India Joins Artemis Accords
For Prelims: Artemis Accords , International Space Station, Outer Space Treaty of 1967, United Nations, Space Launch System, Chandrayaan-3 mission, Gaganyaan
For Mains: Missions under the Artemis Program
Why in News?
Recently, India's Prime Minister announced India's decision to join the Artemis Accords during the visit to the United States.
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) will collaborate to send Indian astronauts, trained at the Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas, to the International Space Station (ISS) in 2024.
What are Artemis Accords?
- About:
- Artemis Accords are established by the U.S. State Department and NASA with seven other founding members: Australia, Canada, Italy, Japan, Luxembourg, the United Arab Emirates, and the United Kingdom in 2020 for setting common principles to govern civil exploration and use of outer space, the moon, Mars, comets, and asteroids, for peaceful purposes.
- It builds upon the foundation of the Outer Space Treaty of 1967.
- The Outer Space Treaty, a multilateral pact under the United Nations, serves as the foundation for international space law.
- The treaty emphasizes space as a shared resource for humanity, prohibits national appropriation, and encourages the peaceful use of space.
- Signatory Countries:

- India became the 27th country to sign the nonbinding Artemis Accords.
- Commitments under the Accords:
- Peaceful Purposes: The signatories will implement memorandum of understanding (MOUs) between governments or agencies to conduct space activities for peaceful purposes in accordance with international law.
- Common Infrastructure: Signatories recognize the importance of common exploration infrastructure to enhance scientific discovery and commercial utilization.
- Registration and Data Sharing: Relevant space objects are registered, and scientific data is openly shared in a timely manner. Private sectors are exempt unless acting on behalf of a signatory.
- Preservation of Heritage: Signatories are expected to preserve historic landing sites, artifacts, and evidence of activity on celestial bodies.
- Utilization of Space Resources: Utilization of space resources should support safe and sustainable activities and not interfere with other signatories' activities. Information on location and nature must be shared to prevent interference.
- Mitigation of Debris: Signatories plan for the safe disposal of spacecraft and limit the generation of harmful debris.
What are the Main Missions under the Artemis Program?
- Artemis-I: Unmanned Mission to the Moon
- The Artemis program began with the launch of the spacecraft named "Orion" on the Space Launch System (SLS) from NASA's Kennedy Space Center on November 16, 2022.
- The SLS, a super heavy-lift launch vehicle, carried Orion on a single mission directly to the moon.
- Artemis-II: Crewed Lunar Flyby Mission:
- Scheduled for 2024, Artemis-II will mark the first crewed mission under the Artemis program.
- Four astronauts will be aboard the SLS as it performs multiple maneuvers on an expanding orbit around Earth.
- The mission will also involve a lunar flyby and return to Earth.
- Artemis-III: Human Return to the Moon:
- Set for 2025, Artemis-III will mark a significant milestone in human space exploration as astronauts return to the moon.
- This mission will go beyond the lunar flyby of Artemis-II, allowing astronauts to land on the lunar surface and study the moon more extensively.
- Also, the establishment of a Lunar Gateway station is planned for 2029. This station will serve as a docking point for astronauts and facilitate scientific research and experiments.
What are the Benefits and Challenges for India Related to the Accord?
- Benefits:
- India's participation in the Artemis Accords facilitates access to advanced training, technological advancements, and scientific opportunities.
- India can leverage the Artemis programme to advance its own lunar exploration goals, such as the Chandrayaan-3 mission.
- Collaborating with NASA would enhance India's capabilities for the Gaganyaan human mission and future ambitious space missions.
- Also, India's cost-effective missions and innovative approach will benefit the Artemis program, promoting mutual advancements in space exploration.
- Challenges:
- The possibility of being seen as aligning with the U.S. against other major space powers, such as China and Russia, who have their own plans for lunar exploration.
- The uncertainty over the legal status and implications of the Artemis Accords, especially regarding the provision that allows for unregulated mining on the moon and other celestial bodies.
