Biodiversity & Environment
Fukushima Water Issue
For Prelims: Fukushima nuclear power plant, Neighbouring Countries of Japan, Earthquake, Tsunami, International Atomic Energy Agency, UN General Assembly, UN Security Council
For Mains: Impacts of Earthquake and Tsunami and Nuclear Waste Disposal
Why in News?
Japan's plan to release over 1 million tons of water, which is claimed to be treated but potentially radioactive, from the Fukushima nuclear power plant into the sea, has sparked strong opposition and anxiety among neighboring countries, particularly South Korea.
 |
 |
What is the Fukushima Water Issue?
- About:
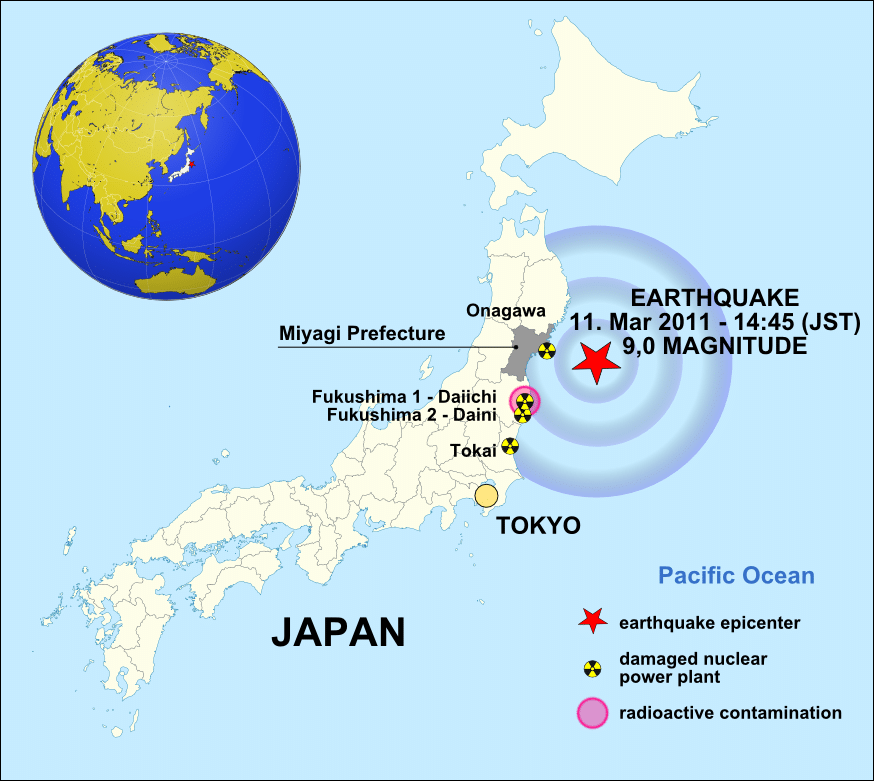
- The Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear power plant suffered a meltdown in 2011 after a massive earthquake and tsunami, releasing large amounts of radioactive materials into the environment.
- No deaths were initially attributed to the incident, although around 18,000 people lost their lives as a result of the earthquake and tsunami.
- Since then, Japan has been storing the cooling water for nuclear fuel and rain and groundwater seeping through the damaged reactor buildings in large tanks on site.
- Recent Developments of the Issue:
- The water is treated using a filtering system called Advanced Liquid Processing System (ALPS), which removes most of the radioactive elements except for tritium, a hydrogen isotope that is difficult to separate.
- Japan says it has no space to keep storing the water, and that releasing it into the sea.
- The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) is assisting Japan to release the water into the sea.
Note: Tritium is radioactive and has a half-life of about 12.5 years.
- Raised Concerns:
- South Korea fears that the water release will contaminate its waters, salt and seafood, affecting its fishing industry and public health.
- The increased demand for salt in South Korea has led to a nearly 27% price surge, attributed to both stockpiling and external factors like weather and lower production.
- China has also criticized Japan's plan, questioned its transparency and expressed concerns about the potential impact on the marine environment and global health.
What are the Other Major Nuclear Disasters of the World?
- Chernobyl Disaster (1986): One of the most well-known and severe nuclear disasters, the Chernobyl disaster took place in Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant in Ukraine.
- A sudden power surge during a safety test led to a series of explosions and fires that destroyed the reactor core and released large amounts of radioactive material into the atmosphere.
- Three Mile Island Accident (1979): This accident occurred in the United States at the Three Mile Island Nuclear Generating Station in Pennsylvania. A partial meltdown of the reactor's core resulted in the release of radioactive gases.
- Kyshtym Disaster (1957): It took place at the Mayak Production Association in the Soviet Union (now Russia).
- It involved a nuclear waste storage tank explosion, releasing a significant amount of radioactive materials into the environment.
