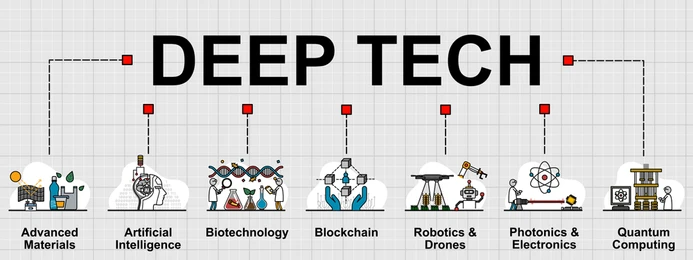
Deep Tech Startups
For Prelims: Deep Tech Startups, Deep Tech, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Internet of Things, Big Data, quantum computing
For Mains: Deep Tech Startups and India
Why in News?
Government will launch the Digital India Innovation Fund to support deep tech startups.
What is Deep Tech?
- About:
- Deep tech or deep technology refers to a class of startup businesses that develop new offerings based on tangible engineering innovation or scientific discoveries and advances.
- Usually, such startups operate on, but are not limited to, agriculture, life sciences, chemistry, aerospace and green energy.
- Deep tech fields like Artificial Intelligence, advanced materials, blockchain, biotechnology, robotics, drones, photonics, and quantum computing are moving more and more quickly from early research to market applications.
- Characteristics of Deep Tech:
- Impact: The deep tech innovations are very radical and disrupt an existing market or develop a new one. Innovations based on deep tech often change lives, economies, and societies.
- Time & Scale: The time required for deep technology to develop the technology and reach the market-ready maturity is way more than shallow technology development (like mobile apps and websites). It took decades for artificial intelligence to develop and it is still not perfect.
- Capital: Deep tech often requires a lot of early-stage funding for research and development, prototyping, validating hypothesis, and technology development.
What is the State of India’s Deep Tech Startups?
- India had over 3,000 deep-tech start-ups, dabbling in new-age technologies like Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning (ML), Internet of Things, Big Data, quantum computing, robotics, etc., at the end of 2021.
- According to NASSCOM, deep-tech start-ups in India raised USD 2.7 billion in venture funding in 2021, and now account for over 12% of the country’s overall startup ecosystem.
- In the last decade India’s deep tech ecosystem has grown 53% and is at par with that in developed markets like the US, China, Israel, and Europe.
- Bengaluru accounts for 25-30% of India’s deep-tech start-ups, followed by Delhi-NCR (15-20%) and Mumbai (10-12%).
- Deep-tech start-ups are making their presence felt across sectors like drone delivery and cold chain management to climate action and clean energy.
What are the Challenges Faced by Deep Tech?
- For deep-tech startups, funding is one of the biggest challenges. Less than 20% of startups receive financing.
- Government funds are underutilized, and domestic capital is lacking for such startups.
- Talent and market access, research guidance, investors’ understanding of deep-tech, customer acquisition and cost for talent are the major challenges faced by them.
What are the Related Initiatives?
- The Atal New India Challenge has been launched under the Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) of the Niti Aayog, with an objective to serve as a platform for the promotion of Innovation Hubs, Grand Challenges, startup businesses, and other self-employment activities, particularly in technology-driven areas.
- Launched in 2021, NASSCOM's Deep Tech Club (DTC) 2.0 is aimed at scaling the impact to over 1,000 firms that are leveraging technologies such as AI, ML, Internet of Things, robotics, and blockchain.
Way Forward
- Reevaluate the Roadmaps:
- As the continual growth of the Indian start-up ecosystem is fueled by the ongoing era of constantly emerging new technologies, organizations and the government would need to reevaluate their roadmaps for adopting deep tech.
- As technologies such as 5G, understandable artificial intelligence, quantum computing, cloud-native technologies, cybersecurity meshes, and customer data platforms will be used in the future. There are a number of factors that can help the booming and resilient Indian startup ecosystem become global leaders in deep technology.
- CSR Budget Utilization:
- The social sector has traditionally benefited from Corporate Social Responsibility. However, this growing corpus should also be used to develop strategic technologies.
- A large corporation can be encouraged to contribute to the strategic needs of the nation with some of its budget. There is a need for the government to allow these funds to flow into certain strategic tech startups.
