India-Italy Migration and Mobility Agreement
For Prelims: India-Italy Migration and Mobility Agreement, European Union, Location of Italy, India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor, Global Biofuel Alliance, Blue-Raman project
For Mains: Areas of Cooperation Between India and Italy
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Cabinet granted ex-post facto approval to the Migration and Mobility Agreement between India and Italy.
What is Migration and Mobility Agreement between India and Italy?
- About:
- The agreement is set to strengthen cooperation on issues related to irregular migration while bolstering people-to-people ties between India and Italy.
- It facilitates mobility for various segments, including students, skilled workers, businesspersons, and young professionals, fostering exchange and collaboration.
- Key Provisions:
- Temporary Residence for Indian Students: Graduates seeking professional exposure in Italy post-academic or vocational training can secure temporary residency for up to 12 months.
- Reserved Quotas for Workers: The agreement outlines quotas for non-seasonal and seasonal Indian workers, with a reserved quota range over the years 2023-2025 under the existing Flows Decree.
- The Italian government's annual "Flow Decree" (Decreto Flussi) sets the maximum number of non-EU citizens who can enter Italy for work and self-employment
- Implementation:
- The agreement will remain in force for 5 years, with automatic renewal unless terminated.
- A Joint Working Group (JWG) will oversee its implementation, convening periodically to evaluate progress and propose supportive measures for effective execution.
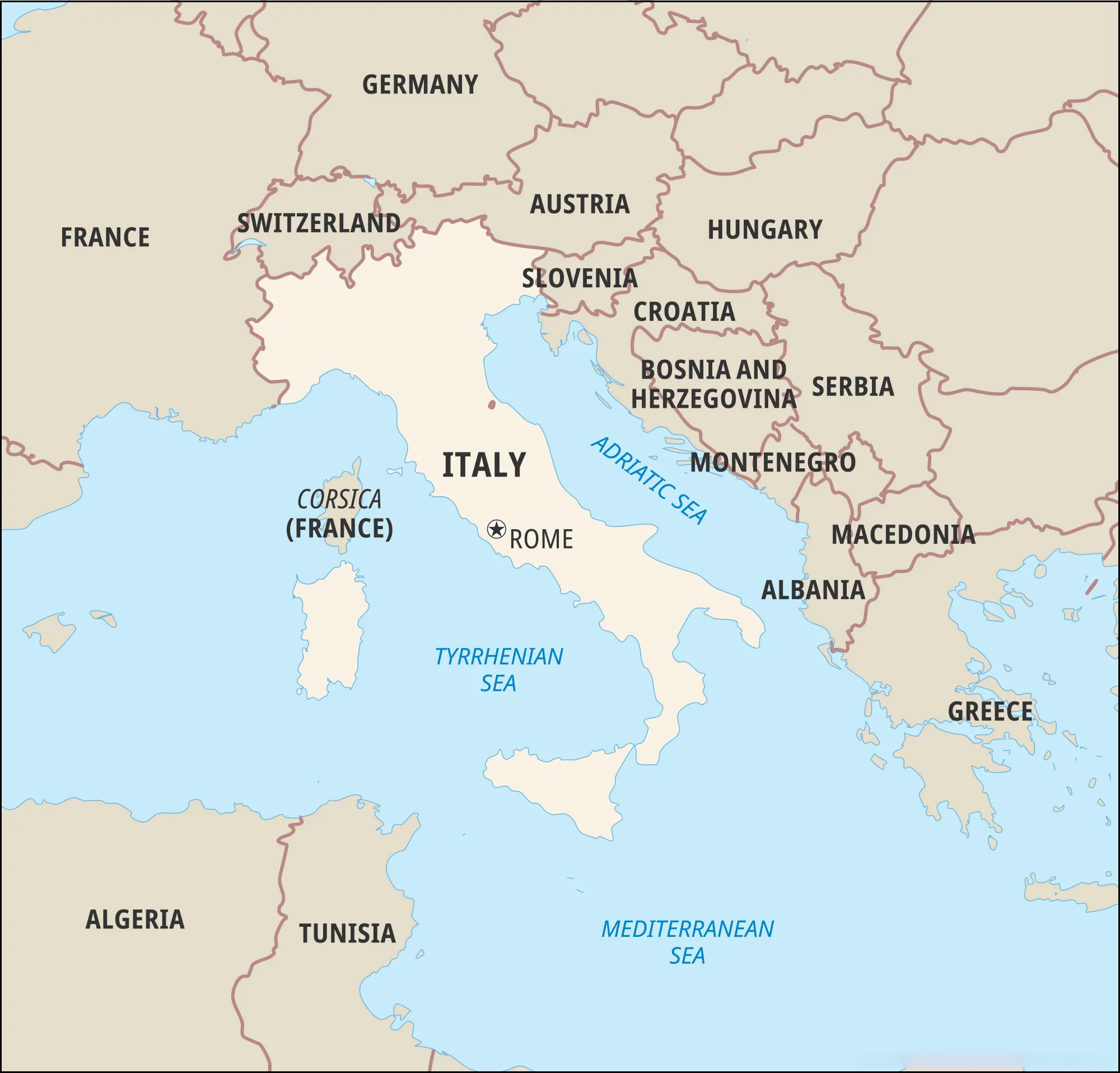
Key Facts About Italy
- About:
- Italy is a boot-shaped peninsula that juts out of southern Europe into the Adriatic Sea, Tyrrhenian Sea, Mediterranean Sea, and other waters.
- Bordering Countries:
- Italy has international borders with Austria, France, the Holy See (Vatican City), San Marino, Slovenia, and Switzerland.
- Italy also shares maritime borders with Albania, Algeria, Croatia, Greece, Libya, Malta, Montenegro, Spain, and Tunisia.
- Form of Government: Republic
- Capital: Rome
- Money: Euro
- Major Mountains: Alps, Apennines
- Major Rivers: Po, Adige, Arno, Tiber
What are the Other Areas of Cooperation Between India and Italy?
- Historical Ties:
- India and Italy are ancient civilizations but young states. Italian port cities were important trading posts on the spice route.
- The Venetian merchant Marco Polo, during his travels to the east, also traveled to India in the 13th century and wrote about his experiences.