- The need to balance its commitments under the Artemis Accords with its obligations under other existing or emerging multilateral frameworks or treaties on outer space.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. What is the purpose of the US Space Agency’s Themis Mission, which was recently in the news? (2008)
(a) To study the possibility of life on Mars
(b) To study the satellites of Saturn
(c) To study the colourful display of high latitude skies
(d) To build a space laboratory to study the stellar explosions
Ans: (c)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2016)
The Mangalyaan launched by ISRO
- is also called the Mars Orbiter Mission
- made India the second country to have a spacecraft orbit the Mars after USA
- made India the only country to be successful in making its spacecraft orbit the Mars in its very first attempt
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q.1 What is India’s plan to have its own space station and how will it benefit our space programme? (2019)
Q.2 Discuss India’s achievements in the field of Space Science and Technology. How the application of this technology has helped India in its socio-economic development? (2016)
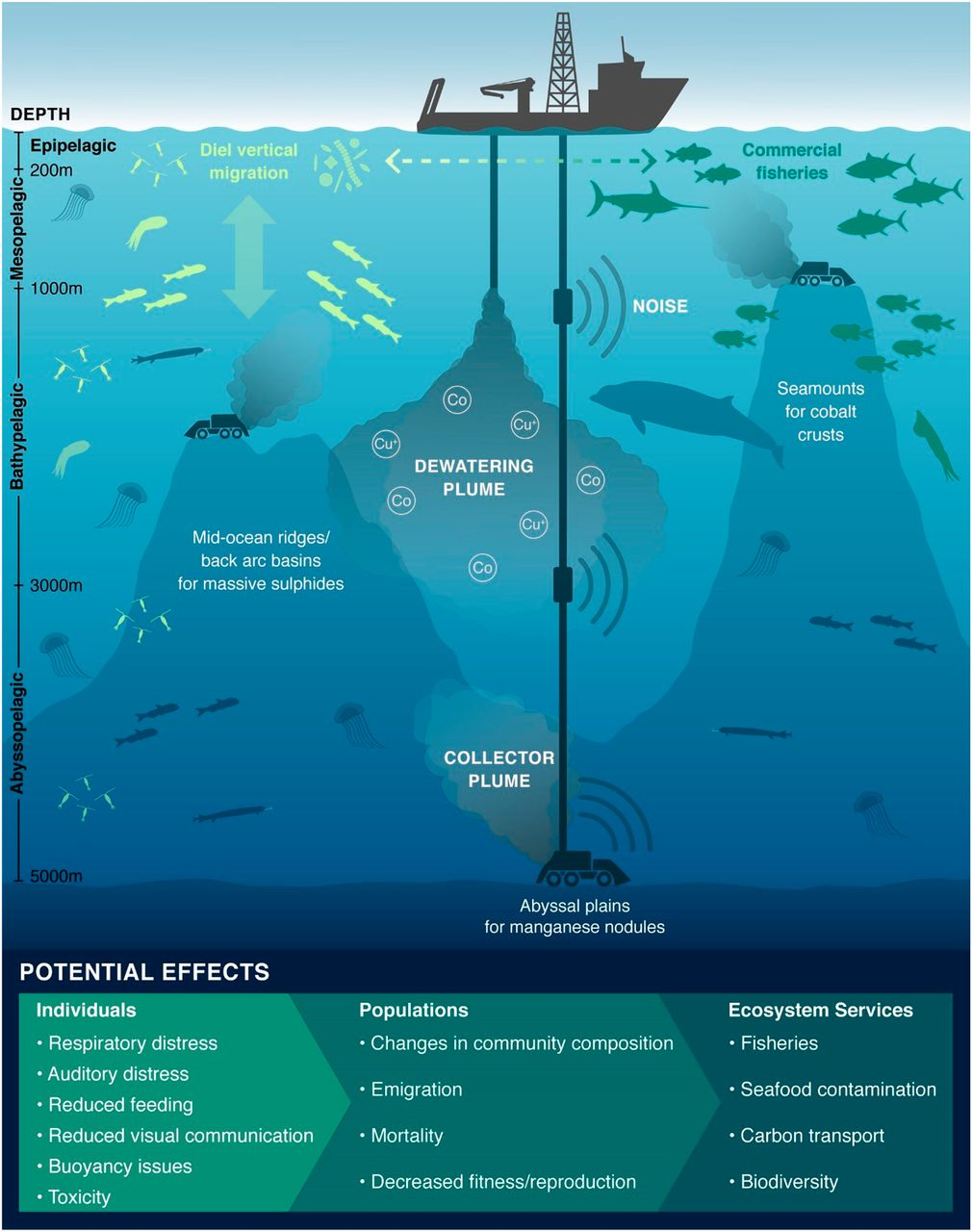
Deep Sea Mining
For Prelims: Deep Sea Mining, ISA, Green Energy, UNCLOS, Renewable Energy.
For Mains: Deep Sea Mining and Environment Concerns.
Why in News?
The International Seabed Authority (ISA) is preparing to allow Deep Sea Mining in the International Seabed, including mining for minerals needed for Green Energy.
- The ISA’s Legal and Technical Commission, which oversees the development of deep sea mining regulations, will meet in early July 2023 to discuss the mining code draft. The earliest that mining under ISA regulations could begin is 2026.
What is Deep Sea Mining?
- Deep sea mining involves removing mineral deposits and metals from the ocean’s seabed.
- There are three types of such mining,
- Taking deposit-rich polymetallic nodules off the ocean floor
- Mining massive seafloor sulfide deposits
- Stripping cobalt crusts from rock.
- These nodules, deposits and crusts contain materials, such as nickel, rare earths, cobalt and more, that are needed for batteries and other materials used in tapping Renewable Energy and also for everyday technology like cellphones and computers.
- Companies and governments view these as strategically important resources that will be needed as onshore reserves are depleted and demand continues to rise.