UPSC Civil Services Exam Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Q. Atal Innovation Mission is set up under the (2019)
(a) Department of Science and Technology
(b) Ministry of Labour and Employment
(c) NITI Aayog
(d) Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship
Ans: (c)
NCW’s Concerns over Sexual Assault
For Prelims: NCW’s Concerns over Sexual Assault, NCW, Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Protection and Redressal) Bill, 2012 (amended Bill) was passed by Parliament in 2013.
For Mains: Background & Mandate of National Commission for Women (NCW).
Why in News?
The National Commission for Women (NCW) has asked all States to ensure strict implementation of the sexual harassment at workplace law.
What are the Concerns of NCW?
- The NCW has expressing concern over incidents of sexual harassment at coaching centres and educational institutes and asked to ensure strict implementation of the Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition and Redressal) Act, 2013 and guidelines established thereunder.
- In recent years, sexual harassment at workplace is becoming one of the most pressing issues affecting women across the globe.
- Nearly 31,000 complaints of crimes committed against women were received by the NCW in 2022, the highest since 2014.
- About 54.5 % of the complaints were received from Uttar Pradesh. Delhi recorded 3,004 complaints, followed by Maharashtra (1,381), Bihar (1,368) and Haryana (1,362).
- Crimes that women were subjected to: Domestic violence, Harassment of married women or dowry harassment, Sexual harasment at workplace, Rape and attempt to rape, Cyber crimes.
What is Protection of Women Against Sexual Harassment Act, 2013
- Background: The Supreme Court in a landmark judgement in the Vishakha and others v State of Rajasthan 1997 case gave ‘Vishakha guidelines.
- These guidelines formed the basis for the Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition and Redressal) Act, 2013 ("Sexual Harassment Act").
- Mechanism: The Act defines sexual harassment at the workplace and creates a mechanism for redressal of complaints.
- Every employer is required to constitute an Internal Complaints Committee at each office or branch with 10 or more employees.
- The Complaints Committees have the powers of civil courts for gathering evidence.
- The Complaints Committees are required to provide for conciliation before initiating an inquiry if requested by the complainant.
- Penal Provisions: Penalties have been prescribed for employers. Non-compliance with the provisions of the Act shall be punishable with a fine.
- Repeated violations may lead to higher penalties and cancellation of license or registration to conduct business.
- Responsibility of Administration: The State Government will notify the District Officer in every district, who will constitute a Local Complaints Committee (LCC) so as to enable women in the unorganised sector or small establishments to work in an environment free of sexual harassment.
What is the Background & Mandate of NCW?
- About:
- Under the National Commission for Women Act, 1990, the NCW was set up as a statutory body in January 1992.
- The First Commission was constituted on 31st January 1992 with Mrs. Jayanti Patnaik as the Chairperson.
- The commission consists of a chairperson, a member secretary and five other members. The chairperson of the NCW is nominated by the Central Government.
- Mandate and Functions:
- Its mission is to strive towards enabling women to achieve equality and equal participation in all spheres of life by securing her due rights and entitlements through suitable policy formulation, legislative measures, etc.
- Its functions are to:
- Review the constitutional and legal safeguards for women.
- Recommend remedial legislative measures.
- Facilitate redressal of grievances.
- Advise the Government on all policy matters affecting women.
- It has received a large number of complaints and acted suo-moto in several cases to provide speedy justice.
- It took up the issue of child marriage, sponsored legal awareness programmes, Parivarik Mahila Lok Adalats and reviewed laws such as:
- Dowry Prohibition Act, 1961,
- Pre-Conception and Pre-Natal Diagnostic Techniques Act 1994,
- Indian Penal Code 1860.
What are the major Legal Frameworks for Welfare of Women?
- Constitutional Safeguards:
- Fundamental Rights:
- It guarantees all Indians the right to equality (Article 14), no discrimination by the State on the basis of gender (Article 15(1)) and special provisions to be made by the State in favour of women (Article 15(3)).
- Fundamental Duties:
- It ensures that practices derogatory to the dignity of women are prohibited under Article 51 (A).
- Fundamental Rights:
- Legislative Framework:
- Women Empowerment Schemes:
- Beti Bachao Beti Padhao Scheme
- One Stop Centre Scheme
- UJJAWALA: A Comprehensive Scheme for Prevention of trafficking and Rescue, Rehabilitation and Re-integration of Victims of Trafficking and Commercial Sexual Exploitation
- SWADHAR Greh
- NARI SHAKTI PURASKAR
- Mahila police Volunteers
- Mahila Shakti Kendras (MSK)
- NIRBHAYA Fund.