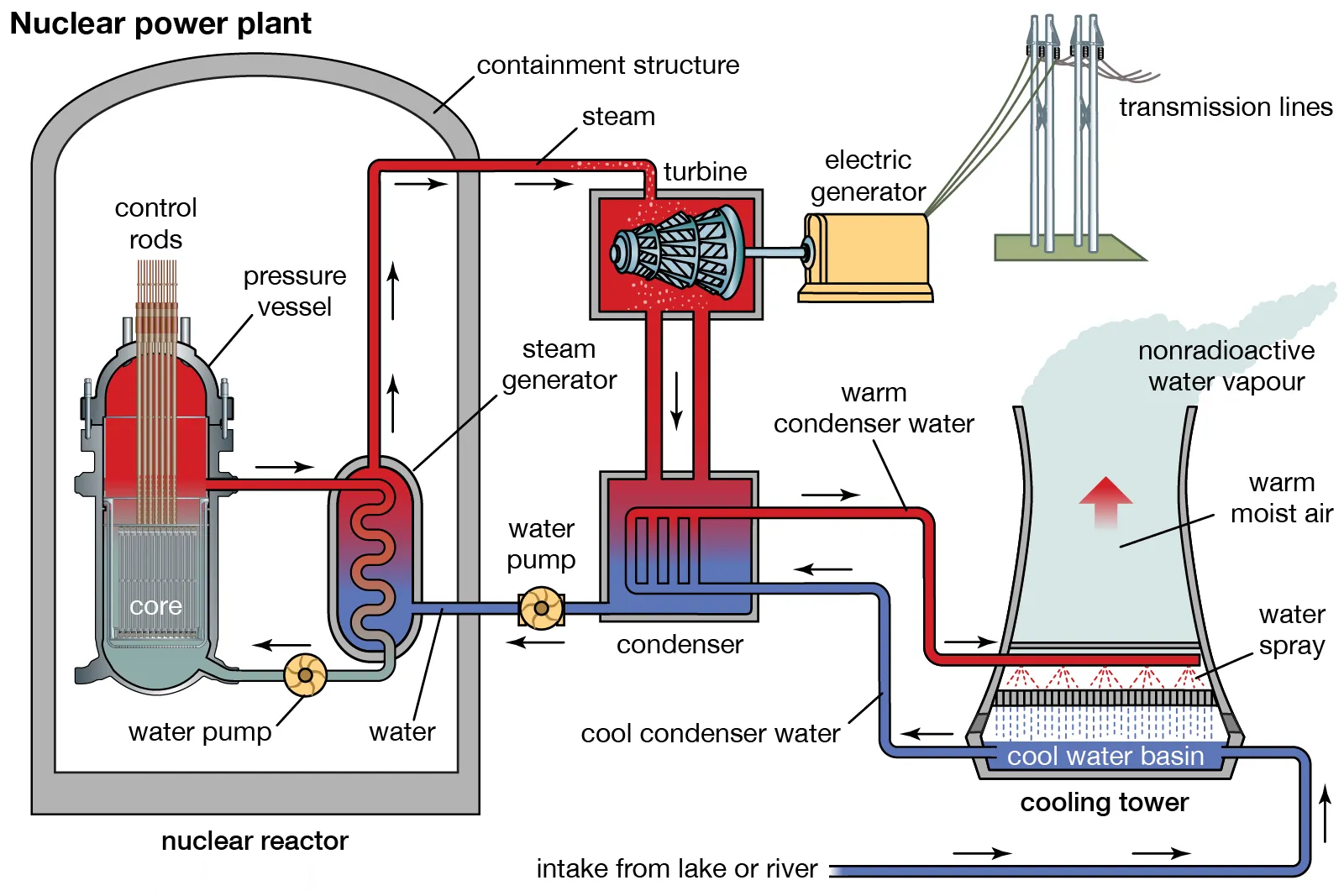
What is a Nuclear Power Plant?
- Nuclear power plants are a type of power plant that use the process of nuclear fission in order to generate electricity.
- In nuclear fission, atoms are split apart to form smaller atoms, releasing energy.
- Fission takes place inside the reactor of a nuclear power plant. At the center of the reactor is the core, which contains uranium fuel.
- In nuclear fission, atoms are split apart to form smaller atoms, releasing energy.
- The heat produced during nuclear fission in the reactor core is used to boil water into steam, which turns the blades of a steam turbine.
- As the turbine blades turn, they drive generators that make electricity.
- Nuclear plants cool the steam back into water in a separate structure at the power plant called a cooling tower, or they use water from ponds, rivers, or the ocean.
- The cooled water is then reused to produce steam.
International Atomic Energy Agency
- IAEA is an intergovernmental organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons.
- It was established in 1957 as the world’s “Atoms for Peace” organization within the United Nations family, and governed by its own founding treaty, the Statute of the IAEA.
- It reports to both the UN General Assembly and the UN Security Council, and is headquartered at the UN Office at Vienna, Austria
- In 2005, it was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize for their work for a safe and peaceful world.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q1. The function of heavy water in a nuclear reactor is to (2011)
(a) Slow down the speed of neutrons
(b) Increase the speed of neutrons
(c) Cool down the reactor
(d) Stop the nuclear reaction
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. With growing energy needs should India keep on expanding its nuclear energy programme? Discuss the facts and fears associated with nuclear energy. (2018)


International Relations
India- Philippines Ties
For Prelims: United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, South China Sea, Act East Policy, BrahMos, ASEAN, ASEAN-India Cooperation Fund, ASEAN-India Green Fund
For Mains: India- Philippines Relations
Why in News?
Recently, 5th meeting of the Joint Commission on Bilateral Cooperation was convened, between Indian External Affairs Minister and his Philippines counterpart.
- India and the Philippines are exploring various avenues to enhance their defence cooperation, with a particular emphasis on maritime security.
What are the Major Highlights of the Meet?
- Defense Cooperation: Both Ministers expressed keen interest to continue to work together on defense cooperation, including through the regular or upgraded official-level interaction among defense agencies, opening of a resident Defense Attache office in Manila, consideration of India’s offer for concessional Line of Credit to meet Philippines’ defense requirements.
- Maritime Security: Both countries aim to cooperate on maritime domain awareness (MDA), joint patrols, and information exchange to enhance MDA capabilities.
- Emphasizing the utility of MDA, the Ministers called for the early operationalization of the standard operating procedure for the White Shipping Agreement between the Indian Navy and the Philippines Coast Guard.