What are the Environmental Concerns related to Deep Sea Mining?
- Deep Sea Mining can damage the Marine Ecosystem and ecosystems. Damage from mining can include noise, vibration and light pollution, as well as possible leaks and spills of fuels and other chemicals used in the mining process.
- Sediment plumes from some mining processes are a major concern. Once valuable materials are extracted, slurry sediment plumes are sometimes pumped back into the sea. That can harm filter feeding species like corals and sponges and could smother or otherwise interfere with some creatures.
- Deep-sea mining would go beyond harming the seabed and have a wider impact on fish populations, marine mammals and the essential function of the deep-sea ecosystems in regulating the climate.
How is Deep Sea Mining Regulated?
- Countries manage their own maritime territory and exclusive economic zones, while the high seas and the international ocean floor are governed by the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Seas (UNCLOS).
- Under the treaty, the seabed and its mineral resources are considered the “common heritage of mankind” that must be managed in a way that protects the interests of humanity through the sharing of economic benefits, support for marine scientific research, and protecting marine environments.
What is the International Seabed Authority?
- About:
- The ISA is an autonomous organization within the United Nations common system, with headquarters located in Kingston, Jamaica.
- All States parties to the 1982 UNCLOS are members of the Authority, amounting to 168 members, including the European Union.
- The Authority is one of the three international institutions established by UNCLOS;
- The other two are the Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf and the International Tribunal for the Law of the Sea.
- The Authority is one of the three international institutions established by UNCLOS;
- Objective:
- Its primary function is to regulate exploration for, and exploitation of deep seabed minerals found in 'the Area', which is defined by the Convention as the seabed and subsoil beyond the limits of national jurisdiction, that is, beyond the outer limits of the continental shelf.
- The Area comprises just over 50 % of the entire seabed on Earth.
- Its primary function is to regulate exploration for, and exploitation of deep seabed minerals found in 'the Area', which is defined by the Convention as the seabed and subsoil beyond the limits of national jurisdiction, that is, beyond the outer limits of the continental shelf.
Way Forward
- Applications for mining must be considered and environmental impact assessments need to be carried out.
- In the meantime, some companies — such as Google, Samsung, BMW and others — have backed the World Wildlife Fund’s call to pledge to avoid using minerals that have been mined from the planet’s oceans.
- More than a dozen countries—including France, Germany and several Pacific Island nations— have officially called for a ban, pause or moratorium on deep sea mining at least until environmental safeguards are in place, although it’s unclear how many other countries support such mining.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2021)
- The Global Ocean Commission grants licences for seabed exploration and mining in international waters.
- India has received licences for seabed mineral exploration in international waters
- ‘Rare earth minerals’ are present on the seafloor in international waters.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Critically evaluate the various resources of the oceans which can be harnessed to meet the resource crisis in the world. (2014)
India-Africa Partnership: Achievements, Challenges, and Roadmap 2030
For Prelims: AEG, ICCR, ITEC, G-20, India-Africa Forum Summit.
For Mains: India-Africa Partnership: Achievements, Challenges, and Roadmap 2030.
Why in News?
Recently, the 20-member Africa Expert Group (AEG), established by the Vivekananda International Foundation, presented a Report titled ‘India-Africa Partnership: Achievements, Challenges and Roadmap 2030’.
- The report highlights India's significant partnership with Africa and emphasizes the importance of regular policy review and implementation to strengthen the relationship.
- With Africa accounting for around 17% of the global population and projected to reach 25% by 2050, India recognizes its crucial role in the partnership as a rising global power.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- Changes in Africa:
- Africa is undergoing significant changes in its demographics, economy, politics, and society. It is gradually moving towards regional integration and is committed to promoting democracy, peace, and progress.
- However, some countries like Ethiopia, Sudan, and the Central African Republic are still grappling with challenges posed by insurgency, ethnic violence, and terrorism.
- Competition and External Players:
- Several external partners, including China, Russia, the United States, the European Union, Japan, Turkey, and the United Arab Emirates, are actively competing to strengthen their relations with different parts of Africa.
- They aim to secure market access, energy and mineral resources, and enhance their political and economic influence in the region.
- China’s Involvement:
- China has stood out as Africa's largest economic partner since 2000. It plays a significant role as an infrastructure developer, resource provider, and financier in Africa.
- China has made substantial investments in terms of finances, materials, and diplomatic efforts.
What are the Recommendations to Strengthen India- Africa Ties?
- Strengthen Political and Diplomatic Cooperation:
- Restore periodic leaders' summits through the India-Africa Forum Summit.
- Indo Africa Forum Summit is a programme fully sponsored by the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) with a view to develop Indo-Africa cooperation by helping African countries to develop their own potential for development in human resource and agriculture etc.
- Seek consensus among G-20 members on the AU's (African Union) full membership.
- Establish a dedicated secretary in the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) for African affairs.
- Restore periodic leaders' summits through the India-Africa Forum Summit.