Way Forward
- There is a need to implement JS Verma Committee recommendations on Sexual Harassment at the Workplace Act:
- Employment Tribunal: Setting up of an employment tribunal instead of an internal complaints committee (ICC) in the Sexual Harassment at the Workplace Act.
- Power to Form Own Procedure: To ensure speedy disposal of complaints, the committee proposed that the tribunal should not function as a civil court but may choose its own procedure to deal with each complaint.
- Expanding Scope of Act: Domestic workers should be included within the purview of the Act.
- The Committee said any “unwelcome behavior” should be seen from the subjective perception of the complainant, thus broadening the scope of the definition of sexual harassment.
- Women's role is continuously expanding in today’s India and the expansion of the role of the NCW is the need of the hour.
- Further, the State Commissions must also widen their ambit.
- Violence against women continues to be an obstacle to achieving equality, development, peace as well as to the fulfillment of women and girls’ human rights.
- All in all, the promise of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) - to leave no one behind - cannot be fulfilled without putting an end to violence against women and girls.
- Crime against women cannot be resolved in the court of law alone. A holistic approach & changing the entire ecosystem is what is required.
- All the stakeholders need to get their act together, including Law makers, police officers, forensic dept, prosecutors, judiciary, medical & health dept, NGOs, rehabilitation centres.
UPSC Civil Services Exam Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Q. We are witnessing increasing instances of sexual violence against women in the country. Despite existing legal provisions against it, the number of such incidences is on the rise. Suggest some innovative measures to tackle this menace. (2014)
Depreciation of Indian Rupee
For Prelims: Depreciation of Indian Rupee, Currency depreciation, inflation, Depreciation Vs Devaluation, Appreciation Vs Depreciation
For Mains: Impact of Depreciation of Indian Rupee on economy
Why in News?
The Indian Rupee depreciated by around 10% against the US dollar and the rupee was the worst-performing Asian currency in 2022.
- This decline was mainly on account of appreciation in the US currency on safe haven appeal amid fears of recession and inflation across many parts of the world and Russia-Ukraine war.
How did the Rupee Perform in 2022?
- During the year, the rupee fell to a lifetime low of 83.2 against the dollar. Compared to rupee, depreciation of other Asian currencies was to a lesser extent.
- During the year, the Chinese Yuan, Philippine Peso and Indonesian Rupiah fell around 9%. South Korean Won and Malaysian Ringgit declined by nearly 7% and 6%, respectively.
- However, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) heavily intervened in the forex market to defend rupee. Since the beginning of 2022, the country’s foreign exchange reserves have fallen by USD 70 billion. It stood at USD 562.81 billion as of 23rd December 2022.
- Reserves have witnessed a bit of erosion but the central bank is now starting to again build up its reserves and that would act as a buffer in times of uncertainty.
What was the Reason for Capital Outflows?
- The US Fed aggressively raised interest rates by 425 basis point (bps) in 2022 in its fight against inflation. This led to a higher interest rate differential between the US and India, and investors pulled out money from the domestic market and started investing in the US market to take advantage of higher rates.
- In 2022, Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs) pulled out Rs 1.34 lakh crore from the Indian markets – the highest-ever yearly net outflow.
- They withdrew Rs 1.21 lakh crore from the stock markets and Rs 16,682 crore from the debt market in 2022, putting pressure on the rupee.
- Russian invasion of Ukraine accentuated the FPI withdrawals with the global economic slowdown making inflows tougher.
What may be the Impact of Depreciation on the Indian Economy?
- Positive:
- Weaker rupee should theoretically give a boost to India’s exports, but in an environment of uncertainty and weak global demand, a fall in the external value of rupee may not translate into higher exports.
- Negative:
- It poses risk of imported inflation, and may make it difficult for the central bank to maintain interest rates at a record low for longer.
- India meets more than two-thirds of its domestic oil requirements through imports.
- India is also one of the top importers of edible oils. A weaker currency will further escalate imported edible oil prices and lead to a higher food inflation.
What is the Outlook on Rupee for 2023?
- Even though the outlook on the rupee remains weak in the near future, the depreciation in local currency may not continue for a longer period as India remains the fastest-growing economy.
