Simultaneous Elections
For Prelims: Simultaneous Elections, Lok Sabha, Rajya Sabha, Election Commission of India, Representation of the People Act, 1951.
For Mains: Simultaneous Elections, Significance and Challenges.
Why in News?
The Central government set up a panel headed by former President Ram Nath Kovind to explore the feasibility of the ‘one nation, one election’ (ONOE) plan.
- Despite Logistical and other challenges, the idea of holding Simultaneous Elections/ ONOE to the Lok Sabha (Parliament) and state Assemblies in India has been a topic of discussion.
What are Simultaneous Elections?
- About:
- The idea is about structuring the Indian election cycle in a manner so that elections to the Lok Sabha and the State Assemblies are synchronised together so that the election to both can be held within a given span of time.
- While this concept had been practiced until 1967, it gradually fell out of sync due to the frequent dissolution of Assemblies and Lok Sabhas before their terms ended.
- Currently, only a few states (Andhra Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Odisha, and Sikkim) hold elections along with the Lok Sabha polls.
- Advantages:
- According to the draft report on simultaneous elections by the Law Commission of India (LCI) in August 2018, ONOE will lead to the saving of public money, reducing the strain on the administrative setup and security forces, timely implementation of government policies, and administrative focus on development activities rather than electioneering.
What are the Challenges in Holding Simultaneous Elections?
- Feasibility:
- Article 83(2) and Article 172 of the Indian Constitution stipulate that the tenure of Lok Sabha and State Assemblies respectively, will last for five years unless dissolved earlier and there can be circumstances, as in Article 356, wherein assemblies can be dissolved earlier. Therefore, the ONOE plan raises serious issues of feasibility if the Central or State government collapses mid-tenure.
- Amending the Constitution for such a significant change would not only necessitate extensive consideration of various situations and provisions but would also set a concerning precedent for more constitutional amendments.
- The Election Commission of India (ECI) submitted a feasibility report to the government in 2015, suggesting amendments to the Constitution and the Representation of the People Act, 1951.
- Not Aligned with Federalism:
- The idea of ONOE does not square with the concept of ‘federalism’ as it is established on the notion that the entire nation is “one” contradicting the content of Article 1 which envisages India as a “Union of States”.
- Present Form is More Beneficial:
- The present form of recurrent elections can be seen as beneficial in a democracy as it allows voters to have their voices heard more frequently.
- As the underlying issues of national and State polls are different, the present framework prevents the blending of issues, ensuring greater accountability.
- EVM and VVPAT Requirement:
- Approximately 30 lakh Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs) and Voter-Verified Paper Audit Trail (VVPAT) machines would be needed for simultaneous elections.
- Cost Considerations:
- The ECI has highlighted that simultaneous elections would require a substantial budget.
- A total of approximately Rs 9,284.15 crore would be needed for procuring EVMs and VVPATs, with additional costs for replacing machines every 15 years.
- Simultaneous elections would increase warehousing costs due to the storage of machines between elections.
- Impact on Voter Behaviour:
- Some political parties argue that it may influence voter behaviour in a manner that voters would end up voting on national issues even for State elections and this may lead to larger national parties winning both State and Lok Sabha elections thereby marginalizing regional parties.
- Election Issues:
- State and national elections are often fought on different sets of issues — and in simultaneous elections, voters may end up privileging one set over the other in ways they might not have done otherwise.
- Diminished Accountability:
- Having to face the electorate more than once every 5 years enhances the accountability of politicians and keeps them on their toes. Finally, a lot of jobs are also created during the elections, which boosts the economy at the grassroots levels.
How can Simultaneous Elections be Restored in India?
- According to the Recommendations of the Law Commission Working Paper (2018),
- Simultaneous elections may be restored through an amendment of the Constitution, Representation of the People Act, 1951 and Rules of Procedure of Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assemblies. A definition may be added to section 2 of the 1951 Act.
- The no-confidence motion may be replaced with a constructive vote of no-confidence through amendments in Lok Sabha and State Assemblies rules of business.
- Anti-Defection Law may be suitably diluted to prevent stalemate in case of a hung Assembly or Parliament
- The statutory limit of six months for issuance of notification of general elections may be extended for securing flexibility as a one-time measure.
What are the Countries where Simultaneous Elections are conducted?
- In South Africa, elections to national as well as provincial legislatures are held simultaneously for five years and municipal elections are held two years later.
- In Sweden elections to the national legislature (Riksdag) and provincial legislature/county council (Landsting) and local bodies/municipal Assemblies (Kommunfullmaktige) are held on a fixed date i.e. second Sunday in September for four years. But most other large democracies do not have any such system of simultaneous elections.