- Cyber Security Cooperation: Discussions focused on expanding cooperation in existing domains, including anti-terrorism measures and intelligence exchange. Both countries explored avenues for collaboration in cyber security, artificial intelligence, and space cooperation.
- Regional and International Issues: The Ministers engaged in wide-ranging discussions on regional and international issues of mutual interest for e.g., China’s growing assertiveness and territorial claims in the South China Sea.
- Emphasizing the need for a peaceful settlement of disputes and adherence to international law, including the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) and the 2016 Arbitral Award on the South China Sea.
How is India’s Relations with Philippines?
- About: India and the Philippines are two democratic countries in the Indo-Pacific region that share common approach towards the Indo-Pacific, emphasizing the importance of a free, open, and stable region.
- Political Relations: India and the Philippines formally established diplomatic relations on 26 November 1949, shortly after both countries gained independence. (Philippines in 1946 and India in 1947).
- When India launched Look East Policy and intensified partnership with Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) in 1992, it also resulted in intensified relations with the Philippines both bilaterally and in the regional context.
- With the Act East Policy (2014), the relationship with the Philippines has diversified further into political-security; trade and industry, etc.
- Economic Relations: India is currently the Philippines' fifteenth largest trading partner, with trade worth approximately USD 3 billion in the 2022.
- Also, Philippines has been a net importer in goods trade with India.
- Defence Cooperation: India and the Philippines have a growing defense and security partnership. One of the most significant developments in defence cooperation between India and the Philippines is the BrahMos missile deal, which is expected to be finalised soon.
- The BrahMos is a supersonic cruise missile co-developed by India and Russia, which can be launched from land, sea or air platforms.
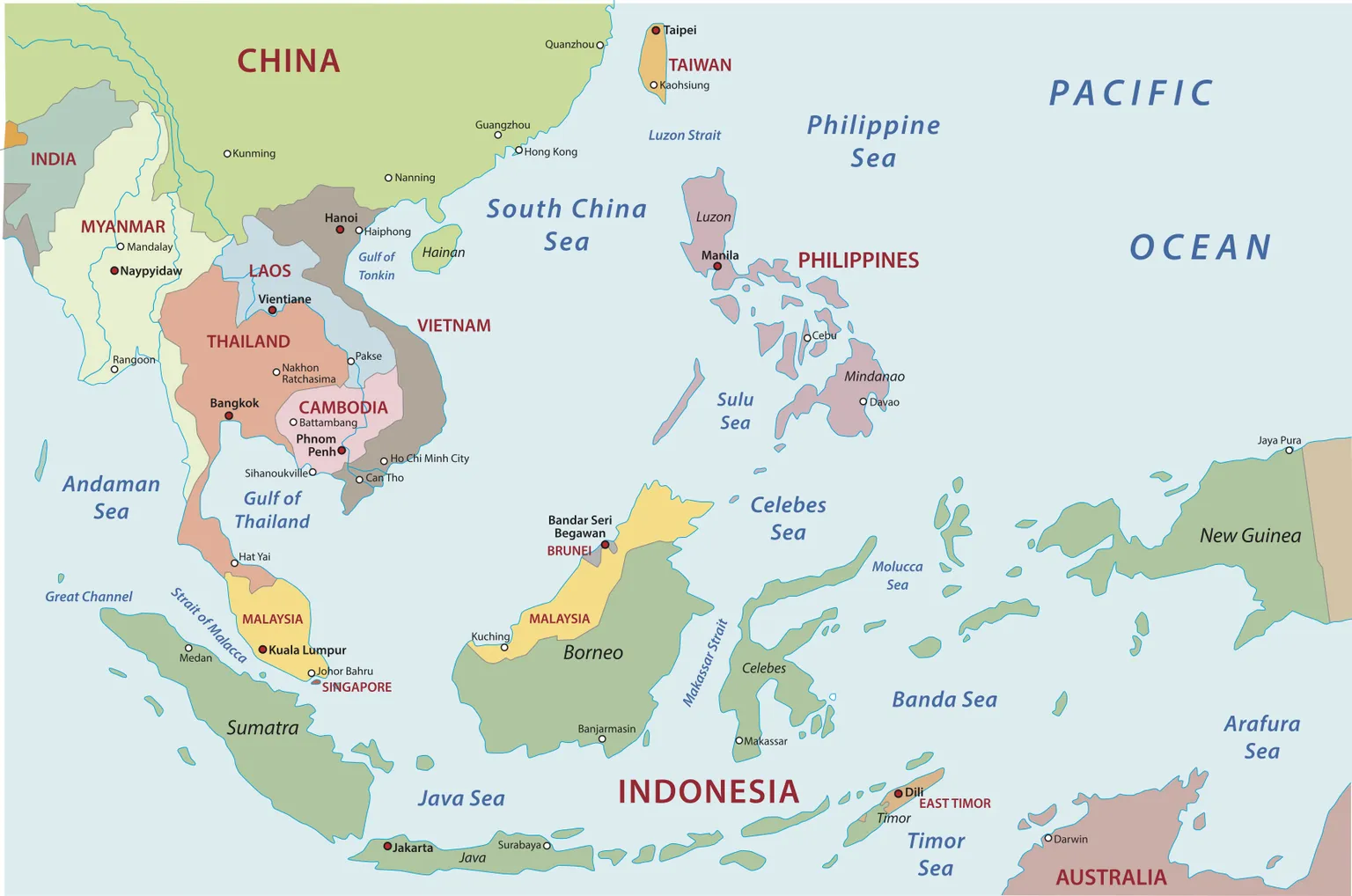
What are the Key Facts About Philippines?
- The Philippines is an archipelago located in Southeast Asia, bordered by the Philippine Sea to the east, the South China Sea to the west, and the Celebes Sea to the south.
