Biodiversity & Environment
International Biosphere Reserve Day 2023
For Prelims: Biosphere Reserve, World Biosphere Reserve Day, Man and the Biosphere (MAB) Programme
For Mains: Biosphere Reserves Main Zones, Functions
Why in News?
The second anniversary of International Biosphere Reserve Day, celebrated on November 3, annually highlights the critical importance of biosphere reserves(BR) in safeguarding our environment and promoting sustainability.
- In this context, the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) partnered with the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change and the National Centre for Sustainable Coastal Management, concluded the 10th South and Central Asian Biosphere Reserve Network Meeting (SACAM) in Chennai, India.
- The SACAM event, themed "Ridge to Reef," facilitated collaboration on sustainable environmental practices in South and Central Asia.
What is World Biosphere Reserve Day?
- This day celebrates the role of biosphere reserves in conserving biodiversity and promoting sustainable development.
- Established by UNESCO in 2022, to be observed annually on November 3.
- Aims to raise awareness, share best practices, and showcase achievements of the World Network of Biosphere Reserves (WNBR).
What is a Biosphere Reserve?
- About:
- Biosphere reserves are ‘learning places for sustainable development’.
- They are sites for testing interdisciplinary approaches to understanding and managing changes and interactions between social and ecological systems, including conflict prevention and management of biodiversity.
- They are places that provide local solutions to global challenges. Biosphere reserves include terrestrial, marine and coastal ecosystems.
- Each site promotes solutions reconciling the conservation of biodiversity with its sustainable use.
- Features:
- Biosphere reserves consist of three main zones:
- The core area is the strictly protected zone, where natural processes and biodiversity are preserved.
- The buffer zone surrounds the core area, where human activities are ccompatible with conservation and research objectives.
- The transition area is the outermost zone, where sustainable development and human well-being are promoted.
- Biosphere reserves consist of three main zones:
- Biosphere reserves are nominated by national governments and remain under the sovereign jurisdiction of the states where they are located.
- Biosphere reserves are designated by UNESCO under the Man and the Biosphere (MAB) Programme which was launched in 1971.
- The MAB Programme aims to improve the relationship between people and their environment and to foster the integration of natural and social sciences.
- The MAB Programme also supports the implementation of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and the post-2020 global biodiversity framework.
- Biosphere reserves are part of the World Network of Biosphere Reserves (WNBR), which currently comprises 748 sites in 134 countries, including 22 transboundary sites.
- The WNBR facilitates the exchange of information, knowledge, and best practices among biosphere reserves and their stakeholders.
- The WNBR also fosters cooperation and innovation for addressing global challenges such as climate change, biodiversity loss, poverty, and pandemics.
- Biosphere reserves are nominated by national governments and remain under the sovereign jurisdiction of the states where they are located.
- Biosphere reserves are also supported by other United Nations agencies, for example, the United Nations Development Programme, the United Nations Environment Programme, as well as the International Union for Conservation of Nature.
- Biosphere Reserves in India:
What is the Importance of Biosphere Reserves?
- Biosphere reserves play a crucial role as carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and contributing to climate change mitigation.
- Acting as pockets of hope in the face of the climate crisis, the UNESCO biosphere reserves are hidden oases, protecting biodiversity, reducing pollution, and enhancing climate resilience.
- Biosphere reserves act as sanctuaries for a wide variety of ecosystems, including tropical rainforests, alpine deserts, and coastal areas, providing habitats for countless unique and endangered plant and animal species.
- Biosphere reserves are home to more than 250 million people, who depend on the ecosystem services and natural resources for their livelihoods.
- They promote sustainable economic development by offering opportunities for eco-tourism and other environmentally friendly activities, benefiting local communities.
- Biosphere reserves also showcase how to involve local communities, indigenous peoples, women, youth, and other stakeholders in decision-making and management processes.
What are the Challenges for Biosphere Reserves?
- Rapid deforestation threatens the integrity of ecosystems within biosphere reserves.
- Overharvesting of natural resources, such as timber and wildlife, can deplete reserves' ecological resources.
- Habitat loss due to human activities and urban expansion endangers various plant and animal species.
- The introduction of invasive species disrupts the balance of native ecosystems, impacting biodiversity.
- Controlling and managing invasive species is an ongoing challenge.
- Climate change poses a significant threat, affecting the stability and resilience of ecosystems within biosphere reserves.
- Altered weather patterns, rising temperatures, and extreme events can lead to ecosystem disturbances.
- Changes in land use, such as agriculture, mining, and infrastructure development, impact the natural landscape of reserves.
- Pollution from agricultural runoff, industrial activities, and waste disposal can harm the environment within biosphere reserves.
- Maintaining water quality and mitigating pollution is crucial for ecosystem health.
