SCO Summit 2023
For Prelims: Shanghai Cooperation Organization, BRI, POK, Terrorism, UNSC.
For Mains: SCO Summit 2023.
Why in News?
Recently, India has chaired the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) virtual Summit, leaders called for the formation of a “more representative” and multipolar world order in the global interest.
- During this 23rd Summit, Iran officially joined the SCO as the Ninth Member Country.
- The theme of India's chairpersonship of SCO is 'Towards a SECURE SCO’, which is derived from the acronym coined by the Indian PM at the 2018 SCO Qingadao Summit.
- It stands for: S: Security, E: Economic development, C: Connectivity, U: Unity, R: Respect for sovereignty and territorial integrity, E: Environmental protection.
Note: India, which was admitted as a full member of the SCO at the Astana Summit in 2017, holds the rotating presidency of the grouping for the first time in 2023. The SCO grouping now comprises China, India, Iran, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Pakistan, Russia, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan.
What are the Key Highlights of the 23rd SCO Summit?
- New Delhi Declaration:
- The New Delhi Declaration was signed by the member nations, which states that the international community must come together to "counter the activities of terrorist, separatist and extremist groups, paying special attention to preventing the spread of religious intolerance, aggressive nationalism, ethnic and racial discrimination, xenophobia, ideas of fascism and chauvinism."
- Joint Statements:
- The leaders adopted two thematic joint statements - one on cooperation in countering the radicalisation leading to separatism, extremism, and terrorism & the second one cooperation in the field of digital transformation.
- New Pillars of Cooperation:
- India has created five new pillars and focus area for cooperation in the SCO, which include,
- Startups and Innovation
- Traditional Medicine
- Youth Empowerment
- Digital Inclusion
- Shared Buddhist Heritage
- India has created five new pillars and focus area for cooperation in the SCO, which include,
- India's Reservations on BRI:
- India refused to be part of the BRI (Belt and Road Initiative) of the SCO members’ economic strategy statement, mentioning “interested member states’.
- India's opposition to the BRI stems from its inclusion of projects in Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (POK), which India considers a violation of its sovereignty.
- Indian Prime Minister’s Address:
- The Indian PM highlighted the significance of connectivity for enhancing mutual trade and trust among SCO member states.
- However, he stressed the need to uphold the fundamental principles of the SCO charter, specifically respecting member states' sovereignty and regional integrity.
- Other Perspectives:
- The Indian PM criticized countries that employ Cross-Border Terrorism as an instrument of their policies and provide shelter to terrorists, urging the SCO not to hesitate in condemning such nations and emphasized the importance of consistency in addressing these critical issues.
- The Chinese President, while celebrating the ten-year anniversary of the BRI, mentioned his new Global Security Initiative (GSI), calling for political resolutions to international and regional conflicts to establish a solid security shield in the region.
- He urged SCO members to formulate foreign policies independently and remain vigilant against external attempts to instigate a new Cold War or camp-based confrontation.
- The Russian President, attending his first multilateral gathering since the failed rebellion by the Wagner Group, indirectly attributed Ukraine's anti-Russian sentiment to external forces supplying weapons to the country.
- He emphasized Russia's resilience against external pressures, sanctions, and provocations, citing the unity of Russian political circles and society against attempted armed rebellions.
What is Shanghai Cooperation Organization?
- About:
- SCO is a permanent intergovernmental international organization.
- It’s a political, economic and military organization aiming to maintain peace, security and stability in the region.
- It was created in 2001.
- The SCO Charter was signed in 2002 and entered into force in 2003.
- Objectives:
- Strengthening mutual trust and neighborliness among the member states.
- Promoting effective cooperation in -politics, trade & economy, research & technology and culture.
- Enhancing ties in education, energy, transport, tourism, environmental protection, etc.
- Maintain and ensure peace, security and stability in the region.
- Establishment of a democratic, fair and rational new international political & economic order.
- Structure:
- Heads of State Council: The supreme SCO body which decides its internal functioning and its interaction with other States & international organisations, and considers international issues.
- Heads of Government Council: Approves the budget, considers and decides upon issues related to economic spheres of interaction within SCO.
- Council of Ministers of Foreign Affairs: Considers issues related to day-to-day activities.
- Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS): Established to combat terrorism, separatism and extremism.
- SCO Secretariat:
- Based in Beijing to provide informational, analytical & organizational support.
- Official language:
- The official working language of the SCO Secretariat is Russian and Chinese.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following: (2022)
- Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank
- Missile Technology Control Regime
- Shanghai Cooperation Organisation
India is a member of which of the above?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Explanation:
- MTCR is an informal and voluntary partnership among 35 countries to prevent the proliferation of missiles and unmanned aerial vehicle technology capable of carrying greater than 500 kg payload for more than 300 km.