- The terminal interest rate for the US Fed was anticipated, but it cannot be the case that their monetary policy will be tightened endlessly.
- When the (US Fed) tightening is over, the tide will surely turn.
What is Appreciation vs Depreciation of Currency?
- In a floating exchange rate system, market forces (based on demand and supply of a currency) determine the value of a currency.
- Currency Appreciation: It is an increase in the value of one currency in relation to another currency.
- Currencies appreciate against each other for a variety of reasons, including government policy, interest rates, trade balances and business cycles.
- Currency appreciation discourages a country's export activity as its products and services become costlier to buy.
- Currency Depreciation: It is a fall in the value of a currency in a floating exchange rate system.
- Economic fundamentals, political instability, or risk aversion can cause currency depreciation.
- Currency depreciation encourages a country's export activity as its products and services become cheaper to buy.
What are Devaluation and Depreciation?
- In general, devaluation and depreciation are often used interchangeably.
- They both have the same effect – a fall in the value of the currency which makes imports more expensive, and exports more competitive.
- However, there is a difference in the way they are applied.
- A devaluation occurs when a country’s central bank makes a conscious decision to lower its exchange rate in a fixed or semi-fixed exchange rate.
- A depreciation is when there is a fall in the value of a currency in a floating exchange rate.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. Which one of the following is not the most likely measure the Government/RBI takes to stop the slide of Indian rupee? (2019)
(a) Curbing imports of non-essential goods and promoting exports
(b) Encouraging Indian borrowers to issue rupee denominated Masala Bonds
(c) Easing conditions relating to external commercial borrowing
(d) Following an expansionary monetary policy
Ans: (d)
Q2. Consider the following statements:
The effect of devaluation of a currency is that it necessarily
- improves the competitiveness of the domestic exports in the foreign markets
- increases the foreign value of domestic currency
- improves the trade balance
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2
(c) 3 only
(d) 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. How would the recent phenomena of protectionism and currency manipulations in world trade affect macroeconomic stability of India? (2018)
Year-End Review-2022: Department of Space
Prelims: ISRO, Chandrayaan-2 Mission, 50th PSLV Launch, One Web, Launch Vehicle Mark 3, IAD, Atma Nirbharta, UNNATI, Young Scientist Programme.
Mains: Key achievements of the Department of Space.
Why in News?
Recently, the Year-End-Review of the Department of Space for the year 2022 under the Ministry of Science and Technology was released.
What are the Key achievements of the Department of Space?
- Key Missions: Altogether 44 spacecraft missions, 42 launch vehicle missions and 5 technology demonstrators, have been successfully realized, since 2014.
- Chandrayaan-2 Mission: In 2019, Chandrayaan-2 was successfully launched.
- It is providing valuable science data for the research community.
- 50th PSLV Launch:
- The launch of PSLV-C48/ RISAT-2BR1 in Dec 2019 marked the 50th launch of PSLV, the workhorse launch vehicle.
- RISAT-2BR1 will keep a check on infiltration by allowing round-the-clock surveillance across the border.
- ISRO System for Safe & Sustained Operations Management (IS4OM):
- In July 2022, the Ministry of science dedicated ISRO System for Safe & Sustained Operations Management (IS4OM) to the nation in.
- It is a facility that is conceived with a holistic approach towards ensuring safety and sustainability while reaping the benefits of sustainable utilization of outer space for national development.
- Launch Vehicle Mark (LVM) 3:
- LVM3 /OneWeb India-1 Mission was successfully accomplished in October 2022.
- With this launch, LVM3 exemplifies Atmanirbharata and enhances India’s competitive edge in the global commercial launch service market.
- Integrated Main Parachute Airdrop Test (IMAT):
- As part of Gaganyaan programme, IMAT of crew module deceleration system was successfully carried out at Babina Field Fire Range (BFFR), Jhansi, Uttar Pradesh in November 2022.
- Inflatable Aerodynamic Decelerator:
- Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully demonstrated new technology with Inflatable Aerodynamic Decelerator (IAD) – a game changer with multiple applications for future missions.
- The IAD has huge potential in a variety of space applications like recovery of spent stages of rocket, for landing payloads on to Mars or Venus and in making space habitat for human space flight missions.
- PSLV-C54:
- PSLV-C54 successfully launched EOS-06 satellite in November 2022 along with Eight Nano-satellites including INDIA-BHUTAN SAT (INS-2B).
