Self-Reliant India Fund for MSMEs
For Prelims: Self Reliant India, MSME, SEBI, Venture Capital Fund, Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro & Small Enterprises, Raising and Accelerating MSME Performance
For Mains: Challenges Related to MSME Sector in India, Related Government Policies.
Why in News?
Recently, the Minister of State for Micro Small and Medium Enterprises provided valuable insights into the Self Reliant India Fund during a written reply in the Lok Sabha.
What is Self-Reliant India (SRI) Fund?
- About:
- As part of the Atmanirbhar Bharat package, the Indian government announced the allocation of Rs. 50,000 crores for equity infusion in MSMEs through the Self-Reliant India (SRI) Fund.
- SRI fund operates through a mother-fund and daughter-fund structure for equity or quasi-equity investments.
- The National Small Industries Corporation (NSIC) Venture Capital Fund Limited (NVCFL) was designated as the Mother Fund for the implementation of the SRI Fund.
- It was registered as a Category-II Alternative Investment Fund (AIF) with SEBI.
- Objectives of the SRI Fund:
- To provide equity funding to viable and high-potential MSMEs, fostering their growth and transformation into larger enterprises.
- To bolster the MSME sector's contribution to the Indian economy by promoting innovation, entrepreneurship, and competitiveness.
- To create an environment conducive to technological upgradation, research and development, and increased market access for MSMEs.
- Composition of the SRI Fund:
- The Rs. 50,000 crore SRI Fund comprises:
- Rs. 10,000 Crore from the Government of India to initiate equity infusion in select MSMEs.
- Rs. 40,000 Crore sourced through Private Equity (PE) and Venture Capital (VC) funds, leveraging private sector expertise and investment.
- The Rs. 50,000 crore SRI Fund comprises:
Note:
- Equity Infusion: It refers to the process of injecting fresh capital or funds into a company by issuing additional shares to existing shareholders or new investors.
- Venture Capital Fund: It is a type of investment fund that provides capital to early-stage and startup companies with high growth potential.
- The primary objective of a venture capital fund is to identify promising startups and invest in them in exchange for equity (ownership) in the company.
- SEBI: It is a Statutory Body established on 12th April, 1992 in accordance with the provisions of the Securities and Exchange Board of India Act, 1992.
- The basic functions of SEBI is to protect the interests of investors in securities and to promote and regulate the securities market.
What is the Status of MSME Sector in India?
- About:
- MSME stands for Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises. The MSME sector of India contributes around 33% of the country's total GDP and is predicted to contribute worth USD 1 trillion to India's total exports by 2028.
- Significance:
- Employment Generation: MSMEs provide about 110 million jobs which is 22-23% of the total employment in India.
- It contributes to reducing unemployment and underemployment, supporting inclusive growth and poverty reduction.
- Promotion of Entrepreneurship and Innovation: The MSME sector fosters a culture of entrepreneurship and innovation.
- It encourages individuals to start their own businesses, promotes indigenous technologies, and contributes to the development of new products and services.
- Boon for Rural Development: Compared with large-scale companies, MSMEs aided in the industrialisation of rural areas at minimal capital cost.
- Employment Generation: MSMEs provide about 110 million jobs which is 22-23% of the total employment in India.
- Challenges:
- Infrastructure and Technology: Outdated infrastructure and limited access to modern technology due to limited finance and expertise can hinder the growth and efficiency of MSMEs.
- The lack of proper transportation, power supply, and communication networks affects their ability to compete on a global scale.
- Complex Regulatory Environment: Cumbersome and complex regulations can be challenging for small businesses to navigate.
- Compliance with various laws related to taxation, labor, environmental norms, etc., requires time, effort, and expertise.
- Inadequate Working Capital Management: Many MSMEs struggle with managing their working capital effectively.
- Late payments from customers and long payment cycles with suppliers can create cash flow issues.
- Vulnerability to Economic Fluctuations: The MSME sector is particularly vulnerable to economic downturns, as they may not have the financial buffers or scale to withstand challenging economic conditions.
