Indian Economy
Women in Corporates Roles in India
For Prelims: India Employment Report 2024, Unemployment rates, Institute for Human Development (IHD), International Labour Organisation (ILO), Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR).
For Mains: India Employment Report 2024: ILO, Major Issues Related to Unemployment in India.
Why in News?
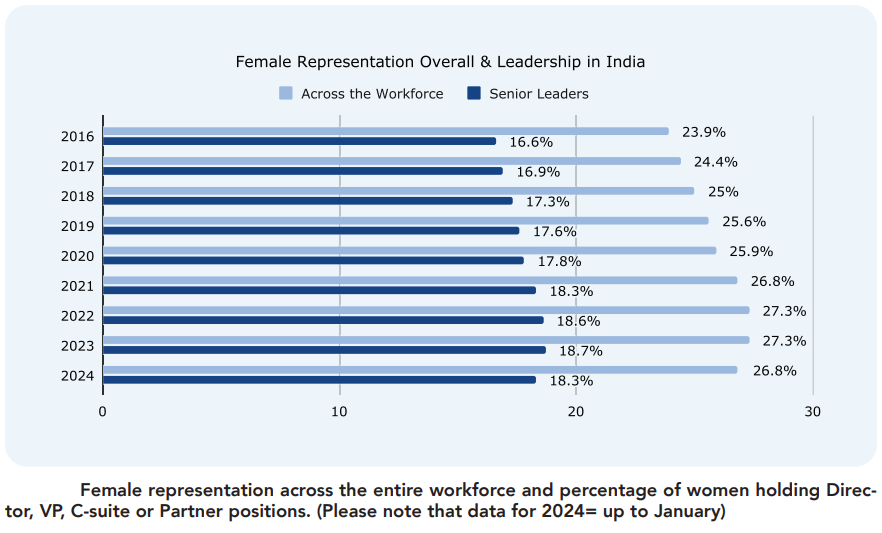
A recent report titled “Women in Leadership in Corporate India” by a networking platform called LinkedIn has shown a persistent underrepresentation of women in leadership positions across Indian corporates.
- The percentage has remained stagnant below 30% for a considerable period.
- LinkedIn is a business-oriented social media platform, launched in 2003, that focuses on professional networking.
- Unlike general social media sites like Facebook or Twitter, LinkedIn focuses on career-related aspects.
- The data is based on LinkedIn members in India, where the firm has over 100 million people registered
What are the Findings of the Report?
- Stagnation of Women Representation in Corporates:
- Women representation across the workforce and in senior leadership positions is below 30% all the time, and is on a declining trend post-pandemic.
- This can be attributed to the slowdown in fresh hires of women for leadership roles.
- Women in Leadership Lowest, Moderate and Highest in Sectors:.
- Lowest Representation: Construction, Oil, Gas, and Mining, and Utilities (11%), Wholesale and Manufacturing(12%), and Accommodation and Food Services (15%).
- Slightly Better (12%): Wholesale, Manufacturing
- Moderate Representation: Technology, Information & Media, Financial Services (19%)
- Highest Representation: Education (30%) and Government Administration (29%)
- Breaking the Law:
- Reports show that laws such as the Companies Act, 2013, which mandates women directors on company boards, are not being followed strictly.
- Between April 2018 and December 2023, 507 companies were fined for flouting this norm. Of them, 90% were listed companies.
India Employment Report 2024 by the International Labour Organization (ILO)
- The female labour force participation rate in India was 24.5% in 2024, a slight increase from 23.3% in 2019 (lower than the global average of 47.2%).
- Women in India are more likely to be employed in the informal sector, with 86% of working women in informal employment compared to 82% of men.
- The Covid-19 pandemic has disproportionately impacted women's employment, with women 1.8 times more likely to lose their jobs compared to men.
- Women also face significant challenges in re-entering the labour force after the pandemic, due to increased care responsibilities and gender biases.
Labour Force Participation Rate
- It is the section of the working population in the age group of 16-64 in the economy currently employed or seeking employment.
- Persons still undergoing studies, housewives and persons above the age of 64 are not seen as a part of the labour force.
What are the Factors Contributing to Lower Representation of Women in Corporates?
- Unconscious Bias: Deeply ingrained societal biases and stereotypes about women's abilities, leadership styles, and career ambitions can lead to unfair assessments and limited opportunities for advancement.
- Reduction in Work-from-home Options: The reduction in the availability of hybrid or work-from-home roles may have contributed to the stagnation, as these arrangements often facilitate the participation of women in the corporate workforce.
- Work-Life Balance Challenges: The disproportionate burden of domestic and caregiving responsibilities that often falls on women can make it difficult to demonstrate the same level of commitment and availability as their male counterparts.
- Safety Concerns: Migration and safety concerns further limit women's access to employment. Inadequate urban infrastructure, along with safety issues in public spaces, can discourage women from seeking and retaining jobs, particularly in urban areas.
- Lack of Mentorship and Sponsorship: Women often have less access to influential mentors and sponsors who can advocate for their career progression and help them navigate the corporate landscape.
- Limited Representation in Leadership: The scarcity of women in senior leadership positions creates a lack of visible role models and makes it harder for women to envision themselves in these positions.
International Labour Organisation (ILO)’s Framework for Bridging the Workforce Gender Gap
- Closing the Pay Gap:
- Enforce laws ensuring equal pay for work of equal value.
- Implement salary transparency measures to expose and address pay discrepancies.
- Utilise objective criteria for job evaluation that are not biassed by gender stereotypes.
- Deconstructing Occupational Segregation:
- Dismantle preconceived notions about the suitability of certain jobs for specific genders.
- Promote women's participation in traditionally male-dominated fields like STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics).
- Fostering a Safe and Inclusive Work Environment:
- Implement strong legal frameworks to prohibit gender discrimination and harassment.
- Example, India's the Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition and Redressal) Act, 2013.
- Raise awareness about gender bias and create a culture of zero tolerance.
- Promoting Work-Life Balance:
- Provide adequate maternity and paternity leave policies to support parents during childbirth and early parenthood.
- Design social protection measures that support working families, including affordable childcare options.