- India was inducted into the Missile Technology Control Regime in 2016 as the 35th member.
- AIIB is a multilateral development bank with a mission to improve social and economic outcomes in Asia.
- Membership in the AIIB is open to all members of the World Bank or the Asian Development Bank and is divided into regional and non-regional members.
- India is the second-largest shareholder, contributing USD 8.4 billion.
- SCO is a permanent intergovernmental international organisation. It’s a Eurasian political, economic and military organisation aiming to maintain peace, security and stability in the region.
- India and Pakistan joined SCO as full member on 9 June 2017.
- Hence, option (d) is correct.
Mains
Q. Critically examine the aims and objectives of SCO. What importance does it hold for India? (2021)
Bharat 6G Alliance
For Prelims: 6G technology, 5G technology, Bharat 6G Alliance
For Mains: Potential impact of 6G technology in India, India's telecom sector, 6G.
Why in News?
Recently, the Department of Telecommunications (DoT) under the Ministry of Communications launched the Bharat 6G Alliance (B6GA) to foster innovation and leadership in 6G technology, the next frontier of wireless communication.
- In addition, with a grant of 240.51 crores under the Telecom Technology Development Fund (TTDF), two agreements were signed for projects.
What is the Bharat 6G Alliance (B6GA)?
- About:
- The B6GA is a collaborative platform comprising public and private companies, academia, research institutions, and standards development organizations.
- The alliance will forge partnerships and synergies with other 6G global alliances to facilitate international collaboration and knowledge exchange.
- Objective:
- Its primary objective is to understand the business and societal needs of 6G technology, foster consensus, and drive high-impact research and development initiatives.
- Importance:
- It will help India to take a lead role in the development and adoption of 6G technology, which will have a huge impact on the economy, society, and environment.
- It will also help India to leverage its strengths in software, hardware, and manufacturing, as well as its large talent pool and market potential.
What is 6G Technology?
- 6G technology is the successor of 5G technology, which is currently being deployed in various countries, including India.
- 6G technology is expected to offer speeds up to 100 times faster than 5G, as well as ultra-low latency, high reliability, and massive connectivity.
- 6G technology is also envisioned to enable new applications and services such as holographic communication, brain-computer interface, quantum internet, and artificial intelligence.
- Holographic communication in 6G refers to the transmission and reception of 3D holographic images in real-time, enabling immersive and lifelike communication experiences.
- Brain-computer interface in 6G is a futuristic technology that will enable users to control computers and devices with their thoughts.
- It seeks to utilize the terahertz band of frequency which is currently unutilized.
- Terahertz waves fall between infrared waves and microwaves on the electromagnetic spectrum.
- These waves are extremely tiny and fragile, but there's a huge amount of free spectrum up there that would allow for spectacular data rates.
How has India's Telecom Sector Evolved in Recent Years?
- India is the world's second-largest telecommunications market with a subscriber base of 1,170.38 million in December 2022.
- Significant reductions in data costs, from Rs. 300/GB in 2014 to Rs. 10/GB in 2023.
- Drastic improvements in regulatory processes, including a reduction in the Right of Way permission duration from 230 to 9 days.
- Expansion of BTS sites by four times, reaching 25 lakh installations.
- Increased Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in the telecom sector, amounting to 24 billion dollars.
- Streamlined allocation of spectrum to Telecom Service Providers (TSPs) within 24 hours.
- Japan has aligned with India on Digital Payment system of India.
- Achievements of BSNL in stabilizing the market and generating operating profits.
- India's successful technology exports to 12 countries, including the USA.
What is Telecom Technology Development Fund (TTDF) Scheme?
- It was launched by DoT/ Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF) in 2022.
- 5% of annual collections from USOF will be available for TTDF Scheme for funding research & development of technologies, products, and services.
- The scheme is envisaged to bridge the digital divide by developing and manufacturing state-of-the-art technologies and to form synergies among academia, start-ups, research institutes, and the industry to build and develop the telecom ecosystem.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Which of the following is/are the aims/aims of the “Digital India” Plan of the Government of India? (2018)
- Formation of India’s own Internet companies like China did.
- Establish a policy framework to encourage overseas multinational corporations that collect Big Data to build their large data centers within our national geographical boundaries.