- Political:
- Political relations between India and Italy were established in 1947.
- In March 2023, India and Italy elevated their relationship to a Strategic Partnership.
- Economic:
- The bilateral trade between the two countries was valued at USD 14.25 billion in 2022-23.
- Italy is among India's top 5 trading partners in the European Union.
- Main items of Indian exports to Italy are ready-made garments, leather, iron ore, motor vehicles, textiles, chemicals, gems & jewelry.
- The main items of import from Italy are general and special purpose machinery, machine tools, metallurgical products, and engineering items.
- The bilateral trade between the two countries was valued at USD 14.25 billion in 2022-23.
- Security:
- The India-Italy Military Cooperation Group (MCG) is a forum established to boost defense cooperation between the both countries.
- Other Initiatives Involving India and Italy:
- India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor
- Global Biofuel Alliance
- Blue-Raman project
Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra Adds Beneficiaries to PM-Kisan
For Prelims: Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra, Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-Kisan), Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) Scheme, Aadhaar linkage, Saturation Drive
For Mains: Saturation Drive and its impact on the PM Kisan Beneficiaries through Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra.
Why in News?
Recently, the number of Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-Kisan) scheme beneficiaries has declined by more than 20%, decreasing from a peak of 10.47 crore in April-July 2022 to 8.12 crore.
- The government's proactive measures, particularly the "saturation drive" initiated under the Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra, have added 34 lakh farmers back to the list of beneficiaries.
What is Vikasit Bharat Sankalp Yatra?
- About:
- It is a nationwide campaign to raise awareness through outreach activities to achieve saturation of schemes of Govt. of India across the country covering all Gram Panchayats, Nagar Panchayats and Urban Local Bodies.
- The campaign is being taken up by adopting a whole of government approach with active involvement of various Ministries/Departments of Government of India, State Governments, Central Govt. Organizations and Institutions.
- Objectives:
- Reach out to the vulnerable who are eligible under various schemes but have not availed benefit so far.
- Dissemination of information and generating awareness about schemes.