- Valuing Care Work:
- Invest in creating quality care jobs with fair wages and decent working conditions.
- Strengthen regulations for care professionals, who are predominantly women.
- India needs to ratify the Domestic worker convention of ILO (Domestic Workers Convention, 2011 (No. 189)) and frame domestic law accordingly.
- Crisis Resilience for Women's Employment:
- Develop policies that safeguard women's employment during economic downturns, such as targeted training programs or financial support.
What Measures can be Adopted to Enhance Gender Diversity in Corporate Leadership?
- Flexible or hybrid work policies:
- This is important for retaining women, especially at the junior and middle management levels, as this is when they often have to balance career aspirations and family commitments.
- 'Skills-First' Approach to Hiring:
- Adopting a 'skills-first' approach to hiring, rather than making gendered assumptions about a prospective employee's capabilities, can help reduce biases and promote meritocracy.
- This involves focusing on the candidate's relevant skills, qualifications, and experience, rather than relying on gender-based stereotypes.
- Promoting Diversity in Senior Leadership:
- The government can promote diversity in senior leadership through initiatives to raise awareness of board diversity in listed companies.
- As an example, the Japanese Ministry of Economy collaborated with the Tokyo Stock Exchange to introduce the "Nadeshiko Brands" program.
- This highlights companies that encourage women's empowerment and leadership as attractive investment opportunities.
- The government can promote diversity in senior leadership through initiatives to raise awareness of board diversity in listed companies.
- Establish Networking and Support Groups for Women:
- Creating a Strong Network: These groups for women professionals can foster connections and collaboration, empowering women to navigate the path to leadership.
- Peer Learning and Support: Through these, women can share experiences, learn from each other's successes and challenges, and build a strong support system.
- Mentorship and Networking Opportunities:
- Providing mentorship and networking opportunities for women can help them navigate the corporate ladder more effectively.
- Experienced female leaders can guide and support aspiring women, sharing insights and strategies for career advancement.
- Shared Parental Leave Policies:
- These can promote a more equitable distribution of caregiving responsibilities between men and women.
- Paid paternity leave policy, especially in the private sector, can help promote a more equitable distribution of caregiving responsibilities between men and women.
Conclusion
The stagnation in the representation of women in corporate leadership roles in India is a concerning trend that requires concerted efforts to address. Implementing a multifaceted approach, including policy changes, organisational reforms, and cultural shifts, is essential to enhance gender diversity and unlock the full potential of women in the corporate sector.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Despite numerous efforts and policies, the proportion of women in the workforce in India has remained stagnant. Analyze the causes of this stagnation and propose steps that can be taken. (250 words) |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Disguised unemployment generally means (2013)
(a) large number of people remain unemployed
(b) alternative employment is not available
(c) marginal productivity of labour is zero
(d) productivity of workers is low
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. Most of the unemployment in India is structural in nature. Examine the methodology adopted to compute unemployment in the country and suggest improvements. (2023)


Biodiversity & Environment
KAZA Summit 2024 and Wildlife Product Trade
For Prelims: Kavango-Zambezi Trans-Frontier Conservation Area (KAZA-TFCA), Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES), Elephant Trade Information System (ETIS), International Consortium on Combating Wildlife Crime (ICCWC), TRAFFIC (Wildlife Trade Monitoring Network).
For Mains: Issue of Ivory trade and Solutions, Wildlife conservation, Human-wildlife conflict, Sustainable conservation, Wildlife management, International agreements.
Why in News?
Recently, the 2024 Heads of State Summit for the Kavango-Zambezi Trans-Frontier Conservation Area (KAZA-TFCA) took place in Livingstone, Zambia, where member states renewed their calls to withdraw from the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES).
- The call came in backdrop of repeated denying of permission to sell off their abundant ivory and other wildlife products.
What are the Key Issues Discussed at the 2024 Summit?
- The KAZA-TFCA Initiative:
- KAZA-TFCA spans across five southern African nations namely, Angola, Botswana, Namibia, Zambia, and Zimbabwe along the Okavango and Zambezi river basins.
- About 70% of KAZA land is under conservation made up of 103 wildlife management areas and 85 forest reserves.
- This region harbours over two-thirds of Africa's elephant population (approx 450,000) with Botswana (132,000) and Zimbabwe (100,000) alone holding significant portions of this population.
- KAZA-TFCA spans across five southern African nations namely, Angola, Botswana, Namibia, Zambia, and Zimbabwe along the Okavango and Zambezi river basins.
- Historical Dispute with CITES:
- Like this summit, at the 2022 Conference of Parties in Panama, southern African countries advocated for legalising the ivory trade to finance conservation and reduce human-wildlife conflicts.
- Despite having large elephant populations and related challenges, their proposal was rejected, as these countries accused it of prioritising anti-trade ideologies over scientific conservation methods.
- Key Issues Discussed at the 2024 Summit:
- Delegates at the Livingstone Summit emphasized the economic pitfalls of existing CITES restrictions, advocating for wildlife product sales rights while highlighting elephant mortality rates and the loss of economic potential from ivory stockpiles.
- The ban on ivory and wildlife product trade affects conservation funding, as revenue from sales could aid wildlife management.
- Delegates argued that decisions are not based on scientific evidence but on populism and political agendas, undermining the effectiveness of CITES in promoting sustainable conservation.
- The summit featured renewed appeals to exit CITES, with proponents suggesting it could prompt CITES to reconsider or empower KAZA states to autonomously handle their wildlife resources.
- In response to increasing restrictions on trophy hunting imports by western countries, Zimbabwe and other KAZA states are exploring alternative markets, particularly in the East.
- Trophy hunting involves selectively hunting wild animals, often large mammals, to obtain body parts like antlers or horns, serving as symbols of achievement or for display.
What is Ivory?
- Elephants' ivory tusks, akin to oversized teeth, consist mainly of durable dentine encased in resilient enamel.
- Both male and female African elephants have tusks, but only some male Asian elephants do.