- In Britain, the Fixed-term Parliaments Act, 2011 was passed to provide a sense of stability and predictability to the British Parliament and its tenure. It provided that the first elections would be held on the 7th of May, 2015 and on the first Thursday of May every fifth year thereafter.
- Article 67 of Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany proposes a constructive vote of non-confidence (electing a successor while dismissing the incumbent).
Way Forward
- Elections are held at different places every few months and it hampers the developmental work. Therefore, it’s a must to have a deep study and deliberation on the idea in order to prevent the impact of the model code of conduct on development works every few months.
- There needs to be a consensus on whether the country needs one nation, one poll or not. All political parties should at least cooperate in debating this issue, once the debate starts, the public opinion can be taken into consideration. India being a mature democracy, can then follow the outcome of the debate.
Aditya-L1 Mission
For Prelims: Indian Space Research Organisation, Aditya-L1, ISRO’s Launch Vehicles, Lagrange Points in the Sun-Earth System, Solar flares, Coronal mass ejections.
For Mains: Significance of Exploring the Sun, India’s achievements in the field of Space Science and Technology.
Why in News?
Recently, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has accomplished the launch of Aditya-L1, its inaugural Solar Mission.
- The launch was conducted using the PSLV-C57 rocket. The PSLV's fourth stage was fired twice, a first in ISRO's history, to precisely insert the spacecraft into its elliptical orbit.
What is Aditya-L1 Mission?
- About:
- Aditya-L1 is the first space based observatory class Indian solar mission to study the Sun from a substantial distance of 1.5 million kilometers. It will take approximately 125 days to reach the L1 point.
- Aditya-L1 is also ISRO’s second astronomy observatory-class mission after AstroSat (2015).
- The mission's journey is notably shorter than India's previous Mars orbiter mission, Mangalyaan.
- The spacecraft is planned to be placed in a halo orbit around the Lagrangian point 1 (L1) of the Sun-Earth system.
- Aditya-L1 is the first space based observatory class Indian solar mission to study the Sun from a substantial distance of 1.5 million kilometers. It will take approximately 125 days to reach the L1 point.
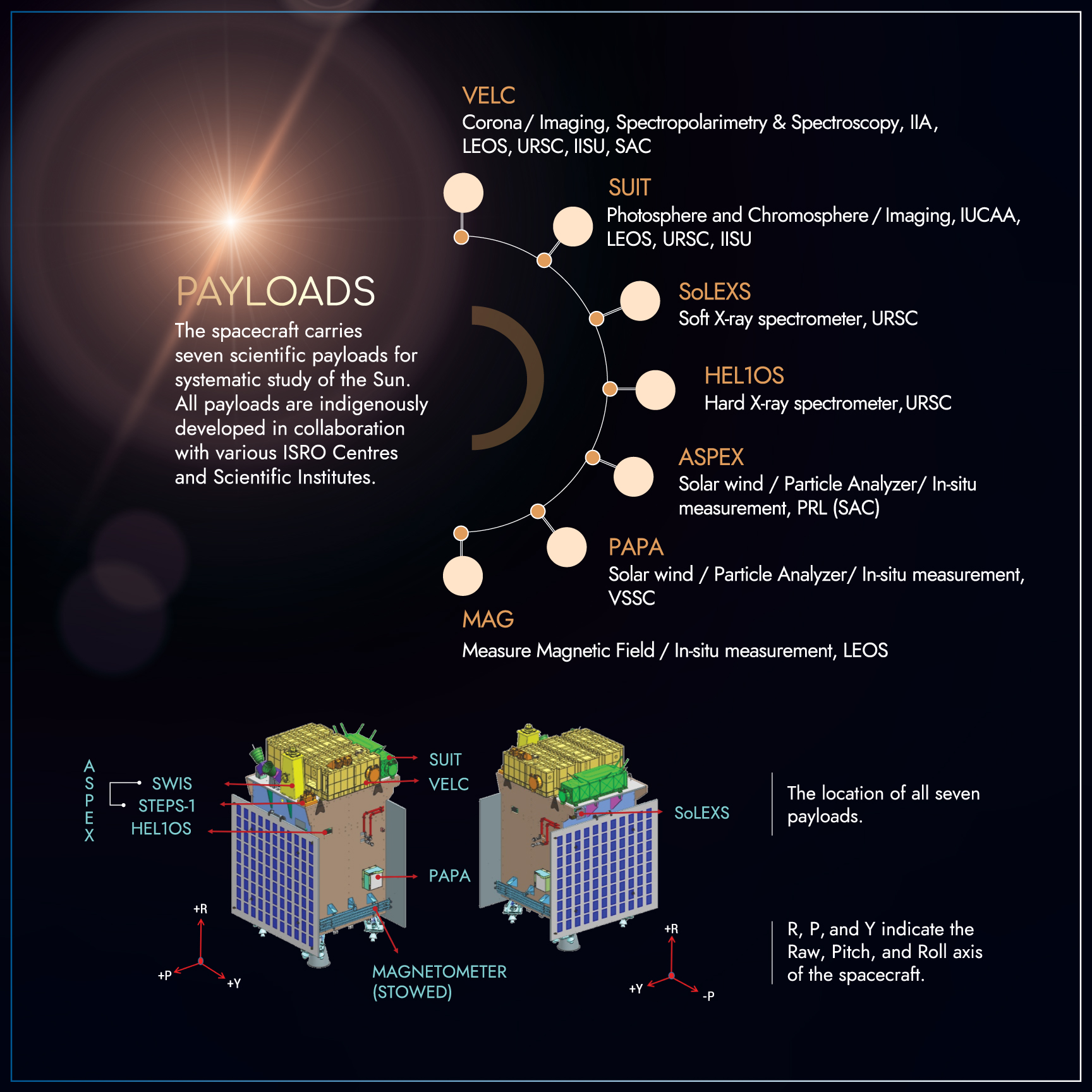
- Payloads:
- Objective:
- The mission aims to provide valuable insights into the solar corona, photosphere, chromosphere, and solar wind.