- Infrastructure and Technology: Outdated infrastructure and limited access to modern technology due to limited finance and expertise can hinder the growth and efficiency of MSMEs.
- Government Initiatives for the MSME Sector:
- MSME Champions Scheme: Comprising MSME-Sustainable (ZED), MSME-Competitive (Lean), and MSME-Innovative (for incubation, IPR, Design, and Digital MSME), this scheme provides financial assistance to MSMEs to enhance their competitiveness and innovation capabilities.
- Infusion in Credit Guarantee Fund: As part of the Budget 2023-24, the government announced an infusion of Rs. 9,000 crore in the corpus of Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro & Small Enterprises.
- Raising and Accelerating MSME Performance (RAMP): This initiative focuses on strengthening institutions and governance of MSME programs at both the central and state levels.
- Amendment in Income Tax Act: The Finance Act 2023 brought about an amendment in Section 43B of the Income Tax Act, 1961, to offer more favorable tax provisions for MSMEs.
Way Forward
- Ease of Doing Business: There is a need to continuously work towards improving the ease of doing business for MSMEs, reducing bureaucratic red tape, and simplifying regulatory compliance
- Mobile Innovation Labs: There is a need to set up mobile innovation labs that travel to different regions, especially in rural areas, to provide MSMEs with access to cutting-edge technologies, training, and mentorship.
- This initiative would help bridge the technology gap and promote innovation in remote areas.
- Government-Private Sector Co-Innovation Funds: It's a time to create co-investment funds where the government partners with private sector companies to invest in promising MSME innovations.
- This collaboration would not only support the growth of innovative businesses but also enhance public-private partnerships.
- Innovation Impact Assessment: There is a need to develop a standardized impact assessment framework that measures the societal and environmental benefits of MSME innovations.
- Businesses that can demonstrate a positive impact through their innovations can receive additional recognition and support.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q.1 What is/are the recent policy initiative(s)of Government of India to promote the growth of the manufacturing sector? (2012)
- Setting up of National Investment and Manufacturing Zones
- Providing the benefit of ‘single window clearance’
- Establishing the Technology Acquisition and Development Fund
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q.2. Which of the following can aid in furthering the Government’s objective of inclusive growth? (2011)
- Promoting Self-Help Groups
- Promoting Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises
- Implementing the Right to Education Act
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q.3 Consider the following statements with reference to India : (2023)
- According to the ‘Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises Development (MSMED) Act, 2006, the ‘medium enterprises’ are those with investments in plant and machinery between `15 crore and `25 crore.
- All bank loans to the Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises qualify under the priority sector.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Barrier to Women's Labor Force Participation
For Prelims: Women's Labor Force Participation, Wage Disparities, Gender Disparity, Female Labor Force Participation Rate, Human Capital Development.
For Mains: Barrier to Women's Labor Force Participation.
Why in News?
Recently, the Tamil Nadu government has launched the Kalaignar Magalir Urimai Thogai Thittam, a women's basic income scheme, recognizing Women's Unpaid Labor. The scheme will provide Rs 1,000 per month to women in eligible households
- In Marriages, the wife bears and rears children and minds the home, and therefore bears the brunt of unpaid care and domestic work, hindering their Participation in Labor Force.
What are the Causes of Lower Women Participation in the Labour Force?
- Patriarchal Social Norms:
- Deep-rooted patriarchal norms and traditional gender roles often limit women's access to education and employment opportunities.
- Societal expectations may prioritize women's roles as caregivers and homemakers, discouraging their active participation in the labor force.
- Gender Wage Gap:
- Women in India often face wage disparities compared to men for similar work.
- According to World Inequality Report, 2022 , men in India capture 82% of labour income, while women earn just 18%.
- This wage gap can discourage women from seeking formal employment opportunities.
- Women in India often face wage disparities compared to men for similar work.
- Unpaid Care Work:
- The burden of unpaid care and domestic work falls disproportionately on women, limiting their time and energy for paid employment.
- Married women in India spend over 7 hours per day on unpaid care and domestic work, while men spend less than 3 hours.