- It consists of 7,641 islands, with Luzon and Mindanao being the largest.
- The capital city is Manila, situated on Luzon Island.
- Mount Apo (2,954 meters) on Mindanao Island is the highest peak, and it is an active volcano.
- The Philippines has a tropical climate with high temperatures and humidity year-round, experiencing wet and dry seasons.
- The Philippines is considered one of the world's biodiversity hotspots.
- The Philippines is also a part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, which makes it geologically active. It has more than 20 active volcanoes, including Mayon (recently erupted in 2023), Taal, and Mount Pinatubo (erupted in 1991).
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. Consider the following countries: (2018)
- Australia
- Canada
- China
- India
- Japan
- USA
Which of the above are among the ‘free-trade partners’ of ASEAN?
(a) 1, 2, 4 and 5
(b) 3, 4, 5 and 6
(c) 1, 3, 4 and 5
(d) 2, 3, 4 and 6
Ans: (c)
Q2. The term ‘Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership’ often appears in the news in the context of the affairs of a group of countries known as (2016)
(a) G20
(b) ASEAN
(c) SCO
(d) SAARC
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Evaluate the economic and strategic dimensions of India’s Look East Policy in the context of the post-Cold War international scenario. (2016)


Indian Economy
Open Market Sale Scheme for Wheat and Rice
For Prelims: Food Corporation of India, Open Market Sale Scheme, Wheat, Rice
For Mains: Role of OMSS to enhance food grain supply, Food Corporation of India (FCI) in managing the food security.
Why in News?
Recently, in response to the Food Corporation of India's (FCI) imposition of quantity restrictions and denial of states' participation in the Open Market Sale Scheme (OMSS), states have been exploring alternative methods to procure wheat and rice.
What is the Open Market Sale Scheme?
- About:
- The OMSS is a program implemented by the FCI to facilitate the sale of surplus food grains, primarily wheat, and rice, from the central pool in the open market.
- Purpose and Objectives:
- Enhance food grain supply during lean seasons.
- Moderate open market prices and control inflation.
- Ensure food security and availability of grains in deficit regions.
- Facilitate the sale of surplus food grains from the central pool.
- Implementation and Process:
- Conduct e-auctions by the FCI for traders, bulk consumers, and retail chains to purchase specified quantities of food grains at pre-determined prices.
- Allow states to procure additional food grains through OMSS for distribution under the National Food Security Act,2013 (NFSA).
- FCI conducts weekly auctions for the OMSS for wheat on the platform of the National Commodity and Derivatives Exchange Limited (NCDEX).
- NCDEX is a commodity exchange platform in India that provides a platform for trading in various agricultural and other commodities.
What are the Recent Revised OMSS Restrictions?
- Revised OMSS Restrictions:
- The OMSS underwent a recent revision with a focus on limiting the quantity that a single bidder can purchase in a single bid.
- Previously, the maximum allowed quantity per bid was 3,000 metric tonnes. However, it has now been reduced to a range of 10-100 metric tonnes.
- The aim of this change is to promote wider participation by accommodating small and marginal buyers.
- By encouraging competitive bids from smaller buyers, the revised OMSS seeks to curb retail prices and create a more level playing field.
- Discontinuation of OMSS Sales to States:
- The Centre decided to discontinue the sale of rice and wheat from the central pool to state governments under the OMSS.
- Additionally, private bidders are no longer allowed to sell their OMSS supplies to states.
- The rationale behind this decision is to control inflationary trends and maintain adequate stock levels in the central pool.
- By ensuring that food security obligations are met, the discontinuation of OMSS sales to states aims to streamline the distribution and allocation of food grains.
How have the States Reacted?
- Karnataka and Tamil Nadu have criticized the Centre's decision.
- Karnataka has temporarily replaced its free grain distribution scheme for below-poverty-line (BPL) families, known as the Anna Bhagya Scheme, with cash transfers to beneficiaries due to being unable to procure enough rice in the market at a reasonable cost in time to meet the requirements of the scheme.
What is the Food Corporation of India?
- FCI is a statutory body set up in 1965 under the Food Corporations Act of 1964. It was established against the backdrop of a major shortage of grains, especially wheat.
- The FCI manages the food security system in India.
- The FCI also maintains buffer stocks of food grains to ensure food security during times of scarcity or crisis.
- The FCI is also responsible for distributing foodgrains throughout the country for the public distribution system.
- FCI also conducts e-auction as one of the methods to dispose of its surplus food grains.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. With reference to the provisions made under the National Food Security Act, 2013, consider the following statements: (2018)
- The families coming under the category of ‘below poverty line (BPL)’ only are eligible to receive subsidised food grains.
- The eldest woman in a household, of age 18 years or above, shall be the head of the household for the purpose of issuance of a ration card.
- Pregnant women and lactating mothers are entitled to a ‘take-home ration’ of 1600 calories per day during pregnancy and for six months thereafter.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 3 only
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q.1 In what way could replacement of price subsidy with Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) change the scenario of subsidies in India? Discuss. (2015)


Biodiversity & Environment
Additions to India's Faunal and Floral Databases
For Prelims: Zoological Survey of India, Botanical Survey of India, Bamboo-dwelling bat, Macaque, Western Ghats
For Mains: India's Faunal and Floral Diversity
Why in News?
India witnessed significant advancements in its biodiversity knowledge in the year 2022 with the addition of numerous animal and plant species to its faunal and floral databases.
- The findings were compiled in two publications: "Animal Discoveries - New Species and New Records 2023" by the Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) and "Plant Discoveries 2022" by the Botanical Survey of India (BSI).
What are the Major Additions in India’s Faunal and Floral Database?