- World Wildlife Fund (WWF) highlights the issue of ivory poaching, noting that "ivory" encompasses materials from various species like mastodons, mammoths, hippos, narwhals, and walruses, which are not included in the US elephant ivory ban but may be regulated by other laws like CITES.
- Every ivory item, from tusks to trinkets, comes from an elephant killed by poachers, with about 20,000 elephants killed annually to meet mainly Asian demand for ivory.
What are the Causes of the Wildlife Product Trade?
- Organised Commercial Illegal Sourcing: Organized crime engages in remote operations, including elephant and tiger poaching, often merging with other criminal networks, exploiting power dynamics, illicit weapons, and money laundering avenues.
- Black Markets Create New Demands: When legal sales drop, illegal traders may find new ways to keep selling the product, like rare animals or endangered species trophies, where scarcity can make illegal markets more appealing to buyers.
- Supplementary Livelihoods and Opportunism: While big criminal groups might be behind some trafficking, many poor people are just trying to make ends meet.
- Corruption: It significantly undermines efforts to disrupt and deter wildlife trafficking, ranging from bribery at inspection points to higher-level influence on permit issuance and legal decisions.
- Cultural Roots of Poaching: Wildlife poaching isn't solely driven by financial motives but can also be cultural.
- For example, In Chinko reserve in the Central African Republic elephant hunting represents cultural heritage, symbolising courage and masculinity.
- Existence of Legal Market for Wildlife Product: Legal Market for Wildlife Product (E.g, Lao PDR permits trade in bear bile) makes it difficult to recognise the product's origin as collected from wild or originated from illegal poaching.
- Japan is the world's most significant legal legal ivory market.
What are the Measures Needed to Tackle Wildlife Crime?
- Banning Illegal Wildlife Products: This approach aims to reduce demand by making possessing or trading goods derived from illegally obtained wildlife illegal.
- Effective Funding for Wildlife Protection: The funds should go directly to support agencies that protect wildlife, such as park rangers and anti-poaching teams.
- Public Awareness and Empowerment: Educating people about the consequences of wildlife trafficking and teaching them about the value of wildlife can lower the demand for illegal products.
- Ivory Specific Measures:
- Both sides could agree on an independent scientific review to assess the sustainability of a potential ivory trade from KAZA countries.
- CITES and KAZA countries could collaborate on exploring alternative sources of income for conservation, such as promoting ecotourism ventures and carbon offset programs within the KAZA region.
- Best Practice:
- Trade Records Analysis of Flora and Fauna in Commerce’s (TRAFFIC) technical expertise supported a World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) campaign in Thailand, significantly reforming Thai legislation and nearly eliminating the domestic ivory market.
- In China the office of WWF, alongside other NGOs, also played crucial role in implementing a domestic ivory ban.
- Gabon, Congo, and the USA have recently destroyed stockpiles of confiscated ivory to prevent its return to the black market and to condemn ivory trade and poaching publicly.
- Trade Records Analysis of Flora and Fauna in Commerce’s (TRAFFIC) technical expertise supported a World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) campaign in Thailand, significantly reforming Thai legislation and nearly eliminating the domestic ivory market.
Legal Frameworks for Wildlife Conservation
- Global Wildlife Conservation Efforts (India being Party):
- Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES)
- Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS)
- Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)
- The Wildlife Trade Monitoring Network (TRAFFIC)
- United Nations Forum on Forests (UNFF)
- International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN)
- Global Tiger Forum (GTF)
- Legal Framework in India:
|
Dristhi Mains Question: Q. Explore the challenges and possible approaches in balancing trade regulation with the preservation of wildlife? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. With reference to the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) and the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES), which of the following statements is/are correct? (2015)
1. IUCN is an organ of the United Nations and CITES is an international agreement between governments.
2. IUCN runs thousands of field projects around the world to better manage natural environments.
3. CITES is legally binding on the States that have joined it, but this Convention does not take the place of national laws.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Q. Consider the following statements in respect of Trade Related Analysis of Fauna and Flora in Commerce (TRAFFIC): (2017)
1. TRAFFIC is a bureau under United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP).
2. The mission of TRAFFIC is to ensure that trade in wild plants and animals is not a threat to the conservation of nature.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)


Governance
AMRUT (Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation) Scheme
For Prelims: AMRUT, Pey Jal Survekshan, Technology Sub-Mission for Water, National Water Policy, National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG), River Cities Alliance (RCA), Swachh Bharat Mission, National Clean Air Programme, Public-Private Partnership (PPP), Covid-19, Ayushman Bharat
For Mains: Challenges in Implementation, Steps to Revamp AMRUT, Nature-Based Solutions, People-Centric Approach, Empowering Local Bodies
Why in News?
Recently, the AMRUT scheme has garnered attention due to the challenges it is facing in addressing infrastructure issues related to water, mobility, and pollution.
What is AMRUT Scheme?
- About:
- Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) was launched on 25th June 2015 in 500 selected cities across the country, covering around 60% of the urban population.
- The mission targets enhancing basic infrastructure and implementing urban reforms for selected cities, encompassing water supply, sewerage, drainage, green spaces, non-motorised transport, and capacity building.
- AMRUT 2.0 Scheme:
- The scheme was launched on 1st October 2021, subsuming AMRUT 1.0 for the period of 5 years i.e. from the financial year (FY) 2021-22 to the FY 2025-26.
- Its objective are universal coverage of water supply from 500 cities to about 4,900 statutory towns in the country and coverage of sewerage/septage management in 500 cities covered in the first phase of the AMRUT scheme.
- AMRUT 2.0 aims to promote the circular economy of water through the development of a City Water Balance Plan (CWBP) by recycling/reuse of treated sewage, rejuvenation of water bodies and water conservation.
- The mission also has a reform agenda on ease of living of citizens through the reduction of non-revenue water, urban planning, strengthening urban finance etc.
- Other components of AMRUT 2.0:
- Pey Jal Survekshan to ascertain equitable distribution of water, reuse of wastewater, mapping of water bodies and promote healthy competition among the cities /towns.
- Technology Sub-Mission for Water to leverage the latest global technologies in the field of water.
- Information, Education and Communication (IEC) campaign to spread awareness among the masses about the conservation of water.