- Interaction with beneficiaries of government schemes through their personal stories/ experience sharing.
- Enrolment of potential beneficiaries through details ascertained during the Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra.
What is PM Kisan Samman Nidhi Yojana (PM-Kisan)?
- About:
- It was launched to supplement financial needs of land holding farmers.
- It has become operational from December, 2018.
- Financial Benefits:
- Financial benefit of Rs 6000/- per year in three equal installments, every four month is transferred into the bank accounts of farmers’ families across the country through Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) mode.
- Scope of the Scheme:
- The scheme was initially meant for Small and Marginal Farmers (SMFs) having landholding upto 2 hectares but scope of the scheme was extended to cover all landholding farmers.
- Funding and Implementation:
- It is a Central Sector Scheme with 100% funding from the Government of India.
- It is being implemented by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- Objectives:
- To supplement the financial needs of the Small and Marginal Farmers in procuring various inputs to ensure proper crop health and appropriate yields, commensurate with the anticipated farm income at the end of each crop cycle.
- To protect them from falling in the clutches of moneylenders for meeting such expenses and ensure their continuance in the farming activities.
- PM-KISAN Mobile App:
- It was developed and designed by the National Informatics Centre in collaboration with the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology.
- Physical Verification Module:
- A mandatory physical verification of 5% beneficiary every year is being done as per the provisions laid down in the scheme.
What are the Challenges of PM-Kisan?
- Mandatory Provisions and Aadhaar Linkage:
- The mandatory land seeding provisions and the requirement to link Aadhaar with active bank accounts have introduced complexity, leading to challenges for farmers in complying with these prerequisites.
- Farmers, especially those in remote areas, may face technical challenges in fulfilling the Aadhaar linkage and land seeding requirements, hindering their access to PM-Kisan benefits.
- Awareness and Outreach:
- Many eligible farmers may still be unaware of the PM-Kisan scheme or may not have sufficient information about the application process.
- Despite efforts, outreach initiatives may struggle to reach all segments of the farming community, particularly in remote or marginalized areas.
- Technology Accessibility:
- Disparities in technology access, including smartphones and internet connectivity, may hinder farmers' ability to engage with the online processes required for PM-Kisan enrollment and compliance.
Way Forward
- Conduct a comprehensive review of mandatory land seeding provisions and Aadhaar linkage requirements for simplicity and efficiency.
- Utilize technology to create user-friendly platforms for seamless compliance.
- Establish community-level engagement programs to reach vulnerable farmers.
- Collaborate with local authorities, agricultural services, and NGOs to identify and support eligible farmers unaware of PM-Kisan benefits.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2018)
- Aadhaar card can be used as a proof of citizenship or domicile.
- Once issued, Aadhaar number cannot be deactivated or omitted by the Issuing Authority.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- The Aadhaar platform helps service providers authenticate identity of residents electronically, in a safe and quick manner, making service delivery more cost effective and efficient. According to the GoI and UIDAI, Aadhaar is not proof of citizenship.
- However, UIDAI has also published a set of contingencies when the Aadhaar issued by it is liable for rejection. An Aadhaar with mixed or anomalous biometric information or multiple names in a single name (like Urf or Alias) can be deactivated. Aadhaar can also get deactivated upon non-usage of the same for three consecutive years.
Pegasus Spyware
For Prelims: Pegasus spyware, Zero-click and Zero-day vulnerabilities, National Cyber Security Strategy, Cyber Surakshit Bharat
For Mains: Spyware and Privacy Concerns, Cyber Attacks, Government Initiatives
Why in News?
The Pegasus spyware has once again ignited a debate on privacy and security. Recent reports by Amnesty International point to its utilization in targeting the phones of two prominent Indian journalists, prompting inquiries into potential government involvement.
- Amnesty International is a global movement of more than 10 million people who are committed to creating a future where human rights are enjoyed by everyone.