- Many biosphere reserves lack sufficient resources and funding for conservation and management efforts.
Way Forward
- Strengthening Local Initiatives:
- Encouraging and supporting local communities to take an active role in managing and protecting these vital ecosystems is a critical way forward.
- The successes of local community-driven conservation efforts, such as those in the Sundarban Biosphere Reserve and the Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve, should be highlighted.
- In the Sundarban Biosphere Reserve in India, local communities are working together to manage mangrove forests and protect the biodiversity of the region.
- In the Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve in India, local communities, including women, are contributing towards conservation efforts by forming self-help groups, while the youth are getting engaged in eco-tourism.
- The concept of 'plastic checkpoints' introduced in the Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve can serve as a model for addressing plastic waste in other biosphere reserves.
- Empowering Sustainable Practices:
- Promote sustainable practices within biosphere reserves, emphasizing eco-friendly tourism and community involvement.
- Encourage sustainable agriculture, responsible resource management, and waste reduction measures to minimize the ecological footprint.
- Climate Resilience and Adaptation:
- Establish climate-resilient strategies within biosphere reserves, including measures to combat the impacts of climate change.
- Develop adaptation plans to safeguard ecosystems and reduce vulnerabilities to changing weather patterns.
- Resource Allocation and Funding:
- Advocate for increased financial and technical support for biosphere reserves, enabling them to fulfill their conservation and management goals.
- Seek collaboration with international organizations, governmental bodies, and nonprofit entities to secure resources and expertise.
- Advocate for increased financial and technical support for biosphere reserves, enabling them to fulfill their conservation and management goals.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question
Prelims
Q.1 Consider the following pairs: (2013)
- Nokrek Biosphere Reserve : Garo Hills
- Logtak (Loktak) Lake : Barail Range
- Namdapha National Park : Dafla Hills
Which of the above pairs is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) None
Ans: (a)
Q.2 The most important strategy for the conservation of biodiversity together with traditional human life is the establishment of (2014)
(a) biosphere reserves
(b) botanical gardens
(c) national parks
(d) wildlife sanctuaries
Ans: (a)
Q.3 Out of all the Biosphere Reserves in India, four have been recognized on the World Network by UNESCO. Which one of the following is not one of them? (2008)
(a) Gulf of Mannar
(b) Kanchenjunga
(c) Nanda Devi
(d) Sunderbans
Ans: (b)
Internal Security
State-Sponsored Cyber Attacks
For Prelims: State-Sponsored Attacks, Pegasus Project, Cyber Attack, Privacy Violations, Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C), Cyber Security.
For Mains: Pegasus Project and Need for Surveillance Reforms, Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Why in news?
Recently, Apple Inc. has sent notification to individuals, including opposition leaders and journalists, about “State-Sponsored Attackers who are remotely trying to compromise” their iPhones.
- This is the second time that Opposition politicians and civil society actors in India have been warned that they have been targets of spying attempts.
- In 2021, the Paris-based Forbidden Stories collective reported that the Pegasus spyware, which was sold only to government agencies by an Israeli firm NSO Group, was allegedly used on a range of journalists, civil society groups and politicians in India.
Note
A cyber attack is a malicious and deliberate attempt to breach the security of computer systems, networks, or digital devices, with the intent of stealing, damaging, altering, or accessing sensitive data, disrupting operations, or causing harm in the digital realm.
What are State-Sponsored Cyber Attacks?
- About:
- State-sponsored cyber attacks, also known as nation-state cyber attacks are cyberattacks conducted or supported by governments or government agencies against other nations, organizations, or individuals.
- These attacks are characterized by their high level of sophistication, organization, and resources, as they are backed by the extensive capabilities and funding of a nation-state.
- Examples of state-sponsored cyberattacks include the Stuxnet worm, which targeted Iran's nuclear program, the alleged Russian interference in the 2016 U.S. presidential election, and the 2017 WannaCry ransomware attack, which was linked to North Korea.
- Implications on National Security:
- Data Theft: State-sponsored attacks can lead to the theft of sensitive national security information, military secrets, and critical infrastructure data. Such breaches can compromise a nation's defense capabilities.
- Economic Impact: Attacks on key industries and critical infrastructure can result in economic losses. For instance, the disruption of energy or financial systems can have severe economic consequences.
- Political Influence: Cyberattacks can be used to manipulate public opinion, influence elections, and undermine political stability. Disinformation campaigns and hacking can have far-reaching political implications.
- National Sovereignty: Cyberattacks can infringe upon a nation's sovereignty and compromise its ability to govern and protect its citizens.
What is Pegasus?
- About:
- It is a type of malicious software or malware classified as a spyware.
- It is designed to gain access to devices, without the knowledge of users, and gather personal information and relay it back to whoever it is that is using the software to spy.