- Faunal Discoveries:
- In 2022, India added a total of 664 animal species to its faunal database. This includes 467 new species and 197 new records, which are species found in India for the first time.
- The discoveries encompassed various categories: three new species and one new record of mammals, two new records of birds, 30 new species and two new records of reptiles, 6 new species and one new record of amphibians, and 28 new species and eight new records of fish.
- Invertebrates accounted for the majority of new faunal discoveries with 583 species, while vertebrates constituted 81 species.
- Insects comprised the largest group among invertebrates, and fish dominated among vertebrates.
Note:
- Vertebrates: Animals with a backbone/spine, well-developed internal skeleton, distinct head with a brain, bilateral symmetry, and complex internal organs. Examples: mammals, birds, reptiles.
- Invertebrates: Animals without a backbone/spine, typically have an exoskeleton or soft body varying body plans, and simpler internal organ systems. Examples: insects, worms, jellyfish.
- Kerala recorded the highest number of new discoveries, contributing 14.6% of the total, followed by Karnataka (13.2%) and Tamil Nadu (12.6%).
- The Andaman and Nicobar Islands, West Bengal, and Arunachal Pradesh also made significant contributions.
- The new mammal species included Miniopterus phillipsi, a long-fingered bat, and Glischropus meghalayanus, a bamboo-dwelling bat, both found in Meghalaya.

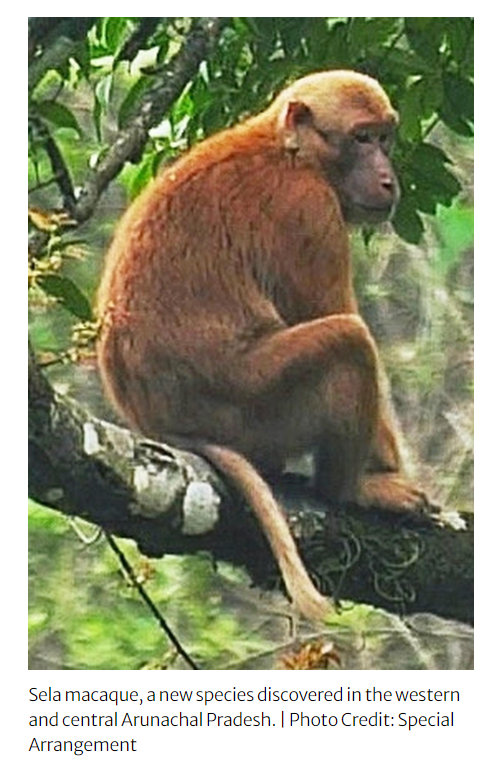
- Another significant discovery was the Sela macaque (Macaca selai), a new macaque species found in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Notable new records include the sighting of Macaca leucogenys, a white-cheeked macaque, in West Siang, Arunachal Pradesh that was previously found in southeastern Tibet.
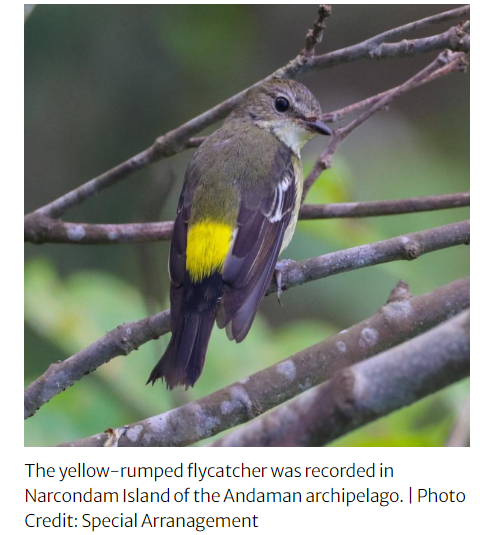
- The yellow-rumped flycatcher (Ficedula zanthopygia) was also found in Narcondam Island of the Andaman archipelago after being known from various other regions.
- With the addition of these new discoveries and records, India's faunal diversity increased to 103,922 species.
- Floral Discoveries:
- India added 339 new plant taxa to its floral database in 2022, consisting of 186 taxa new to science and 153 taxa as new distributional records within the country.
- The discoveries encompassed various plant groups: 37% seed plants, 29% fungi, 16% lichens, 8% algae, 6% bryophytes, 3% microbes, and 1% pteridophytes.
- Seed plants constituted the largest proportion of new discoveries, with dicotyledons accounting for 73% and monocotyledons for 27%.
Note:
- Dicotyledons (Dicots): Dicotyledons are plants that have embryos with two cotyledons or seed leaves.
- They encompass a wide range of plants such as trees, shrubs, herbs, and many familiar flowering plants like roses.
- Monocotyledons (Monocots): Monocotyledons are plants that have embryos with a single cotyledon or seed leaf.
- Monocots include plants such as grasses, corn, orchids, and onion.
- The Western Himalayas and the Western Ghats were the regions where a significant number of discoveries were made, contributing 21% and 16% respectively.
- Kerala stood out as the state with the highest number of plant discoveries, accounting for 16.8% of the total.
- Among the notable plant discoveries were the new genera Nandadevia Pusalkar, found in the Uttarakhand Himalayas, and Nilgiriella Pusalkar, endemic to the southern Western Ghats in Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu.