- Connect many of our villages to the Internet and bring Wi-Fi to many of our schools, public places and major tourist centers.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Scheme to Support Pregnant Minor Victims of Sexual Assault
For Prelims: POCSO Act, First Information Report, Nirbhaya Fund, Child care institutions, National Crime Records Bureau, Mission Vatsalya, Sustainable Development Goals, Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act 2015.
For Mains: Schemes or Initiatives for Supporting Victims of Sexual Assault
Why in News?
The Ministry of Women and Child Development, Government of India has unveiled a new scheme aimed at providing critical care and support to pregnant minor victims of sexual assault who lack family support.
- The scheme, with an outlay of Rs 74.10 crore, will offer shelter, food, legal aid, and other necessary assistance to these victims across the country.
What are the Major Provisions of the Scheme?
- About:
- The scheme seeks to assist minor girls who have been abandoned by their families due to forced pregnancies resulting from rape or gang rape.
- It acknowledges the physical and emotional trauma experienced by minor victims of rape and aggravated assault, especially in cases where they become pregnant.
- Eligibility Criteria and Documentation:
- Victims below the age of 18, who become pregnant due to rape or assault as per the provisions of the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012, and are either orphans or abandoned by their families, will be covered under the scheme.
- It is not mandatory for victims to possess a copy of the First Information Report (FIR) to avail the benefits provided by the scheme.
- Provisions:
- It aims to provide medical, financial, and infrastructural support to such victims under the Nirbhaya Fund.
- The funds will be utilized to set up shelters dedicated to these victims, either as standalone shelters or designated wards within existing child care institutions (CCIs).
- In the case of wards within CCIs, separate safe spaces will be provided for minor rape victims to cater to their specific needs.
- The integrated support under the scheme aims to provide immediate and non-emergency access to various services, including education, police assistance, healthcare, and legal support.
- Insurance coverage will also be provided for the minor victim and her newborn, ensuring access to justice and rehabilitation.
- Implementation:
- The scheme will leverage the administrative structure of Mission Vatsalya in collaboration with State governments and CCIs to actualise this support to minor victims.
- Also, 415 POCSO fast-track courts are already established across India to expedite justice for minor victims of rape.
- Need:
- According to the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) data from 2021, 51,863 cases were reported under the POCSO Act.
- Out of these cases, 64% were reported under sections 3 and 5 of the Act, which pertain to penetrative sexual assault and aggravated penetrative sexual assault, respectively.
- The majority of the victims were girls, and many of them became pregnant, exacerbating their physical and mental health concerns when disowned or abandoned by their families.
Note:
- Nirbhaya Fund:
- The Nirbhaya Fund established in 2013, provides for a non-lapsable corpus fund for safety and security of women.
- It is administered by the Department of Economic Affairs (DEA) of the Ministry of Finance (MoF).
- Also, the Ministry of Women and Child Development (MWCD) is the nodal Ministry to appraise/recommend proposals and schemes to be funded under Nirbhaya Fund.
- Mission Vatsalya:
- It is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme launched by the Ministry of Women and Child Development to provide a roadmap to achieve development and child protection priorities aligned with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Child Care Institutions:
- They are defined under the Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act 2015 as Children Home, Open Shelter, Observation Home, Special Home, Place of Safety, Specialised Adoption Agency and a Fit Facility for providing care and protection to children who are in need of such services.
- National Crime Records Bureau:
- NCRB, headquartered in New Delhi, was set-up in 1986 under the Ministry of Home Affairs to function as a repository of information on crime and criminals so as to assist the investigators in linking crime to the perpetrators.
- It was set up based on the recommendations of the National Police Commission (1977-1981) and the MHA’s Task Force (1985).
- The Bureau has been entrusted to maintain National Database of Sexual Offenders (NDSO) and share it with the States/UTs on regular basis.
What are Some Other Schemes or Initiatives for Supporting Victims of Sexual Assault?
- Central Victim Compensation Fund (CVCF): It provides financial assistance to victims of various crimes including rape/gang rape under Section 357A of CrPC.
- One Stop Centers (OSCs): It provide integrated services such as medical aid, police assistance, legal aid/counselling, psycho-social counselling and temporary shelter to women affected by violence under any circumstances.
- Usha Mehra Commission recommended the establishment of a one-stop centre.
- Mahila Police Volunteer (MPV): It facilitates public-police interface at the grassroots level through women volunteers who act as a link between police and community and help women in distress.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Mains
Q. We are witnessing increasing instances of sexual violence against women in the country. Despite existing legal provisions against it, the number of such incidences is on the rise. Suggest some innovative measures to tackle this menace. (2014)
Buddha's Relevance to the Modern Youth
For Prelims: Dharma Chakra Pravartana Divas, Lord Buddha, Maha Bodhi Temple, Four Noble Truths, Noble Eightfold Path, Four Sublime States.