- This trend is consistent across income levels and caste groups, leading to a significant Gender Disparity in domestic responsibilities.
- This unequal distribution of household responsibilities can be a significant barrier to women's participation in the labor force.
- The burden of unpaid care and domestic work falls disproportionately on women, limiting their time and energy for paid employment.
- Social and Cultural Stigma:
- In some communities, there may be stigma or resistance associated with women working outside the home, leading to lower labor force participation rates.
What are the Statistics Regarding Unpaid Care of Women?
- Female Labor Force Participation Rate (LFPR):
- Despite a surge in the enrollment rate for girls in Class 10, India's Female LFPR has declined from 30% to 24% over the past two decades.
- The burden of domestic work is a key factor contributing to lower female LFPR, even among educated women.
- India's female LFPR (24%) is the lowest among BRICS countries and select South Asian countries.
- China, with the highest female population, boasts the highest female LFPR at 61%.
- Impact on Women's Employment:
- Women not in the labor force spend the most time on unpaid domestic/care work, averaging 457 minutes (7.5 hours) per day.
- Employed women follow closely, spending 348 minutes (5.8 hours) per day on such chores, impacting their ability to engage in paid work.
How can Higher Women Labor Participation Impact the Society at Large?
- Economic Growth:
- Women's participation in the labor force is directly linked to economic growth. When a significant portion of the female population remains underutilized, it results in a loss of potential productivity and economic output.
- Increased women's labor force participation can contribute to higher GDP (Gross Domestic Product) and overall economic prosperity.
- Poverty Reduction:
- When women have access to income-generating opportunities, it can lift households out of poverty, leading to better living standards and improved well-being for families.
- Human Capital Development:
- Educated and economically active women can positively influence the education and health outcomes of their children, leading to intergenerational benefits.
- Gender Equality and Empowerment:
- Higher women's participation in the labor force can challenge traditional gender roles and norms, promoting gender equality.
- Economic empowerment enables women to have greater control over their lives, decision-making power, and autonomy.
- Fertility and Population Growth:
- Studies have shown that as women's labor force participation increases, fertility rates tend to decline.
- This phenomenon, known as the "fertility transition," is associated with improved access to education, healthcare, and family planning, leading to more sustainable population growth.
- Reduced Gender-Based Violence:
- Economic empowerment can enhance women's bargaining power and reduce their vulnerability to gender-based violence and abusive relationships.
- Labor Market and Talent Pool:
- Increasing women's participation in the labor force can help address skill shortages and labor market imbalances, leading to a more efficient allocation of talent and resources.
What are the Government Schemes Related to Women Empowerment?
Way Forward
- Gender equality discussions should move beyond compartmentalizing women's lives into work and life and recognize the comprehensive valuation of all kinds of work, both formal and informal, that women do.
- Policy solutions must be derived from women's own negotiations within their cultural context, focusing on increasing autonomy and flexible work options.
- Promoting and supporting higher women's labor force participation is not only a matter of gender equality but also a crucial driver of societal progress and development.
- By unlocking the full potential of women in the workforce, societies can reap the benefits of economic growth, poverty reduction, improved human capital, and more inclusive and equitable communities.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following gives ‘Global Gender Gap Index’ ranking to the countries of the world? (2017)
(a) World Economic Forum
(b) UN Human Rights Council
(c) UN Women
(d) World Health Organization
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. ‘’Empowering women is the key to control the population growth.’’ Discuss. (2019)
Post-Quantum Cryptography
For Prelims: Post-Quantum Cryptography, Quantum Computing, Rivest-Shamir-Adleman, ECC Elliptic Curves Cryptography, Diffie-Hellman, Quantum Bits.
For Mains: Post-Quantum Cryptography, Related Challenges and Way Forward.
Why in News?
Computation has transformed various facets of human civilization, from banking to warfare, however, the emergence of Quantum Computing has raised concerns about its impact on Computer Security in the Future.
What is Quantum Computing?
- About:
- Quantum computing is a rapidly emerging technology that harnesses the laws of quantum mechanics to solve problems that are too complex for classical computers.
