Infographics
Governance
Forest Certification
Prelims: Forest Certification, Deforestation, Climate Change, Forest Stewardship Council.
Mains: Forest Certification and standards.
Why in News?
With climate change, Deforestation has become a critically sensitive issue globally in recent years, making imperative for Forest Certification to regulate the entry and sale of forest-based products.
- At the Glasgow climate meeting in 2021, more than 100 countries made a pledge to stop, and start reversing, deforestation by 2030.
What is Forest Certification?
- Need:
- Forests absorb large amounts of carbon dioxide that is emitted in various economic activities, keeping a check on global warming.
- Many Countries are trying to avoid consumption of any product that might be the result of deforestation or illegal logging.
- And therefore, Europe and the United States have passed laws that regulate the entry and sale of forest-based products in their markets, creating the need for Forest Certification.
- Forest Certification:
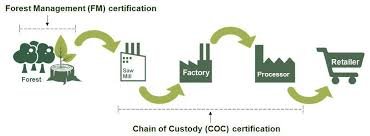
- It is a mechanism for forest monitoring, tracing and labelling timber, wood and pulp products and non-timber forest products.
- It is a process through which quality of management from environmental, social and economic perspectives is judged against a series of agreed standards.
- There are two major international standards for sustainable management of forests and forest-based products,
- One has been developed by Forest Stewardship Council (FSC);
- The other by Programme for Endorsement of Forest Certifications (PEFC).
- FSC certification is more popular and in demand, and also more expensive.
- Two Types of Certifications:
- Forest management (FM) and Chain of Custody (CoC).
- CoC certification is meant to guarantee the traceability of a forest product like timber throughout the supply chain from origin to market.
- Forest management (FM) and Chain of Custody (CoC).
- Forest Certification in India:
- The forest certification industry has been operating in India for the last 15 years.
- Currently, forests in only Uttar Pradesh are certified.
- Forty-one divisions of the UP-Forest Corporation (UPFC) are PEFC-certified, meaning they are being managed according to standards endorsed by PEFC.
- Some other states too obtained certifications, but subsequently dropped out.
- Forest certification in India is still at an early stage and therefore the nation has not been able to make use of the benefits of forest certification.
What are India Specific Standards?
- India allows the export of only processed wood, not timber. In fact, the timber harvested from Indian forests is not enough to meet the domestic demand for housing, furniture, and other products.
- India’s forests contribute just about five million cubic metres of wood every year. Almost 85% of the demand for wood and wood products is met by trees outside forests (ToF). About 10 % is imported.
- India’s wood import bill is Rs 50,000-60,000 crore per year.
- Since ToF are so important, new certification standards are being developed for their sustainable management.
- PEFC already has certification for TOF and in 2022, FSC came up with India-specific standards that included certification for ToF.


Indian Polity
Article 142
Prelims: Article 142, Supreme Court, Consumer Protection Rules, 2020, Consumer Protection Act 2019, Doctrine of ‘separation of powers.
Mains: Article 142, Consumer Protection Act 2019.
Why in News?
Recently, the Supreme Court (SC) under Article 142 ruled that the lawyers and professionals with 10 years of experience will be eligible for appointment as President and member of the state consumer commission and district forums.
- The SC upheld the Bombay High Court judgement quashing the provisions of Consumer Protection Rules, 2020, under section 101 of Consumer Protection Act 2019, which prescribe a minimum professional experience of 20 years and 15 years for adjudicating members to the State consumer commissions and District forums respectively.
What is the Court's Ruling?
- The Central government and the state governments concerned have to come up with an amendment in the Consumer Protection (Qualification for appointment, method of recruitment, procedure of appointment, term of office, resignation and removal of President and Members of State Commission and District Commission) Rules, 2020 to provide for 10 years' experience to become eligible for appointment as President and member of the state commission and district forums instead of 20 years and 15 years respectively.
- Till suitable amendments are made, the Lawyers and professionals with a bachelor's degree who has 10 years of experience in consumer affairs, law, public affairs, administration, economics, commerce, industry, finance, management, engineering, technology, public health or medicine will be eligible for appointment as President and member of the state consumer commission and district forums.
- It also introduced written exams and viva voce to check the candidates’ performance.
What is Article 142?
- About:
- Article 142 provides discretionary power to the Supreme Court as it states that the SC in the exercise of its jurisdiction may pass such decree or make such order as is necessary for doing complete justice in any cause or matter pending before it.
