotics have fueled the rise of drug-resistant bacteria, posing a global health concern.
- The WHO lists infections such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, and foodborne diseases as becoming harder to treat with existing medication due to increasing anti-bacterial resistance.
Note:
- Superbugs are bacteria that are resistant to several types of antibiotics.
- WHO’s list of superbugs highlighted bacteria that have built-in abilities to find new ways to resist treatment and can pass along genetic material that allows other bacteria to become drug resistant as well. They can also be fungi.
What is Abaucin?
- About:
- Abaucin is a compound that shows useful activity as a narrow-spectrum antibiotic.
- It is effective against Acinetobacter baumannii.
- Discovery:
- Abaucin was discovered with the assistance of AI using a machine-learning model approach.
- Network was trained with a dataset of ~7,500 molecules screened for inhibiting Acinetobacter baumannii growth.
- The network predicted structurally different molecules with activity against A. baumannii, including abaucin.
- Abaucin was experimentally validated and found to have potent antibacterial activity.
- Mechanism of Action:
- Abaucin disrupts the normal function of the CCR2 protein in bacteria.
- This disruption hinders the movement of certain molecules inside the bacteria, preventing them from reaching the outer membrane.
- As a result, the growth of Acinetobacter baumannii is inhibited, reducing its ability to cause infections.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following are the reasons for the occurrence of multi-drug resistance in microbial pathogens in India? (2019)
1. Genetic predisposition of some people
2. Taking incorrect doses of antibiotics to cure diseases
3. Using antibiotics in livestock farming
4. Multiple chronic diseases in some people
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4
(d) 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Can overuse and free availability of antibiotics without Doctor’s prescription, be contributors to the emergence of drug-resistant diseasesin India? What are the available mechanisms for monitoring and control? Critically discuss the various issues involved. (2014)
International Relations
Kosovo-Serbia Conflict
For Prelims: Kosovo-Serbia Conflict, NATO, Albanians, World War 2, Soviet Union.
For Mains: Kosovo-Serbia Conflict.
Why in News?
Serbian protesters and NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) peacekeepers recently clashed in Kosovo, leading to more than 60 injuries. It is the most serious violence seen in the region in over a decade.
What is the Cause for Current Tension?
- Northern Kosovo experiences frequent tensions stemming from the larger ethnic and political divide between ethnic Serbs and Albanians.
- Ethnic Serbs, who form a majority in northern Kosovo, attempted to block Albanian mayors from taking charge in local councils.
- Serbs boycotted local elections in April 2023, resulting in a low voter turnout of less than 3.5%. The election results were rejected by Serbs as illegitimate.
What is the Kosovo-Serbia Conflict About?
- Geography:
- Serbia: Serbia is a landlocked country in eastern Europe that shares borders with Hungary, Romania, and Bulgaria, etc.
- Kosovo: Kosovo is a small landlocked region that lies to Serbia’s southwest, sharing borders with North Macedonia, Albania, and Montenegro. Many Serbs consider Kosovo the birthplace of their nation.
- Kosovo declared independence from Serbia in 2008, but Serbia does not recognize Kosovo’s statehood.
- Ethnic Background:
- Kosovo is a region where Serbs and Albanians, representing different ethnicities and religious backgrounds, have been living for centuries.
- 1.8 million people living in Kosovo, 92% are Albanian and only 6% Serbian. The rest are Bosniaks, Gorans, Turks and Roma.
- Serbs are primarily Eastern Orthodox Christians, while Albanians in Kosovo are predominantly Muslim. Other minority groups include Bosnians and Turks. Serbs form the majority in Serbia, while Albanians are the majority in Kosovo.
- Kosovo is a region where Serbs and Albanians, representing different ethnicities and religious backgrounds, have been living for centuries.
- Battle Of Kososvo:
- Serbian nationalists view the 1389 Battle of Kosovo between the Serbian prince Lazar Hrebeljanovic and the Ottoman Sultan Murad Hudavendigar as a defining moment in their national struggle.
- On the other hand, Kosovo’s majority ethnic Albanians view Kosovo as belonging to them and accuse Serbia of occupation and repression.
- Disintegration of Yugoslavia:
- From 1945 after the end of World War II to 1992, the area in the Balkans comprising present-day Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, and Slovenia, was one country, officially known as the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY) with Belgrade as its capital. Serbia included autonomous provinces of Kosovo and Vojvodina.
- Following the collapse of the Soviet Union, Yugoslavia disintegrated, with each republic becoming an independent country.
- Slovenia was the first to secede in 1991.
- The late 1980s and early 1990s saw the weakening of the central government in Yugoslavia, accompanied by resurgent nationalism.
- Political leaders exploited nationalist rhetoric, eroding the common Yugoslav identity and fueling fear and mistrust among ethnic groups.
- In 1998, ethnic Albanian rebels formed the Kosovo Liberation Army (KLA) to challenge Serbian rule.
- Intervention of NATO:
- NATO intervened in 1999 after Serbia's brutal response, leading to a 78-day air campaign against Kosovo and Serbia.
- Serbia agreed to withdraw its forces from Kosovo, resulting in the return of Albanian refugees and the displacement of many Serbs who feared reprisals.
- In June 1999, Kosovo came under international administration, with its final status remaining unresolved. Several Serbian leaders, including President Milošević, were indicted for war crimes by the UN's tribunal.
What is the Current Status of Kosovo?
- While Kosovo declared independence in 2008, Serbia still considers it to be an integral part of Serbian territory.
- Countries such as India, China, and Russia do not recognise Kosovo as a separate country, while the US, the majority of EU countries, Japan and Australia do so.
- A total of 99 out of 193 United Nations (UN) countries now recognize Kosovo's independence.
What was India’s Stand on the Staus of Kosovo?
- India claims that Kosovo does not fulfill the three principles required for recognition: a defined territory, a duly constituted government accepted by the people, and effective control over an area of governance.