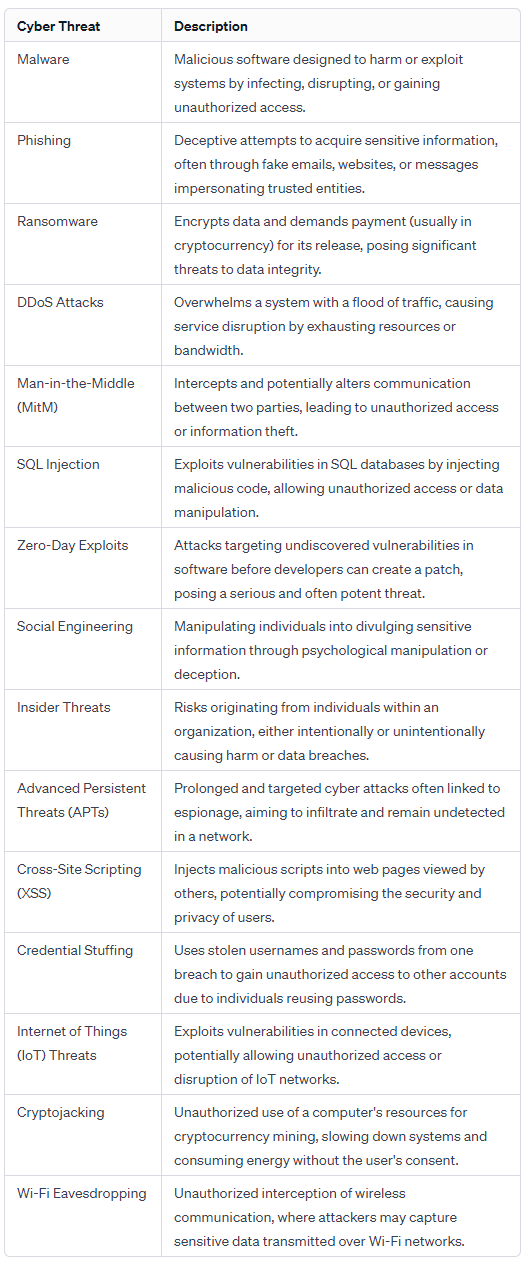
What is Pegasus Spyware?
- About:
- Pegasus spyware is a highly invasive mobile surveillance tool that can secretly infiltrate and monitor smartphones, collecting data and information from various apps and sources.
- It was developed by the Israeli cyber-intelligence firm NSO Group, which claims to sell it only to government agencies for fighting crime and terrorism.
- NSO emphasizes mechanisms in place to avoid targeting journalists, lawyers, and human rights defenders not involved in terror or serious crimes.
- Operating Procedure:
- Pegasus uses “zero-click” methods to infect devices; it is a malicious software that allows spyware to be installed on a device without the device owner’s consent.
- The spyware doesn't necessitate any user actions for installation, distinguishing it from regular apps that require explicit user confirmation.
- It can exploit vulnerabilities in apps such as WhatsApp, iMessage, or FaceTime, and send a message or a call that triggers the installation of the spyware, even if the user does not open or answer it.
- Pegasus is a spyware that can exploit zero-day vulnerabilities to deploy spyware on Apple products.
- A zero-day vulnerability is an undiscovered flaw or bug in an operating system that the mobile phone’s manufacturer does not yet know about and so has not been able to fix.
- Pegasus uses “zero-click” methods to infect devices; it is a malicious software that allows spyware to be installed on a device without the device owner’s consent.
- Targets:
- Several investigations and reports have revealed that Pegasus spyware has been used to spy on journalists, human rights activists, lawyers, opposition leaders, and heads of state.
- Some of the countries that have been accused of using Pegasus spyware to target their critics and enemies include Saudi Arabia, Mexico, India, Morocco, Hungary, Azerbaijan, and Rwanda.
- Implications:
- Pegasus spyware threatens privacy and security for individuals and groups exposing corruption, defending human rights, and advocating democracy.
- It undermines press freedom by exposing journalists' sources, methods, and materials, compromising their independence.
- The spyware poses a risk to the sovereignty and stability of nations, enabling foreign interference and espionage in internal affairs and decision-making processes.
- Challenges:
- Pegasus spyware is difficult to detect and remove, as it can hide its presence and activity on the device, and can self-destruct if it senses that it is being discovered or analyzed.