- Pegasus has been developed by the Israeli firm NSO Group that was set up in 2010.
- Pegasus infections can be achieved through so-called “zero-click” attacks by exploiting flaws in operating system, which do not require any interaction from the phone’s owner in order to succeed.
- It is a type of malicious software or malware classified as a spyware.
- Target:
- Human Rights activists, journalists and lawyers around the world have been targeted with phone malware sold to authoritarian governments by an Israeli surveillance firm.
- Indian ministers, government officials and opposition leaders also figure in the list of people whose phones may have been compromised by the spyware.
- In 2019, WhatsApp filed a lawsuit in the US court against Israel's NSO Group, alleging that the firm was incorporating cyber-attacks on the application by infecting mobile devices with malicious software.
What are the Initiatives to Foster Cyber Security?
- Indian:
- Cyber Surakshit Bharat Initiative
- National Cyber security Coordination Centre (NCCC).
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra
- Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C)
- Computer Emergency Response Team - India (CERT-IN)
- International Mechanisms:
Way Forward
- There is a need to develop and implement comprehensive national cybersecurity policies and strategies that address both defense and offense in the cyber domain.
- Allocate resources to bolster cybersecurity infrastructure, including advanced intrusion detection systems, secure networks, and cybersecurity training for government agencies.
- Collaborate with other nations and international organizations to share threat intelligence and coordinate responses to state-sponsored threats.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 In India, under cyber insurance for individuals, which of the following benefits are generally covered, in addition to payment for the loss of funds and other benefits? (2020)
- Cost of restoration of the computer system in case of malware disrupting access to one’s computer
- Cost of a new computer if some miscreant wilfully damages it, if proved so
- Cost of hiring a specialised consultant to minimise the loss in case of cyber extortion
- Cost of defence in the Court of Law if any third party files a suit
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 4 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)
Q.2 In India, it is legally mandatory for which of the following to report on cyber security incidents? (2017)
- Service providers
- Data centres
- Body corporate
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. What are the different elements of cyber security ? Keeping in view the challenges in cyber security, examine the extent to which India has successfully developed a comprehensive National Cyber Security Strategy. (2022)
Economy
QCI hosts 3rd International Convention on Sustainable Trade and Standards
For Prelims: Quality Council of India (QCI), International Convention on Sustainable Trade and Standards, United Nations Forum on Sustainability Standards, Good Agricultural Practices, Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC)
For Mains: Quality Council of India (QCI) and its Contribution, Food Safety and Standards
Why in News?
The Quality Council of India (QCI), an autonomous organization of the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry hosted the 3rd International Convention on Sustainable Trade and Standards (ICSTS) in New Delhi.
- ICSTS, a two-day event, has been organized by the India National Platform on Private Sustainability Standards (India PSS Platform) and hosted by QCI in collaboration with the United Nations Forum on Sustainability Standards (UNFSS).
- The ICSTS aims to raise awareness and foster dialogue on the challenges and opportunities of voluntary sustainability standards (VSS), which are tools to improve the environmental and social aspects of global value chains.
What are the Key Highlights of ICSTS?
- QCI and the African Organisation for Standardisation (ARSO) signed a bilateral agreement to strengthen trade relations and harmonize standards, promoting global trade landscape.
- India has forged partnerships with Brazil and Mexico and has now extended cooperation with the ARSO regarding Voluntary Sustainability Standards.
- Sustainability Standards are special rules that guarantee the products you buy do not hurt the environment and the people who make them.
- The Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) initiative was highlighted as it is driving the digitalization initiative, revolutionizing e-commerce in India and making trade more accessible and efficient in the digital age.
- This initiative aligns with international standards, ensuring data confidentiality and trustworthiness.
- ONDC identified QCI to assess the digital Readiness of entities to smoothly join the ONDC Network's Seller App.
- At ICSTS, India Good Agricultural Practices(IndG.AP.) standards were compared to GLOBAL Good Agricultural Practices(GLOBALG.A.P.) standards through the National Technical Working Group (NTWG) mechanism and creation of National Interpretation Guidelines (NIG) also took place at the ICSTS.
- This helps align Indian agricultural practices with global standards. The creation of NIG provides guidelines for applying these standards in India.
- These efforts will benefit around 12,000 farmers by ensuring they meet international quality and sustainability standards.
Key Terms
- India National Platform on Private Sustainability Standards (INPPSS):
- It was initiated under the Secretarial oversight of the QCI. It is a first-of-its-kind initiative in the world for addressing PSS issues in a national context.
- It aims to facilitate dialogue between core public and private stakeholders on how to maximize the sustainable development benefits and market access opportunities.
- United Nations Forum on Sustainability Standards (UNFSS):
- UNFSS, is a platform that aims to promote the use of voluntary sustainability standards (VSS) for achieving sustainable development goals (SDGs).