- Quantum mechanics is a subfield of physics that describes the behavior of particles — atoms, electrons, photons, and almost everything in the molecular and sub molecular realm.
- It is an exciting new technology that will shape our world tomorrow by providing us with an edge and a myriad of possibilities.
- It is a fundamentally different way of processing information compared to today’s classical computing systems.
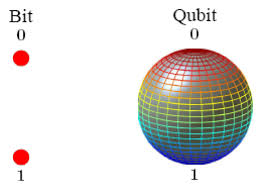
- Features:
- While today’s classical computers store information as binary 0 and 1 states, quantum computers draw on the fundamental laws of nature to carry out calculations using quantum bits (Qubits).
- Unlike a bit that has to be a 0 or a 1, a qubit can be in a combination of states, which allows for exponentially larger calculations and gives them the potential to solve complex problems which even the most powerful classical supercomputers are not capable of.
- Significance:
- Quantum computers can tap into the quantum mechanical phenomenon to manipulate information and are expected to shed light on processes of molecular and chemical interactions, address difficult optimization problems, and boost the power of artificial intelligence.
- These could open the door to new scientific discoveries, life-saving drugs, and improvements in supply chains, logistics and the modeling of financial data.
What are the Post Quantum Concerns of Quantum Computing?
- Vulnerabilities in Current Security Techniques:
- Current security measures, such as RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman), ECC (Elliptic Curves Cryptography), and Diffie-Hellman key exchange, rely on "hard" mathematical problems that could be broken with using Shor's Quantum Algorithm.
- In 1994, Peter Shor developed a quantum algorithm that (with certain modifications) can break all of these security measures with ease.
- As quantum computing progresses, the security measures will eventually become vulnerable, necessitating the exploration of alternative techniques.
- Current security measures, such as RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman), ECC (Elliptic Curves Cryptography), and Diffie-Hellman key exchange, rely on "hard" mathematical problems that could be broken with using Shor's Quantum Algorithm.
Note:
- RSA is a widely used cryptographic algorithm and one of the fundamental building blocks of modern computer security. RSA is primarily used for secure communication and data encryption, providing confidentiality and authentication in various applications.
- Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) is a modern and widely used cryptographic technique that provides security and efficiency for various computer security applications.
- Diffie-Hellman (DH) is a key exchange algorithm used to establish a shared secret key between two parties over an insecure channel. It was introduced by Whitfield Diffie and Martin Hellman in 1976 and is considered one of the fundamental building blocks of modern public-key cryptography.
- Scalability and Practicality:
- Quantum Cryptography systems can be challenging to implement and scale to large networks due to the requirement for specialized hardware and tight environmental constraints.
- Quantum Key Distribution Over Long Distances:
- Quantum Cryptography systems like QKD face limitations in terms of the distance over which secure keys can be distributed. Extending the range of secure key distribution is a significant challenge for Quantum Cryptography researchers.
- Quantum Network Infrastructure:
- Building a robust quantum network infrastructure to support Quantum Cryptography is a complex task.
- This involves developing reliable quantum repeaters, quantum routers, and quantum memory, among other components, to ensure the secure transmission of quantum information.
- Quantum Cryptography in a Hybrid World:
- As the transition to post-quantum cryptography progresses, hybrid communication scenarios will arise where both classical and quantum communication systems coexist.
- Ensuring seamless integration and secure communication between these systems presents a challenge.
Way Forward
- Post-quantum cryptography involves researching alternative cryptographic techniques to counter vulnerabilities against quantum attacks.
- The urgency in this area arises from attackers recording messages to exploit potential quantum weaknesses in the future.
- While practical and dangerous quantum computers might be decades away, preparing for a quantum future is essential. Governments, organizations, and individuals must transition to technologies secure against quantum attacks well in advance to safeguard sensitive data and digital infrastructure.
- The field of post-quantum cryptography continues to evolve rapidly, requiring ongoing research and collaborative efforts to develop robust security measures that can withstand quantum attacks. A proactive and carefully planned transition to quantum-safe technologies will be crucial to secure data and maintain the integrity of digital infrastructure in the quantum era.