- The primary objective of Aditya-L1 is to gain a deeper understanding of the Sun's behavior, including its radiation, heat, particle flow, and magnetic fields, and how they impact Earth.
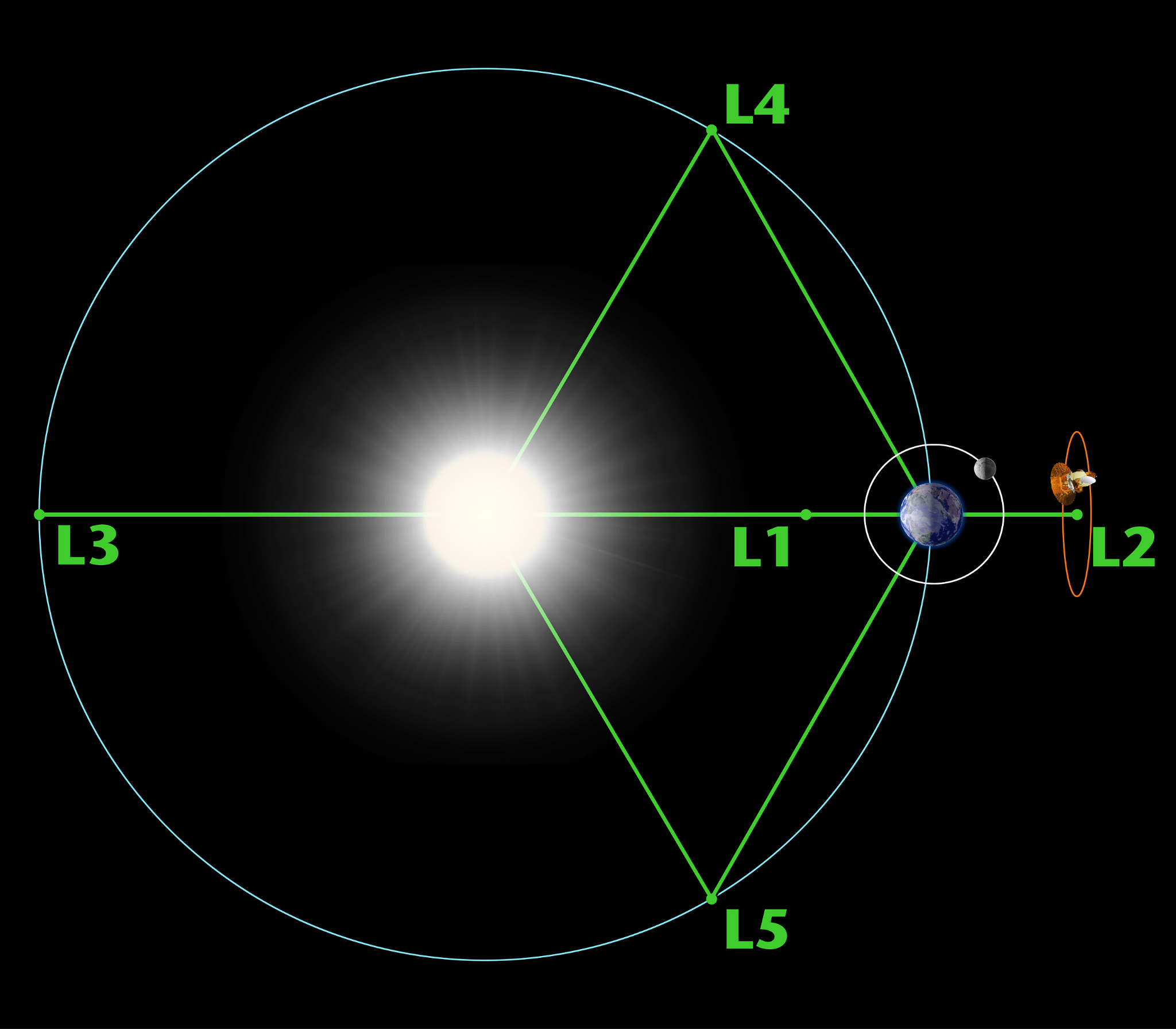
What are Lagrange Points?