What is the Status of the AMRUT 2.0 Scheme?
- Fund Allocation:
- The total outlay for AMRUT 2.0 is Rs. 2,99,000 crore for ongoing projects until March 2023.
- Impact:
- AMRUT has impacted the lives of women in many positive ways . Women can now utilise their time in a more productive way due to a decrease in effort in fetching water.
- It has further led to a decrease in disease load due to availability of safe drinking water.
- Challenges:
- Despite the implementation of the scheme, around 200,000 people die annually due to inadequate water, sanitation, and hygiene.
- India's 2016 disease burden from unsafe water and sanitation is 40 times higher per person than China's and showing little improvement.
- A NITI Aayog report indicates that around 21 major cities will deplete their groundwater, leaving 40% of India's population without access to drinking water by 2030.
- Nearly 31% of urban Indian households lack piped water while 67.3% are not connected to a piped sewerage system.
Other Initiatives
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Urban (PMAY-U)
- Climate Smart Cities Assessment Framework 2.0
- TULIP-The Urban Learning Internship Program
- Smart Cities Mission (SCM)
- National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG)
- River Cities Alliance (RCA)
- National Water Policy, 2012 advocates rainwater harvesting and de-salinization in urban and industrial areas, wherever techno-economically feasible, to increase the availability of utilizable water.
What are the Challenges in the Implementation of AMRUT Scheme?
- State Project Implementation: Despite regular fund releases, states like Bihar and Assam have yet to complete projects or utilise the PPP model, resulting in less than 50% execution completion in most states.
- AMRUT Program Scope: The scheme entails a project-focused approach instead of a holistic perspective.
- Potential Overlaps and Convergence Challenges: The overlap between AMRUT and other schemes, like Swachh Bharat mission, could result funding allocation challenges, and increased workload in addressing specific urban issues.
- Unaddressed Air Pollution: National Clean Air Programme was launched as deterioration of air quality persisted since AMRUT 2.0 shifted solely to water and sewerage, leaving the unresolved air quality issues from AMRUT 1.0.
- Non-Inclusive Governance Structure: The mechanically designed scheme without organic participation from elected city governments, making it less inclusive scheme for urban people.
What are the Steps Needed to Revamp AMRUT Scheme?
- Financial Challenges and Solutions: Local urban bodies need to diversify financial resources to implement local projects instead of relying on top-down funding approach.
- Holistic Approach: Considering the climate change , rainfall patterns, and existing infrastructure, urban water management should cater to the evolving challenges.
- The scheme needs nature-based solutions and a comprehensive methodology with a people-centric approach and empowering local bodies.
- Community Engagement: Encouraging participation from community groups, including NGOs and resident associations, can enhance the effectiveness of housing schemes by soliciting ideas and feedback from the grassroots level.
- Learning from Success Stories: Studying successful case studies where hygiene and sanitation were significantly improved, can provide valuable insights for addressing similar challenges in housing initiatives.
- For example, “Water Availability for All” initiative in Dahanu Taluka aimed at making potable drinking water available to local tribal communities.
- Innovation and Research: Establishing innovation hubs to foster industry-specific research and development related to health and housing issues can spur innovative solutions and technologies.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Discuss the challenges encountered in the implementation of the Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) scheme. Suggest potential strategies to overcome these challenges. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. With reference to Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission, consider the following statements: (2022)
1. Private and public hospitals must adopt it.
2. As it aims to achieve universal, health coverage, every citizen of India should be part of it ultimately.
3. It has seamless portability across the country.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2011)
In India, a Metropolitan Planning Committee
1. is constituted under the provisions of the Constitution of India.
2. prepares the draft development plans for metropolitan area.
3. has the sole responsibility for implementing Government sponsored schemes in the metropolitan area.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. With a brief background of quality of urban life in India, introduce the objectives and strategy of the ‘Smart City Programme.’ (2016)


Science & Technology
Philippines Halted Production of GM Crops
For Prelims: Genetically Modified Organism (GMO), DNA, Recombinant DNA Technology, Genetically Modified (GM) crops, Bt cotton, Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC), Dhara Mustard Hybrid-11 (DMH-11), ‘Early Heera-2’ mustard, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens,
For Mains: Implication of Genetically Modified Organism (GMO) on Human Health, Significance of Genetically Modified Crops in achieving Sustainable Development Goal 2: Zero Hunger.
Why in News?
Recently, a court in the Philippines has canceled the permits that allowed for the commercial cultivation of Genetically Modified (GM) Golden Rice and Bt Eggplant in the country.
- Critics argue that the decision could harm children with vitamin A deficiency, but the court's concerns about safety violations are being ignored.
Note
- In 2013, the World Health Organization (WHO) identified vitamin A deficiency as a public health issue that impacted approximately one third of children between the ages of 6 and 59 months, with the highest prevalence in sub-Saharan Africa (48%) and South Asia (44%).
What is GM Golden Rice and Bt Eggplant?
- GM Golden Rice:
- It was first developed in the late 1990s by researchers at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology and the International Rice Research Institute.
- Golden rice is a type of rice that has been genetically modified to have higher amounts of iron and zinc, as well as beta-carotene, which the body can turn into vitamin A.
- This rice gets its name from its distinctive yellow colour.
- This was developed to address vitamin A deficiency, a significant public health issue in many developing countries.
- Vitamin A deficiency is a major cause of blindness and increases the risk of death from common childhood illnesses, especially in low- and middle-income countries.
- Golden Rice has the potential to provide up to 50% of the recommended daily intake of vitamin A, helping to address this critical public health issue.
- Bt Eggplant:
- It was developed by the Indian seed company Mahyco (Maharashtra Hybrid Seeds Company) in collaboration with the University of Agricultural Sciences, Dharwad.
- Bt eggplant is a genetically modified variety of eggplant (Brijal) that has been engineered to produce a protein from the Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) bacteria, which is toxic to certain insect pests.
- This helps reduce the need for pesticide applications.
- It was approved for cultivation in Bangladesh in 2013, making it the first GM food crop to be approved in South Asia.