- India has opposed Kosovo's membership in international bodies such as UNESCO, Apostille Convention, Convention for the Pacific Settlement of International Disputes, and Egmont Group of Financial Intelligence Units.
- India's non-recognition of Kosovo is based on its support for the sovereignty and territorial integrity of Serbia, with whom it has a long-standing relationship.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following pairs : (2023)
Regiona often Reason for being in news mentioned in news
- North Kivu and Ituri : War between Armenia and Azerbaijan
- Nagorno-Karabakh: Insurgency in Mozambique
- Kherson and Zaporizhzhia: Dispute between Israel and Lebanon
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- Kivu and Ituri are related to the Republic of Congo. A war between the Republic of congo and Rawanda started in 1994 with genocide of 800,000 Rawandan Tutsis and Hutus. Hence, pair 1 is NOT correctly matched.
- Nagorno-Karabakh is a region of southwestern Azerbaijan. It is used to refer to an autonomous oblast (province) of the former Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic (S.S.R.) and to the Republic of Nagorno-Karabakh, a self-declared country whose independence is not internationally recognized. The old autonomous region occupied an area of about 1,700 square miles (4,400 square km), while the forces of the self-proclaimed Republic of Nagorno-Karabakh presently occupy some 2,700 square miles (7,000 square km). Hence, pair 2 is NOT correctly matched.
- Kherson and Zaporizhzhia are related to Ukraine and they are related to the dispute between Ukraine and Russia. Hence, pair 3 is NOT correctly matched.
Indian Economy
India's Renewable Energy Growth Praised by IRENA
For Prelims: Low-cost finance for energy transition report, IRENA, IREDA, green hydrogen,Green bonds, Sovereign Bonds
For Mains: Achievements of India in renewable energy
Why in News?
- A recent report called 'Low-cost finance for energy transition,' released by the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), has recognized and praised India's outstanding progress in expanding its renewable energy capacity.
- The report describes India's achievements as "unprecedented".
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- Unprecedented Growth in Renewable Energy Sector:
- National Targets:
- India aims to achieve 175 GW (100 GW from solar, 60 GW from wind) of renewable energy capacity by 2022 and 500 GW of non-fossil fuel capacity by 2030.
- Net-zero Target:
- India aims to achieve net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2070, requiring an estimated $10 trillion of investment.
- Renewable Energy Attractive Index:
- India ranked third on the index in 2021, showcasing its commitment to renewable energy development.
- Solar and Wind Power Base:
- India possesses the fourth-largest solar and wind power base globally, experiencing rapid growth.
- Supportive Policy Framework:
- The Indian government's comprehensive policies have effectively supported the achievement of national targets.
- National Targets:
- Praiseworthy role played by IREDA:
- Financing Renewable Energy Projects:
- IREDA (Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency) has played a crucial role in commissioning approximately 20 GW of renewable energy capacity through financing to developers.
- Mobilizing Private Sector Capital:
- Green bonds attract private sector investment, reducing the cost of capital for green projects.
- Overall green bond issuance in India has reached $18.3 billion cumulatively, with a record issuance of $7 billion in 2021
- Pioneering New Technologies:
- IREDA has promoted emerging technologies such as battery energy storage systems, green hydrogen electrolysers, e-mobility, and waste-to-energy through innovative financing policies.
- Financing Renewable Energy Projects:
- Supportive Government:
- Issuance of Sovereign Bonds:
- The Indian government's sovereign bond issuance aims to reduce supply from non-green bonds, lowering overall bond yields.
- Investor Participation:
- Local banks and insurance companies predominantly purchased the bonds, with some foreign bank involvement.
- Regulatory Benefits:
- Green bond investments qualify towards the Reserve Bank of India's statutory liquidity ratio and are classified as infrastructure investments by insurance companies.
- Fully Accessible Route for Foreign Investors:
- Investment in sovereign green bonds is categorized as specified securities, allowing unlimited investment by foreign investors.
- Issuance of Sovereign Bonds:
What is IRENA?
- About:
- It is an intergovernmental organisation, it was officially founded in Bonn, Germany, in January 2009.
- Currently it has 167 members, India is the 77th Founding Member of IRENA.
- It has its headquarters in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates.
- Major Functions:
- It supports countries in their transition to a sustainable energy future, and serves as the principal platform for international cooperation, a centre of excellence, and a repository of policy, technology, resource and financial knowledge on renewable energy.
- It promotes the widespread adoption and sustainable use of all forms of renewable energy, including bioenergy, geothermal, hydropower, ocean, solar and wind energy in the pursuit of sustainable development, energy access, energy security and low-carbon economic growth and prosperity.
What is IREDA?
- Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency Limited (IREDA) is a Mini Ratna (Category – I) Government of India Enterprise under the administrative control of Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE).
- IREDA is a Public Limited Government Company established as a Non-Banking Financial Institution in 1987 engaged in promoting, developing and extending financial assistance for setting up projects relating to new and renewable sources of energy and energy efficiency/conservation
- The motto of the IREDA is “ENERGY FOR EVER”.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
With reference to the Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency Limited (IREDA), which of the following statements is/are correct? (2015)
1. It is a Public Limited Government Company.
2. It is a Non-Banking Financial Company.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency Limited (IREDA) is a Mini Ratna (category-I) GoI enterprise under the administrative control of Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE).
- It is a Public Limited Government Company established as a Non-Banking Financial Institution in 1987 engaged in promoting, developing and extending financial assistance for setting up projects relating to new and renewable sources of energy.
Hence, statements 1 and 2 are correct.
Mains:
Q. India has immense potential of solar energy though there are regional variations in its developments. Elaborate (2020)
International Relations
Indonesia's Peace Plan to End Russia-Ukraine Conflict
For Prelims: Russia and Ukraine War, European Union, Shangri La Dialogue (SLD), United Nations peacekeeping forces, European Union.