For Mains: Major Teachings of Lord Buddha, Buddha's Relevance to the Modern Youth.
Why in News?
The President of India, urged the youth to draw inspiration from the teachings of Lord Buddha, on the occasion of Dharma Chakra Pravartana Divas (3rd July 2023).
- The President reflected on how Lord Buddha's first sermon on Asadha Purnima planted the seeds of the middle path of the Dhamma.
Lord Buddha
- About:
- Lord Buddha (Siddhartha Gautam) was born into royal family of Sakya clan who ruled from Kapilvastu, in Lumbini located in the Terai plains of southern Nepal.
- At the age of 29, Gautama left home and rejected his life of riches and embraced a lifestyle of asceticism, or extreme self-discipline.
- After 49 consecutive days of meditation, Gautama attained Bodhi (enlightenment) under a pipal tree at Bodhgaya, a village in Bihar.
- Buddha gave his first sermon in the village of Sarnath, near Varanasi in Uttar Pradesh on Asadha Purnima. This event is known as Dharma Chakra Pravartana (turning of the wheel of law).
- The day is also observed as Guru Poornima by both Buddhists and Hindus as a day to mark reverence to their Gurus.
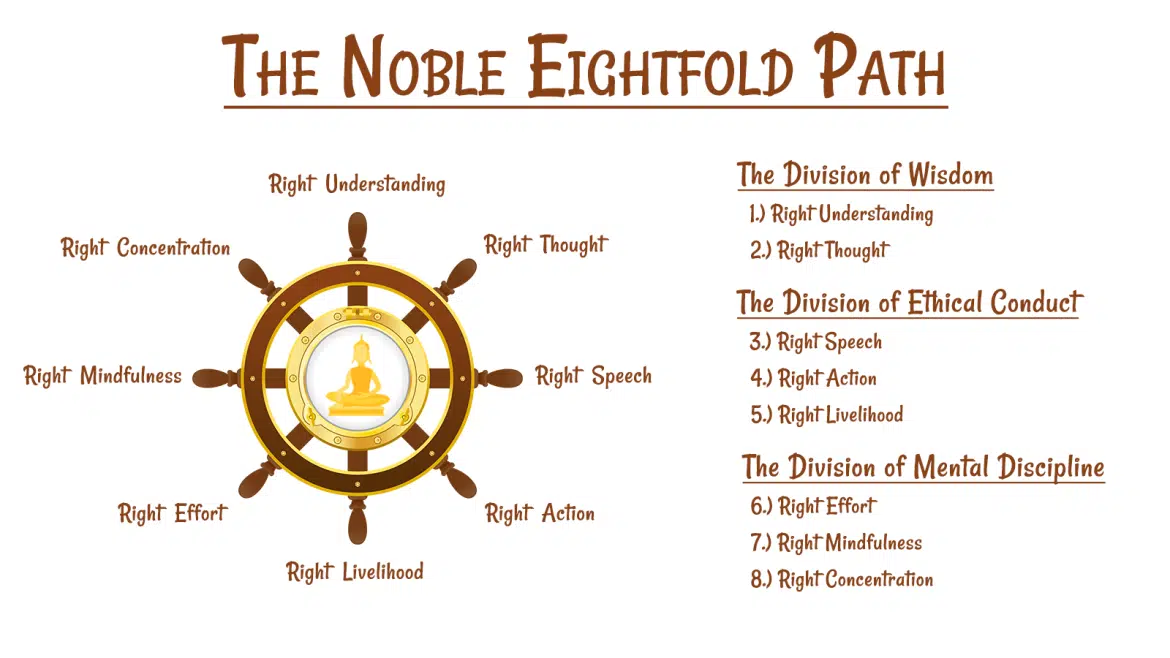
- Major Teachings of Lord Buddha:
- The Three Marks of Existence: These are the characteristics of all phenomena that one should understand and accept. They are impermanence (anicca), unsatisfactoriness (dukkha), and non-self (anatta).
- The Four Noble Truths: These are the truths about the nature of suffering, its cause, its cessation, and the path to its cessation. The cause of suffering is ignorance, attachment, and aversion.
- The Four Sublime States: These are the positive mental qualities that one should cultivate and radiate to all beings. They are loving-kindness (metta), compassion (karuna), sympathetic joy (mudita), and equanimity (upekkha).
- By developing these states, one can foster harmony, empathy, altruism, and peace.
- The Five Precepts: These are the basic ethical principles that Buddha laid down for his lay followers.