- About:
- Lagrange points are special positions in space where the gravitational forces of two large orbiting bodies, such as the Sun and the Earth, balance each other out.
- This means that a small object, such as a spacecraft, can stay at these points without using much fuel to maintain its orbit.
- There are five Lagrange Points, each with distinct characteristics. These points enable a small mass to orbit in a stable pattern amid two larger masses.
- Lagrange points are special positions in space where the gravitational forces of two large orbiting bodies, such as the Sun and the Earth, balance each other out.
- Lagrange Points in the Sun-Earth System:
- L1: L1 is considered the most significant of the Lagrange points for solar observations. A satellite placed in the halo orbit around the L1 has the major advantage of continuously viewing the Sun without any occultation/ eclipses.
- It is currently home to the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory Satellite (SOHO).
- L2: Positioned directly 'behind' Earth as viewed from the Sun, L2 is excellent for observing the larger Universe without Earth's shadow interference.
- The James Webb Space Telescope orbits the Sun near L2.
- L3: Positioned behind the Sun, opposite Earth, and just beyond Earth's orbit, it offers potential observations of the far side of the Sun.
- L4 and L5: Objects at L4 and L5 maintain stable positions, forming an equilateral triangle with the two larger bodies.
- They are often used for space observatories, such as those studying asteroids.
- L1: L1 is considered the most significant of the Lagrange points for solar observations. A satellite placed in the halo orbit around the L1 has the major advantage of continuously viewing the Sun without any occultation/ eclipses.
Note: L1, L2, and L3 points are unstable, meaning that a small perturbation can cause an object to drift away from them. Therefore, satellites orbiting these points need regular course corrections to maintain their positions
What is the Significance of Exploring the Sun?
- Understanding Our Solar System: The Sun is the center of our solar system, and its characteristics greatly influence the behavior of all other celestial bodies. Studying the Sun enhances our understanding of the dynamics of our solar neighborhood.
- Space Weather Prediction: Solar activities, such as solar flares and coronal mass ejections, can impact Earth's space environment.
- Understanding these phenomena is crucial for predicting and mitigating potential disruptions to communication systems, navigation, and power grids.
- Advancing Solar Physics: Exploring the Sun's complex behavior, including its magnetic fields, heating mechanisms, and plasma dynamics, contributes to advances in fundamental physics and astrophysics.
- Enhancing Energy Research: The Sun is a natural fusion reactor. Insights gained from studying its core and nuclear reactions can inform our pursuit of clean and sustainable fusion energy on Earth.
- Improving Satellite Operations: Solar radiation and solar wind affect the functioning of satellites and spacecraft. Understanding these solar interactions allows for better spacecraft design and operation.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Discuss India’s achievements in the field of Space Science and Technology. How has the application of this technology has helped India in its socio-economic development? (2016)
Role of UPI in Shaping Foreign Policy
For Prelims: India Stack, Data Empowerment and Protection Architecture(DEPA), Digital public infrastructure, United Payments Interface
For Mains: Significance of UPI's success to attract foreign investments, How digital diplomacy can contribute to India's global influence.
Why in News?
India's digital strength has reached new heights with the United Payments Interface (UPI) surpassing 10 billion transactions, signifying not only domestic success but also its vital role in foreign policy.
- Transactions on UPI have grown by over 50% year-on-year. UPI crossed 1 billion monthly transactions for the first time in October 2019.
How does UPI Contribute to India’s Foreign Policy?
- Digital Diplomacy:
- India aims to assume a leadership role in the Global South by pioneering digital governance.
- India's digital public infrastructure (DPI) push is a differentiator from China's focus on physical infrastructure development in developing countries.
- International Expansion:
- Since June 2023, India has signed agreements with countries like Armenia, Sierra Leone, Suriname, Antigua & Barbuda and Papua New Guinea to share India Stack.
- Similarly, UPI has also been taken to international markets such as France, UAE, Singapore and Sri Lanka, with countries like Japan, Mauritius, and Saudi Arabia having shown an interest in adopting the payment system.
- Global Digital Public Infrastructure Repository (GDPIR):
- India plans to establish the GDPIR to share DPI practices globally.
- The GDPIR aims to facilitate the exchange of tools and resources related to DPI among G20 members and beyond.