- UNFSS is coordinated by five UN agencies:
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), International Trade Centre (ITC), United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), United Nations Environment Programme (UN Environment), United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO).
- UNFSS produces reports, organizes events, and provides technical assistance on VSS-related issues.
- India Good Agricultural Practices (IndG.AP.):
- IndG.AP, is a certification scheme developed by the QCI to promote the production of safe and quality agricultural products in India.
- IndG.AP. covers various aspects of farming such as soil, water, crop health, environmental protection, worker welfare, and food safety.
- GLOBAL Good Agricultural Practices (GLOBALG.A.P.):
- It is an internationally recognized standard that ensures quality management, safety, and traceability in the field of growing plants, vegetables, tubers, fruits, poultry, cattle, and aquatic products.
- National Technical Working Group (NTWG):
- The NTWG is a group that bridges the gap between global and local issues. They identify adaptation and application challenges at a national level and develop national interpretation guidelines (NIGs). NIGs support cost-effective audit processes around the world.
What is the Quality Council of India (QCI)?
- About:
- QCI is a non-profit organization registered under the Societies Registration Act XXI of 1860.
- It was jointly established by the Government of India and the Indian Industry represented by the three premier industry associations, Associated Chambers of Commerce and Industry of India (ASSOCHAM), Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) and Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry (FICCI) in 1997.
- QCI was established to promote and enhance quality standards across various sectors in India.
- It is responsible for accreditation, certification, and quality promotion in India.
- The DPIIT, Ministry of Commerce and Industry was designated as the nodal point for all matters connected with quality and QCI to structure and help implement the Cabinet decision.
- Members:
- QCI is governed by a Council of 39 members including the Chairperson and Secretary General.
- Chairperson (Nominated by the Prime Minister of India).
- The Council has an equal representation of Government, Industry and other Stakeholders.
- QCI is governed by a Council of 39 members including the Chairperson and Secretary General.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. With reference to ‘Quality Council of India (QCI)’, consider the following statements: (2017)
- QCI was set up jointly by the Government of India and the Indian Industry.
- Chairman of QCI is appointed by the Prime Minister on the recommendations of the industry to the Government.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
Governance
Universal Basic Income
For Prelims: Universal Basic Income, WorkFREE Pilot Project, Direct Benefits Transfers (DBT), Conditional Cash Transfers (CCT), MGNREGA.
For Mains: Universal Basic Income, Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Why in News?
Recently, the positive outcome Universal Basic Income (UBI), can have on individuals and families has been highlighted through the WorkFREE pilot project, started in 2022 in Telangana.
What is a WorkFREE Pilot Project?
- About:
- The project is a collaborative effort between the University of Bath, Montfort Social Institute, Hyderabad and the India Network for Basic Income, with funding from the European Research Council.
- Under the pilot, an adult gets Rs 1,000 and a child Rs 500 a month for 18 months.
- The pilot supports 1,250 residents in five slums in the Hyderabad.
- The WorkFREE pilot project is presented as a transformative initiative, highlighting the positive outcomes it has had on individuals and families.
- Some of the Residents in Telangana were adversely affected by the relocation, and have found financial stability through the UBI support. They used the cash support to start a bangle business and significantly improve her income.
- The residents also used the cash to buy food, fuel, clothes and pay utility bills, which usually account for a bulk of monthly expenditure.
- Other Similar Pilot Project:
- The Self-Employed Women’s Association (SEWA) pilot was conducted in Delhi and Madhya Pradesh in 2011. In Delhi, about 100 families living below the poverty line received Rs 1,000 a month.
What is Universal Basic Income (UBI)?
- About:
- UBI is a social welfare proposal in which all the beneficiaries regularly receive a guaranteed income in the form of an unconditional transfer payment.
- The goals of a basic income system are to alleviate poverty and replace other need-based social programs that potentially require greater bureaucratic involvement.
- UBI is typically intended to reach all (or a very large portion of the population) with no (or minimal) conditions.
- Pros:
- Poverty Alleviation: Reduces poverty and income inequality by providing a minimum income floor for everyone, especially the most vulnerable and marginalized groups. It can also help people afford basic needs such as food, health, education, and housing.
- A Health Stimulus: Improves physical and mental health by reducing stress, anxiety, and depression associated with poverty and financial insecurity. It can also enable people to access better health care, sanitation, and nutrition.
- Simplified Welfare System: Can streamline the existing welfare system by replacing various targeted social assistance programs. This reduces administrative costs and eliminates the complexities associated with means-testing, eligibility requirements, and benefit cliffs.
- Enhancing Individual Freedom: UBI provides individuals with financial security and greater freedom to make choices about their work, education, and personal lives.