For Mains: Shangri La Dialogue Defence Summit, Issue Between Russia and Ukraine.
Why in News?
Indonesia's Defence Minister presented a peace plan on June 3rd during the Shangri-La Dialogue defence summit in Singapore, aimed at resolving the ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine.
What are the Major Highlights of Shangri-La Dialogue Defence Summit?
- Indonesia’s Peace Proposal:
- Immediate Cessation of Hostilities: Calling upon both Russia and Ukraine to halt the ongoing hostilities, recognizing the severe economic and food supply impact the conflict has had on Asian nations.
- Ceasefire at Present Positions: The plan suggests a ceasefire at the current frontlines, aiming to bring an end to the fighting and minimise further casualties.
- Establishment of Demilitarized Zones: Proposed the creation of demilitarised zones, which would be observed and guaranteed by international observers and United Nations peacekeeping forces.
- UN-Organized Referendum: The plan suggests conducting a referendum in the disputed areas, organised and overseen by the United Nations, to determine the aspirations of the affected population.
- Other Highlights:
- Chinese Peace Plan: China's Ministry of Foreign Affairs released a 12-point peace plan proposed by China to end the hostilities between Russia and Ukraine.
- The plan includes calling for a ceasefire, considering Russia's security concerns, providing humanitarian assistance to Ukraine, facilitating prisoner exchanges, and lifting unilateral sanctions, among other measures.
- Western Allies' Aid to Ukraine: In contrast to China, the United States and Western allies have provided significant military assistance and aid to Ukraine since Russia's invasion.
- Chinese Peace Plan: China's Ministry of Foreign Affairs released a 12-point peace plan proposed by China to end the hostilities between Russia and Ukraine.
What is the Shangri La Dialogue?
- The Shangri La Dialogue (SLD) is an annual inter-governmental security conference held in Singapore by an independent think tank, the International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS).
- The dialogue is attended by Defence ministers, permanent heads of ministries and military chiefs of mostly Asia-Pacific states, as well as legislators, academic experts, journalists and business delegates.
- The dialogue is named after the Shangri-La Hotel in Singapore, where it has been held since 2002.
- The forum aims to cultivate a sense of community among the most important policymakers in the defence and security community in the region, and to foster practical security cooperation.
What is the Issue Between Russia and Ukraine?
- Historical Background:
- As part of the Soviet Union, Ukraine was the second-most powerful Soviet republic after Russia, and was crucial strategically, economically and culturally.
- Ever since Ukraine split from the Soviet Union, both Russia and the West have vied for greater influence in the country in order to keep the balance of power in the region in their favour.
- Beginning of the Conflict:
- The conflict began in February 2014 when Russia covertly invaded and annexed Crimea, a Ukrainian autonomous republic with a large ethnic Russian population and a strategic naval base.
- Russia also supported pro-Russian separatists who took up arms against the Ukrainian government in the eastern regions of Donetsk and Luhansk, collectively known as the Donbas.
- The conflict has also involved naval incidents, cyberattacks, propaganda campaigns, and political assassinations.
- It has strained relations between Russia and the West as well, which have imposed sanctions on each other and accused each other of interference and aggression.
- Russia-Ukraine War 2022:
- In 2022, Russia launched a full-scale invasion of Ukraine, targeting cities across the country with missile strikes and advancing its troops and proxies on multiple fronts. The invasion triggered a global crisis and a humanitarian catastrophe.
- The main causes of the conflict are historical, geopolitical, and ideological.
- Russia sees Ukraine as part of its sphere of influence and resents its pro-Western orientation and aspirations to join NATO and the EU.
- Ukraine sees Russia as an aggressor and a threat to its sovereignty and territorial integrity.
- The main goals of the conflict are disputed. Russia claims to protect the rights and interests of ethnic Russians and Russian speakers in Ukraine, to restore historical justice, and to counter Western encroachment.
- Ukraine claims to defend its independence, democracy, and European integration.
- Implications:
- The main implications of the conflict are profound and far-reaching. They affect the security, stability, and prosperity of the globe, the balance of power and order in the world, the norms and values of international law and human rights, the prospects for democracy and development in the region, and the lives and futures of millions of people.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question:
Q. Consider the following countries: (2023)
- Bulgaria
- Czech Republic
- Hungary
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Romania
How many of the above-mentioned countries share a land border with Ukraine?
(a) Only two
(b) Only three
(c) Only four
(d) Only five
Governance
G20 India Presidency: 3rd HWG Meeting
For Prelims: G20, Digital health, Intellectual property rights, Aadhaar, CoWIN, Aarogya Setu, World Health Organization (WHO), Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), Ayushman Bharat Yojna, Climate change.
For Mains: India’s Priorities for G20 presidency on Health, Challenges Posing Risk to the Health Sector Globally.
Why in News?
The recent 3rd Health Working Group meeting at Hyderabad, Telangana under the G20 India Presidency highlighted the ongoing threat of pandemics and the urgent need for global collaboration in the health sector.
- Several key proposals were put forth by India, emphasising the importance of integrated surveillance systems, medical countermeasures, digital health initiatives, and vaccine research and development at global level.
What are India's Major Proposals for Global Collaboration in the Health sector?
- India proposed a Global initiative on Digital Health, a WHO-managed network to converge ongoing initiatives in use of technology in the global health arena.
- This initiative can enable bridging the digital divide amongst nations and ensure that the fruits of technology are made available to every citizen of the world.
- Building consensus for an end-to-end Global Medical Countermeasure (MCM) ecosystem.
- Creation of an interim platform guided by the Intergovernmental Negotiating Body (INB) process for the Global Medical Countermeasure (MCM) ecosystem.
- Advocating against intellectual property rights barriers that hinder access to medical countermeasures in times of crisis.