- Economic Diplomacy:
- UPI's success attracts foreign investments and partnerships, contributing to India's economic diplomacy efforts and strengthening bilateral relations.
What is India Stack?
- India Stack is a set of APIs (Application programming interfaces) that allows governments, businesses, startups, and developers to utilize a unique digital Infrastructure to solve India’s hard problems towards presence-less, paperless, and cashless service delivery.
- India Stack is a government-led initiative that focuses on building a robust digital infrastructure to enable various digital services across different sectors.
- The components of this collection are owned and maintained by different agencies.
- INDIA STACK aims to streamline and enhance identity verification, data exchange, and digital payment processes to make them more accessible and efficient for citizens.
- It includes digital public goods, which are digital resources and tools made available to the public to support various digital services and initiatives.
- The India Stack comprises three key layers: identity, payments, and data management.
- Identity Layer (Aadhaar):
- Aadhaar serves as the cornerstone of India Stack, offering digital identity products.
- It is issued by the Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI) under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology.
- Aadhaar is considered a proof of residence and not a proof of citizenship, and it does not grant any rights to domicile in India.
- Payments Layer (UPI):
- UPI forms the second layer, ensuring interoperability among money custodians, payment rails, and front-end payment applications.
- Managed by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI), UPI is licensed to third-party private entities like PhonePe, Google Pay, and Paytm.
- Data Governance Layer:
- Digital Locker is built on Data Empowerment and Protection Architecture(DEPA) ; it incorporates a consent management system, enabling the secure sharing of information for better financial, health, and telecom-related products and services.
- It consists of a set of digital identity products centered around Aadhaar. It can be used to remotely authenticate via two-factor or biometric authentication, receive digitally signed records such as driver’s licenses, educational diplomas, and insurance policies, and sign documents or messages using a government-backed digital signature service.
- Identity Layer (Aadhaar):
- Aside from UPI, a number of digital solutions that the Indian government has rolled out in the last few years, including CoWin, DigiLocker, Aarogya Setu, and Government e-Marketplace (GeM), all utilize the three fundamental layers of the Indian Stack.
- The vision of India Stack is not limited to one country (India); it can be applied to any nation, be it a developed one or an emerging one.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2018)
- Aadhaar card can be used as a proof of citizenship or domicile.
- Once issued, Aadhaar number cannot be deactivated or omitted by the Issuing Authority.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
NCERT Attains Deemed University Status
For Prelims: National Council of Educational Research and Training, Deemed-to-be-University, National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, De novo Category.
For Mains: Deemed University Status and its Benefits, Reforms in Indian Education System.
Why in News?
The 63rd Foundation Day of the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) was recently observed in New Delhi, accompanied by the notable achievement of NCERT being granted the esteemed Deemed-to-be-University status.
What are the Major Highlights of the Event?
- 'Jadui Pitara' Revolutionizes Early Education:
- At the event, a play-based educational resource named 'Jadui Pitara' received acclaim for its suitability for children aged 3 to 8.
- With the capacity to positively impact a staggering 100 million children across the country, 'Jadui Pitara' is positioned to play a crucial role in revolutionizing the field of education.
- At the event, a play-based educational resource named 'Jadui Pitara' received acclaim for its suitability for children aged 3 to 8.
- Promotion of Mother Tongue and Integration of Advanced Technologies:
- In an effort to preserve and promote regional languages, emphasis was placed on the critical importance of developing educational content in mother tongues.
- Additionally, it was highlighted that NCERT is committed to developing educational materials in all 22 languages with the help of software like Anuvadini.
- A visionary proposal was made for the establishment of Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality, and Artificial Intelligence laboratories in all seven regional centers under the aegis of NCERT.
- The ultimate goal is to equip these centers with state-of-the-art global technologies, thereby nurturing an environment conducive to innovation and advanced research.
- In an effort to preserve and promote regional languages, emphasis was placed on the critical importance of developing educational content in mother tongues.
- Standardization of Teacher Training and Readiness for Industry 4.0:
- The event called to standardize the teacher training curriculum, aligning it with the principles of the Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) framework.
- With a focus on preparing India's youth for the challenges posed by Industry 4.0, a proposal was made to create concise booklets covering contemporary topics such as India's Covid-19 Pandemic management and Chandrayaan 3.
- The aim is to keep the younger generations informed about the latest developments while instilling Indian values and ethos.
What is NCERT?
- The National Council of Educational Research and Training is an autonomous organization that was established in 1961 under the Societies Registration Act.
- It is the apex body for advising the central and state governments on matters related to school education.