- Economic Stimulus: Injects money directly into the hands of individuals, stimulating consumer spending and driving economic growth. It can boost local businesses, create demand for goods and services, and generate employment opportunities.
- It can empower people to pursue entrepreneurship, take risks, and engage in creative or socially beneficial activities that may not be economically viable otherwise.
- Cons:
- Cost and Fiscal Sustainability: UBI is very expensive and would require higher taxes, spending cuts, or debt to finance it. It could also create inflation, distort the labor market, and reduce economic growth.
- Creates Perverse Incentives: Decreases motivation to work and reduces productivity and efficiency. It could also create a culture of dependency, entitlement, and laziness. It could also discourage people from acquiring skills, education, and training.
- Inflationary Pressures: It could contribute to inflationary pressures. If everyone receives a fixed amount of money, it may drive up prices for goods and services as businesses adjust their pricing strategies to capture the additional income available in the market.
- Potential for Dependency: UBI may create a reliance on government support, and there is a risk that some individuals might become complacent or dependent on the basic income, leading to reduced motivation for personal and professional growth.
What are the other Alternatives of Universal Basic Income?
- Quasi UBRI: QUBRI is a variant of UBI, which is defined as a transfer that is provided universally, unconditionally, and in cash. The idea was proposed by former Chief Economic Adviser to provide a direct cash transfer of Rs 18,000 per year to each rural household in India, except those which are “demonstrably well-off” to tackle agrarian distress.
- Direct Benefits Transfers (DBT): This is a scheme that transfers subsidies or cash directly to the bank accounts of the beneficiaries, instead of through intermediaries or in-kind transfers. DBT aims to improve the efficiency, transparency, and accountability of welfare delivery, as well as to reduce leakages and corruption.
- Schemes like PM Kisan, Pradhanmantri Jan Dhan Yojana etc are fine examples of success of DBT.
- Conditional Cash Transfers (CCT): This is a scheme that provides cash to poor households on the condition that they fulfil certain requirements, such as sending their children to school, immunizing them, or attending health check-ups. CCT aims to improve the human capital and long-term outcomes of the poor, as well as to incentivize behavioural change.
- Other Income Support Schemes: These are schemes that provide cash or in-kind assistance to specific groups of people who are in need, such as farmers, women, elderly, disabled, etc. These schemes aim to address the specific vulnerabilities and challenges faced by these groups, as well as to promote their empowerment and inclusion.
- Employment Guarantee Schemes: India already has a successful example of this with the MGNREGA. Such schemes provide a legal guarantee of employment to rural households for a certain number of days in a year. Expanding and strengthening such programs can ensure that individuals have access to job opportunities and can earn a livelihood.
- Universal Basic Services: Instead of focusing on providing a universal basic income, India can prioritize the provision of essential services such as education, healthcare, clean water, and sanitation. By ensuring access to these services for all citizens, the government can improve the overall standard of living and reduce inequality.
Way Forward
- The amount provided should be carefully balanced to avoid discouraging work while supporting recipients. Robust support systems, including universal healthcare and education, are suggested as complementary measures to enhance the effectiveness of UBI.
- While these schemes such as cash transfer, align with UBI principles, they often target specific demographics, thus can carry the risk of excluding potential beneficiaries.
- To reduce misallocation of funds and decrease leakages in existing welfare schemes, introducing UBI is suggested as a more efficient option.
Important Facts For Prelims
Sixth Assembly of International Solar Alliance
Why in News?
Recently, the Sixth Assembly of the International Solar Alliance (ISA) was convened at Bharat Mandapam in New Delhi.
What are the Major Highlights of the Assembly?
- The Assembly discussed the ISA’s broader strategy, emphasizing the need to focus on energy access before transitioning to renewable sources, echoing the organization’s philosophy of "access first and then transition."
- The assembly announced an increase in Viability Gap Funding (VGF) for projects, raising it from 10% to a range of 10% to 35% to foster greater investments, particularly in African countries.
- Four projects supported by the ISA were inaugurated during the assembly. These initiatives spanned across different countries:
- Solarization of the Malawi Parliament
- Solarization of rural healthcare centers in Fiji
- Installation of a solar-powered cold storage in Seychelles
- Solarization of a school in Kiribati
- India reaffirmed the commitment to make solar energy the primary energy source and emphasized that renewable energy could potentially supply 65% of the world's total electricity by 2030 and decarbonize 90% of the power sector by 2050.
Note
Around 80% of the global population reside in countries that depend on fossil fuel imports.
What is the International Solar Alliance?
- The International Solar Alliance is an action-oriented, member-driven, collaborative platform for increased deployment of solar energy technologies as a means for bringing energy access, ensuring energy security, and driving energy transition in its member countries.