- Enhance Defence and Security Cooperation:
- Increase the number of defence attachés in Africa and expand dialogue on defence issues.
- Strengthen maritime collaboration and extend Lines of Credit to facilitate defence exports.
- Expand cooperation in counterterrorism, cyber security, and emerging technologies.
- Deepen Economic and Development Cooperation:
- Promote India-Africa trade through the creation of an Africa Growth Fund (AGF) to enhance access to finance.
- Implement measures to improve project exports and enhance cooperation in the shipping domain.
- Focus on trilateral cooperation and deepen science and technology collaboration.
- Increase Socio-Cultural Cooperation:
- Facilitate greater interaction between Indian and African universities, think tanks, civil society, and media organizations.
- Establish a National Centre for African Studies.
- Rename Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) and Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR) scholarships after famous African figures.
- Liberalize visa measures for African students pursuing higher education in India and provide short-term work visas.
- Implementing the ‘Roadmap 2030’:
- Establish a special mechanism for implementing the 'Roadmap 2030' through collaboration between the MEA and the National Security Council Secretariat.
- Create a team of officials led jointly by the Secretary, Africa in the MEA, and a designated Deputy National Security Adviser.
- By following this roadmap and implementing the recommended measures, India can further strengthen its partnership with Africa, leveraging the continent's potential and contributing to its own global stature.
What are the Achievements of India-Africa Relations?
- Economic Cooperation:
- For Indian businesses, Africa presents a massive untapped market for manufacturing goods such as textiles, pharmaceuticals, automobiles and light machinery.
- From 2011–2022, shows an increase in India's total goods trade with Africa from USD 68.54 billion to USD 90.52 billion. Also, in 2022, for the first time, India reached a positive trade balance.
- Development Assistance:
- The ITEC program offers training and capacity building programs to African professionals. India has also extended lines of credit and grants for infrastructure projects, agricultural development, and capacity building.
- Health Collaboration:
- Indian pharmaceutical companies have provided affordable generic medicines to African countries, contributing to improved healthcare access. India has also deployed medical teams and offered technical assistance to combat diseases like HIV/AIDS, malaria, and Ebola.
- Defence Cooperation:
- India has signed MoUs with all African nations on the Indian Ocean Rim (IOR) is evidence of increased defence engagement with African countries.
- The hosting of two India-Africa Defence Dialogue (IADD) at the defense ministers’ level, on the sidelines of the Defence Expo at Lucknow (2020) and Gandhinagar (2022), also underlines the growing importance of the defence domain in India-Africa engagement.
- In 2022, India started the first edition of the Trilateral Maritime Exercise with Tanzania and Mozambique to enhance maritime cooperation in the region
- Technology and Digital Cooperation:
- Under the Pan African e-Network Project (initiated in 2009), India has set up a fibre-optic network to provide satellite connectivity, tele-medicine and tele-education to countries of Africa.
- The subsequent phase, e-VidyaBharti and e-ArogyaBharti (e-VBAB), introduced in 2019, focused on providing free tele-education to African students and continuing medical education for healthcare professionals.
What is the Importance of Africa for India?
- Africa is home to over half a dozen of the fastest growing countries of this decade such as Rwanda, Senegal, Tanzania, etc. making it one of the growth poles of the world.
- Real GDP in Africa and Sub-Saharan Africa in the past decade has grown by more than twice the rate in the 1980s and 90's.
- The African continent has a population of over one billion with a combined GDP of 2.5 trillion dollars making it a huge potential market.
- Africa is a resource rich nation dominated by commodities like crude oil, gas, pulses and lentils, leather, gold and other metals, all of which India lacks in sufficient quantities.
- Namibia and Niger are among the top ten global producers of uranium.
- South Africa is the world's largest producer of platinum and chromium.
- India is seeking diversification of its oil supplies away from the Middle East and Africa can play an important role in India’s energy matrix.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2016)
The India-Africa Summit
- held in 2015 was the third such Summit
- was actually initiated by Jawaharlal Nehru in 1951
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- India-Africa Summit is a forum to re-initiate and reboot relation between India and African countries.
- It started from 2008 with New Delhi as its first venue. Since then, the summit has been held every three years, alternately in India and Africa. Hence, statement 2 is not correct.
- The second summit was held in Addis Ababa in 2011. The third summit, scheduled to be held in 2014, was postponed because of the Ebola outbreak, and took place in October, 2015 in New Delhi. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. How does India see its place in the economic space of rising natural resource rich Africa? (2014)
Q. Increasing interest of India in Africa has its pro and cons. Critically Examine. (2015)
Dark Patterns
For Prelims: Dark Pattern, Deceptive Patterns, Consumer Protection Act, 2019.
For Mains: Dark Pattern, Use of Dark Pattern by Companies, Harm of Dark Pattern to Users
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution, Government of India, has established a 17-member task force to develop guidelines for consumer protection to address the issue of Dark Patterns.