- It undertakes various activities and programmes related tp:
- Educational research and innovation
- Curriculum development and revision
- Development of textbooks and other teaching-learning materials
- Teacher education and professional development
- Educational evaluation and assessment
- International cooperation in education
- As per the National Education Policy(NEP) 2020, NCERT is the nodal agency to develop National Curriculum Frameworks (NCFs) for: Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE), School Education, and Adult Education.
What is a Deemed University?
- About:
- A deemed university is an institution of higher education that is recognised by the University Grants Commission (UGC) under Section 3 of the UGC Act, 1956.
- It is not established or incorporated by an Act of Parliament or State Legislature, but is conferred the status of a university by the central government on the recommendation of the UGC.
- A deemed university enjoys academic autonomy and can design its own courses, syllabi, admission criteria, fee structure, faculty recruitment and examination system.
- A deemed university is an institution of higher education that is recognised by the University Grants Commission (UGC) under Section 3 of the UGC Act, 1956.
- De Novo Category:
- The NCERT has been granted the deemed university status under the ‘de novo’ category, which means that it has been recognised for its excellence in a new or emerging area of knowledge.
- De-novo Institution means an institution devoted to innovations in teaching and research in unique and “emerging areas of knowledge” such as biotechnology, nanotechnology, space science, etc.
- The NCERT has been granted the deemed university status under the ‘de novo’ category, which means that it has been recognised for its excellence in a new or emerging area of knowledge.
- Benefits of Getting the Deemed University Status:
- They can also launch new courses and programmes that are relevant to the changing needs and demands of the education sector without having to seek approval from any other authority.
- They can collaborate with national and international universities and institutions for academic exchange, research projects, faculty development and student mobility.
- They can attract more students and faculty from diverse backgrounds and regions, as well as more funding from various sources.
- They can play a more active role in implementing the NEP 2020, which envisages a transformation of the school education system in India.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Regarding Wood’s Dispatch, which of the following statements are true? (2018)
- Grants-in-Aid system was introduced.
- Establishment of universities was recommended.
- English as a medium of instruction at all levels of education was recommended.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Global Fund Secures Deal to Slash HIV Treatment Price
For Prelims: Global Fund, Tenofovir disoproxil, Lamivudine, Dolutegravir(TLD), Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
For Mains: AIDS, HIV and Related Initiatives
Why in News?
The price of a cutting-edge Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) drug, Tenofovir disoproxil, Lamivudine and Dolutegravir (TLD), will be slashed as the Global Fund announced a deal with generic pharmaceutical manufacturers.
What are the Key Highlights of the Deal?
- Reduction in Cost:
- It is possible to provide the advanced pill known as TLD for under USD 45 per person per year with a price reduction of 25%
- Impact of Deal:
- Reduced pricing for TLD means governments and other implementers of Global Fund grants can expand treatment programmes to reach around 19 million more people are living with HIV in resource-constrained settings.
What is Global Fund?
- About:
- The Global Fund is a worldwide movement established in 2002 to defeat HIV, tuberclosis (TB) and Malaria and ensure a healthier, safer, more equitable future for all.
- The Global Fund raises funds on a three-year cycle, bringing longer term predictability in the fight against AIDS, TB and malaria.
- Governments, the private sector and nongovernmental organizations pledge funds to support their mission.
- Mission:
- Raise and invest USD 4 billion a year to fight the deadliest infectious diseases, challenge the injustice that fuels them and strengthen health systems in more than 100 countries.
- Global Fund Strategy (2023-2028) :
- Fighting Pandemics and Building a Healthier and More Equitable World:
- Strategy’s primary goal is to end AIDS, tuberculosis and malaria, with a particular focus on making catalytic investments and leveraging innovations to spur faster progress in reducing new infections.
- Fighting Pandemics and Building a Healthier and More Equitable World:
What is a TLD?
- The mainstay of treatment for more than 85% HIV is Tablet TLD (a fixed-dose combination of three antiretroviral drugs, namely, Tenofovir+Lamivudine +Dolutegravir.)
- The World Health Organization has recommended it as the preferred first-line HIV treatment for adults and adolescents since it rapidly suppresses the virus that causes AIDS, has fewer side effects and is easy to take.
What is HIV?
- About:
- HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus, which is a virus that attacks the immune system in the human body.
- It primarily targets and damages CD4 immune cells, which are essential for the body's ability to fight infections and diseases.
- Over time, HIV weakens the immune system, leaving the body vulnerable to opportunistic infections and cancers.
- Transmission:
- HIV is primarily spread through the exchange of certain bodily fluids such as blood, semen, vaginal fluids, and breast milk.
- Severity:
- If left untreated, the virus destroys a person’s immune system and they are said to be in the Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome stage (AIDS) where they get several opportunistic infections that may result in death.
- Cure:
- Although there are no cures for the infection at present, the disease can be managed using antiretroviral therapy.