- Accelerating vaccine research and development (R&D) for emerging pathogens and strengthening pandemic preparedness efforts.
- Establishing a Global Vaccine Research Collaborative to address gaps in vaccine development, enhance coordination, and foster an enabling environment for vaccine R&D.
- Emphasising equity in access to diagnostics, drugs, and vaccines during health emergencies.
- Mapping and integrating global initiatives for quick decision making and planning during crises. Addressing the challenges of zoonotic spillover of diseases transferring from animals to humans.
What are India’s Priorities for G20 Presidency on Health?
- About:
- India is recognized as the "Pharmacy of the World," contributing a significant portion of the global vaccine production.
- Genome Valley in Hyderabad alone contributes close to 33% of the world's vaccine production. Also, India’s Ayurveda and Yoga are significant practices that develop a holistic well-being.
- Priorities:
- Digital Public Infrastructure: India aims to leverage its experience in developing digital platforms such as Aadhaar, CoWIN, and Aarogya Setu to enhance access, affordability, and quality of health services for all.
- India also intends to share its best practices and learnings with other G20 countries and support them in building their own digital public infrastructure for health.’
- Health Security: India plans to work with other G20 countries to strengthen the global health security architecture and ensure preparedness for future pandemics.
- India will also support the reform of the World Health Organization (WHO) and other multilateral institutions to make them more responsive, transparent, and accountable.
- Universal Health Coverage: India will promote the goal of achieving universal health coverage (UHC) by 2030, as envisaged by the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- India will also showcase its achievements in expanding health coverage through schemes such as Ayushman Bharat Yojna and will encourage other G20 countries to adopt similar policies that can improve health outcomes and reduce poverty.
- Digital Public Infrastructure: India aims to leverage its experience in developing digital platforms such as Aadhaar, CoWIN, and Aarogya Setu to enhance access, affordability, and quality of health services for all.
What are the Challenges Posing Risk to the Health Sector Globally?
- Inadequate Infrastructure and Practitioners: Many countries, particularly in low-income regions, lack sufficient healthcare infrastructure, including doctors, hospitals, and diagnostic facilities.
- This limits their capacity to deliver timely and quality healthcare services to the population.
- India’s rural healthcare system continues to be plagued by shortfall on two critical fronts — doctors and infrastructure. There is a shortage of 83.2% of surgeons, 74.2% of obstetricians and gynaecologists, 79.1% of physicians and 81.6% of paediatricians, according to the Rural Health Statistics 2021-2022.
- Infectious Disease Outbreaks: The emergence and reemergence of infectious diseases pose a significant risk to global health.
- Recent examples include the Covid-19 pandemic and Ebola outbreaks.
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR): Antimicrobial Resistance is reducing the effectiveness of medicines, making infections and diseases difficult or impossible to treat.
- WHO has declared that AMR is one of the top 10 global public health threats facing humanity.
Note: AMR occurs when microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, parasites, and fungi evolve and develop resistance to the drugs used to treat them, rendering them resistance. This can happen naturally over time, but it is accelerated by the overuse and misuse of antimicrobial drugs.
- Climate Change Hazard: Climate change threatens the essential ingredients of good health - clean air, safe drinking water, nutritious food supply and safe shelter.
- Climate change exacerbates extreme weather events like drought and floods, which increase food insecurity, malnutrition rates, and help spread infectious diseases.
- Rising Commercialisation: Though commercialization of healthcare promises better infrastructure, medical facilities, and technological advancement, but due to high charges, poor and middle-class people cannot afford it. This contradicts the very purpose of having a better healthcare system.
- Further, doctors collaborate with pharmaceutical companies with a profit motive to prescribe branded medicines that are more expensive than generic versions despite the same formula, which hampers access to timely healthcare.
Way Forward
- Global Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing: There is a need to encourage international collaboration and knowledge sharing among healthcare professionals, researchers, and institutions.
- This can facilitate the dissemination of best practices, encourages innovation, and accelerates the development of new treatments and therapies.
- Genetic Surveillance: Genetic surveillance can be a way forward to understand the evolution of different disease carriers across the globe, specially viruses.
- Genetic surveillance of pathogens provides insights by following a molecular approach for contact tracing and understanding the transmission of the pathogen across the globe.
- Patient Empowerment and Engagement: There is a need to prioritise patient-centric care by empowering individuals to take an active role in managing their health.
- Provide tools and resources that promote health literacy, enable self-monitoring, and facilitate patient-provider communication for better treatment adherence and outcomes.
- Towards Global Pandemic Treaty: In recognition of the need to further strengthen international cooperation in health sector, WHO has now commenced the process for the development and adoption of a new international treaty with an aim to ensure better preparedness and equitable response for future pandemics, and to advance the principles of equity, solidarity and health for all.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 Consider the following statements about G-20: (2023)
- The G20 group was originally established as a platform for finance ministers and central bank governors to discuss international economic and financial issues.
- Digital public infrastructure is one of India's G-20 priorities
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: C
Q.2 ‘Doctors Without Borders (Médecins Sans Frontières)’, often in the news, is (2016)
(a) a division of World Health Organisation
(b) a non-governmental international organisation
(c) an inter-governmental agency sponsored by European Union
(d) a specialised agency of the United Nations
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q.1 Appropriate local community level healthcare intervention is a prerequisite to achieve ‘Health for All’ in India. Explain (2018)
Q.2 Public health system has limitations in providing universal health coverage. Do you think that the private sector could help in bridging the gap? What other viable alternatives would you suggest? (2015)
Social Justice
Denied Property Rights to ST Women Under Hindu Succession Act
For Prelims: Scheduled Tribe, Hindu Succession Amendment Act, 2005, Article 14 of the Constitution, Mitakshara school of Hindu law, Inheritance Rights in India.
For Mains: Issues related to Women in India.
Why in News?