- Pegasus spyware is difficult to regulate and control due to its operation in legal grey areas.
- NSO Group and its clients commonly deny or evade responsibility for the misuse and abuse of spyware.
What are the Related Cybersecurity Initiatives?
- India:
- International Mechanisms:
Way Forward
- Establish an international oversight mechanism to hold companies accountable for any unethical use of surveillance tools and facilitate independent audits.
- Strengthen national and international legal frameworks to explicitly address the use of spyware and protect the privacy and human rights of individuals targeted.
- Conduct public awareness campaigns to educate individuals about the risks posed by spyware and how to safeguard their devices against potential infiltration.
- Strengthen national cybersecurity infrastructure to proactively detect and neutralize cyber threats, including the continuous monitoring of potential spyware activities.
- Encourage tech companies to adopt ethical guidelines that align with human rights principles, promoting responsible corporate behaviour.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. The terms ‘WannaCry, Petya and EternalBlue’ sometimes mentioned in the news recently are related to (2018)
(a) Exoplanets
(b) Cryptocurrency
(c) Cyber attacks
(d) Mini satellites
Ans: (c)
Q. In India, under cyber insurance for individuals, which of the following benefits are generally covered, in addition to payment for the loss of funds and other benefits? (2020)
- Cost of restoration of the computer system in case of malware disrupting access to one’s computer
- Cost of a new computer if some miscreant wilfully damages it, if proved so
- Cost of hiring a specialized consultant to minimize the loss in case of cyber extortion
- Cost of defence in the Court of Law if any third party files a suit
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 4 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)
Q. In India, it is legally mandatory for which of the following to report on cyber security incidents? (2017)
- Service providers
- Data centres
- Body corporate
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. What are the different elements of cyber security? Keeping in view the challenges in cyber security, examine the extent to which India has successfully developed a comprehensive National Cyber Security Strategy. (2022)
X-ray Polarimeter Satellite: ISRO
Why in News?
Recently, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has launched its first X-ray Polarimeter Satellite (XpoSat) to study X-ray polarisation and its cosmic sources, like Black holes, Neutron stars, and Magnetars.
- The mission is propelled by the PSLV-C58 rocket in Low Earth Orbit.
What is an X-ray Polarimeter Satellite (XpoSat)?
- Purpose:
- XPoSat is designed to study X-ray polarization in the medium X-ray band, offering insights into celestial sources' radiation mechanisms and geometry.
- This study is crucial for understanding the physics behind these celestial bodies.
- Payloads:
- The satellite carries two main payloads, POLIX (Polarimeter Instrument in X-rays) and XSPECT (X-ray Spectroscopy and Timing).
- POLIX will observe about 40 bright astronomical sources, while XSPECT will study the electromagnetic spectrum generated by different matter.
- Development:
- Entirely built by two Bengaluru-based institutes—ISRO’s UR Rao Satellite Centre and Raman Research Institute—XPoSat's development began in 2008, with a formal agreement signed with ISRO in 2015.
- Global Context:
- XPoSat is only the world's second mission dedicated to X-ray polarization in the medium X-ray band. NASA's Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE), launched in 2021, was the first such mission by a space agency.
- National Contribution:
What is X Ray and How will it Study the Celestial Objects?
- X-rays are electromagnetic radiation whose wavelength is 0.01-10 nanometres.
- Electromagnetic radiation is characterised by an electric field and a magnetic field vibrating perpendicular to each other.
- The polarisation of electromagnetic radiation refers to the orientation of these two fields as the radiation moves through space.
- Electromagnetic radiation is characterised by an electric field and a magnetic field vibrating perpendicular to each other.
- X-rays can be polarised when they get scattered. Polarised X-rays are also produced when the path of a fast-moving charged particle is bent by a magnetic field.
- Measuring the polarization of X-rays using instruments like POLIX enables astronomers to understand the orientation and strength of magnetic fields in celestial objects. This, in turn, provides crucial insights into the nature and behavior of pulsars, regions around black holes, and other cosmic phenomena emitting X-rays.
Lithium-Deal with Argentina
Why in News?