- These medicines suppress the replication of the virus within the body, allowing the number of CD4 immune cells to bounce back.
- Although there are no cures for the infection at present, the disease can be managed using antiretroviral therapy.
What are India’s Initiatives to Curb AIDS Disease?
- HIV and AIDS (Prevention and Control) Act, 2017: According to this act, the central and state governments shall take measures to prevent the spread of HIV or AIDS.
- Access to ART: India has made Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) affordable and accessible to over 90% of people living with HIV in the world.
- Project Sunrise: Project Sunrise was launched by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare in 2016, to tackle the rising HIV prevalence in north-eastern states in India, especially among people injecting drugs.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Which of the following diseases can be transmitted from one person to another through tattooing? (2013)
- Chikungunya
- Hepatitis B
- HIV-AIDS
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
National Teachers' Award 2023
Why in News?
Recently, the Prime Minister of India interacted with the winners of the National Teachers’ Award 2023 on the eve of Teachers’ Day.
What is the National Teachers’ Award?
- The purpose of the National Teachers’ Award is to celebrate the unique contribution of some of the finest teachers in the country and to honour those teachers who, through their commitment, have not only improved the quality of education but also enriched the lives of their students.
- The awards are conferred by the President of India on 5th September.
- The awards consist of a silver medal, a certificate and a cash prize of Rs. 50,000.
- This year, the scope of the award has been expanded from including teachers selected by the Department of School Education & Literacy to now also including teachers selected by Department of Higher Education and Ministry of Skill Development.
Why is Teacher’s Day Celebrated in India?
- Teachers' Day, celebrated annually on 5th September since 1962, honours the contributions of educators, including teachers, researchers, and professors in India.
- Dr. Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan, the President of India at the time, suggested observing his birthday as Teachers' Day in response to students' requests for celebration.
- About Radhakrishnan:
- Birth:
- He was born into a Telugu family in Tiruttani town of Tamil Nadu, on 5th September, 1888.
- Academics:
- He studied philosophy at Christian College, Madras, and later became a professor at Madras Presidency College and the University of Mysore.
- Employment:
- He served as the first Vice-President of India from 1952 to 1962 and the second President of India from 1962 to 1967.
- He was also the Ambassador of India to the Soviet Union from 1949 to 1952. He was the fourth Vice-Chancellor of Banaras Hindu University from 1939 to 1948.
- Recognition:
- In 1984, he was posthumously (after death) awarded the Bharat Ratna.
- Notable Works:
- Reign of Religion in Contemporary Philosophy, Philosophy of Rabindranath Tagore, The Hindu View of Life, Kalki or the Future of Civilisation, An Idealist View of Life, The Religion We Need, India and China, and Gautama the Buddha.
- Birth:
Minimal-Genome Cells Evolve as Fast as Normal Cells
Why in News?
Researchers from Indiana University, Bloomington, shed light on the evolutionary potential of cells with minimal genes (smallest set of genes that are essential for the survival and reproduction of an organism).
- Their study, published in the journal Nature, explores how cells stripped down to only essential genes can adapt and evolve, challenging conventional notions of genetic flexibility and mutation rates.
What are the Key Findings from the Study?
- The study concentrated on a synthetic minimal-cell version of Mycoplasma mycoides, a bacterial species that can cause respiratory disease in goats and cattle.
- This minimal version has only 493 essential genes, in contrast to the non-minimal strain with 901 genes, and the study spanned over 300 days.
- Mycoplasma mycoides has the highest recorded mutation rate for any cellular organism.
- Cells with minimal essential genes can adapt and evolve at a rate comparable to normal cells.
- Minimal cells exhibited mutation rates similar to non-minimal cells, despite their reduced genetic material.
- Genome minimization did not hinder the rate of adaptation in minimal cells.
- Understanding the evolution of minimal cells has implications for fields like synthetic biology, where researchers employ engineering principles to design organisms for applications in medicine and fuel production.
- This study reveals that engineered cells are not static; they undergo evolution, shedding light on how synthetic organisms might adapt when facing the inevitable forces of evolution.
- Gene:
- A gene is a segment of Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that codes for a specific protein or function. Genes are the basic units of heredity and can be inherited from parents or mutated by environmental factors.
- Gene Mutation:
- A gene mutation is a change in the DNA sequence of a gene that may affect its function or expression.
- Gene mutations can be caused by errors during DNA replication, exposure to radiation or chemicals, or other factors.
- Genome:
- A genome is the complete set of genetic information of an organism or a virus.
- Genetic Sequencing:
- It is the process of determining the order of nucleotides or bases (A, G, C, and T) in a DNA or RNA molecule
- Genome Editing:
- It is a type of genetic engineering in which DNA is inserted, deleted, modified or replaced in the genome of a living organism.