The Union government is examining whether to issue notification under the Hindu Succession Act to apply beneficial provisions to Scheduled Tribe (ST) women, who profess Hinduism, to enable them to inherit equal share over properties of father/ Hindu Undivided Family (HUF)
What are the Issues Highlighted Around Inheritance Rights?
- Exclusion from the Act:
- Scheduled Tribe women who profess Hinduism have been excluded from the beneficial provisions of the Hindu Succession Act, 1956.
- This exclusion denies them equal rights to inherit ancestral property compared to women from other Hindu communities.
- Denial of Equal Inheritance Rights:
- Due to the exclusion, ST women are not entitled to an equal share of their father's or Hindu Undivided Family's (HUF) property.
- This inequality in inheritance rights perpetuates gender disparities and hampers the financial empowerment of ST women.
- Discrimination Based on Tribal Identity:
- The denial of equal inheritance rights to ST women who profess Hinduism is a form of discrimination based on their tribal identity.
- It contradicts the principles of equality and non-discrimination enshrined in the Indian Constitution.
- Supreme Court Directive:
- The Supreme Court, in the case of Kamla Neti Vs Special Land acquisition Officer and Ors., directed the Central government to examine whether amendments are necessary to withdraw exemptions provided under the Hindu Succession Act concerning the applicability of its provisions to Scheduled Tribes.
What is Hindu Succession Act, 1956?
- About:
- The Mitakshara school of Hindu law codified as the Hindu Succession Act, 1956 governed succession and inheritance of property but only recognised males as legal heirs.
- Applicability:
- It applies to everyone who is not a Muslim, Christian, Parsi or Jew by religion.
- Buddhists, Sikhs, Jains and followers of Arya Samaj, Brahmo Samaj, are also considered Hindus for this law.
- Traditionally, only male descendants of a common ancestor along with their mothers, wives and unmarried daughters are considered a joint Hindu family. The legal heirs hold the family property jointly.
- Hindu Succession (Amendment) Act, 2005:
- The 1956 Act was amended in September 2005 and women were recognised as coparceners for property partitions arising from 2005.
- Section 6 of the Act was amended to make a daughter of a coparcener also a coparcener by birth “in her own right in the same manner as the son”.
- It also gave the daughter the same rights and liabilities “in the coparcenary property as she would have had if she had been a son”.
- The law applies to ancestral property and to intestate succession in personal property, where succession happens as per law and not through a will.
- Class I Heirs:
- The Act categorizes relatives into different classes of heirs.
- Class I heirs include the deceased's children, grandchildren, and their respective mothers.
- In the absence of Class I heirs, the property goes to Class II heirs which includes Father, Son's daughter's son, brother, sister, Father's widow; brother's widow etc.
- Testamentary Succession:
- The Act also recognizes testamentary succession, where a person can dispose of his/her property through a valid will.
- The individual has the freedom to distribute the property according to his/her wishes, subject to certain restrictions and legal requirements.
- Rights of Widows:
- The Act recognizes the rights of widows to inherit property from their deceased husbands.
- A widow has a share in the property left by her husband, along with other legal heirs.
What Do Schools of Hindu Laws Say about Property Inheritance?
| Schools of Hindu Laws | |
| Mitakshara Law School | Dayabhaga Law School |
| The term Mitakshara is derived from the name of a commentary written by Vigneswaran, on the Yajnavalkya Smriti. | The term Dayabhaga is derived from a similarly named text written by Jimutavahana. |
| It is observed in all parts of India and subdivided into the Benares, the Mithila, the Maharashtra and the Dravida schools. | It is observed in Bengal Assam. |
| A son, by birth acquires an interest in the ancestral property of the joint family. | A son has no automatic ownership right by birth but acquires it on death of his father. |
| A coparcener’s share is not defined and cannot be disposed of. | The share of each coparcener is defined and can be disposed of. |
| A wife cannot demand partition but has the right to a share in any partition between her husband and her sons. |
Here, the same right does not exist for the women because the sons cannot demand partition as the father is the absolute owner. |
| All the members enjoy coparcenary rights during the father’s lifetime. |
Sons do not enjoy coparcenary rights when the father is alive. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. With reference to the history of ancient India, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2021)
- Mitakshara was the civil law for upper castes and Dayabhaga was the civil law for lower castes.
- In the Mitakshara system, the sons can claim right to the property during the lifetime of the father, whereas in the Dayabhaga system, it is only after the death of the father that the sons can claim right to the property.
- The Mitakshara system deals with the matters related to the property held by male members only of a family, whereas the Dayabhaga system deals with the matters related to the property held by both male and female members of a family.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 3 only
Ans: (b)
Explanation:
- Mitakshara and Dayabhaga terms were used to denote regions. It is not related to the caste system. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- The difference between Dayabhaga and Mitakshara is in the basic idea of them. Dayabhaga does not give anyone the right to property before the death of their forefathers whereas Mitakshara gives anyone the right to property just after their birth. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- Dayabhaga system prevails in West Bengal and allows both the male and female members of the family to be coparceners. Mitakshara system, on the other hand, prevails all over India except West Bengal and allows only the male members to be coparceners. Hence, statement 3 is not correct.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Economy
Global Trade Momentum and Outlook for India
For Prelims: Merchandise Exports, Inflation, Monetary Policies, Russia-Ukraine, PMI.
For Mains: Global Trade Momentum and Outlook for India.
Why in News?
India's Merchandise Exports in April 2023 contracted by 12.7% compared to the previous year, reaching a six-month low of USD 34.66 billion. Similarly, imports also experienced a sharp decline of 14%, amounting to USD 49.90 billion during the same period.
- These declines in both imports and exports are not exclusive to India and are indicative of a broader trend of slowing global demand.
What are the Current Trends in Global Trade?
- Weaker Economic Activities:
- There has been a slowdown in economic growth globally, which has had a negative impact on international trade.