- In India, the commercial release of Bt eggplant was halted in 2010 due to concerns raised by environmental activists and some state governments.
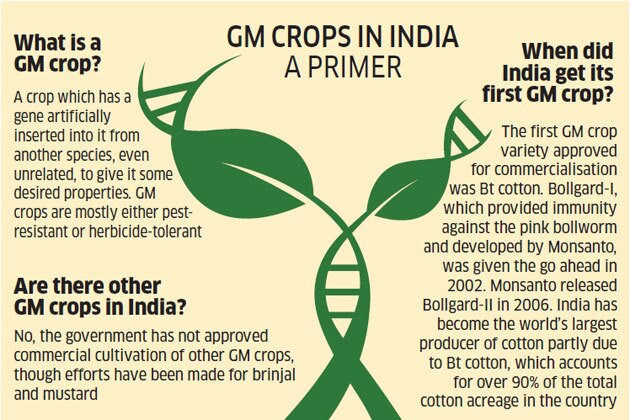
What are Genetically Modified (GM) Crops?
- About:
- Cultivation: Global Scenario and India:
- According to the International Service for the Acquisition of Agri-biotech Applications (ISAAA), the global area under GM crops reached 191.7 million hectares in 2020.
- India first and only commercially approved the cultivation of Bt cotton, a GM crop, in 2002.
- Since then, the area under Bt cotton has grown significantly, reaching 11.6 million hectares in 2020, which is 94% of the total cotton area in the country.
- GM Organism (GMO) vs Transgenic Organisms:
- GMO and transgenic organism are two terms that are used interchangeably.
- Although both have altered genomes, a transgenic organism is a GMO containing a DNA sequence or a gene from a different species.
- While a GMO is an animal, plant, or microbe whose DNA has been altered using genetic engineering techniques.
- Thus, all transgenic organisms are GMOs, but not all GMOs are transgenic.
- Potential Benefits of GM Crops:
- Increased Productivity: GM crops can be engineered to have higher yields, improved resistance to pests and diseases, and better tolerance to environmental stresses like drought, salinity, or extreme temperatures.
- Enhanced Nutritional Value: GM crops can be modified to have increased levels of vitamins, minerals, or other beneficial compounds, potentially improving food security and nutrition.
- Reduced Reliance on Pesticides: GM crops with built-in pest resistance can reduce the need for chemical pesticides, leading to lower environmental impact and reduced agricultural costs.
- Potential Concerns:
- Environmental Risks: There are concerns about the potential for GM crops to have unintended ecological consequences, such as the development of herbicide-resistant weeds or the impact on non-target organisms.
- Human Health Risks: Long-term effects of consuming GM foods on human health are not yet fully understood, and there are concerns about potential allergenicity or toxicity.
- Impact on Non-target Organisms: The possibility of unintended consequences on beneficial insects and other organisms in the ecosystem due to GM crops needs careful evaluation.
- Ethical and Socioeconomic Considerations: There are debates around the concentration of ownership and control of GM technologies, as well as the impact on small-scale farmers and traditional agricultural practices.
- Self-Terminating seeds (sterile seeds after plant harvest) produced by GM technology will make it impossible for farmers to use their traditional right to save the seed of their harvest for planting in the next crop season.
Fortification of Food
- It refers to addition of key vitamins and minerals such as iron, iodine, zinc, Vitamin A & D to staple foods such as rice, milk and salt to improve their nutritional content.
- Example, the addition of iodine to salt is crucial for preventing thyroid-related disorders.
- These nutrients may or may not have been originally present in the food before processing.
- It can be used to address the issue of high levels of malnutrition among women and children in India.
- In India, every second woman in the country is anemic and every third child is stunted.
- Rice Fortification:
- Fortifying rice is a cost-effective way to increase its vitamin and mineral content like iron, folic acid, and Vitamin B-12 and other micronutrients like zinc.
- Initiatives:
- Nationwide Fortification Regulations: In 2016, the FSSAI implemented regulations to fortify staple foods like wheat flour, rice, milk, and edible oil. This adds essential nutrients like iron, vitamin B12, folic acid, vitamins A & D, and iodine to commonly consumed items.
- Pilot Programs: Milk Fortification Project.
What is the Regulatory Framework for GM Crops in India?
- Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) is responsible for evaluating and approving the cultivation of GM crops.
- The committee is also responsible for appraisal of proposals relating to release of genetically engineered (GE) organisms and products into the environment including experimental field trials.
- GEAC is chaired by the Special Secretary/Additional Secretary of MoEF&CC and co-chaired by a representative from the Department of Biotechnology (DBT).
- GM foods are also subjected to regulations by the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) under the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006.
- Acts and Rules that Regulate GM Crops in India:
- Environment Protection Act, 1986 (EPA),
- Biological Diversity Act, 2002,
- Plant Quarantine Order, 2003,
- GM policy under Foreign Trade Policy, Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006,
- Drugs and Cosmetics Rule (8th Amendment), 1988.
Way Forward
- Strengthening the Regulatory Umbrella: The existing regulatory system should be bolstered with enhanced transparency, robust scientific evaluation processes, and clear communication with stakeholders. This will inspire public confidence and ensure responsible adoption of GM technology.
- Streamlining Approvals for Innovation: India can explore streamlining technology approval processes without compromising scientific rigour. Time-bound evaluations based on robust scientific data can expedite the introduction of beneficial GM crops while upholding safety standards.
- Science-Driven Decision Making: Policy decisions regarding GM crops should be firmly rooted in scientific evidence. Independent, transparent scientific assessments can guide regulatory processes and public discourse, fostering trust and informed decision-making.
- Rigorous Monitoring and Enforcement: A robust monitoring system is essential to ensure strict adherence to safety protocols throughout the GM crop cultivation cycle.
- Stringent enforcement mechanisms are crucial to prevent the spread of unapproved or illegal GM crops, safeguarding the integrity of the agricultural sector.