- Genetic Modification:
- It is the process of changing the DNA of an organism, such as a bacterium, plant or animal, by introducing elements of DNA from a different organism.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions
Prelims
Q. With reference to agriculture in India, how can the technique of ‘genome sequencing’, often seen in the news, be used in the immediate future? (2017)
- Genome sequencing can be used to identify genetic markers for disease resistance and drought tolerance in various crop plants.
- This technique helps in reducing the time required to develop new varieties of crop plants.
- It can be used to decipher the host-pathogen relationships in crops.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only,
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: D
Exp:
- Chinese scientists decoded rice genome in 2002. The Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI) scientists used the genome sequencing to develop better varieties of rice such as Pusa Basmati-1 and Pusa Basmati-1121, which currently makes up substantially in India’s rice export. Several transgenic varieties have also been developed, including insect resistant cotton, herbicide tolerant soybean, and virus resistant papaya. Hence, 1 is correct.
- In conventional breeding, plant breeders scrutinize their fields and search for individual plants that exhibit desirable traits. These traits arise spontaneously through a process called mutation, but the natural rate of mutation is very slow and unreliable to produce all the plant traits that breeders would like to see. However, in genome sequencing it takes less time, thus it is more preferable. Hence, 2 is correct.
- The host-pathogen interaction is defined as how microbes or viruses sustain themselves within host organisms on a molecular, cellular, organism or population level. The genome sequencing enables the study of the entire DNA sequence of a crop, thus it aids in understanding of pathogens’ survival or breeding zone. Hence, 3 is correct.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
WHO's Gujarat Declaration
The World Health Organization (WHO) has released the outcome document of the first WHO Traditional Medicine Global Summit 2023 in the form of the “Gujarat Declaration”.
- India hosted the first WHO Global Traditional Medicine Centre in Gujarat.
- The declaration reaffirmed global commitments towards indigenous knowledge, biodiversity and traditional, complementary and integrative medicine.
- The Gujarat Declaration aims to advance evidence-based traditional medicine interventions for universal health coverage and health-related Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- It calls for standardized documentation and data collection on traditional medicine.
- The summit explored the role of digital health technologies, including AI, in traditional medicine.
Read more: Global Centre for Traditional Medicine: Gujrat
Uncertainty of Andhra Pradesh students’ Local Quota
Andhra Pradesh students' 'local quota' in educational institutions, protected by Article 371 D, faces uncertainty as the Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act, 2014 expires in May 2024.
- Article 371 of the Constitution provides “special provisions” for 11 states, including six states of the Northeast (excluding Tripura and Meghalaya).
- Article 371 D was incorporated as the 32nd amendment to the Constitution in 1973.
- It particularly applies to the regions of Andhra Pradesh, addressing agitations in the early 1970s.
- Article 371 D was introduced to safeguard the rights of local students in education and employment.
- Under Article 371 D, 85% of seats in educational institutions are reserved for local students.
- The provision has played a crucial role in ensuring access to education for students in specific regions.
Read more: Stalemate Between Telangana and AP,
Electricity's Surge in Indian Irrigation: MIC 6th Edition Report
The recently published sixth edition of the Minor Irrigation Census (MIC) report offers significant insights into the power sources employed in Indian irrigation.
- The MIC highlights a noteworthy transformation in the primary power source for irrigation in India, where electricity has taken center stage.
- In 2011, electricity was the predominant power source for 56% of irrigation, a figure that surged to 70% by 2017.
- However, these findings are specific to the 2017-18 period and do not provide an accurate representation of the present state of irrigation practices.
Read more: India's 6th Minor Irrigation Census
IAF's Trishul Exercise Tests Western Air Command's Readiness
The Indian Air Force (IAF) has launched its annual mega training exercise, Trishul, with the activation of all combat assets under the Western Air Command (WAC).
- This internal exercise encompasses a wide range of frontline assets, including fighter jets, transport aircraft, and helicopters, deployed from Leh in Kashmir to Nal in Rajasthan.
- Trishul serves as a crucial test of the command's operational preparedness, requiring a high level of coordination and readiness due to its scale and complexity.
Read more: Need to Modernise Indian Air Force
Israeli PM Proposes Fiber Optic Link from Asia and the Middle East to Europe
Israel's Prime Minister has put forward the idea of a fibre optic cable project, to connect Asia and the Arabian Peninsula with Europe through Israel and Cyprus.
- It highlights that the fibre optic connection serves as a cost-effective and secure route for international communication.
- This proposal extends Israel's collaboration with Cyprus and Greece on energy projects, such as the EurAsia Interconnector, a 2,000-megawatt undersea electricity cable.
- Additionally, there are plans for energy diversification, including gas pipelines and liquefied natural gas processing plants, to strengthen the East Mediterranean basin's link to Europe.
Read more: Optical Fibre