- The Ministry has started classifying complaints received on the National Consumer Helpline to compile information on Dark Patterns, which can be used by the Central Consumer Protection Authority to initiate action under the Consumer Protection Act, 2019.
What are the Dark Patterns?
- About:
- Dark patterns, also known as deceptive patterns, refer to strategies employed by websites and apps to make users perform actions they did not intend to or discourage behaviors that are not advantageous for the companies.
- The term was coined by Harry Brignull, a user experience (UX) designer, in 2010.
- These patterns often exploit cognitive biases and employ tactics such as false urgency, forced actions, hidden costs etc.
- They can range from overtly noticeable tricks to more subtle methods that users may not immediately recognize.
- Types of Dark Patterns: The Consumer Affairs Ministry has identified nine types of dark patterns being used by e-commerce companies:
- False Urgency: Creates a sense of urgency or scarcity to pressure consumers into making a purchase or taking an action;
- Basket Sneaking: Dark patterns are used to add additional products or services to the shopping cart without the user’s consent;
- Confirm Shaming: Uses guilt to make consumers adhere; criticises or attacks consumers for not conforming to a particular belief or viewpoint;
- Forced Action: Pushes consumers into taking an action they may not want to take, such as signing up for a service in order to access content;
- Nagging: Persistent criticism, complaints, and requests for action;
- Subscription traps: Easy to sign up for a service but difficult to quit or cancel; option is hidden or requires multiple steps;
- Bait & Switch: Advertising a certain product/ service but delivering another, often of lower quality;
- Hidden costs: Hiding additional costs until consumers are already committed to making a purchase;
- Disguised ads: Designed to look like content, such as news articles or user-generated content.
- Consequences:
- Dark patterns endanger the experience of Internet users and make them more susceptible to financial and data exploitation by Big Tech firms.
- Dark patterns confuse users, introduce online obstacles, make simple tasks time-consuming, have users sign up for unwanted services/products, and force them to pay more money or share more personal information than they intended.
How do Companies Use Dark Patterns?
- Social media companies and Big Tech firms such as Apple, Amazon, Skype, Facebook, LinkedIn, Microsoft, and Google use dark or deceptive patterns to downgrade the user experience to their advantage.
- Amazon came under fire in the European Union for its confusing, multi-step cancelling process in Amazon Prime subscription. Amazon, in 2022, made its cancellation process easier for online customers in European countries.
- LinkedIn users often receive unsolicited, sponsored messages from influencers.
- Disabling this option is a difficult process with multiple steps that requires users to be familiar with the platform controls.
- Google-owned YouTube nags users to sign up for YouTube Premium with pop-ups, obscuring final seconds of a video with thumbnails of other videos.
What are the Global Efforts to Combat Dark Patterns?
- In March 2021, California in the US passed amendments to the California Consumer Privacy Act, prohibiting dark patterns that hindered consumers from exercising their privacy rights.
- The UK issued guidelines in April 2019, which were later enforceable under the Data Protection Act, 2018, restricting companies from using manipulative tactics to lure underage users into low privacy settings.
Way Forward
- By establishing a task force and working towards developing guidelines, the government aims to prevent deceptive practices and safeguard user interests. This move aligns with similar efforts undertaken by countries like the US and the UK.
- It is crucial to raise awareness among users about dark patterns and empower them to recognize and avoid manipulative tactics employed by websites and apps.
Gravitational Waves
For Prelims: India’s Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope, Gravitational Waves, Pulsars
For Mains: Gravitational Waves
Why in News?
Recently, an international team of astronomers announced scientific evidence confirming the presence of gravitational waves using pulsar observations.
- India’s Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (GMRT) was among the world’s six large telescopes that played a vital role in providing this evidence.
What are the Key Findings?
- They reported the first direct evidence for the relentless vibrations of space-time caused by ultra-low frequency gravitational waves.
- They also set new limits on the strength and frequency of these waves, which are consistent with theoretical predictions.
- They are also tantalisingly close to the discovery of nanohertz gravitational waves, which would open up new possibilities for studying galaxy evolution, cosmology, and fundamental physics.
How Does GMRT Detect Gravitational Waves?
- GMRT detects gravitational waves by using pulsars-the only accessible celestial clocks for humans, which are rapidly rotating neutron stars.
- Pulsars emit regular pulses of radio waves that can be used to measure their rotation periods and distances with high precision.
- By observing Pulsar timing arrays (PTAs) distributed across the sky, GMRT can look for tiny variations in their pulse arrival times caused by gravitational waves passing through the Earth-pulsar line of sight. This technique is known as pulsar timing.
- GMRT is a crucial player in the PTA experiment, as it provides unique data at low radio frequencies and high sensitivity.
Note:
- PTAs are international collaborations of radio telescopes that observe hundreds of pulsars over many years to search for gravitational waves in the nanohertz band.
- GMRT is part of the Indian Pulsar Timing Array (InPTA), which is a collaboration of Indian and Japanese researchers that uses GMRT data along with other telescopes.