- Constructive Application:
- In the early years of the evolution of Article 142, the general public and the lawyers both lauded the SC for its efforts to bring complete justice to various deprived sections of society or to protect the environment.
- The Cleansing of Taj Mahal and justice to many undertrials is a result of the invocation of this article only.
- In the early years of the evolution of Article 142, the general public and the lawyers both lauded the SC for its efforts to bring complete justice to various deprived sections of society or to protect the environment.
- Cases of Judicial Overreach:
- In recent years, there have been several judgments of the Supreme Court wherein it has been foraying into areas which had long been forbidden to the judiciary by reason of the doctrine of ‘separation of powers’, which is part of the basic structure of the Constitution. One such example is:
- The ban on the sale of alcohol along national and state highways: While the notification by the central government prohibited liquor stores along National Highways only, the Supreme Court put in place a ban on a distance of 500 metres by invoking Article 142.
- Additionally, and in the absence of any similar notification by any of the State governments, the court extended the ban to State highways as well.
- Such judgments have created uncertainty about the discretion vested in the court to invoke Article 142 where even fundamental rights of individuals are being ignored.
- In recent years, there have been several judgments of the Supreme Court wherein it has been foraying into areas which had long been forbidden to the judiciary by reason of the doctrine of ‘separation of powers’, which is part of the basic structure of the Constitution. One such example is:
UPSC Civil Services Exam, Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Q. With reference to the Constitution of India, prohibitions or limitations or provisions contained in ordinary laws cannot act as prohibitions or limitations on the constitutional powers under Article 142. It could mean which one of the following? (2019)
(a) The decisions taken by the Election Commission of India while discharging its duties cannot be challenged in any court of law.
(b) The Supreme Court of India is not constrained in the exercise of its powers by laws made by the Parliament.
(c) In the event of grave financial crisis in the country, the President of India can declare Financial Emergency without the counsel from the Cabinet.
(d) State Legislatures cannot make laws on certain matters without the concurrence of Union Legislature.
Ans: (b)


Social Justice
Social Protection for Children: ILO-UNICEF
Prelims: Social Protection for Children, ILO, UNICEF, Covid-19, Poverty, SDG, PM CARES for Children.
Mains: Social Protection for Children: ILO-UNICEF.
Why in News?
Recently, ILO (International Labour Organization) and UNICEF (United Nations Children's Fund) has released a report titled- “More than a billion reasons: The urgent need to build universal social protection for children”, which states that just 1 in 4 children are shielded by social protection, leaving others exposed to poverty, exclusion and multidimensional deprivations.
What is the Need for Social Protection?
- Social protection is a universal human right and a precondition for a world free from poverty.
- It is also a vital foundation to help the world’s most vulnerable children fulfill their potential.
- Social protection helps increase access to food, nutrition, education and healthcare.
- It can help prevent child labour and child marriage and address the drivers of gender inequality and exclusion.
- It can also reduce stress and even domestic violence, while supporting household livelihoods.
- And by tackling monetary poverty directly, it can also mitigate the stigma and exclusion so many children living in poverty experience – and the pain that a childhood feeling “less than” can produce.
What are the Findings of the Report?
- Global Scenario:
- 1.77 billion children aged 0-18 years lack access to a child or family cash benefit, a fundamental pillar of a social protection system.
- Children are twice as likely to live in extreme poverty as adults.
- Approximately 800 million children are subsisting below the poverty line of USD 3.20 a day, and 1 billion children are experiencing multidimensional poverty.
- Only 26.4% of children aged 0-15 years are shielded by social protection, leaving the remaining 73.6% exposed to poverty, exclusion and multidimensional deprivations.
- Globally, all 2.4 billion children need social protection to be healthy and happy.
- Social Protection Coverage:
- Child and family social protection coverage rates fell or stagnated in every region in the world between 2016 and 2020, leaving no country on track to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) of achieving substantial social protection coverage by 2030.
- In Latin America and the Caribbean, coverage fell significantly from approximately 51% to 42 %.
- In many other regions, coverage has stalled and remains low.
- Child and family social protection coverage rates fell or stagnated in every region in the world between 2016 and 2020, leaving no country on track to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) of achieving substantial social protection coverage by 2030.
- Risk:
- Multiple crises are likely to push more children into poverty, necessitating an immediate increase in social protection measures.