The Ministry of Mines, Government of India through the state-owned Khanij Bidesh India Ltd (KABIL), has entered into a draft exploration and development agreement with Argentinan miner CAMYEN for possible acquisition and development of five-odd lithium blocks.
- The company has also entered into a non-disclosure agreement with Chilean miner ENAMI for “possible exploration, extraction, processing and commercialisation” of the mineral.
What is Lithium?
- About:
- Lithium is an alkali mineral, also called ‘white gold’. It is soft, silvery-white metal, the lightest metal of the periodic table.
- Major Properties:
- High Reactivity
- Low Density
- Excellent Electrochemical Properties
- Occurrence and Top Producers:
- Lithium is found naturally in various minerals, including spodumene, petalite, and lepidolite.
- It is extracted from these minerals and refined into lithium metal or its compounds.
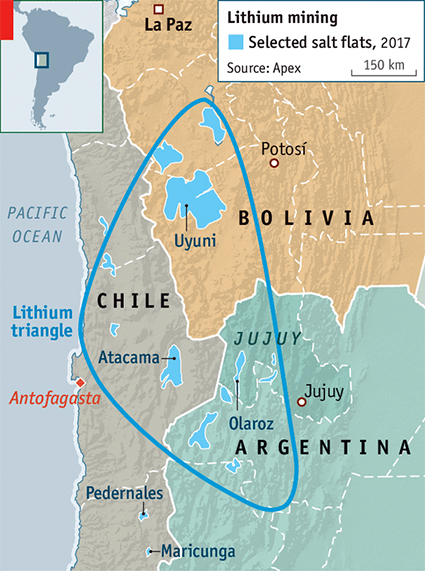
- The top producers of lithium are Australia, Chile, China, and Argentina.
- In 2022, Australia was the world leader in terms of lithium mine production. Chile and China ranked second and third.
- Recently, a massive lithium deposit beneath California’s Salton Sea (US), holding an estimated 18 million tons of lithium, was discovered.
- Lithium is found naturally in various minerals, including spodumene, petalite, and lepidolite.
Note
Lithium triangle made up of Argentina, Chile, and Bolivia—contain roughly half the world's known lithium.
- Applications:
- Batteries: Lithium is a crucial component of rechargeable batteries used in smartphones, laptops, electric vehicles, and other electronics.
- Glass and Ceramics: Lithium compounds are used to strengthen glass and ceramics, making them more durable and heat-resistant.
- Medicine: Lithium is used as a mood stabilizer in the treatment of bipolar disorder.
- Lubricants: Lithium greases are used in high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
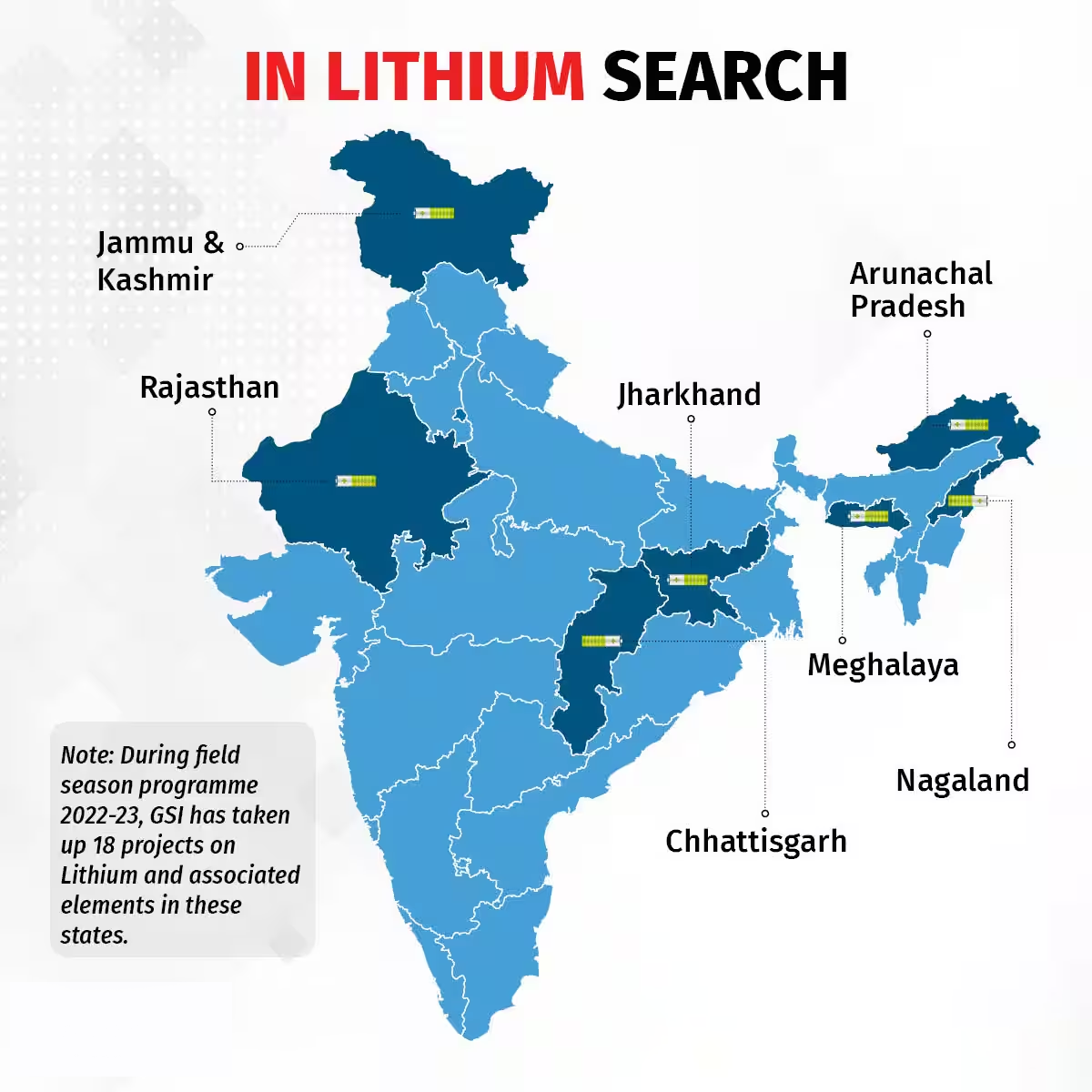
- Lithium in India:
- 2023 saw a surge in lithium discoveries:
- Massive reserves unearthed in Salal-Haimna areas of Reasi district of Jammu and Kashmir (estimated 5.9 million tonnes).
- Additional reserves identified in Koderma and Giridih regions of Jharkhand.
- However, India has put up lithium blocks for auction: one in J&K and another in Chhattisgarh, with most of its domestic requirements, across categories like EVs, lithium-ion battery making, and other energy storage solutions, being met completely through imports. Import bill is pegged at around ₹24,000 crore.
- 2023 saw a surge in lithium discoveries:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Which one of the following pairs of metals constitutes the lightest metal and the heaviest metal, respectively? (2008)
(a) Lithium and mercury
(b) Lithium and osmium
(c) Aluminium and osmium
(d) Aluminium and mercury
Ans: (b)
Huntington's Disease
Why in News?
Recently, a study by researchers from the University of Szeged in Hungary published in Scientific Reports has uncovered new insights into Huntington's disease using fruit flies (Drosophila melanogaster) as a model organism.
- This innovative approach has provided promising revelations about disease progression and potential therapeutic targets.
What is Huntington's Disease?
- About:
- Huntington's disease is a severe neurodegenerative disorder affecting the central nervous system.
- It is caused by a mutation in the HTT gene, producing a faulty huntingtin (Htt) protein.
- Mutant Htt proteins are cleaved into toxic fragments, disrupting various cellular processes.
- HTT Gene and Polyglutamine Tract:
- The HTT gene codes for the huntingtin protein crucial for nerve cell functioning.
- Mutations in the HTT gene result in an expanded polyglutamine tract in the Htt protein, leading to misfolding and dysfunction.
- The severity of Huntington's disease correlates with the length of the expanded polyglutamine tract.
- Huntington's disease is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, which means that a person only needs to inherit one copy of the mutated gene from either parent to develop the condition.