What is GMRT?
- GMRT is a low-frequency radio telescope consisting of an array of 30 fully steerable parabolic radio telescopes of 45-meter diameter.
- It is located near Narayangaon, Pune in India, and operated by the National Centre for Radio Astrophysics (NCRA), a part of the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Mumbai.
- It is one of the largest and most sensitive radio telescope array in the world at low frequencies.
- GMRT has recently undergone significant upgrades in its receivers and electronics, which have improved its sensitivity and bandwidth. It is now known as the upgraded GMRT (uGMRT).
What are Gravitational Waves?
- About:
- Gravitational waves are ripples in space-time caused by violent and energetic processes in the Universe.
- Albert Einstein predicted their existence in his general theory of Relativity in 1916.
- Production of Gravitational Waves
- Cataclysmic Events: The strongest gravitational waves originate from colliding black holes, supernovae, and colliding neutron stars.
- Neutron Star Rotation: Gravitational waves can also be produced by the rotation of non-perfectly spherical neutron stars and possibly remnants of gravitational radiation from the Big Bang.
- Features and Detection
- Gravitational waves are challenging to detect due to their weak interaction with matter.
- Gravitational waves were first detected in 2015 using an experiment involving Laser Interferometer Gravitational Observatory (LIGO) detectors.
- Sensitive instruments like interferometers, such as the LIGO, are developed to detect gravitational waves by measuring tiny disturbances in space-time.
- Gravitational waves are challenging to detect due to their weak interaction with matter.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Recently, scientists observed the merger of giant ‘blackholes’ billions of light-years away from the Earth. What is the significance of this observation? (2019)
(a) ‘Higgs boson particles’ were detected.
(b) ‘Gravitational waves’ were detected.
(c) Possibility of intergalactic space travel through ‘wormhole’ was confirmed.
(d) It enabled the scientists to understand ‘singularity’
Ans: (b)
Q. What is the purpose of ‘evolved Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (eLISA)’ project? (2017)
(a) To detect neutrinos
(b) To detect gravitational waves
(c) To detect the effectiveness of missile defence system
(d) To study the effect of solar flares on our communication systems
Ans: (b)
- “evolved Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (eLISA)” is a project to measure gravitational waves in the frequency range of 0.1mHz to 100mHz.
- The project consists of 3 spacecrafts which will fly in a triangular path around the earth. The arm length of each edge of this imaginary triangle will be about 50 million km.
- Inside these spacecrafts will be placed free falling cubes with 46 mm side. If these free falling cubes are hit by gravitational waves, then the change in the distance between these cubes will be accurately measured by Laser interferometer.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer
Energy Transition Index 2023: WEF
Why in News?
Recently, the World Economic Forum (WEF) has ranked India at the 67th place globally on its Energy Transition Index (ETI).
- The Index highlights India as the sole major economy with energy transition momentum accelerating across all dimensions and Singapore is the only other major economy showing "true momentum by advancing sustainability, energy security and equity in a balanced way.
Note: The ETI benchmarks 120 economies on the current performance of their energy systems across economic development and growth, environmental sustainability and energy security and access indicators and their readiness for transition to secure, sustainable, affordable and inclusive energy systems.
What are the Key Highlights of the Energy Transition Index?
- Rankings:
- Sweden topped the list and was followed by Denmark, Norway, Finland and Switzerland in the top five on the list of 120 countries.
- France (7) was the only G20 Country in the top 10, followed closely by Germany (11), the U.S. (12), and the U.K. (13).
- Global Outlook:
- Global average ETI scores increased by 10% since 2014 but showed only marginal growth in the past three years.
- Only 41 countries have made steady progress in the past decade.
What are the Contributors to India’s Energy Transition Progress and Concerns?
- Contributors: Universal electricity access, clean cooking options, and renewable energy deployment have improved India's performance.
- Low reliance on natural gas and effective utilization of existing capacities helped India withstand the recent energy crisis.
- Concerns: Rising import dependence amid global energy market volatilities, predominantly carbon-intensive energy mix. Challenges include balancing economic growth and creating quality jobs for the growing working-age population.
- Recommendations: Sustained momentum, effective policy management, and partnerships are crucial for achieving long-term energy transition goals. This entails promoting clean energy investments, innovation, and energy efficiency while ensuring inclusivity.
- Building a skilled workforce, fostering public-private collaboration, and investing in low-carbon technology research and development are essential for India's successful energy transition.
What is World Economic Forum?
- About:
- WEF is a Swiss nonprofit foundation established in 1971, based in Geneva, Switzerland.
- Recognized by the Swiss authorities as the international institution for public-private cooperation.
- Mission:
- Committed to improving the state of the world by engaging business, political, academic, and other leaders of society to shape global, regional, and industry agendas.
- Founder and Executive Chairman: Klaus Schwab.
- Major Reports published by WEF are:
- Global Competitiveness Report.