- Weaker economic conditions in various countries have led to reduced consumer spending and investment, affecting trade volumes.
- Inflation and Tightening Monetary Policies:
- Many countries are facing rising Inflation, which has prompted central banks to implement tighter Monetary Policies.
- Higher interest rates and stricter lending conditions can affect trade by reducing consumer purchasing power and increasing the cost of borrowing for businesses.
- Disrupted Supply Chains due to the Russia-Ukraine Conflict:
- The ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine has disrupted supply chains, particularly in Europe.
- This conflict has led to higher energy and commodity prices, affecting trade flows and increasing costs for businesses.
- Financial Instability:
- The collapse of financial institutions, such as the Crypto exchange FTX and several banks in the US, has created financial instability.
- This loss of confidence in the financial sector raises concerns about potential contagion and can negatively impact global trade.
How has been the Trade Situation in India, Europe and the US?
- European Union (EU):
- The European Economic Forecast in February 2023 predicted that the region would narrowly avoid entering a recession that had started to develop around September 2022.
- In terms of inflation in the Euro area, the food, alcohol, and tobacco had the highest annual rate of price increase in May 2022. This was followed by non-energy industrial goods, services, and energy.
- The European Economic Forecast in February 2023 predicted that the region would narrowly avoid entering a recession that had started to develop around September 2022.
- The US:
- In the United States, according to the Federal Reserve in May 2023, inflation had improved compared to the middle of the previous year. However, inflation pressures remain high, and it is expected to take a long time for inflation to decrease to the desired target of 2%.
- The JP Morgan Global Manufacturing Purchasing Managers' Index (PMI), remained at 49.6 in May for the third consecutive month, indicating a slight decline in business conditions. Production showed growth for four months, but mainly due to fulfilling existing orders rather than new ones.
- In the United States, according to the Federal Reserve in May 2023, inflation had improved compared to the middle of the previous year. However, inflation pressures remain high, and it is expected to take a long time for inflation to decrease to the desired target of 2%.
- Outlook for India:
- The EU is India's third-largest trading partner, following the US and China.
- Global demand from markets like the EU and the US is not favorable, and the demand outlook for the next few months is not optimistic.
- India can face a potential impact of a global slowdown, especially in the US, which is a major trading partner for India.
- The slowdown may affect demand for India's merchandise exports, although services exports are expected to remain strong.
- Import levels may stay low as commodity prices stabilize and the value of the Indian rupee remains steady. However, a faster recovery could put pressure on import demand.
- Certain non-crude and non-jewelry segments have shown a growth of 15% in the previous fiscal year 2022-23, surpassing the long-term average growth.
- This indicates that domestic demand in India remains robust.
- The decrease in imports can be attributed to stable oil prices, which have reduced India's import bills.
How does Economic Slowdown Impact International Trade and Individual’s Purchasing Power?
- During an economic slowdown, international trade, including both exports and imports, declines significantly due to reduced overall demand for goods and services.
- People tend to avoid discretionary spending, which particularly impacts certain imports and postponable expenses.
- As a result, the exports of engineering goods, gems and jewelry, chemicals, readymade garments, plastics, and petroleum products have contracted or grown at a slower pace in 2023.
- Inflation, the uneven increase in prices, especially for essentials like food and energy, erodes individuals' purchasing power. However, if imported products are cheaper than domestic alternatives, people may opt for imports.
- The Exchange Rate between currencies also plays a role in determining the purchasing power of an individual. Additionally, inflation affects the flow of capital to developing countries.
Way Forward
- The government should engage in discussions between ministries to explore ways to diversify and sustain export momentum in response to this situation.
- To address concerns about lower imports, it is crucial to recognize that certain non-crude and non-jewelry segments have shown strong growth, indicating robust domestic demand. This provides a positive outlook for the Indian economy. Stability in commodity prices and the value of the Indian rupee can help maintain low import levels.
- It is important to monitor global economic conditions, adapt export strategies to target emerging markets, and continue to foster domestic demand to sustain economic growth.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question:
Q. Consider the following statements: (2023)
Statement-I: In the post-pandemic recent past, many Central Banks worldwide had carried out interest rate hikes.
Statement-II: Central Banks generally assume that they have the ability to counteract the rising consumer prices via monetary policy means.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
(a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-1
(b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-1
(c) Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
(d) Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- In the post-pandemic recent past, many Central Banks worldwide had carried out interest rate hikes to contain the post pandemic inflation. For Example, since May 2022, the Monetary Policy Committee (RBI) has gone for rate hikes many times. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- The central banks generally are mandated with the task of containing the rising prices of the commodities. Central banks use monetary policy to manage economic fluctuations and achieve price stability. Hence, Statement 2 is correct.
Important Facts For Prelims
Government Bans 14 Combination Drugs
Why in News?
The Central Government of India has issued a gazette notification banning 14 fixed-dose combination (FDC) medicines commonly used to treat cough, fever, and infections.
- The ban, which takes immediate effect, follows recommendations from an expert committee appointed to assess the efficacy of these drug combinations.
What are FDC Medicines?
- Definition:
- According to the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO), FDCs refer to products containing one or more active ingredients used for a particular indication(s).
- Reason for the Ban:
- The ban follows the recommendations of the expert committee and the Drugs Technical Advisory Board.
- The committee concluded that the banned FDCs lack therapeutic relevance and may pose risks to human beings.
What are the Challenges of FDC?
- Increased Risk of Side Effects:
- Combining multiple active ingredients in FDC drugs can lead to a higher risk of adverse drug interactions and increased susceptibility to side effects.
- Some patients may experience heightened sensitivity or allergic reactions to one or more components of the FDC drug, which may be difficult to identify and manage due to the fixed combination.
- For example, A combination of Paracetamol, Bromhexine, Phenylephrine, Chlorpheniramine, and Guaiphenesin in a single FDC drug may increase the risk of side effects such as drowsiness, dizziness, and elevated blood pressure.