- They are: to abstain from killing, stealing, sexual misconduct, lying and intoxication.
- They help us to avoid harming ourselves and others, to respect life and property, to maintain purity and honesty and to preserve clarity and awareness.
How can Youth Draw Inspiration from Buddha to Navigate Life's Challenges?
- Mindfulness as a Foundation: One of the central tenets of Buddha's teachings is the practice of mindfulness.
- Mindfulness encourages individuals to cultivate a deep awareness of the present moment, fostering an enhanced understanding of their thoughts, emotions, and actions.
- In a world saturated with distractions, young people can draw inspiration from Buddha's emphasis on being fully present and engaged.
- By practicing mindfulness, youth can learn to manage stress, improve focus and concentration, and nurture a greater sense of self-awareness, leading to improved mental well-being and personal growth.
- Impermanence and Non-Attachment: Buddha's teachings emphasize the impermanence (the state or fact of lasting for only a limited period of time) of all phenomena and the futility of attachment.
- In a materialistic society driven by instant gratification, youth can find solace and inspiration in the understanding that everything is transient.
- By recognizing the impermanence of both joy and suffering, young individuals can cultivate a mindset that is adaptable, resilient, and open to change.
- Learning to let go of attachment to outcomes, possessions, and even relationships can free the youth from unnecessary suffering and allow them to embrace life with greater equanimity.
- Compassion and Empathy: In a world where divisions and conflicts persist, young people can find inspiration in Buddha's teachings on loving-kindness and compassion.
- By cultivating empathy, youth can develop a deeper understanding of others' struggles, fostering a sense of unity and connection.
- Self-Discovery and Inner Transformation: Young people, often grappling with questions of identity and purpose, can draw inspiration from Buddha's teachings on self-exploration.
- By engaging in introspection and self-reflection, youth can gain insights into their true nature, passions, and aspirations.
- Engaging in Social and Environmental Responsibility: Buddha's teachings emphasize the interconnectedness of all beings and advocate for responsible action.
- The youth can actively engage in social and environmental responsibility by working towards equality, justice, and sustainable practices.
- They can participate in community initiatives, advocate for marginalized groups, and champion environmental conservation.
- By embodying these teachings, they contribute to building a more equitable, harmonious, and environmentally conscious society.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to the religious history of India, consider the following statements: (2020)
- Sthaviravadins belong to Mahayana Buddhism.
- Lokottaravadin sect was an offshoot of Mahasanghika sect of Buddhism.
- The deification of Buddha by Mahasanghikas fostered the Mahayana Buddhism.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Q. With reference to the religious history of India, consider the following statements: (2016)
- The concept of Bodhisattva is central to Hinayana sect of Buddhism.
- Bodhisattva is a compassionate one on his way to Enlightenment.
- Bodhisattva delays achieving his own salvation to help all sentient beings on their path to it.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Pala period is the most significant phase in the history of Buddhism in India. Enumerate. (2020)
Solar Radiation Management
Why in News?
Solar radiation management (SRM) has emerged as a potential tool to counter the effects of global warming by reflecting sunlight back into space.
- A recently released report by the US government highlights the need for comprehensive research and a governance framework to assess the risks and benefits associated with SRM.
What is Solar Radiation Management?
- About:
- Solar radiation management is a form of climate engineering that aims to reduce global warming by reflecting some of the sun's energy back into space before it can heat up the Earth.
- SRM is an idea born of desperation, as the world faces an ongoing and accelerating climate crisis that threatens human well-being and planetary health.