Conclusion
The debate around GM crops remains complex, with proponents highlighting the potential benefits and critics raising valid concerns. Continued research, transparent regulation, and inclusive stakeholder dialogue will be crucial in navigating the opportunities and challenges of this technology to ensure sustainable and equitable agricultural development.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Analyse the concerns associated with GM crops. How can India navigate these concerns to ensure the responsible adoption of this technology? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. Other than resistance to pests, what are the prospects for which genetically engineered plants have been created? (2012)
- To enable them to withstand drought
- To increase the nutritive value of the produce
- To enable them to grow and do photosynthesis in spaceships and space stations
- To increase their shelf life
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Mains:
Q. What are the present challenges before crop diversification? How do emerging technologies provide an opportunity for crop diversification? (2021)
Q. What are the research and developmental achievements in applied biotechnology? How will these achievements help to uplift the poorer sections of the society? (2021)
Q. How is science interwoven deeply with our lives? What are the striking changes in agriculture triggered off by science-based technologies? (2020)
Q. How was India benefited from the contributions of Sir M. Visvesvaraya and Dr. M.S. Swaminathan in the fields of water engineering and agricultural science respectively? (2019)


Important Facts For Prelims
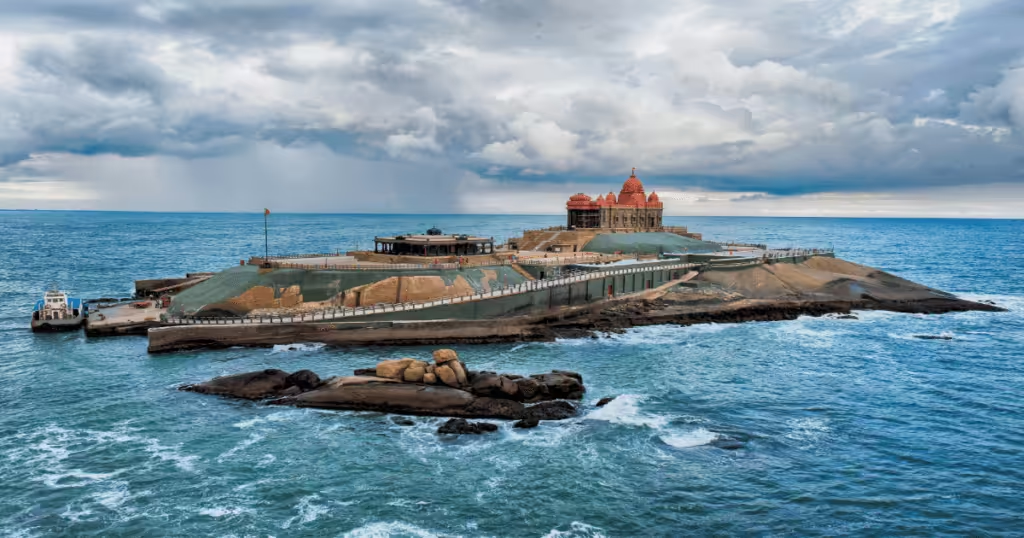
Kanyakumari’s Vivekananda Rock
Why in News?
Recently, the Prime Minister announced his plan to visit and meditate at the Vivekananda Rock Memorial in Kanyakumari, Tamil Nadu marking the culmination of the Lok Sabha election campaign.
What are the Key Facts Related to Vivekananda Rock Memorial?
- Swami Vivekananda's Spiritual Experience:
- In 1892, Swami Vivekananda was said to have swum to the rock from the shores of Kanyakumari for meditation. He spent three days and nights there, resulting in his enlightenment.
- Swami Vivekananda's letter to Swami Ramkrishnananda in 1894 suggests that his core philosophy crystallised after meditation at the Dhyan Mandapam on the rock.
- Location:
- The memorial stands on one of the two rocks located about 500 meters off the mainland of Vavathurai, Tamil Nadu.
- The Vivekananda rock is a small rocky islet, surrounded by the Laccadive Sea where the Bay of Bengal, the Indian Ocean and the Arabian Sea form a confluence presenting a picturesque view.
- The memorial consists of two main structures, viz Vivekananda Mandapam and Shripada Mandapam.
- Significance as a Memorial:
- The memorial was constructed to honour Swami Vivekananda, a prominent Indian spiritual leader.
- It was formally inaugurated in 1970 by the then-President of India, V V Giri.
What are the Key Facts About the Swami Vivekananda?
- Birth and Early Life:
- Swami Vivekananda, originally born as Narendranath Datta on 12th January 1863, hailed from a conventional Bengali family in Calcutta.
- His exceesive appetite for knowledge led him to explore various subjects, including philosophy, literature, Indian scriptures, as well as western philosophies.
- Towards Spiritualism:
- He became the chief disciple of the 19th-century mystic Ramakrishna Paramhansa in 1881.
- Initially sceptical of Ramakrishna's teachings, Vivekananda eventually embraced his guru's philosophy, leading to his initiation into monastic life.
- In 1893, upon the request of Maharaja Ajit Singh of the Khetri State, he took the name ‘Vivekananda.’
- Associated Organisations:
- The Ramakrishna movement (initiated by Vivekananda) had two goals:
- To train monks dedicated to a life of renunciation and practical spirituality to spread Vedanta teachings and
- To guide lay disciples to carry on preaching, philanthropic and charitable works.
- He established the Ramakrishna Mission in 1897 to fulfil the second objective of the Ramakrishna movement whereas Paramhansa himself fulfilled the first objective through Ramkrishna Math.
- The Ramakrishna movement (initiated by Vivekananda) had two goals:
- His Contributions:
- He introduced the world to the Indian philosophies of Vedanta and Yoga.
- He preached ‘neo-Vedanta’, an interpretation of Hinduism through a Western lens, and believed in combining spirituality with material progress.
- His powerful speech at the 1893 World Parliament of Religion in Chicago captivated the audience and placed Hinduism on the global stage.
- His teachings also offered different paths to spiritual liberation (moksha) through his writings, outlining the four yogas: Raja-yoga (yoga of the mind), Karma-yoga (yoga of action), Jnana-yoga (yoga of knowledge), and Bhakti-yoga (yoga of devotion).
- His famous quote, “Service of man is the service of God”,is still relevant today.
- Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose had called Vivekananda the “Maker of modern India.”