Heat Waves and Heat Index
For Prelims: Heat Index, Heat Waves, India Meteorological Department
For Mains: Role of India Meteorological Department (IMD) in mitigating severe weather events, Concept of the Heat Index
Why in News?
India has witnessed a significant decline in heat-related deaths in recent years, reflecting the country's efforts to combat the adverse effects of heatwaves.
- The India Meteorological Department (IMD) plays a vital role in this endeavor, issuing timely forecasts and warnings to mitigate the impact of severe weather events, including heatwaves.
- Recently, IMD introduced the Heat Index, a valuable tool that considers humidity's influence on temperatures.
What are Heat Waves?
- About:
- Heat waves are prolonged periods of excessively hot weather that can cause adverse impacts on human health, the environment, and the economy.
- India, being a tropical country, is particularly vulnerable to heat waves, which have become more frequent and intense in recent years.
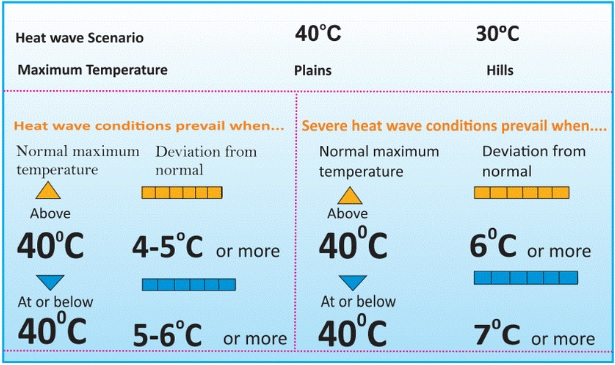
- IMD Criteria for Declaring Heat Wave in India:
- Heat wave is considered if the maximum temperature of a station reaches at least 40°C or more for Plains and at least 30°C or more for Hilly regions.
- Based on Departure from Normal:
- Heat Wave: Departure from normal is 4.5°C to 6.4°C.
- Severe Heat Wave: Departure from normal is >6.4°C.
- Based on Actual Maximum Temperature:
- Heat Wave: When actual maximum temperature ≥ 45°C.
- Severe Heat Wave: When actual maximum temperature ≥47°C.
- Based on Departure from Normal:
- Heat wave is considered if the maximum temperature of a station reaches at least 40°C or more for Plains and at least 30°C or more for Hilly regions.
- IMD's Initiatives and Tools to Combat Heat Waves:
- Timely issuance of heat wave forecasts to keep the public informed.
- Warnings provided to disaster management authorities for necessary preparedness.
- IMD offers Seasonal outlook and extended range forecast offering additional insights into temperature trends.
- Daily forecasts for the next five days with real-time updates.
- Color-coded warnings for severe weather events, including heat waves.
- Cooperation with National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) and local health departments for heat action plans.
- Implementation of plans in vulnerable regions to minimize heat-related risks.
What is Heat Index?
- About:
- The Heat Index is a parameter that considers both temperature and humidity to calculate the apparent temperature or "feel like" temperature for human beings.
- It helps in understanding the impact of humidity on high temperatures and how it contributes to human discomfort during hot weather.
- The Heat Index has been launched on an experimental basis by the India Meteorological Department (IMD).
- It aims to provide general guidance for regions experiencing higher apparent temperatures causing discomfort to people.
- Indication of Heat Stress:
- High Heat Index values indicate a greater risk of heat-related stress and health issues.
- It serves as a warning for potential heat-related illnesses and dangers.
- Categorization of Heat Levels:
- The Heat Index categorizes the apparent temperature into different levels using color codes:
- Green: Experimental heat Index less than 35°C.
- Yellow: Experimental heat Index in the range 36-45°C.
- Orange: Experimental heat Index in the range 46-55°C.
- Red: Experimental heat Index greater than 55°C.
- The Heat Index categorizes the apparent temperature into different levels using color codes:
- Useful Tool for Public Health:
- By understanding the Heat Index, individuals and communities can take proactive steps to protect public health during heatwaves.