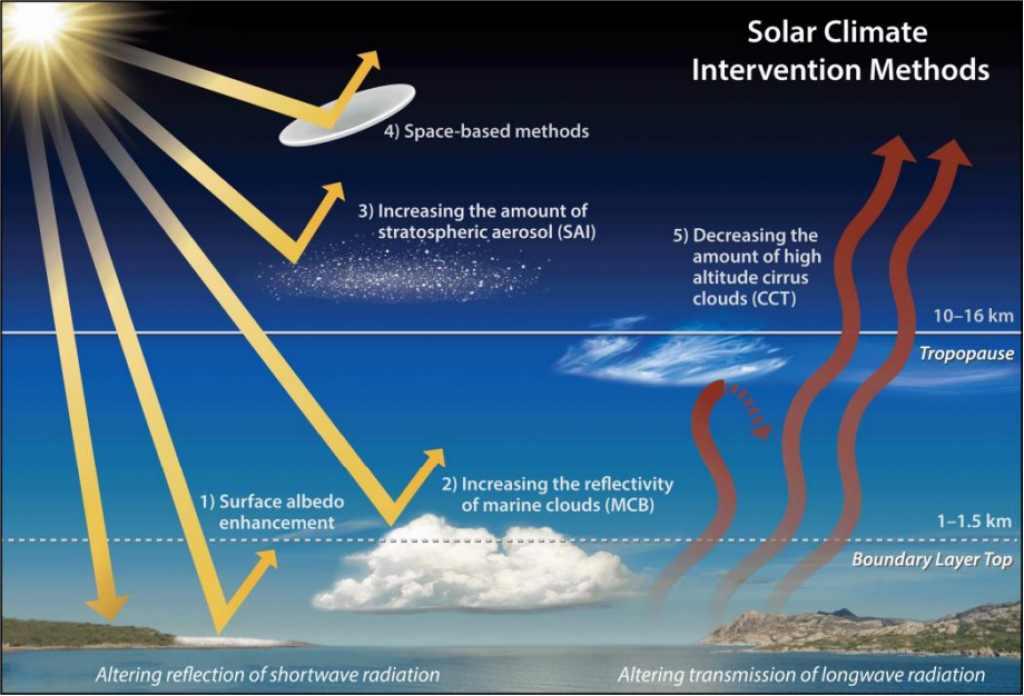
- Some of Most Discussed Methods of SRM:
- Stratospheric Aerosol Injection (SAI): This involves injecting reflective particles, such as sulfate aerosols, into the upper atmosphere (stratosphere), where they would scatter some of the incoming solar radiation back into space.
- This would mimic the cooling effect of volcanic eruptions, which also release aerosols into the stratosphere.
- Marine Cloud Brightening (MCB): This involves spraying fine droplets of seawater or other substances into low-level clouds (marine stratocumulus) over the oceans, where they would act as cloud condensation nuclei and increase the reflectivity and persistence of the clouds.
- This would enhance the cooling effect of clouds, which already reflect about 20% of the incoming solar radiation.
- MCB is considered to be more localized and reversible than SAI, but also more technically challenging and dependent on weather conditions.
- Space Sunshades: This involves placing large mirrors or screens in orbit around the Earth or at a stable point between the Earth and the sun (Lagrange point 1), where they would block or deflect some of the incoming solar radiation.
- This would reduce the amount of solar energy reaching the Earth’s surface.
- Space sunshades are considered to be more controllable and adjustable than SAI or MCB, but also more expensive and complex to deploy and maintain.
- Stratospheric Aerosol Injection (SAI): This involves injecting reflective particles, such as sulfate aerosols, into the upper atmosphere (stratosphere), where they would scatter some of the incoming solar radiation back into space.
- Advantages:
- SRM could potentially provide a quick reduction in global temperatures, providing temporary relief from extreme climate events.
- It could be cost-effective compared to other options, depending on the method used and the scale required.
- SRM could be reversible on short timescales if stopped or adjusted.
- Disadvantages:
- SRM could not address all aspects of climate change, such as ocean acidification, biodiversity loss, or sea level rise due to thermal expansion.
- It could have negative or unintended side effects on regional or global climate systems, such as altering precipitation patterns, affecting monsoons, droughts, storms, or crop yields.