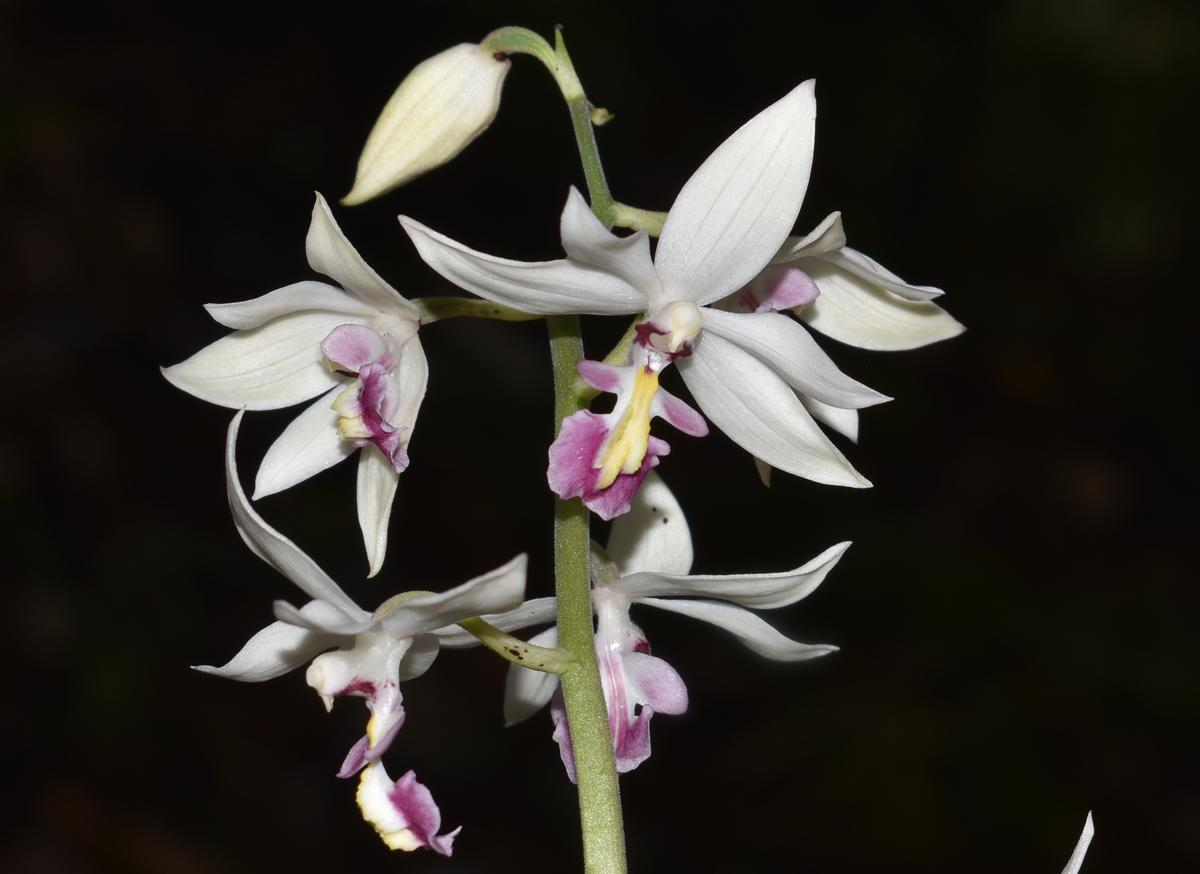
- Additionally, Calanthe lamellosa, an orchid species previously recorded in China and Myanmar, was found for the first time in India in the Japfu mountain range in Kohima, Nagaland.
Botanical Survey of India
- It is the apex research organization under the Ministry of Environment and Forests (MoEFCC) for carrying out taxonomic and floristic studies on wild plant resources of the country. It was established in 1890.
- It has nine regional circles situated at different regions of the country. However the headquarter is in Kolkata, West Bengal.
Zoological Survey of India
- ZSI is also a subordinate organization of the MoEFCC and was established in 1916 as a national center for the faunistic survey and exploration of the resources leading to the advancement of knowledge on the exceptionally rich faunal diversity of the country.
- ZSI has its headquarters at Kolkata and 16 regional stations located in different geographic locations of the country.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Recently, our scientists have discovered a new and distinct species of banana plant which attains a height of about 11 meters and has orange coloured fruit pulp. In which part of India has it been discovered? (2016)
(a) Andaman Islands
(b) Anaimalai Forests
(c) Maikala Hills
(d) Tropical rain forests of northeast
Ans: (a)
Q. Biodiversity forms the basis for human existence in the following ways: (2011)
- Soil formation
- Prevention of soil erosion
- Recycling of waste
- Pollination of crops
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. How does biodiversity vary in India? How is the Biological Diversity Act,2002 helpful in the conservation of flora and fauna? (2018)


Important Facts For Prelims
Global Environment Facility
Why in News?
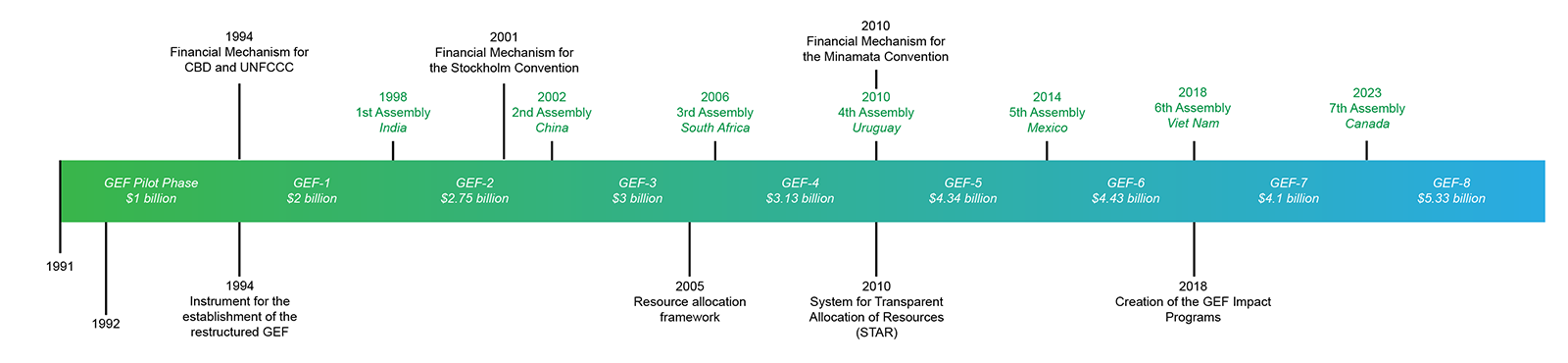
Recently, at the 64th Global Environment Facility (GEF) council meeting in Brazil, the governing body approved the disbursement of USD 1.4 billion to accelerate efforts to tackle the climate, biodiversity and pollution crises.