- Each child of a parent with Huntington's disease has a 50% chance of inheriting the mutation.
- The HTT gene codes for the huntingtin protein crucial for nerve cell functioning.
- Symptoms:
- Initial symptoms include forgetfulness, loss of balance, and clumsiness in daily tasks.
- Symptoms worsen over time, affecting mood, and reasoning, and leading to uncontrollable movements. Patients face difficulties in speaking, swallowing, and walking as the disease advances.
- Symptoms typically emerge between ages 30-50.
- Treatment:
- There is currently no cure for Huntington's disease, and available treatments only alleviate symptoms.
What are the Key Highlights of the Study?
- Researchers engineered fruit flies to express the polyglutamine tract of a mutated human HTT gene in their nervous system.
- They used a gene called Gal4 from baker’s yeast(Saccharomyces cerevisiae), which activates the expression of genes when bound to a DNA sequence called the upstream activating sequence (UAS).
- The Gal4/UAS system works in the fruit fly genome, allowing the expression of proteins specifically in neurons.
- Fruit flies with the mutated HTT gene displayed neuronal degeneration, impaired climbing ability, and lower viability and longevity.
- A 'control' group of fruit flies with a normal range of glutamine units in the HTT protein showed little to no effect.
- The study found that expressing a longer glutamine tract produced symptoms resembling Huntington’s disease in humans, while the shorter tract did not.
- Researchers found that overexpression of one gene (out of 32 investigated genes in flies) called Yod1 gene in flies effectively eliminated disease-like effects associated with Huntington's disease, including neurodegeneration and motor impairments.
India-UAE Joint Exercise 'Desert Cyclone 2024'
India and UAE will hold 'Desert Cyclone 2024' joint military exercise in Rajasthan from 2nd January to 15th January, 2024.
- The exercise aims to enhance interoperability by learning & sharing best practices in Urban Operations.
- It is also expected to not only strengthen the defense ties between India and the UAE but also contribute to the broader goal of fostering regional peace and security.
- India has also been a regular participant at the biennial International Defence Exhibition (IDEX) in Abu Dhabi.
Read more: India-UAE Relations
No Tsunami Threat to India
The Indian Tsunami Early Warning Centre (ITEWC), part of the Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS) in Hyderabad, confirmed that India faces no tsunami threat despite a 7.5 magnitude earthquake near Honshu, Japan.
- The Pacific Ocean Tsunami Warning Centre (PTWC) and Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) issued a tsunami bulletin for Japan.
- ITEWC monitors sea level changes near the epicentral region and reports in case of a tsunami threat.
- Epicentre is a point on the Earth's surface directly above the hypocenter (or focus) of an earthquake. It is the location on the surface of the Earth that is directly above the earthquake's point of origin within the Earth's crust.
- INCOIS is an autonomous body under the Ministry of Earth Sciences, tasked with delivering optimal ocean information and advisory services to society, industry, government agencies, and the scientific community.
Read more: Tsunami Early Warning System in India
Samvid Gurukulam Girls Sainik School
Recently, the Defence Minister of India, inaugurated Samvid Gurukulam Girls Sainik School in Vrindavan, Uttar Pradesh. This significant step reflects the government's commitment to providing equal opportunities for girls in the field of defence.
- The school is strategically positioned to play a pivotal role in furthering the government's initiative to establish 100 new Sainik Schools across all states and union territories, aligning with the objectives outlined in the National Education Policy 2020.
- The initiative aims to provide quality education, better career opportunities, and encourage girls to join the Armed Forces.
Read more: Representation of Women in Armed Forces
K-SMART App
Recently, Kerala Government has launched K-SMART (Kerala Solutions for Managing Administrative Reformation and Transformation) application, which will bring all services of the three-tier local self-government institutions on a unified digital platform.
- It aims to bridge the digital divide and particularly benefit expatriates by eliminating the need for physical visits to government offices.
- Notably, K-SMART's technological framework encompasses an array of cutting-edge disciplines such as blockchain, Artificial Intelligence, GIS, chatbots, machine learning, and IoT.
Read more: e-Governance

, 2023.png)