- National Youth Day is celebrated every year to observe the birth anniversary of Swami Vivekananda.
- He introduced the world to the Indian philosophies of Vedanta and Yoga.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Annie Besant was: (2013)
- Responsible for starting the Home Rule Movement
- The founder of the Theosophical Society
- Once the President of the Indian National Congress
Select the correct statement/statements using the codes given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans (c)
Q. Consider the following statements:
- Shah Abdul Aziz and Syed Ahmed Khan popularized the ideas of the Wahhabi Movement in India.
- Wahabi Movement was a revivalist movement which tried to purify Islam by eliminating all the un-Islamic practices.
- Wahabi’s played an important role in the revolt of 1857 in spreading anti-British feelings.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1 and 2 only
Ans (b)
Mains
Q. Several foreigners made India their homeland and participated in various movements. Analyse their role in the Indian struggle for freedom. (2013)


Important Facts For Prelims
Coal Gasification
Why in News?
The Ministry of Coal requested proposals from public and private sector participants for coal gasification projects as part of an Rs 8,500 crore viability gap funding (VGF) scheme.
- Viability Gap Funding (VGF) is a financial tool used to support projects that are economically justified but not financially viable on their own.
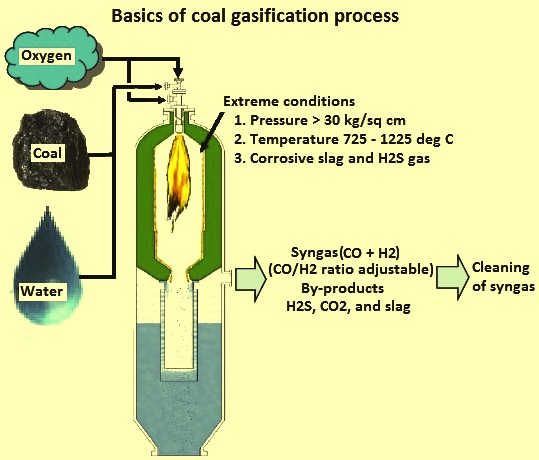
What is Coal Gasification?
- Coal gasification is a process that transforms Coal into a Synthetic gas (Syngas), consisting of mixture of gasses such as Carbon monoxide (CO), Hydrogen (H2), Carbon dioxide (CO2), Methane (CH4) and Water vapor (H2O).
- Coal is reacted at high temperatures (typically 1,000–1,400°C) with a controlled amount of oxygen and steam.
- Syngas can be used to produce a wide range of Fertilizers, Fuels, solvents and synthetic materials.
- The Process is as given:
- Preparation: Coal is crushed into a fine powder to increase its surface area and enhance the chemical reactions during the process.
- Gasification Reactor: The crushed coal is introduced into a high-temperature and high-pressure reactor along with limited oxygen or air and steam.
- Chemical Reactions: In the absence of sufficient oxygen for complete combustion, the coal undergoes a series of complex chemical reactions.
- These reactions break down the coal molecules into the components of syngas.
- Gas Cleaning: The raw syngas produced from the reactor contains impurities like tar, sulfur, and dust. These impurities need to be removed through a gas cleaning process before the syngas can be used further.
- Benefits of Coal Gasification:
- Cleaner Alternative to Coal Combustion: Coal gasification burns cleaner than coal for electricity. It captures pollutants before using the gas for power generation.
- Versatile Syngas Usage: The syngas produced can be used for various purposes, including electricity generation, production of cleaner fuels like hydrogen and production of chemicals like ammonia and methanol.
Note
- The Government is promoting coal-to-chemical and gasification processes due to the expected surplus of domestic coal in the future after meeting the power and other sectors' needs.
- India aims for 100 million tonnes (MT) coal gasification by 2030 with investments worth over Rs. 4 lakh crores.
- In addition to VGF, the government is supporting the coal industry in 2 ways:
- Long-term linkage window: This creates a stable market for coal producers.
- Coal utilization for gasification: Coal mine owners can use their coal for gasification projects and get a discount on revenue sharing.
- Production of coal and lignite reached 1 billion tonnes in FY 2024, target of 1.08 billion tonnes is set for the current fiscal year 2024-25.
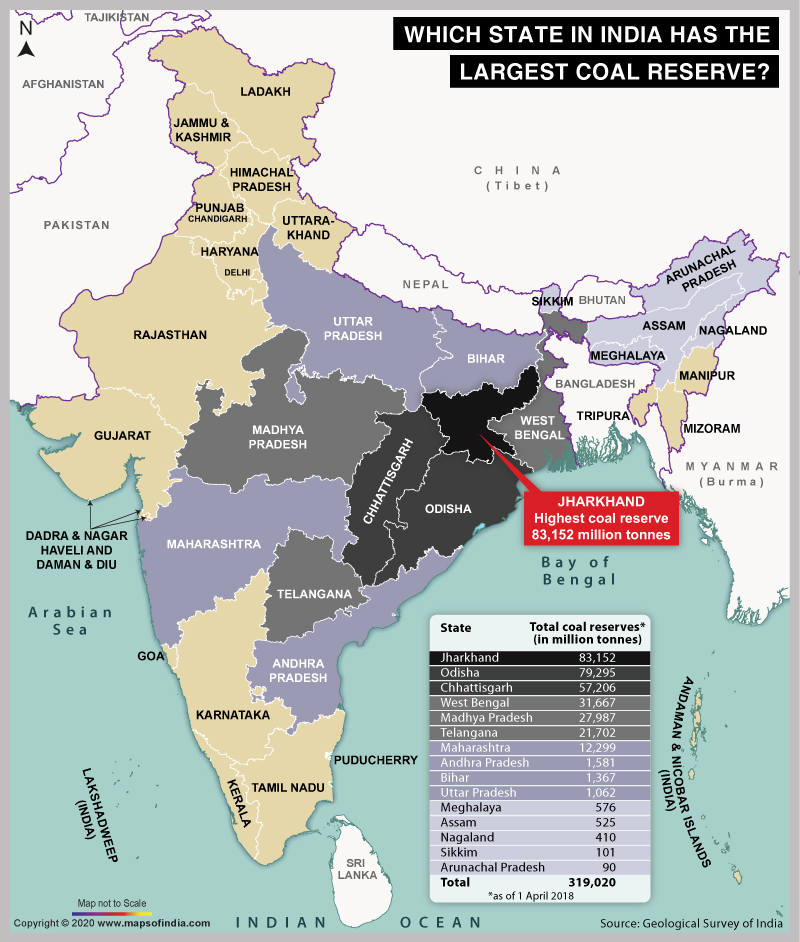
- India has the fourth largest coal reserves in the world, with reserves of 361.41 billion tonnes.