- Initially conceived as a joint effort by India and France, ISA was conceptualized during the 21st Conference of Parties (COP21) in 2015.
- With its framework Agreement amended in 2020, all UN member states are eligible to join ISA.
- Currently, 116 countries are signatories, with 94 having completed the necessary ratification to become full members.
- The ISA is guided by its ‘Towards 1000’ strategy which aims to mobilize USD 1,000 billion of investments in solar energy solutions by 2030, while delivering energy access to 1,000 million people using clean energy solutions and resulting in installation of 1,000 GW of solar energy capacity.
- This would help mitigate global solar emissions to the tune of 1,000 million tonnes of CO2 every year.
- The Assembly is the apex decision-making body of ISA, in which each Member Country is represented.
- This body makes decisions concerning the implementation of the ISA’s Framework Agreement and coordinated actions to be taken to achieve its objective.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Consider the following statements: (2016)
- The International Solar Alliance was launched at the United Nations Climate Change Conference in 2015.
- The Alliance includes all the member countries of the United Nations.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (a)
Important Facts For Prelims
Haemoglobin in Chondrocytes
Why in News?
A recent serendipitous discovery in a study published in Nature found that chondrocytes, which produce cartilage, also produce and rely on haemoglobin for their survival, revealing that haemoglobin isn't exclusive to red blood cells (RBCs).
- Chondrocytes are the cells that make cartilage, the connecting tissue between bones.
What are Haemoglobin Bodies or ‘Hedy’?
- Discovery:
- In 2017, a pathologist in China, came across spherical structures (while studying growth plates, which are cartilaginous tissue at the end of certain long bones) that bore a striking resemblance to RBCs and contained haemoglobin.
- The discovery of functional haemoglobin in cartilage also leads to the possibility that it plays a role in certain joint diseases as there are many bone deformities that develop from defects in chondrocytes.
- In 2017, a pathologist in China, came across spherical structures (while studying growth plates, which are cartilaginous tissue at the end of certain long bones) that bore a striking resemblance to RBCs and contained haemoglobin.
- Formation of Haemoglobin Bodies:
- The structures, referred to as 'haemoglobin bodies' or 'Hedy,' were found within chondrocytes in the cartilage, and they appeared to form via a process similar to phase separation, akin to oil separating from water.
- Insights into Stem Cells:
- Research found a special group of stem cells in the growth plate in 2018, and is excited about the potential implications of this discovery for stem cells in the growth plate.
- One exciting idea is that the haemoglobin in the growth plate might influence the destiny of these stem cells.
- Research found a special group of stem cells in the growth plate in 2018, and is excited about the potential implications of this discovery for stem cells in the growth plate.
Stem Cells
- Stem cells are the body's raw materials — cells from which all other cells with specialized functions are generated.
- Under certain conditions in the body or a laboratory, stem cells divide to form more cells called daughter cells.
What is the Significance of Haemoglobin in Chondrocytes?
- Haemoglobin's Importance in Chondrocytes:
- Haemoglobin is essential for the survival of chondrocytes, the cells that form cartilage. Without haemoglobin, chondrocytes die and cause embryonic lethality in mice (as experiments were conducted on mice).
- Haemoglobin's Role in Oxygen Transport and Storage in Chondrocytes:
- Haemoglobin helps chondrocytes cope with low oxygen levels by transporting oxygen within the cells. Without haemoglobin, chondrocytes suffer from hypoxic stress and impaired function.
- Haemoglobin acts as an oxygen reservoir for chondrocytes, releasing oxygen when needed. Without haemoglobin, chondrocytes cannot maintain adequate oxygen levels and die.
Red Blood Cell
- The Red Blood Cells (RBCs) are also known as Erythrocytes.
- RBCs contain the iron-rich protein called haemoglobin that gives blood its red colour.