- SRM could pose ethical or geopolitical challenges, such as creating winners and losers among countries or regions, raising questions of justice, equity, consent, liability, or responsibility.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. In the context of which of the following do some scientists suggest the use of cirrus cloud thinning technique and the injection of sulphate aerosol into stratosphere? (2019)
(a) Creating the artificial rains in some regions
(b) Reducing the frequency and intensity of tropical cyclones
(c) Reducing the adverse effects of solar wind on the Earth
(d) Reducing the global warming
Ans: (d)
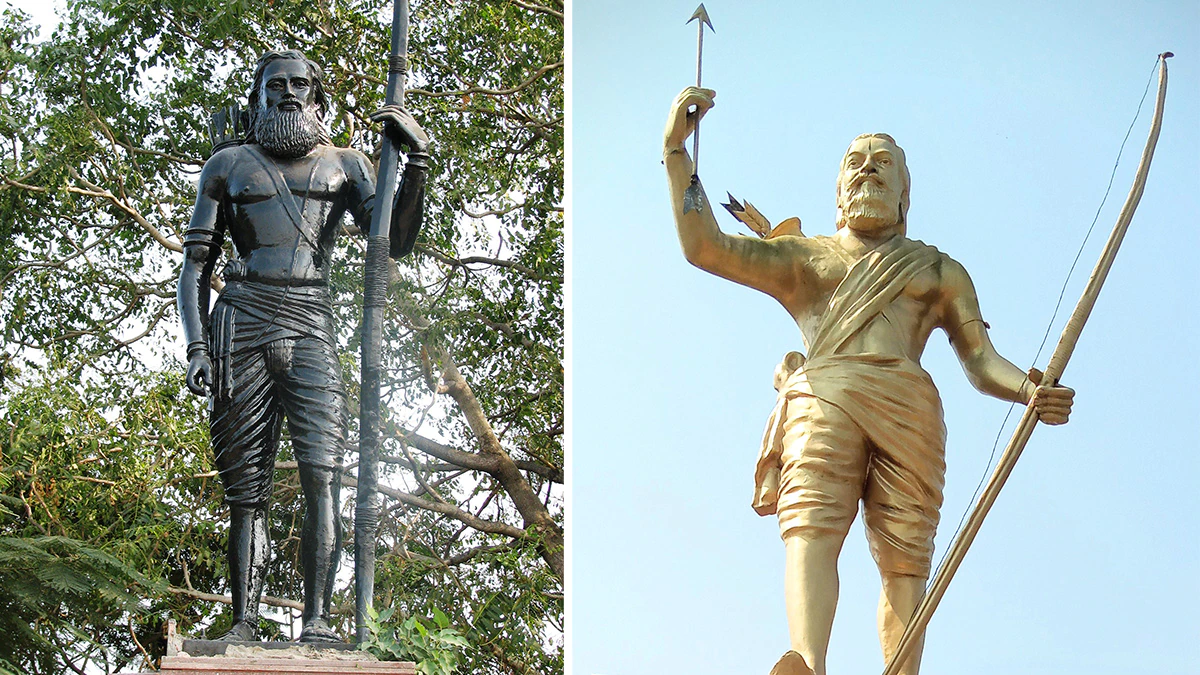
Alluri Sitarama Raju
Why in News?
Recently, the President of India attended the closing ceremony of the 125th Birth Anniversary of Alluri Sitarama Raju in Hyderabad.
- The 125th ceremony of Alluri Sitha Rama Raju was a year-long celebration of the birth anniversary of the legendary freedom fighter. The ceremony was launched by the Prime Minister on July 4, 2022.
Who was Alluri Sitarama Raju?
- About:
- Alluri Sitarama Raju was an Indian revolutionary who fought against the British colonial rule in India.
- He led a guerrilla campaign in the Eastern Ghats region of present-day Andhra Pradesh, mobilizing the tribal people against the oppressive forest laws and policies of the British government.
- He is widely regarded as a hero of the jungle or Manyam Veerudu by the local people for his bravery and sacrifice.
- Early Life and Background:
- He was born on 4 July 1897 or 1898 in Pandrangi village, Visakhapatnam district, Andhra Pradesh.
- He belonged to a Telugu-speaking Kshatriya family.
- Rampa Rebellion (or Manyam Rebellion) of 1922-1924:
- Alluri Sitarama Raju joined the Non-cooperation movement led by Mahatma Gandhi and witnessed the exploitation of tribal people in the Eastern Ghats region by British authorities.
- The tribal people practiced podu or shifting cultivation, which involved clearing patches of forest land for agriculture and moving to another area after a few years. This was their traditional and sustainable way of life, which also ensured their food security and cultural identity.
- The Madras Forest Act of 1882 imposed restrictions on the tribal people's movement and prohibited their collection of minor forest produce, forcing them into low-wage labor for the forest department or contractors.
- Alluri Sitarama Raju formed a guerrilla army and used Guerrilla warfare to launch attacks on British police stations and outposts.
- Guerrilla warfare is a form of irregular warfare in which small groups of combatants use military tactics including ambushes, sabotage, raids, petty warfare, hit-and-run tactics, and mobility, to fight a larger and less-mobile traditional military.
- He aimed to liberate the tribal people and drive the British out of the Eastern Ghats.
- Death and Legacy:
- Alluri Sitarama Raju was captured and killed by British forces in Koyyuru village on 7 May 1924, marking the end of the Rampa Rebellion.
- Alluri Sitarama Raju's life exemplified the unity of society without discrimination based on caste and class.
- A postal stamp issued by the Government of India in 1986 featuring Alluri Sitarama Raju.
- A biographical film titled Alluri Seetharama Raju was released in 1974.
Tamil Nadu's Namakkal District Excels in Water Management
Why in News?
Recently, Namakkal district in Tamil Nadu, India, with a population of 1.7 million, has achieved remarkable success in addressing its water scarcity challenges.