- The impacts of lack of social protection for children are both immediate and lifelong, heightening rights violations such as child labour and child marriage, and diminishing children’s aspirations and opportunities.
- And this unrealized human potential has inevitable adverse and long-term implications for communities, societies and economies more broadly.
- Significance of Social Protection:
- Before the Covid-19 pandemic, children were more than twice as likely to be living in extreme poverty than adults.
- One billion children live in multidimensional poverty without access to education, health, housing, nutrition, sanitation or water.
- The Covid-19 pandemic highlighted that social protection is a critical response in times of crisis.
- Nearly every government in the world either rapidly adapted existing schemes or introduced new social protection programmes to support children and families.
- In 2022, South Africa introduced a welfare scheme, Child Support Grant (CSG) Top-Up, aiming to increase the CSG amount for orphans and children heading or living in child-headed households.
- 31 states in India had implemented the national ‘PM CARES for Children’ scheme, a package of measures for 10,793 full orphans and 151,322 half-orphans. So far, 4,302 children have received support from the scheme.
What are the Recommendations?
- Policymakers should take action towards universal social protection for all children, including investments in benefits that offer proven and cost-effective ways to combat child poverty.
- Authorities are also advised to provide child benefits through national social protection systems that also connect families to crucial health and social services, such as free or affordable quality childcare.
- There is a need for securing sustainable financing for schemes by mobilizing domestic resources, increasing budget allocation for children, strengthening social protection for parents and caregivers and guaranteeing access to decent work and adequate employee benefits.
UPSC Civil Services Exam, Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Q. International Labour Organization’s Conventions 138 and 182 are related to (2018)
(a) Child Labour
(b) Adaptation of agricultural practices to global climate change
(c) Regulation of food prices and food security
(d) Gender parity at the workplace
Ans: (a)


Important Facts For Prelims
Great Seahorse Migration
Why in News?
A study indicated that extensive fishing off the Coromandel coast could be forcing the great seahorse to migrate towards Odisha.
- Though, fishing is less intense off the Odisha coastline but still it may not be the new comfort zone for the Seahorse due to lack of suitable habitat.
What are the Key Facts about Seahorse?
- About:
- Sea horses are tiny fish that are named for the shape of their head, which looks like the head of a tiny horse. They are classified as fish, in the genus Hippocampus.
- There are 46 species of seahorses reported worldwide. The coastal ecosystems of India house 9 out of 12 species found in the Indo-Pacific.
- They are found in shallow coastal waters in latitudes from about 52° N to 45°S.

- Seahorse populations in India are distributed across diverse ecosystems such as seagrass, mangroves, macroalgal beds, and coral reefs.
- Distribution in India:
- These 9 species are distributed along the coasts of eight States and five Union Territories from Gujarat to Odisha, apart from Lakshadweep and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- Slow Swimmers:
- When swimming they maintain a vertical position and propel themselves forward using a soft-rayed dorsal fin.
- They migrate by rafting, clinging to floating substrata such as macroalgae or plastic debris for dispersal by ocean currents.
- Unique Reproductive Habits:
- The male gives birth to child as the female uses an ovipositor (egg duct) to place her eggs into a brood pouch located at the base of the male’s tail where the eggs are later fertilized.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN status-Vulnerable
- CITES: Appendix II
What are the Reasons for Decline and Migration?
- The population of the Great seahorse is declining due to its Overexploitation for
- Traditional Chinese medicines
- Ornamental fish
- General destructive fishing
- Fisheries bycatch.
- This creates immense pressure on the seahorse populations that have a high dependency on local habitats to maintain their extensive and long-life history traits.
- The 1,300 km northward migration of the great seahorse from Palk Bay and the Gulf of Mannar to Odisha is likely a response to extensive fishing activities around the southern coast of India.
- Around 13 million individuals are caught per year on Coromandel coast.
What are the Challenges with Migration?
- Lack of Suitable Habitats: Odisha coast does not have coral reefs or seagrass meadows to make a suitable habitat, except within the Chilika region.
- Thus, it is going to be difficult for the species, unless the fishing nets that catch them are banned or the fishing practices such as Bottom trawling are stopped.
- Lack of Conservation Measures: This highlights the lack of monitoring of the coastal ecosystems of India on the east coast and reaffirms the need better conservation and management of the remaining seahorse populations.