- The launch of the new satellite is part of India’s efforts to back Bhutanese King Jigme Khesar Namgyel Wangchuck’s plans to use advanced technology, including ICT and space technology, for the development of Bhutan.
- Chandrayaan-2 Mission: In 2019, Chandrayaan-2 was successfully launched.
- Academic Support, Capacity building and Outreach:
- Space Technology Incubation Centers (STIC):
- In order to boost the space research activities, STIC have been established, since 2018.
- Under this initiative, nine Space Technology Cells (STC), Six STIC and Six Regional Academic Centre for Space (RACS) are operational.
- Satish Dhawan Centre for Space Sciences:
- Recently, Satish Dhawan Centre for Space Sciences was jointly established by ISRO/DoS and Central University of Jammu.
- Unispace Nanosatellite Assembly & Training by ISRO:
- In June 2018, India announced a capacity building training programme UNNATI (UNispace Nanosatellite Assembly & Training by ISRO) on Nanosatellites development through a combination of theoretical coursework and hands-on training on Assembly, Integration and Testing (AIT).
- Young Scientist Programme:
- In 2019, ISRO launched an annual special programme called "Young Scientist Programme" or the "Yuva VIgyani KAryakram" (YUVIKA) in line with the Government's vision "Jai Vigyan, Jai Anusandhan”.
- The Program is primarily aimed at imparting basic knowledge on Space Technology, Space Science and Space Applications to the young talents with the intent of encouraging them in the fascinating domain of outer space.
- SpaceTech Innovation Network (SpIN):
- ISRO and Social Alpha signed an MoU in December 2022 to launch SpaceTech Innovation Network (SpIN), India’s first dedicated platform for innovation curation and venture development for the burgeoning space entrepreneurial ecosystem.
- Space Technology Incubation Centers (STIC):
- Reforms and Enhanced Participation of Industries:
- NewSpace India Limited (NSIL):
- In 2019, the NSIL got incorporated as a wholly owned Government of India Undertaking/ Central Public Sector Enterprise (CPSE).
- It was aimed at enabling Indian Industries to scale up high-technology manufacturing base for space programme and to commercially exploit the products and services emanating from the Indian Space Programme for meeting the domestic and global customer needs.
- GSAT-24 communication satellite which is the first demand driven mission of NSIL was launched from Kourou, French Guiana, in June 2022.
- IN-SPACe:
- IN-SPACe was launched to provide a level playing field for private companies to use Indian space infrastructure.
- It acts as a single-point interface between ISRO, and everyone who wants to participate in space-related activities or use India’s space resources.
- Indian Space Association (ISpA):
- ISpA aspires to be the collective voice of the Indian Space industry. ISpA will be represented by leading domestic and global corporations that have advanced capabilities in space and satellite technologies.
- First Private Launchpad & Mission Control Center:
- First private launchpad & mission control center established by M/s Agnikul Cosmos Pvt. Ltd., Chennai in ISRO campus at SDSC, SHAR in November 2022.
- Indian Space Policy – 2022:
- Indian Space Policy – 2022 policy is cleared by the Space Commission. The Policy has undergone extensive deliberations with industry groups, inter-ministerial consultations, has been reviewed by Empowered Technology Group and is under further approval process.
- Disaster Management:
- Monitoring flood inundation, generation of flood hazard zonation atlases of flood prone states, developing flood early warning models, multiple daily detections & dissemination of active forest fires, forecasting cyclone track; intensity & landfall, damage assessment due to earthquakes and landslides, etc. were carried out.
- Covid-19 Related Supports:
- During the Covid-19 pandemic period, devices like Mechanical Ventilator & Medical Oxygen Concentrator were developed and the technologies are transferred to Indian industries.
- NewSpace India Limited (NSIL):
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 In the context of space technology, what is “Bhuvan”, recently in the news? (2010)
(a) A mini satellite launched by ISRO for promoting the distance education in India
(b) The name given to the next Moon Impact Probe, for Chandrayaan-II
(c) A geoportal of ISRO with 3D imaging capabilities of India
(d) A space telescope developed by India
Ans: (c)
Q.2 Consider the following statements: (2016)
The Mangalyaan launched by ISRO
- is also called the Mars Orbiter Mission
- made India the second country to have a spacecraft orbit the Mars after USA
- made India the only country to be successful in making its spacecraft orbit the Mars in its very first attempt
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q.1 What is India’s plan to have its own space station and how will it benefit our space programme? (2019)
Q.2 Discuss India’s achievements in the field of Space Science and Technology. How the application of this technology helped India in its socio-economic development? (2016)
International Year of Millets
For Prelims: Millets and its Significance, UNEP FAO, Food Security
For Mains: International Year of Millets 2023 and its Significance
Why in News?