- The district's strategic approach to water conservation and management has led to a significant improvement in groundwater availability, earning it the second-best district in India in the conservation and management category for the year 2022 according to the Union Jal Shakti Ministry’s annual ranking.
What Led to Namakkal's Water Management Success?
- Comprehensive Approach: Namakkal adopted a holistic approach involving community participation, rainwater harvesting, river rejuvenation, and canal desilting.
- Infrastructure Modernization: The district upgraded the water infrastructure, incorporating advanced technologies for monitoring and controlling water supply networks, reducing leaks, and optimizing water distribution.
- The district rejuvenated its small river by constructing check dams and ponds, leading to improved surface water availability. The surface water quality was also reported to be potable.
- Artificial Recharge Structures: Namakkal constructed numerous artificial recharge structures, such as farm ponds, recharge shafts, and check dams, to replenish groundwater.
- Community Participation and Awareness: Active involvement of residents, along with awareness campaigns and educational programs, fostered a water conservation culture.
What Were the Outcomes of Namakkal's Water Management Efforts?
- Namakkal district improved its groundwater availability and quality significantly. The average water level in 116 dug wells improved from 11.48 metres below ground level (mbgl) in January 2019 to 6 mbgl in January 2022.
- Namakkal district also reduced its water consumption and wastage. The district also reused domestic and industrial wastewater for horticulture and industrial purposes.
What are the Lessons from Namakkal's Water Management Success?
- Implementing efficient rainwater harvesting systems for water conservation.
- Prioritizing the restoration of natural water bodies and tackling pollution and encroachment.
- Utilizing advanced technologies for monitoring, leak detection, and efficient distribution.
- Promoting community awareness and participation through education and collaborative initiatives.
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Death Anniversary of Swami Vivekananda
Prime Minister of India paid homage to Swami Vivekananda on his Punya Tithi (death anniversary) and hailed his inspiring principles for a strong India.
Swami Vivekananda attained Mahasamadhi (death) on July 4, 1902, at the age of 39. It is a day to remember his ideals of service, humanity, and spiritual enlightenment.
Swami Vivekananda was a Hindu monk, philosopher, author, and reformer who introduced Vedanta and Yoga to the Western world. He was the chief disciple of Ramakrishna, a mystic who taught him the unity of all religions. He founded the Ramakrishna Math and Mission, which promotes spiritual and social service, and inspired millions of people with his speeches and writings.
Read more: Swami Vivekananda
The Shape of Flames
Recently, researchers have delved into the intricate dynamics of air flow near a flame and unraveled its complex processes. Flames heat the air around them, making them rise due to being less dense. This creates a low-pressure area near the flame. As a result, cool air from the surroundings flows towards the flame from the sides and below. The presence of oxygen keeps the fuel burning. The air close to the flame gets hotter and moves upwards faster. This process creates a faster outflow of hot air above the flame, with a slower inflow from the sides and below. Eventually, the hot air mixes with the surrounding environment and cools down. It's important to note that this explanation mainly applies to candles or wick stoves and may not be the same for tools like a welder's torch, which have a different fuel supply mechanism.
India's Firms Show Strong Credit Quality and Robust Growth
According to a report by S&P Global Ratings, the companies tracked in India are in a favorable credit position, supported by robust underlying growth and accommodative balance sheets. The report highlights the country's strong economic growth, which is projected to reach 6% in 2023 and 6.9% in 2024, making it the highest in the region. Additionally, the presence of strong onshore liquidity helps counterbalance the challenges posed by tougher external-funding conditions. While companies continue to focus on debt reduction, the pace of deleveraging may slow due to increased capital expenditure.
Deleveraging refers to the process of reducing or eliminating debt in order to improve the financial stability of an individual, company, or economy. It typically involves decreasing the ratio of debt to equity or assets, thereby reducing the overall leverage or indebtedness.
Read more: Credit Ratings
Odisha Government Launches Mo Jungle Jami Yojana
The Odisha government has introduced the Mo Jungle Jami Yojana, a scheme aimed at bolstering forest rights among tribals and forest dwellers across the state's districts. If implemented, Odisha will become the first state in India to recognize community forest rights in addition to individual rights offered by the central government. The scheme aims to ensure livelihood and food security for the Scheduled Tribe and forest dwelling population by granting ownership of land and access to forest resources to the beneficiaries in accordance with their entitlements.
Odisha has a significant number of villages and Scheduled Tribe families that are targeted to benefit from the scheme. With 62 different tribes, including 13 Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs), the state’s tribal population accounts for 22.85% of the overall population.
Read more: Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups, Forest rights