- Global IT Report
- WEF along with INSEAD, and Cornell University publishes this report.
- Global Gender Gap Report.
- Global Risk Report.
- Global Travel and Tourism Report.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q1. Which of the following gives ‘Global Gender Gap Index’ ranking to the countries of the world? (2017)
(a) World Economic Forum
(b) UN Human Rights Council
(c) UN Women
(d) World Health Organization
Ans: (a)
Q2. Who among the following is the founder of World Economic Forum? (2009)
(a) Klaus Schwab
(b) John Kenneth Galbraith
(c) Hobert Zoellick
(d) Paul Krugman
Ans (a)
Q3. The Global Competitiveness Report is published by the (2019)
(a) International Monetary Fund
(b) United Nations Conference on Trade and Development
(c) World Economic Forum
(d) World Bank
Ans: (c)
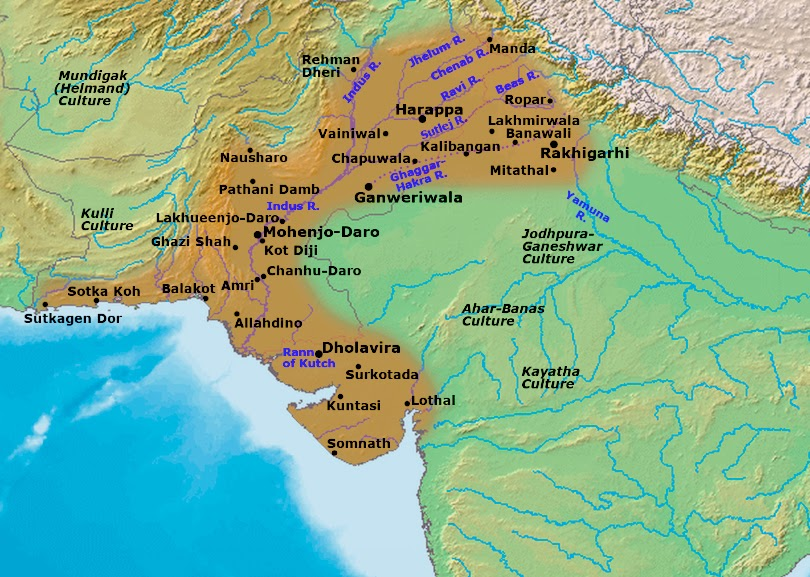
National Maritime Heritage Complex
Why in News?
Recently, Union Minister of Ports, Shipping and Waterways, reviewed the project process of National Maritime Heritage Complex (NMHC), Lothal in Gandhinagar, Gujarat.
- NMHC complex will have Asia’s Biggest Under Water Marine Museum and India’s Grandest Naval Museum.
What is the National Maritime Heritage Complex?
- About:
- The NMHC is being constructed at the historic Indus Valley civilization region of Lothal, Gujarat, under the Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways.
- Its primary objective is to showcase the maritime heritage of India from ancient to modern times, utilizing an edutainment approach and incorporating the latest technology.
- Significance:
- The NMHC is set to become the world's largest maritime museum complex and an international tourist destination.
- It will play a crucial role in educating visitors about India's rich maritime history and elevate India's image in the global maritime sector.
- The project is part of the Sagarmala Programme and is being developed with the participation of public and private institutes, organizations, and corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives. Major ports in India have also contributed funds to support the project.
- Unique Features of NMHC:
- Includes Lothal Mini Recreation; Four theme parks: Memorial, Maritime and Navy, Climate, and Adventure and Amusement; Coastal States Pavilion.
What is Lothal?
- About:
- One of the southernmost sites of the IVC in Gujarat's Bhāl region. Believed to have been built around 2,200 BC.
- It flourished as a trade center around 2,200 BC, with trade connections reaching West Asia and Africa.
- Known for its trade of beads, gems, and ornaments.
- Meaning of "Lothal" in Gujarati is "the mound of the dead."
- The excavated site of Lothal is the only port town of the Indus Valley Civilization.
- Nomination for UNESCO World Heritage Site:
- Lothal was nominated in April 2014 for inclusion on the UNESCO World Heritage List.
- Its application is pending on the tentative list of UNESCO.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. Which one of the following ancient towns is wellknown for its elaborate system of water harvesting and management by building a series of dams and channelizing water into connected reservoirs? (2021)
(a) Dholavira
(b) Kalibangan
(c) Rakhigarhi
(d) Ropar
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- The city of Dholavira was located on Khadir Beyt in the Rann of Kutch, where there was fresh water and fertile soil. Unlike some of the other Harappan cities, which were divided into two parts, Dholavira was divided into three parts, and each part was surrounded with massive stone walls, with entrances through gateways.
- There was also a large open area in the settlement, where public ceremonies could be held. Other finds include large letters of the Harappan script that were carved out of white stone and perhaps inlaid in wood. This is a unique find as generally Harappan writing has been found on small objects such as seals.