UPSC Civil Services Exam, Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following animals: (2013)
- Sea cow
- Sea horse
- Sea lion
Which of the above is/are mammal/mammals?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- Sea cow is a sea-grass eating marine mammal which is found in the Indian Ocean on the western part of the Pacific Ocean. They are the only extant species of the family “Dugongidae”. Hence, 1 is correct.
- Sea horses are tiny fish that are named for the shape of their head, which looks like the head of a tiny horse. Sea horses are not mammals as they are classified as fish, in the “genus Hippocampus”. Hence, 2 is not correct.
- Sea lions are the marine or aquatic mammals as they give live births, breathes air, and suckles its young with milk like all other mammals. They are found primarily in the Pacific waters. Hence, 3 is correct.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.


Important Facts For Prelims
Erythritol
Why in News?
According to recent research, Erythritol, a popular artificial sweetener, is associated with an increased risk of heart attack and stroke.
What was the Result of the Research?
- Results of the research revealed that erythritol made platelets easier to activate and form a clot.
- Erythritol activates platelets, the blood cells which cause clots when they clump together. Such aggregation of platelets blocks blood flow in blood vessels in different parts of the body.
- When that happens in blood vessels supplying blood to the heart or brain, fatal or non-fatal cardiovascular events occur.
What is Erythritol?
- About: It is a type of sugar alcohol commonly used as a sugar substitute in foods and beverages. Unlike traditional sugars, it has no calories and does not raise blood sugar levels.
- Artificial sweeteners are common replacements for table sugar in low-calorie, low-carbohydrate and “keto” products (high in fat and low in carbohydrates).
- Low Glycemic Index (GI): It is also believed to have a lower GI than other sweeteners, meaning it may not impact insulin levels as strongly.
- GI is a value used to measure how much specific foods increase blood sugar levels.
- Uses: Sugar-free products containing Erythritol are often recommended for people who have obesity, diabetes or metabolic syndrome and are looking for options to help manage their sugar or calorie intake.
- People with these conditions also are at higher risk for adverse cardiovascular events like heart attack and stroke.
UPSC Civil Services Exam, Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Q. ‘Triclosan’, considered harmful when exposed to high levels for a long time, is most likely present in which of the following? (2021)
(a) Food preservatives
(b) Fruit-ripening substances
(c) Reused plastic containers
(d) Toiletries
Ans: (d)
- Triclosan is an ingredient added to many consumer products intended to reduce or prevent bacterial contamination. It is added to toiletries like antibacterial soaps and body washes, toothpaste, and some cosmetics.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.


Important Facts For Prelims
Swachh Sujal Shakti Samman 2023
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Jal Shakti has organized the “Swachh Sujal Shakti Samman 2023”, to honor the women champions of the rural water and sanitation sector.
- The event also saw the launch of Jal Shakti Abhiyan – Catch the Rain 2023.
What are the Key Highlights?
- This event was organized in the run up to the International Women’s Day (8th March) and to highlight and acknowledge the leadership and contribution of women at the grass-root level in the journey towards making a ‘Swachh Sujal Bharat’.
- 36 women WASH Champions were conferred with the ‘Swachh Sujal Shakti Samman 2023’.
- They were felicitated for their exceptional and exemplary work at the grassroots level in the implementation of Swachh Bharat Mission – Gramin (SBM-G), Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM), Jal Shakti Abhiyan: Catch the Rain (JSA-CTR).
- On this occasion, the Hon’ble President felicitated the women achievers who have contributed exceptionally in ODF Plus Model Villages, Har Ghar Jal Villages, Water Conservation, etc. under the National Flagship Missions.
What are the Key Points of Catch the Rain 2023?
- The President of India launched ‘Catch the Rain-2023’ as part of efforts to turn conservation of water into a mass campaign in the run-up to the monsoon season.
- Theme 2023: Source Sustainability for Drinking Water.
- Tag line: Catch the rain, where it falls, when it falls.
- Catch the Rain is a Jan Andolan campaign to encourage all stakeholders to create rainwater harvesting structures.
- The campaign is implemented by the National Water Mission (NWM), Ministry of Jal Shakti.
- The campaign takes place across the country, in both rural and urban areas.
What are the Efforts for Water Conservation?
UPSC Civil Services Exam, Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Q. If National Water Mission is properly and completely implemented, how will it impact the country? (2012)
- Part of the water needs of urban areas will be met through recycling of waste-water.