- Regulatory Challenges:
- Regulating FDC drugs can be challenging due to the complexities associated with evaluating the safety and efficacy of multiple active ingredients in a single formulation.
- Ensuring quality control and standardization of FDC drugs becomes more demanding as compared to single-component medications.
- Overuse and Misuse:
- FDC drugs can contribute to overuse and misuse of medications. Patients may unknowingly consume multiple active ingredients unnecessarily or in inappropriate combinations, leading to potential health risks.
- Lack of Evidence-based Clinical Data:
- Some FDC drugs may have been approved based on limited or insufficient clinical evidence supporting their efficacy and safety profiles.
- The absence of robust scientific data can raise concerns about the appropriateness and reliability of FDC drugs for specific medical conditions.
What is the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO)?
- The CDSCO is the Central Drug Authority for discharging functions assigned to the Central Government under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act 1940.
- Major Functions:
- Regulatory control over the import of drugs, approval of new drugs and clinical trials.
- Approval of certain licences as Central Licence Approving Authority
- Drug Controller General of India (DCGI)
- DCGI is responsible for approval of licences of specified categories of drugs such as blood and blood products, IV fluids, vaccines and sera in India.
- It comes under the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare.
Important Facts For Prelims
Helicopter Navigation Demo with GAGAN Satellite Tech
Why in News?
India achieved a significant milestone in the aviation sector by conducting Asia's first demonstration of performance-based navigation for helicopters.
- The demonstration, which utilised the state-of-the-art GAGAN satellite technology, was conducted for a flight from Juhu in Mumbai to Pune.
What is Performance-Based Navigation?
- Performance-based navigation (PBN) is a modern concept of air navigation that allows aircraft to fly accurately along a predefined route using advanced onboard navigation systems and satellite signals.
- PBN improves the safety, efficiency and capacity of air traffic management by reducing the reliance on ground-based navigation aids and allowing more flexible flight paths.
What is GAGAN Satellite Technology?
- About:
- GAGAN, which stands for GPS Aided GEO Augmented Navigation, is a space-based augmentation system jointly developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and the Airports Authority of India (AAI).
- Features:
- The system adds greater accuracy to the output of GPS navigation by providing local geographical positioning, thereby improving the precision of aircraft location for more efficient traffic management.
- It enhances the accuracy and integrity of the GPS signals by correcting the errors caused by atmospheric disturbances, clock drifts and orbital deviations.
- This satellite technology also helps aircraft/ helicopters with guided landing at airports that do not have instrument landing systems for low-visibility operations.
- The system adds greater accuracy to the output of GPS navigation by providing local geographical positioning, thereby improving the precision of aircraft location for more efficient traffic management.
- Benefits:
- Enhanced safety: By providing accurate and reliable navigation information, GAGAN reduces the risk of human errors, collisions, terrain strikes and controlled flight into terrain (CFIT) accidents.
- It also improves situational awareness and emergency response capabilities for pilots and air traffic controllers.
- Improved efficiency: By allowing optimal flight paths and reduced separation standards, GAGAN enables more efficient use of airspace and fuel, resulting in lower emissions and operational costs.
- Increased capacity: By increasing the number of flights that can be accommodated in a given airspace, GAGAN enhances the capacity and connectivity of the aviation network.
- It also enables access to remote and underserved areas that lack conventional navigation infrastructure or have challenging terrain.
- In addition, GAGAN will provide benefits beyond aviation to all modes of transportation, including maritime, highways, and railroads.
- It also enables access to remote and underserved areas that lack conventional navigation infrastructure or have challenging terrain.
- Enhanced safety: By providing accurate and reliable navigation information, GAGAN reduces the risk of human errors, collisions, terrain strikes and controlled flight into terrain (CFIT) accidents.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q.1 Which one of the following countries has its own Satellite Navigation System? (2023)
a. Australia
b. Canada
c. Israel
d. Japan
Ans: (d)
Q.2 With reference to the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), consider the following statements: (2018)
- IRNSS has three satellites in geostationary and four satellites in geosynchronous orbits.
- IRNSS covers entire India and about 5500 sq. Km beyond its borders.
- India will have its own satellite navigation system with full global coverage by the middle of 2019.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) None
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q.1 Why is Indian Regional Navigational Satellite System (IRNSS) needed? How does it help in navigation? (2018)
Important Facts For Prelims
National E-Commerce Policy
Why in News?
The Indian government is set to introduce a national e-commerce policy that aims to create a favorable environment for the development of the sector and drive exports.
- The e-commerce policy was first proposed in 2018 and in 2019, a draft of the e-commerce policy was released.
- Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), the Ministry of Commerce and Industry emphasized the need for a streamlined regulatory framework, technological advancements, and efficient supply chain integration.
What are the Key Points About the Upcoming E-Commerce Policy?
- Aim:
- The national e-commerce policy aims to establish a regulatory framework that facilitates ease of doing business in the sector.
- Boosting Exports:
- The policy recognizes the significant export potential of India's e-commerce sector.
- By 2030, India's e-commerce export potential is estimated to range between 200 billion USD to 300 billion USD annually.
- With global cross-border e-commerce exports projected to reach 2 trillion USD by 2025, India aims to capitalize on this growth opportunity.
- The policy recognizes the significant export potential of India's e-commerce sector.
- Regulatory Body and FDI:
- The possibility of establishing a regulator for the e-commerce sector is being considered, but its implementation may take time.
- Local traders' associations have been advocating for an empowered regulatory body to enforce e-commerce rules and curb violations.
- While 100% foreign direct investment (FDI) is allowed in the marketplace model, FDI is not permitted in the inventory-based model.
- Addressing Trader Concerns:
- Traders have expressed concerns regarding the violation of e-commerce rules, such as deep discounts and preferences given to select sellers.