- RBCs are the most copious blood cell produced in bone marrows. Their main function is to transport oxygen from and to various tissues and organs.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Questions
Q1. With reference to ‘stem cells’, frequently in the news, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2012)
- Stem cells can be derived from mammals only
- Stem cells can be used for screening new drugs
- Stem cells can be used for medical therapies
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Q2. What are the research and developmental achievements in applied biotechnology? How will these achievements help to uplift the poorer sections of the society? (2021)
Important Facts For Prelims
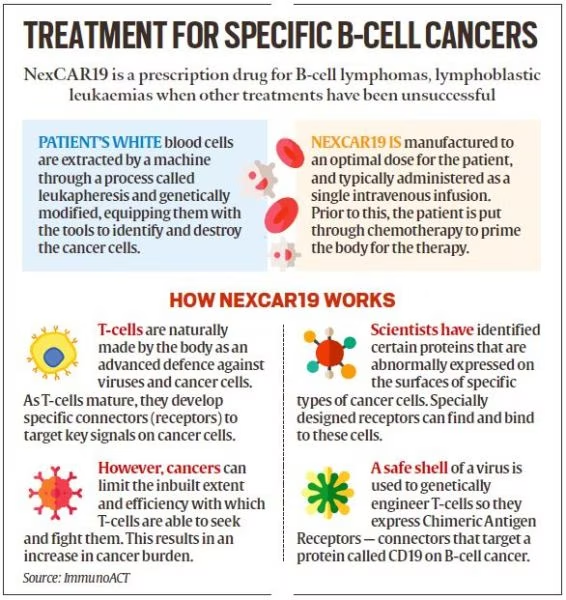
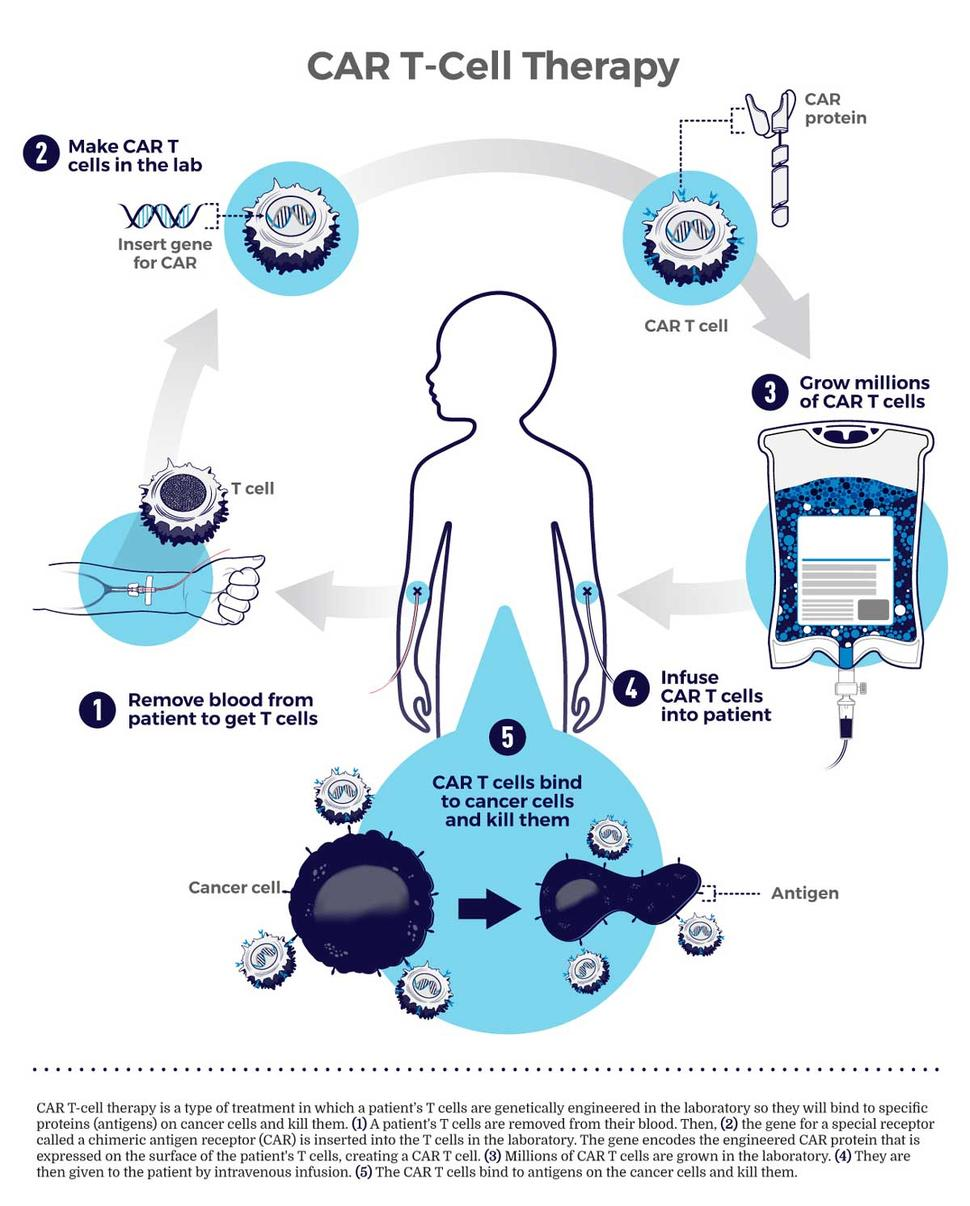
CAR-T Cell Therapy
Why in News?
Recently, The Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) has granted market authorisation for NexCAR19, India’s first indigenously-developed Chimeric Antigen Receptor T cell (CAR-T cell) Therapy.