- The water requirements of coastal cities with inadequate alternative sources of water will be met by adopting appropriate technologies that allow for the use of ocean water.
- All the rivers of Himalayan origin will be linked to the rivers of peninsular India.
- The expenses incurred by farmers for digging bore-wells and for installing motors and pumpsets to draw ground-water will be completely reimbursed by the Government.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)


Important Facts For Prelims
Conference of Global Intelligence Chiefs
Why in News?
On March 1, India held the second conference of intelligence and security chiefs from 26 countries around the world.
- The conference was held for the first time in April 2022, a day before the start of the Raisina Dialogue. It was addressed by the PM of India and National Security Advisor (NSA).
What is the Highlight of the Conference?
- About: As part of Raisina Dialogue, the security conference is organised by the country’s external intelligence agency, the Research and Analysis Wing (R&AW) and the National Security Council Secretariat (NSCS) that reports to NSA.
- Objective: To discuss the ongoing geopolitical tensions, provided an opportunity for participants to exchange views on how to address this crisis and other geopolitical tensions. However, the meeting focused on the Russia-Ukraine conflict.
- Nature of Meeting: It is modelled on the lines of the Munich Security Conference and Singapore’s Shangri-La Dialogue.
- It was coincided with the G20 Foreign Ministers meeting and the Raisina Dialogue. India chairs both G20 and the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) in 2023.
- While the U.S. was absent, intelligence chiefs from the U.K., France, Japan and Bahrain were among those present.
What is Raisina Dialogue?
- The Raisina Dialogue is India’s premier conference on geopolitics and geoeconomics committed to addressing the most challenging issues facing the global community.
- The conference is hosted by the Observer Research Foundation in partnership with the Ministry of External Affairs, Government of India.
- In 2023, it seeks to capture the state of the world through its theme of "Provocation, Uncertainty, Turbulence: Lighthouse in the Tempest?"
- The Dialogue is structured as a multi-stakeholder, cross-sectoral discussion, involving heads of state, cabinet ministers and local government officials, who are joined by thought leaders from the private sector, media and academia.
What is Observer Research Foundation?
- It is an independent think tank based in New Delhi with three centres in Mumbai, Chennai and Kolkata.
- It seeks to lead and aid policy thinking towards building a strong and prosperous India in a fair and equitable world and helps discover and inform India’s choices. It carries Indian voices and ideas to forums shaping global debates.
- It provides non-partisan, independent, well-researched analyses and inputs to diverse decision-makers in governments, business communities, and academia and civil society around the world.


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
World’s First Bamboo Crash Barrier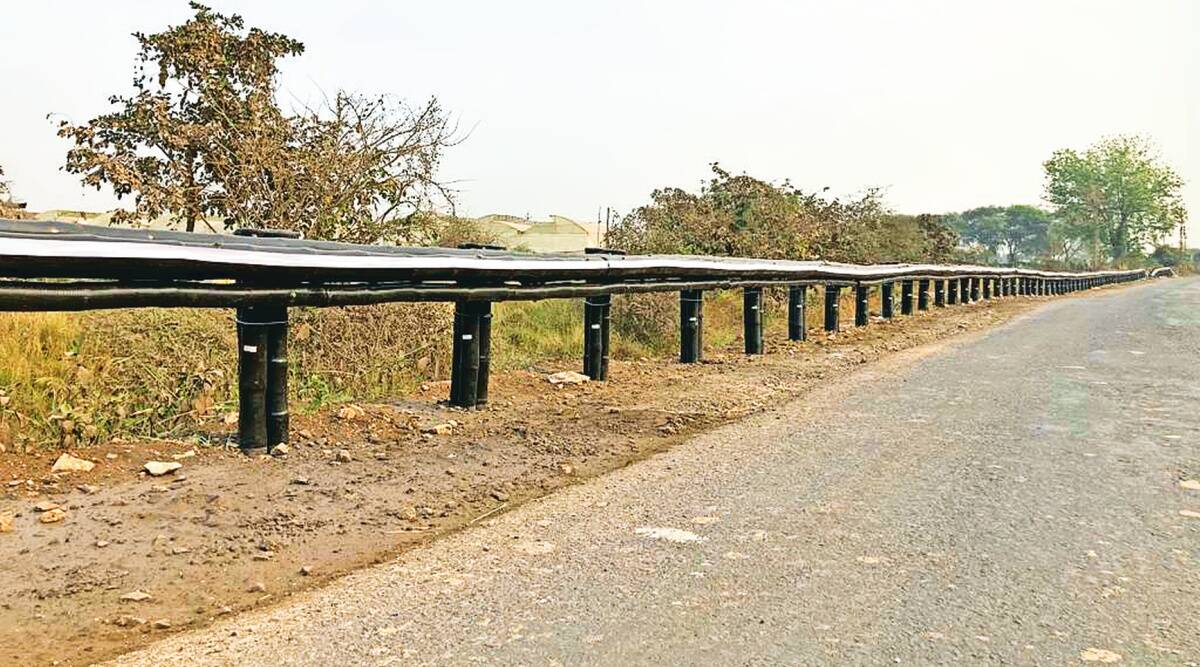
Recently, the world’s first 200-metre-long bamboo crash barrier has been installed on a Vani-Warora Highway connecting Chandrapur and Yavatmal districts in Maharashtra.