- The policy intends to clarify these issues and provide greater transparency in the rules governing FDI in e-commerce.
- The Consumer Protection (e-commerce) Rules 2020 and proposed amendments will be aligned with the e-commerce policy for consistency.
- Comprehensive Framework:
- The e-commerce policy will serve as an overarching framework for the sector, ensuring coherence among various governing acts.
- The sector is governed by the FDI policy, the Consumer Protection Act, of 2019, the Information Technology Act of 2000, and the Competition Act, of 2002.
- The policy aims to streamline these regulations and create a conducive environment for the growth of the e-commerce industry.
- The e-commerce policy will serve as an overarching framework for the sector, ensuring coherence among various governing acts.
What are the Other Related Indian Government's e-commerce Initiatives?
- Launching the BharatNet project:
- Provide internet connectivity in local bodies in every Panchayat, which will increase the reach and access of e-commerce in rural areas.
- Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC):
- A network that aims to provide equal opportunities for Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) to thrive in digital commerce and democratize e-commerce
- Digital India initiative:
- The Digital India initiative has provided solid impetus to other government-led initiatives, including Start Up India and Aatmanirbhar Bharat, which have great potential to translate into global success.
Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Debunking the Health Claims of the Paleo Diet
The paleo diet has recently garnered attention in the news due to ongoing debates surrounding its health claims and efficacy. Supporters of the paleo diet claim that imitating the way our ancestors ate can help people lose weight and lower their chances of getting long-term illnesses. However, critics argue that scientific evidence supporting these claims is lacking. This diet emphasizes the consumption of whole, unprocessed foods such as vegetables, fruits, nuts, and lean meats, while excluding dairy, grains, legumes, and processed sugars. The current version of the paleo diet reflects a lower carbohydrate and higher protein intake compared to conventional dietary guidelines. Studies comparing the paleo diet to conventional recommended diets for weight loss found no significant difference in effectiveness after two years. Similar inconclusive results were observed regarding the diet's impact on type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, a study revealed that the paleo diet led to a higher abundance of gut bacteria associated with cardiovascular disease, contradicting claims of disease prevention.
The paleo diet is an eating plan that tries to mimic the diet of ancient humans who lived in the Paleolithic Era. The paleo diet is based on the assumption that our genes are adapted to the diet of our ancestors and that modern diets are mismatched with our biology. However, genetic research contradicts this notion. Studies on lactase (This enzyme helps to digest lactose, found in dairy products) persistence and adaptations in metabolizing alcohol show that evolution can occur within much shorter timeframes than the paleo diet assumes. This challenges the fundamental rationale behind adopting the paleo diet.
Read more: INDIA’S NUTRITION PROBLEM
India's First International Cruise Vessel MV Empress
The Union Minister of Ports, Shipping & Waterways and Ayush, flagged off India's first international cruise vessel, MV Empress, from Chennai to Sri Lanka. This significant event marked the inauguration of the international cruise tourism terminal in Chennai, which is a testament to the government's commitment to enhancing cruise tourism and maritime trade opportunities. The MV Empress will sail to three Sri Lankan ports: Hanbantota, Trincomalee, and Kankesanturei.
The cruise service is the result of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) signed between Chennai Port and M/S Waterways Leisure Tourism Pvt Ltd during the first Incredible India International Cruise Conference in 2022. The government plans to develop three new international cruise terminals in Andamans, Puducherry, and Lakshadweep, which are expected to be operational by 2024. The government envisions an increase in the number of cruise ships from 208 in 2023 to 500 in 2030 and up to 1100 by 2047, with the number of passengers rising from 9.5 lakhs in 2030 to 45 lakhs in 2047.
Read more: Ganga Vilas Cruise, Potential of Cruise Tourism in India
India's IT Growth: Pillars, Opportunities, and Future Tech Ecosystem
The Software Technology Parks of India (STPI), under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), celebrated its 32nd Foundation Day by hosting a seminar on "Growth avenues for the Indian IT industry and emerging tech ecosystem." The six pillars that contribute to India's IT development were highlighted in the event. These pillars include connectivity, low-cost data, affordable devices, people-friendly policies, future-ready talent, and cybersecurity. Additionally, an agritech report titled "Innovations through Agritech: A study on the adoption and impact of technology on agri and agri-allied sectors" was released. The report aimed to provide insights into the current state of Agritech in India, the challenges faced by the sector, and the opportunities for growth and innovation.
STPI was set up in 1991 as an autonomous society under the MeitY. STPI’s main objective has been the promotion of software exports from the country. STPI has been implementing the Software Technology Park (STP) scheme and the Electronics Hardware Technology Park (EHTP) scheme for the promotion of IT/ITES industry.
Read more: Indian IT industry, Agritech.
Nyaya Vikas Portal
The Nyaya Vikas Portal is part of the Department of Justice's implementation of the Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) for the Development of Infrastructure Facilities for Districts and Subordinate Judiciary, which has been in operation since 1993-94. It has been developed to provide stakeholders with seamless access to crucial information related to funding, documentation, project monitoring, and approval.
This CSS aims to support State Governments and Union Territory Administrations in constructing court halls and residential units for Judicial Officers, Judges of District and Subordinate Courts. Over time, the scheme has evolved to include additional features such as Lawyers Halls, Toilet complexes, and Digital computer rooms to enhance convenience for lawyers and litigants, in addition to court halls and residential units. The funding pattern under the scheme follows a ratio of 60:40 between the Central Government and State Governments (excluding North Eastern and Himalayan States). For North Eastern and Himalayan States, the ratio is 90:10, while Union Territories receive 100% funding. The Nyaya Vikas Portal plays a crucial role in monitoring the implementation of this scheme, ensuring transparency and accountability.
Read more: Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) for the Development of Infrastructure Facilities for Judiciary

.png)