India has shared the vision to make International Year of Millets 2023 a ‘People’s Movement’ alongside positioning India as the ‘Global Hub for Millets’.
What is International Year of Millets?
- About:
- India's proposal to observe an International Year of Millets in 2023 was approved by the Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO) in 2018 and the United Nations General Assembly has declared the year 2023 as the International Year of Millets.
- This was adopted by a United Nations Resolution for which India took the lead and was supported by over 70 nations.
- Objectives:
- Awareness of the contribution of millet to Food Security and nutrition.
- Inspire stakeholders to improve sustainable production and quality of millets.
- Focus on enhanced investment in research and development and extension services to achieve the other two aims.
What is Millet?
- About:
- Millet is a collective term referring to a number of small-seeded annual grasses that are cultivated as grain crops, primarily on marginal lands in dry areas in temperate, subtropical and tropical regions.
- Some of the common millets available in India are Ragi (Finger millet), Jowar (Sorghum), Sama (Little millet), Bajra (Pearl millet), and Variga (Proso millet).
- The earliest evidence for these grains has been found in Indus civilization and was one of the first plants domesticated for food.
- It is grown in about 131 countries and is the traditional food for around 60 crore people in Asia & Africa.
- India is the largest producer of millet in the world.
- It accounts for 20 % of global production and 80% of Asia’s production.
- Global Distribution:
- India, Nigeria and China are the largest producers of millets in the world, accounting for more than 55% of the global production.
- For many years, India was a major producer of millets. However, in recent years, millet production has increased dramatically in Africa.
- Significance:
- Nutritionally Superior:
- Millets are less expensive and nutritionally superior to wheat & rice owing to their high protein, fibre, vitamins and minerals like iron content.
- Millets are also rich in calcium and magnesium. For example, Ragi is known to have the highest calcium content among all the food grains.
- Millets can provide nutritional security and act as a shield against nutritional deficiency, especially among children and women. Its high iron content can fight high prevalence of anaemia in India women of reproductive age and infants.
- Gluten-free a low Glycemic Index:
- Millets can help tackle lifestyle problems and health challenges such as obesity and diabetes as they are gluten-free and have a low glycemic index (a relative ranking of carbohydrate in foods according to how they affect blood glucose levels).
- Super Crop at Growing:
- Millets are Photo-insensitive (do not require a specific photoperiod for flowering) & resilient to climate change. Millets can grow on poor soils with little or no external inputs.
- Millets are less water consuming and are capable of growing under drought conditions, under non-irrigated conditions even in very low rainfall regimes.
- Millets have low carbon and water footprint (rice plants need at least 3 times more water to grow in comparison to millets).
- Nutritionally Superior:
What are the Related Initiatives Taken by the Government?
- Initiative for Nutritional Security through Intensive Millet Promotion (INSIMP)
- Increase in Minimum Support Price (MSP): The government has hiked the Minimum Support Price of Millets, which came as a big price incentive for farmers.
- Further, to provide a steady market for the produce, the government has included millets in the public distribution system.
- Input Support: The government has introduced provision of seed kits and inputs to farmers, building value chains through Farmer Producer Organisations and supporting the marketability of millets.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. With reference to ‘Initiative for Nutritional Security through Intensive Millets Promotion’, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2016)
- This initiative aims to demonstrate the improved production and post-harvest technologies, and to demonstrate value addition techniques, in an integrated manner, with a cluster approach.
- Poor, small, marginal and tribal farmers have a larger stake in this scheme.
- An important objective of the scheme is to encourage farmers of commercial crops to shift to millet cultivation by offering them free kits of critical inputs of nutrients and micro irrigation equipment.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- ‘Initiative for Nutritional Security through Intensive Millets Promotion’ Scheme aims to demonstrate the improved production and post-harvest technologies in an integrated manner with visible impact to catalyse increased production of millets in the country. Besides increasing production of millets, the Scheme, through processing and value addition techniques, is expected to generate consumer demand for millet-based food products. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- Technology demonstrations in compact blocks would be organized in selected districts for four categories of millets – sorghum, pearl millet, finger millet and small millets. Poor, small, marginal and tribal farmers have a larger stake in this scheme. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- There is no such provision to encourage farmers of commercial crops to shift to millet cultivation. Hence, statement 3 is not correct.