- It assists in making informed decisions and formulating heat action plans to ensure the well-being of the population.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. What are the possible limitations of India in mitigating global warming at present and in the immediate future? (2010)
- Appropriate alternate technologies are not sufficiently available.
- India cannot invest huge funds in research and development.
- Many developed countries have already set up their polluting industries in India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. Bring out the causes for the formation of heat islands in the urban habitat of the world. (2013)
Cinematograph (Amendment) Bill, 2023
For Prelims: Intellectual property rights, Central Board of Film Certification, Cinematograph Act, 1952, Shyam Benegal Committee, IT Rules 2021.
For Mains: Required Modification in Cinematograph Act of 1952
Why in News?
Recently, the Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha passed the Cinematograph (Amendment) Bill, 2023. The bill expands the scope of the law from censorship to also cover copyright and introduces stringent anti-piracy provisions.
- The bill aims to amend the existing Cinematograph Act of 1952.
What are the Proposed Provisions in Cinematograph (Amendment) Bill, 2023?
- Anti-Piracy Provisions: The bill aims to deter piracy of films by imposing strict penalties on individuals involved in unauthorized audio-visual recording and distribution of copyrighted content. The provisions include:
- Jail Term: Imprisonment from 3 months to 3 years.
- Fine: From Rs. 3 lakhs to 5% of the audited gross production cost.
- Expansion of Copyright Coverage: It aims to extend the coverage of the Cinematograph Act, 1952, which was primarily focused on censorship, to now encompass copyright protection.
- This move aligns with the evolving landscape of film distribution and aims to safeguard the intellectual property rights of filmmakers and content creators.
- Government's Limited Powers over CBFC: It emphasizes the autonomy of the Central Board of Film Certification (CBFC).
- The Government may no longer have revisional powers over the CBFC's decisions, based on the Supreme Court's judgment in the case of K.M. Shankarappa vs Union of India (2000).
- Age Ratings: The amendment bill introduces a new age rating system for films that require adult supervision. The current U/A rating, which covers a broad age range, will be split into three distinct categories:
- U/A 7+: Films suitable for children above the age of 7 with parental guidance.
- U/A 13+: Films suitable for children above the age of 13 with parental guidance.
- U/A 16+: Films suitable for children above the age of 16 with parental guidance.
- This new classification system aligns with the graded-age classifications implemented for streaming platforms under the IT Rules, 2021 and Shyam Benegal Committee recommendations (2017).
- Recertification for TV and Other Media: Historically, films rated for adults have been prohibited on television since a 2004 Bombay High Court order.
- As a result, broadcasters often voluntarily make cuts to films and seek re-certification from the CBFC for a U/A rating.
- The bill formalizes this practice, allowing films to be recertified for television and "other media."
- As a result, broadcasters often voluntarily make cuts to films and seek re-certification from the CBFC for a U/A rating.
- Perpetual Validity of Certificates: The Act has been amended to remove the 10-year validity restriction on CBFC certificates, thereby granting them perpetual validity.
What is the Cinematograph Act of 1952?
- The Cinematograph Act, 1952 was enacted by the Parliament to ensure that films are exhibited in accordance with the limits of tolerance of Indian society.
- It lays down the principles of guidance for certifying films, such as the interest of sovereignty and integrity of India, the security of the State, friendly relations with foreign States, public order, decency or morality, or involves defamation or contempt of court.
- Section 3 of the Act provides for the establishment of Central Board of Film Certification (CBFC, popularly known as the censor board).
- CBFC is a statutory body under the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting, that regulates the public exhibition of films under the provisions of the Cinematograph Act 1952.
- It also provides for the constitution of an Appellate Tribunal to hear appeals against the decisions of the Board.
States’ Lax Response to Mob Lynching
For Prelims: Cow vigilantism, Mob Violence, lynching, National Federation of Indian Women (NFIW), Tahseen Poonawala versus Union of India Case 2018
For Mains: Mob Lynching and Religious Fundamentalism
Why in News?