Named ‘Bahu Balli’, the bamboo crash barrier underwent rigorous testing at various government-run institutions and was rated as Class 1 during the Fire Rating Test and it has also been accredited by the Indian Road Congress (IRC). This crash barrier offers a perfect alternative to steel and addresses environmental concerns.
IRC is the Apex Body of Highway Engineers in the country. The IRC was set up in 1934 on the recommendations of the Indian Road Development Committee best known as Jayakar Committee (1927) set up by the Government with the objective of Road Development in India.
Bal Mitra Diwas
Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Bureau of India (PMBI) is conducting weeklong celebrations across the nation on the occasion of 5th Jan Aushadhi Diwas. One of the day’s events of Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana (PMBJP) were dedicated to children which was celebrated as ‘Bal Mitra Diwas’.
The aim of celebrating these events is to increase engagement of general public including women, senior citizens, students and children so that benefits of the Pariyojana may reach each and every corner of the country.
PMBJP is a campaign launched by the Department of Pharmaceuticals in 2008 under the name Jan Aushadhi Campaign. The campaign was revamped as PMBJP in 2015-16.
Bureau of Pharma PSUs of India (BPPI) is the implementation agency for PMBJP.
The BPPI works under the Ministry of Chemicals & Fertilisers. BPPI has also developed the Janaushadhi Sugam Application.
Read More: Janaushadhi Diwas
INS Trikand
INS Trikand is participating in the International Maritime Exercise/ Cutlass Express 2023 (IMX/CE-23) being held in the Gulf region from 26 Feb to 16 Mar 2023. Exercises will be held with participants from over 50 nations and international maritime agencies with the common aim of enhancing maritime security and keeping sea lanes in the region safe for maritime commerce.
IMX/CE-23 is one of the largest multinational maritime exercises in the world. While this is the Indian Navy’s maiden IMX participation, it also marks the second occasion where an Indian Naval ship is participating in an exercise conducted by the Combined Maritime Forces (CMF). In November 22, INS Trikand had participated in the CMF-led Operation Sea Sword 2 in the Northwest Arabian Sea.
Read More: Indian Navy
Frog Species Rediscovered After 89 Years
Jerdon's narrow-mouthed frog (Uperodon montanus) was once seen in the Western Ghats' shallow streams. But since it was last studied in 1934, the species faded away permanently. In 2022, a group of zoologists photographed 40 tadpoles of the species in the biodiverse Western Ghats, at the same stage of development as when they were last recorded 89 years ago.
A majority of the amphibians have two different stages: Water-independent adult stage (feeding and breeding) and the aquatic larval stage (feeding) known as tadpoles. These tadpoles / larvae have completely different morphological appearance, feeding, habitat and ecology which is totally different from adults.
The frogs have a longish snout, which gives it its name, and shiny brown skin with darker brown, red and golden spots on the back and head. They are found in rock pools or tree holes filled with rainwater. Its tadpoles are free-swimming and exotrophic (they feed on other species). Change in the tadpole body colouration was observed during the day (comparatively darker) and night (slightly transparent). This frog is considered a montane species and is restricted to higher altitude ranges. They are distributed from near Wayanad south across the Palghat and the Shencottah gaps to the Agasthyamalai hills.
It is classified as ‘Near Threatened’ in the International Union for Conservation (IUCN) of Nature Red List of Threatened Species.
Read More: Western Ghats