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
SAIME Initiative
Why in News?
In Sundarbans, a new shrimp farming initiative offers hope for mangrove restoration.
What is the SAIME Initiative?
- Under Sustainable Aquaculture In Mangrove Ecosystem (SAIME) initiative, farmers have taken up cultivation of shrimp at 30 hectares in West Bengal.
- Additionally, they are restoring mangroves.
- Started in 2019, the community-based initiative of sustainable shrimp cultivation is being conceived by NGOs- Nature Environment and Wildlife Society (NEWS) and Global Nature Fund (GNF), Naturland, Bangladesh Environment and Development Society (BEDS).
- The mangrove ecosystem is integrated with shrimp cultivation, but when fisheries were expanded inwards, the mangrove ecosystem was excluded.
- Fishing, particularly shrimp cultivation, is one of the key occupations of the people of Sundarbans, which is a complex network of rivers and low-lying islands that face a tide surge twice a day.
- Shrimp cultivation is practised in about 15,000 to 20,000 hectares of the unique ecosystem in India.
What is the Significance of the Sundarbans Delta?
- The Sundarbans hosts the largest mangrove forests in the world, lying on the delta of the Ganges, Brahmaputra and Meghna rivers on the Bay of Bengal.
- Mangrove ecosystem is a very specialised environment occurring in between the land and the sea in the tropical and subtropical regions.
- Sundarbans is the natural abode of many groups of animals and a large number of species are known to feed, breed, and take shelter in this ecosystem.
- It is home to many rare and globally threatened wildlife species such as the estuarine crocodile, water monitor lizard, Gangetic dolphin and olive ridley turtle.
- 40% of Sundarbans lies in India and the rest in Bangladesh. Sundarbans was designated a UNESCO World Heritage site in 1987 (India) and 1997 (Bangladesh).
- Sundarbans Wetland, India was recognised as the ‘Wetland of International Importance’ under the Ramsar Convention in January 2019.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. The 2004 Tsunami made people realize that mangroves can serve as a reliable safety hedge against coastal calamities. How do mangroves function as a safety hedge? (2011)
(a) The mangrove swamps separate the human settlements from the sea by a wide zone in which people neither live nor venture out
(b) The mangroves provide both food and medicines which people are in need of after any natural disaster
(c) The mangrove trees are tall with dense canopies and serve as an excellent shelter during a cyclone or tsunami
(d) The mangrove trees do not get uprooted by storms and tides because of their extensive roots
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. Discuss the causes of depletion of mangroves and explain their importance in maintaining coastal ecology. (2019)
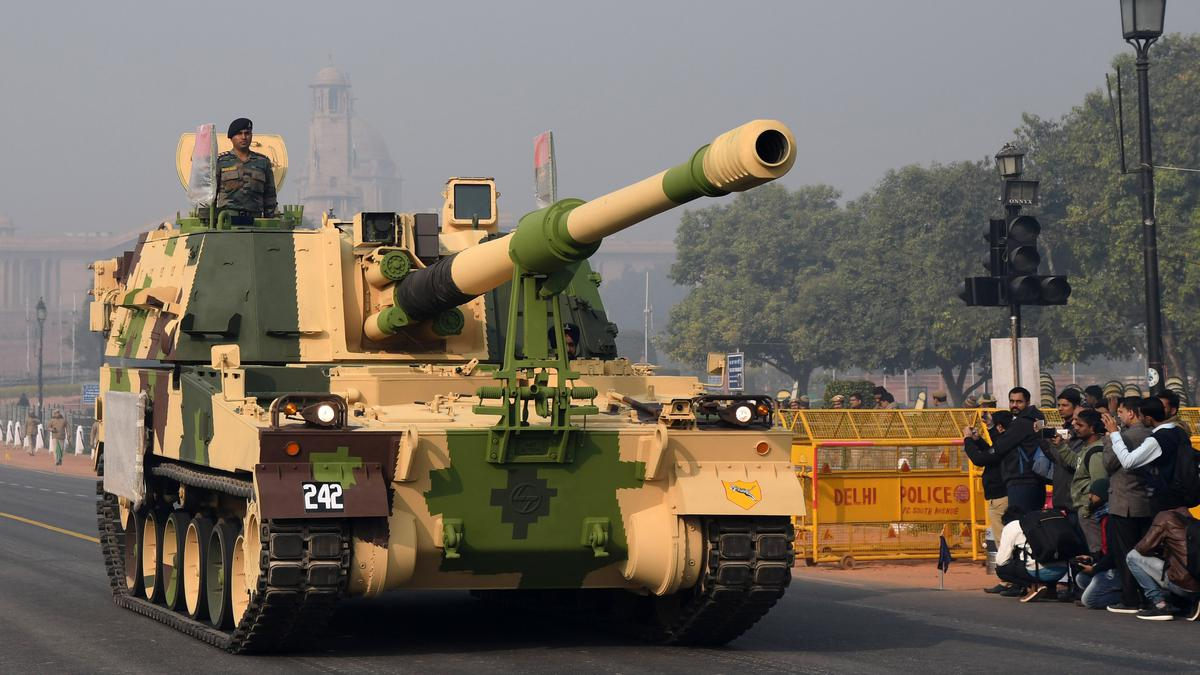
K9-Vajra
Why in News?