- Top 3 Coal Reserves: US, Russia and Australia.
- Top 3 Coal Production: China, India and US.
Read more: Coal Gasification, Coal Logistics Plan and Policy
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q1. Consider the following statements: (2019)
- Coal sector was nationalized by the Government of India under Indira Gandhi.
- Now, coal blocks are allocated on lottery basis.
- Till recently, India imported coal to meet the shortages of domestic supply, but now India is self-sufficient in coal production.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Q2. Which of the following is/are the characteristic/characteristics of Indian coal? (2013)
- High ash content
- Low sulphur content
- Low ash fusion temperature
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)


Rapid Fire
China’s Chang’e-6
Recently, China's Chang’e-6 probe successfully collected rock and soil samples from the moon's far side and lifted off from the lunar surface to return to Earth.
- The probe's landing site was the South Pole-Aitken Basin, an impact crater created more than 4 billion years ago, which is 13 kilometres deep and has a diameter of 2,500 kilometres.
- The landing site for Chandrayaan-3 was near the lunar south pole.
- The mission to the moon’s far side is challenging due to the lack of direct communication with Earth, requiring a relay satellite, and the rugged terrain with fewer flat landing areas.
- The mission is the sixth in the Chang’e moon exploration program, which is named after a Chinese moon goddess. It is the second design to bring back samples, following the Chang’e 5, which did so from the near side in 2020.
- China aims to land astronauts on the moon before 2030, and this mission is a significant step towards that goal.


Rapid Fire
OPEC+ Extends Deep Oil Output Cuts
OPEC+ decided to extend significant oil output cuts through 2025, surpassing market expectations to support prices amid sluggish demand, high interest rates, and increasing US production.
- According to its official website, the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC), established at the 1960 Baghdad Conference, is a permanent intergovernmental organisation with 12 member countries.
- Its headquarters is in the Austrian capital Vienna.
- OPEC member states produce about 40% of the world’s oil, and their exports comprise around 60% of the global petroleum trade.
- Before OPEC was formed, the international oil market was dominated by the “seven sisters” group of multinational energy companies.
- In 2016, OPEC and 10 other oil-producing countries, including Russia formed OPEC+ in response to plummeting oil prices due to increased U.S. shale oil output.


Rapid Fire
Diffraction-Based Tool to Detect Virus
Researchers have developed a method to identify infected cells by observing how they distort light.
- They tracked these distortions over time to mimic a progressing infection and compared them to healthy cells, identifying a unique 'fingerprint' for virus-infected cells.
- Researchers infected pig testicle cells with the pseudorabies virus, shone light through them, and observed distinct diffraction patterns based on contrast and texture.
- Diffraction refers to light waves spreading out after passing through narrow openings or around objects, creating patterns of light and dark stripes.
- The light-based technique detects infections in about two hours, costing a tenth of the required for traditional 40-hour chemical reagent methods, and avoids reagent-related delays and supply chain issues.
- The low cost and ease of use of the light-based detection method make it ideal for the early identification of viral infections in livestock and pets, aiding in breeding, preventing economic losses during outbreaks, and supporting the World Health Organization’s (WHO) rapid response recommendations, especially in resource-limited countries.
- Earlier, scientists have developed a highly accurate holographic imaging method using laser beams to detect viruses and antibodies within 30 minutes, utilizing xSight, an instrument by Spheryx.


Rapid Fire
Volcanism on Venus
Recent scientific analysis has revealed that Venus is more volcanically active than previously known.
- Active volcanic flows have been detected at 2 sites named the Eistla Regio region, which includes the Sif Mons volcano, and the expansive volcanic plain of Niobe Planitia. Earlier its erupting was detected in the 1990s.
- Also, a volcanic vent on Maat Mons in a region called Atla Regio, near the equator has expanded and changed shape.
- These along with additional evidence such as atmospheric sulfur dioxide variations, surface thermal emissions data, confirm volcanic activity on the planet.
Venus:
- Venus is often called Earth's twin is slightly smaller than Earth.
- It is the second planet from the Sun and the sixth largest planet.
- It is the hottest planet in our solar system.
- Venus spins from east to west, which is backward compared to most planets, and it has a day longer than its year.
Read More: Venus' Tectonic History, Venus Mission 2024 Active Volcanoes on Venus


Rapid Fire
Nelson Mandela Award for Health Promotion
Recently, the National Institute of Mental Health and Neuro Sciences (NIMHANS), Bengaluru, has been conferred the prestigious Nelson Mandela Award for Health Promotion by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the year 2024.
- It showcases the country's commitment to addressing mental health challenges and ensuring accessible mental health services for all.
- India has made significant progress in mental health with the establishment of a tele-mental health helpline (Tele MANAS) and Mental Health Units in almost all districts through the National Health Mission.
NIMHANS:
- It is a multi-disciplinary institute focused on both mental health and neuroscience through clinical care, education (undergraduate, postgraduate, PhD programs), and research.
- Established in 1974
- Declared Deemed University in 1994.
- It governed by the act of Parliament titled NIMHANS Act, 2012.
- Declared Institute of National Importance in 2012.
WHO Nelson Mandela Award for Health Promotion:
- Established: 2019, upon the initiative of African Region Health Ministers.
- Awarded to: Individuals, institutions, or NGOs that make significant contributions to health promotion.
Read more: Nelson Mandela - The Harbinger Of Equality In South Africa, Nelson Mandela's Influence on the United Nations and International Diplomacy