- This is the 2nd work program of the GEF-8 funding period, which runs from 2022 and 2026.
What are the Key Highlights of the Meet?
- Global Biodiversity Framework Fund:
- The Governing board has approved the establishment of a new fund, the Global Biodiversity Framework Fund (GBFF), to finance the implementation of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework.
- This fund is crucial as nearly 50% of its resources will be allocated to biodiversity-related work during the GEF-8 period.
- Fund Allocations:
- 20% will be allocated to Indigenous Peoples and local communities (IPLCs), 25% to GEF agencies, 36% to SIDS (Small Island Developing States), and 3% to LDCs (Least Developed Countries).
- The allocation for IPLCs will be reviewed two years after the ratification in August, while the allocations for SIDS and LDCs will be reviewed three years after ratification.
What is Global Environment Facility?
- The GEF was established on the eve of the 1992 Rio Earth Summit.
- It is a family of funds dedicated to confronting biodiversity loss, climate change, pollution, and strains on land and ocean health.
- It has a unique governing structure organized around an Assembly, the Council, the Secretariat, 18 agencies, a Scientific and Technical Advisory Panel, and the Evaluation Office.
- It provides Financial Assistance for five major International Conventions:
- The Minamata Convention on Mercury (signed in 2013 and entered into force in 2017).
- The Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) (adopted in 2001 and entered into force in 2004).
- The United Nations Convention on Biological Diversity (UNCBD ) (entered into force in 1993).
- The United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD) (adopted in 1994).
- The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) (signed in 1992 and entered into force in 1994).
- It has 184 member countries, including India.
- Its secretariat is based in Washington, D.C.
- The World Bank serves as the GEF Trustee, administering the GEF Trust Fund (contributions by donors).
What is GEF Council?
- The Council, the GEF's main governing body, comprises 32 members appointed by constituencies of GEF member countries (14 from developed countries, 16 from developing countries, and two from economies in transition).
- India has formed a permanent Constituency in the Executive Council of the GEF together with Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Bhutan, Nepal and Maldives.
- Council members rotate at different intervals determined by each constituency.
- The Council meets twice annually.
- The Council develops, adopts and evaluates the operational policies and programs for GEF-financed activities.
- It also reviews and approves the work program (projects submitted for approval), making decisions by consensus.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. With reference to ‘Global Environment Facility’, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2014)
(a) It serves as financial mechanism for ‘Convention on Biological Diversity’ and ‘United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change’
(b) It undertakes scientific research on environmental issues at global level
(c) It is an agency under OECD to facilitate the transfer of technology and funds to underdeveloped countries with specific aim to protect their environment
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Ans: (a)


Governance
Panchayat Development Index Report
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Minister of State for Panchayati Raj released the Report on Panchayat Development Index (PDI) at the National Workshop on Panchayat Development Index in New Delhi.
What is the Panchayat Development Index?
- About:
- The PDI is a composite index that measures the performance of panchayats in achieving the Localization of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- It provides a holistic and evidence-based assessment of the development status of panchayats, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses.
- Objective:
- The PDI aims to promote the Localization of SDGs by creating awareness among panchayats and stakeholders about their importance.
- It encourages panchayats to adopt best practices and innovations to improve their performance in achieving SDGs.
- Ranking and Categorization:
- The PDI provides rankings for panchayats at different levels, including district, block, and village, based on their overall scores.
- Panchayats are categorized into four grades: D (scores under 40%), C (40-60%), B (60-75%), A (75-90%), and A+ (above 90%).
- Themes and Focus Areas:
- The PDI considers nine themes, including poverty-free and enhanced livelihood, healthy village, child-friendly village, water-sufficient village, clean and green village, self-sufficient infrastructure, socially just and secured villages, good governance, and women-friendly village.
- Applications and Benefits of the PDI:
- The PDI can be used by states/union territories for Panchayati Raj Awards and to emphasize a data-driven and evidence-based approach to development.
- It serves as a tool for planning, monitoring, and evaluating schemes implemented by panchayats and other agencies aligned with the SDGs.
- The PDI facilitates the sharing of knowledge and experiences among panchayats and stakeholders for learning and replication of successful models and interventions.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report on the PDI?
- The pilot project was carried out in four districts of Maharashtra, namely Pune, Sangli, Satara, and Solapur.
- The data collected from the pilot project was used to compile the report of the Panchayat Development Index Committee.
- The pilot study showed that 70% of the panchayats in the four districts of Maharashtra fall in Category C, while 27% are in Category B.
- The report highlights the need for evidence-based planning, resources must be deployed where required for overall development.
What is Panchayati Raj Institution (PRI)?
- PRI is a system of rural local self-government in India.
- Local Self Government is the management of local affairs by such local bodies who have been elected by the local people.