The Defence Ministry has started the process for the procurement of 100 more K9-Vajra tracked self-propelled howitzers.
- The 100th gun was delivered to the Army in 2021.
What is K9-Vajra?
- The K9 Vajra is a 155 mm, 52-calibre tracked self-propelled howitzer (a short gun for firing shells on high trajectories at low velocities) built in India by Larsen & Toubro (L&T) with technology transferred from South Korean defence major Hanwha Defense based on its K9 Thunder.
- The K9 Thunder platform is made of all-welded steel armour protection material.
- The K9 gun has been developed under the ‘Buy Global’ programme of the Defence Procurement Procedure (DPP) where foreign companies are allowed to participate.
- The K9 Vajra was mainly bought for use in deserts, but the India-China standoff prompted them to be deployed in the mountains as well.
- To ensure that these systems performed optimally in the extreme cold weather conditions of the mountains, the Army also procured winterisation kits for the regiment deployed.
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Spear Phishing
Ahead of the G20 Summit which India will be hosting in 2023, the CERT-In (India’s premier cybersecurity agency) has found that spear phishing will be the “primary vector” to target individuals and organisations associated with the G20 Summit. The suspected “cyber adversaries” are operating on behalf of North Korea, China and Russia.
Spear phishing is an attempt to trick a particular person/group into giving private information over the internet or by email, especially by sending emails that seem to be from someone they know.
Read More - Types of Cyber Attacks
Aymanam in Kottayam to Showcase Women's Talent
In line with Kerala government’s plan to create a women-friendly tourism network, the State authorities have planned to turn the Aymanam village (a Responsible Tourism (RT) village) as a hub of women friendly destinations along with showcasing women’s talent.
80% of the RT units in the village are already run by women. The village has also been included under the Agri Street project of the State.
Responsible Tourism requires operators, hoteliers, governments, local people and tourists to take responsibility, take action to make tourism more sustainable. It is about "making better places for people to live in and better places for people to visit”.
Read More - India’s Tourism Sector
Bhima Koregaon Battle Anniversary
Recently, 205th Anniversary of Bhima-Koregaon battle was celebrated to pay tribute to the Mahar soldiers who fought against the Peshwa forces in the 1818 battle.
The ‘Jaystambh’ in Bhima-Koregaon village commemorates the British EIC soldiers who fell in one of the last battles of Third Anglo Maratha War (1818). In the battle, the British, with just 834 infantrymen (~500 Mahars) defeated the 28,000-strong army of Peshwa Bajirao II (ended the Peshwa domination).
Read More - Bhima-Koregaon Battle
Croatia Becomes Fully Integrated EU Member
On 1st January 2023, Croatia adopted the Euro and removed dozens of border checkpoints to become the 27th nation to join Europe's passport-free travel area (world’s largest).
Adopting the euro will make travelling and doing business easier, removing the hassle of currency exchange for Croats going abroad. Croatia joined the European Union in 2013, but to adopt the Euro it had to fulfil a set of strict economic conditions (having a stable exchange rate, controlling inflation and sound public spending).
Read More - European Union