- Being the 6th largest of more than 1,000 Harappan sites discovered so far, and occupied for over 1,500 years, Dholavira not only witnesses the entire trajectory of the rise and fall of this early civilization of humankind, but also demonstrates its multifaceted achievements in terms of urban planning, construction techniques, water management, social governance and development, art, manufacturing, trading, and belief system.
- With extremely rich artefacts, the well-preserved urban settlement of Dholavira depicts a vivid picture of a regional centre with its distinct characteristics, that also contributes significantly to the existing knowledge of Harappan Civilization as a whole.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Q2. Which of the following characterizes/characterize the people of Indus Civilization? (2013)
- They possessed great palaces and temples.
- They worshipped both male and female deities.
- They employed horse-drawn chariots in warfare.
Select the correct statement/statements using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) None of the statements given above is correct
Ans: (b)
Q3. Which one of the following is not a Harappan site? (2019)
(a) Chanhudaro
(b) Kot Diji
(c) Sohgaura
(d) Desalpur
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- Kot Diji (now in the Sindh region of Pakistan) was an early Harappan site on the east bank of the Indus river and was excavated between 1955 and 1957.
- Chanhudaro in Pakistan and Desalpur in Gujarat are mature Harappan sites.
- Sohgaura in Gorakhpur, Uttar Pradesh, is known for Sohgaura copper plate inscription which is considered to be from the Mauryan period. It is not a Harappan site.
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Political Parties Shift to Online Financial Reporting
The Election Commission of India (ECI) has introduced an online web portal for political parties to file their financial accounts electronically. This initiative aims to simplify the process of submitting Contribution Reports, Audited Annual Accounts, and Election Expenditure Statements, as required by the Representation of People's Act, 1951. The ECI emphasizes the importance of compliance and transparency in financial disclosures, urging political parties to adhere to democratic principles. For those opting not to file online, written justifications must be provided, and the ECI will publish both the reports and the explanations on their platform.
ECI is an autonomous constitutional authority responsible for administering Union and State election processes in India. It was established in accordance with the Constitution on 25th January 1950 (celebrated as national voters' day). The secretariat of the commission is in New Delhi.
Read more: Election Commission of India
Empowering Women Entrepreneurs: eSARAS App
Deendayal Antyodaya Yojna- National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NRLM) has taken a significant step towards supporting women in Self-help Groups (SHGs) by launching the eSARAS mobile App. This app aims to enhance the marketing initiatives for products made by SHGs. Additionally, the eSARAS fulfillment centre, managed by the Foundation for Development of Rural Value Chains (FDRVC), a Not for Profit Company constituted jointly by Ministry of Rural Development and Tata Trust, will handle the processing, packaging, and shipping of products purchased through the eSARAS Portal and App. This provides a user-friendly platform for promoting authentic handicrafts and handlooms but also ensures efficient logistics to deliver online orders directly to customers' doorsteps.
Read more: Self Help Groups
Neeraj Chopra Finishes 1st at Lausanne Diamond League 2023
Neeraj Chopra, the Olympic gold medalist, clinched first place in the javelin event in the Lausanne Diamond League 2023 by achieving a remarkable throw of 87.66 m. The Lausanne meet was Neeraj Chopra’s second competition of the season and the first since the Doha Diamond League.
Lausanne Diamond League 2023 was the sixth meet of the Diamond League athletics series, which took place at the Athletissima stadium in Switzerland.
Read more: Olympics
Indian Refiners Shift to Chinese Yuan for Russian Oil Payments
Indian refiners have turned to the Chinese yuan as an alternative payment method for oil imports from Russia. Indian Oil Corporation, the largest buyer of Russian crude oil in India, became the first state refiner to do so. Western sanctions imposed on Russia following the Russia Ukraine tussle have prompted Russia and its customers to seek alternatives to the U.S. dollar for settling payments.
China, as Russia's top crude supplier, has already shifted to yuan payments for most of its energy imports from Russia. India, now the largest buyer of seaborne Russian oil, has taken the lead in diversifying payment options. While the exact extent of Russian oil purchased by Indian refiners with yuan remains unclear, this development reflects a strategic shift in payment methods amidst evolving geopolitical dynamics.
Read more: Russia Ukraine tussle.
Data Carbon Ladder
Scientists have developed a tool called the Data Carbon Ladder, which enables businesses to calculate the carbon emissions associated with their digital data. With the global data volume projected to exceed 180 zettabytes by 2025 and doubling every two years, understanding the carbon dioxide output of digital data is crucial.
The tool addresses a critical oversight in global decarbonization policies by considering the carbon footprint of data, an often-neglected factor. Data centers, responsible for 2.5% to 3.7% of all human-induced carbon dioxide emissions, surpass the aviation industry's emissions (2.1%). By utilizing this tool, businesses and organizations can improve the sustainability of their data projects, minimizing their environmental impact and creating more efficient and eco-friendly solutions.
Read more: Carbon emissions, Decarbonization