- PRI was constitutionalized through the 73rd Constitutional Amendment Act, 1992 to build democracy at the grass roots level and was entrusted with the task of rural development in the country.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. The fundamental object of Panchayati Raj system is to ensure which among the following? (2015)
- People’s participation in development
- Political accountability
- Democratic decentralization
- Financial mobilization
Select the correct answer using the code given below
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- The most fundamental objective of the Panchayati Raj system is to ensure people’s participation in development and democratic decentralization.
- Establishment of Panchayati Raj Institutions does not automatically lead to political accountability.
- Financial mobilization is not the fundamental objective of Panchayati Raj, although it seeks to transfer finances and resources to the grass root government.


Important Facts For Prelims
PEN Pinter Prize 2023
Why in News?
Michael Rosen, a renowned poet and writer, has been recognized for his literary contributions and honored with the prestigious PEN Pinter Prize 2023.
- Rosen is known for making poetry accessible to children through his work and performances. His themes are often social, political and ethical.
What is the History and Purpose of the PEN Pinter Prize?
- The PEN Pinter Prize was established in 2009 by English PEN, the founding centre of a global literary network that promotes literature and human rights.
- The prize was named after Harold Pinter, who was a vice president of English PEN and an active member of the International PEN Writers in Prison Committee (WiPC).
- It was inspired by Pinter’s Nobel Prize acceptance speech in 2005, titled “Art, Truth and Politics”, in which he spoke about the role of the writer as a “citizen of the world” who questions and exposes the lies of power.
- The prize aims to recognise writers who use their words to defend the dignity and rights of others.
- The Prize is awarded annually to a writer resident in the United Kingdom, the Republic of Ireland, the Commonwealth or former Commonwealth.
- The winner must the author of a significant body of plays, poetry, essays, or fiction of outstanding literary merit, written in English.
- Past recipients of the prestigious award include Hanif Kureishi, Lemn Sissay, and Malorie Blackman.
What are the Other Major Literacy Awards?
- International:
- Nobel Prize in Literature ( 2022- Annie Ernaux)
- Booker Prize
- The UNESCO King Sejong Literacy Prize
- Indian:


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Preparedness for Vector-Borne Diseases
Recently, Union Health Minister virtually assessed state readiness in preventing and controlling vector-borne diseases before the monsoon season, emphasizing proactive measures and the importance of anticipating health requirements to reduce disease burden.
Vector-borne diseases are a group of illnesses transmitted to humans through the bite of infected vectors such as mosquitoes, ticks, fleas, and flies. These diseases include malaria, dengue fever, chikungunya, Japanese encephalitis, lymphatic filariasis, and kala-azar. They are typically seasonal and prone to outbreaks, with most occurring during the monsoon and post-monsoon periods.
Read more: Dengue, Kala-azar Disease, Japanese encephalitis, malaria
India Post and Canada Post Introduce ITPS for E-commerce
India Post and Canada Post have recently signed an agreement to launch the International Tracked Packet Service (ITPS) between the two countries. This service is effective from July 01, 2023.
The ITPS is a competitive service for the transmission and delivery of packets and has been designed to meet the cross-border shipping requirements of e-commerce exporters including MSMEs, small businesses, merchants, etc to promote exports of their products using local post offices. The ITPS, already available with 38 partner countries, including recent additions like Britain, France, UAE, and Egypt, will now include Canada as its 39th partner.
The ITPS rates are kept very economical in comparison to International EMS (Speed Post) and other market products.
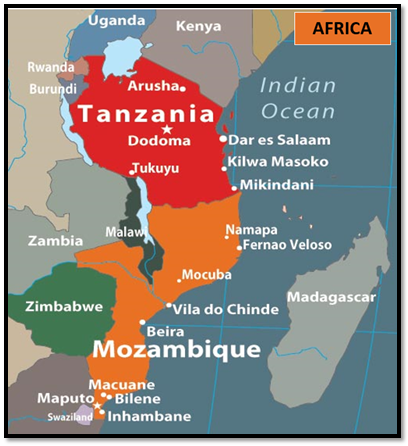
INS Sunayna Visit to Beira, Mozambique
INS Sunayna, a naval vessel of the Indian Navy, recently made a port visit to Beira, Mozambique, highlighting India's commitment to fostering cordial relations with its maritime neighbors and promoting the vision of Security and Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR).
The deployment of INS Sunayna also includes a scheduled joint Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) patrol off the coast of Mozambique, enhancing the security cooperation between the two countries.
SAGAR was launched in 2015. It is India’s strategic vision for the Indian Ocean Region (IOR). Through SAGAR, India seeks to deepen economic and security cooperation with its maritime neighbours and assist in building their maritime security capabilities.
Read more: Security and Growth for All in the Region, Exclusive Economic Zone.
India Claims Eighth Asian Kabaddi Championship Title
India emerged victorious in the Asian Kabaddi Championship 2023, clinching the title for the eighth time in nine editions. The final took place in Busan, South Korea. The Indian kabaddi teams will now set their sights on the upcoming Asian Games in Hangzhou, China, scheduled from September 23 to October 8, 2023. The 1st Asian Kabaddi Championship was held in 1980 and was included as a demonstration game in the 9th Asian Games, New Delhi in 1982.
Kabaddi is best known Indian Traditional Game which basically a combative sport, with seven players on each side; played for a period of 40 minutes with a 5 minutes break (20-5-20). The core idea of the game is to score points by raiding into the opponent’s court and touching as many defense players as possible without getting caught on a single breath.
The All-India Kabaddi Federation was formed in 1950 to look after the promotion of the game. The new body, Amateur Kabaddi Federation of India (AKFI) came into existence from 1972 affiliated to Indian Olympic Association (IOA) with a view to popularize the game in India & neighboring countries of Asia.
Read more: Role of Sport in Aspirational India