- India is now one of the first developing countries to have its indigenous CAR-T and gene therapy platform.
What is NexCAR19?
- About:
- NexCar19 is a type of CAR-T and gene therapy developed indigenously in India by ImmunoACT, which is a company incubated at IIT Bombay.
- It is designed to target cancer cells that carry the CD19 protein.
- This protein acts like a flag on cancer cells, which allows CAR-T cells to recognise and attach themselves to the cancer cells and start the process of elimination.
- Even some developed nations don’t have their own CAR-T therapies; they import them from the United States or Europe.
- Patient Eligibility:
- NexCAR19 therapy is intended for people with B-cell lymphomas who have not responded to standard treatments like chemotherapy and have experienced relapse or recurrence of cancer.
- Initially, the therapy is approved for patients aged 15 years and older.
- Procedure:
- The process commences with the patient donating blood at a transfusion center. The T-cells are genetically modified and reinfused into the patient within a period of 7-10 days.
- Efficacy:
- It leads to significantly lower drug-related toxicities. It causes minimal damage to neurons and the central nervous system, a condition known as neurotoxicity.
- Neurotoxicity can sometimes occur when CAR-T cells recognise the CD19 protein and enter the brain, potentially leading to life-threatening situations.
- This therapy also results in Minimal Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS), which is characterized by inflammation and hyperinflammation in the body due to the death of a significant number of tumour cells, as CAR-T cells are designed to target and eliminate cancer cells.
- It leads to significantly lower drug-related toxicities. It causes minimal damage to neurons and the central nervous system, a condition known as neurotoxicity.
Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Dinosaur-Killing Asteroid and Aftermath
Recent research published in the journal Nature Geoscience has revealed the significant role played by dust ejected into the atmosphere by an asteroid (Chicxulub Impactor) impact on Mexico's Yucatan Peninsula 66 million years ago.
- This research was conducted based on paleoclimate simulations(PS) using sediment from a North Dakota paleontological site called Tanis.
- PS replicates Earth's climate for studying past climates and predicting future changes.
- The impact caused wildfires, quakes and a climate catastrophe, darkening skies, dropping temperatures by 27°F, and blocking photosynthesis, vital for plant life, resulting in an "impact winter" with severe consequences.
- Researchers calculated that the total amount of dust produced by the impact exceeded 2,000 gigatonnes, which was 11 times the weight of Mt. Everest, playing a key role in extinction.
- The asteroid, 6-9 miles wide, ended the Cretaceous Period(which began 145 million years ago and ended 66 million years ago), causing three-quarters of species, including dinosaurs, to vanish. Meanwhile, small, adaptable mammals thrived and eventually rose as Earth's dominant species.
- Recovery took about 20 years, with pre-impact conditions returning in the same timeframe.
Read More: Asteroids
NMC's One Nation One Registration Platform
The National Medical Commission (NMC) plans to transform India's medical registration system with the 'One Nation, One Registration Platform' for easy access to medical practitioner information.
- The NMC's initiative aims to eliminate duplication and bureaucratic hurdles, offering public access to information about every physician in India.
- A National Medical Register(NMR) patch pilot will provide doctors with unique identification numbers for cross-state practice.
- A masked ID will be assigned to undergraduate students, which will be unmasked upon course completion, facilitating qualification updates and cross-state licensing.
- The NMR will centralize data on doctors, including qualifications, registration dates, specialities, and more, streamlining accessibility.
- The NMC also outlines processes for additional qualifications, license renewal, and appeal options for rejected applications.
Read more: National Medical Commission (NMC)
Antarctic Avian Flu Outbreak
Scientists from the British Antarctic Survey (BAS) have identified the presence of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) in the Antarctic region for the first time, raising significant concerns for the delicate populations of penguins and seals in the region.
- The discovery found the HPAI in Brown Skua populations on Bird Island, South Georgia.
- Avian influenza, often referred to as bird flu, is a highly contagious viral infection that primarily affects birds.
- In 1996, highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 virus was first identified in domestic waterfowl in Southern China.
Read more: Avian Influenza
IOM's Global Initiative for Legal Identity Solutions
Recently, a Legal Identity and Rights-Based Return Management Conference was organized by United Nations' International Organization for Migration (IOM) at Copenhagen, Denmark to promote dialogue between countries of origin and destination for people without legal identities.
- It was highlighted that around one billion people globally lack a legal identity, impeding their access to services and freedom of movement, thereby leading to more hazardous and irregular migration routes.
- The initiative was organized within the framework of IOM’s Global Programme Enhancing Readmission and Legal Identity Capacities (RELICA), launched in 2022.
- IOM was established in 1951 and has its head office at Le Grand-Saconnex, Switzerland.
Read more: International Migration Outlook 2022