The National Federation of Indian Women (NFIW) has filed a petition in the Supreme Court.
- The Supreme court seeks an explanation for the consistent failure of the Ministry of Home Affairs and six state governments (Maharashtra, Odisha, Rajasthan, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, and Haryana) to act against lynching and mob violence on Muslims by cow vigilantes.
What is Mob Lynching?
- Mob lynching is an act of collective violence perpetrated by a large group of individuals, involving attacks on either a person's body or property, whether in public or private settings.
- The group, driven by a belief that the victim has committed some perceived wrongdoing, takes matters into their own hands, disregarding legal rules and procedures in the process.
Cow Vigilantism: Cow vigilantism or lynching in the name of Cow Protection poses a serious threat to the secular fabric of the nation. Killing of people just on the suspicion of beef depicts the intolerance among the vigilantes.
What are Some Statistics Related to Lynching in India?
Data compiled by India Spend website on Cow-Linked Violence in India (2010-2017):
- A total of 28 people were killed in 63 incidents of cow-linked violence during the period from 2010 to 2017.
- Almost all of these attacks, around 97%, happened after 2014, showing a sharp increase in such incidents in the last few years.
- About 86% of the people who were killed in these incidents were Muslims, which shows that a specific religious community was being targeted.
What are the Causes of Mob Lynching?
- Perceived Threat to Culture or Identity: Mobs engages in lynching when they believe that certain actions or behaviors of individuals or groups pose a threat to their cultural or religious identity.
- For example: inter-caste or inter-religious relationships, consumption of certain foods, or customs that are perceived as challenging traditional norms.
- Rumors and Misinformation: Mob lynching incidents are often triggered by rumors or misinformation spread through social media, word of mouth, or other channels.
- Economic and Social Tensions: Issues related to land disputes, economic opportunities, and competition for resources can escalate into violent confrontations.
- Political Manipulation: Political interests and agendas may fuel mob lynching incidents.
- Ethnic or Communal Divisions: Long-standing ethnic, religious, or communal divisions can contribute to mob lynching.
- Moral Vigilantism: Individuals or groups may take the role of self-appointed moral vigilantes, enforcing their interpretation of social norms and values through violence.
What are the Issues Related to Mob Lynching?
- Mob lynching is a violation of human dignity, Article 21 of the Constitution, and a gross infringement of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
- Such incidents violate the Right to Equality(Articles 14) and Prohibition of discrimination, (Article 15)
- Mob Lynching is nowhere mentioned in the law of the land and is to put it simply, it cannot be classified as murder as it has not been included in the Indian Penal Code.
What was the Supreme Court Observation in Tahseen Poonawala Case?
- In July 2017, the Supreme Court in the case of Tahseen s. Poonawala v. UOI said that it was the “sacrosanct duty” of the state to protect the lives of its citizens.
- The Supreme Court in this case aptly referred to mob lynching as a ‘horrendous act of mobocracy.’
What are the Seven Remedial Directions Given by the Supreme Court?
- Appointment of designated nodal officer:
- A designated nodal officer, not below the rank of Superintendent of Police, should be appointed to take measures to prevent prejudice-motivated crimes like mob violence and lynching.
- Immediate lodging of FIR and Informing the nodal officer:
- If an incident of lynching or mob violence comes to the notice of the local police, they must immediately lodge an FIR.
- The Station House Officer who registers the FIR must inform the nodal officer in the district about the incident.
- Personal monitoring of investigation:
- The nodal officer must personally monitor the investigation of the crime.
- Timely filing of chargesheet:
- The investigation and chargesheet should be filed within the stipulated period as per the law.
- Scheme for victim compensation:
- There should be a scheme in place to compensate victims of prejudice-motivated violence.
- Action against non-compliance:
- Non-compliance with the court's directions by a police or district administration officer would be deemed deliberate negligence/misconduct, and appropriate action, beyond departmental proceedings, must be taken within six months.
- Disciplinary action against officials:
- States must impose disciplinary action on officials who, despite prior knowledge, fail to prevent mob lynching incidents or delay in apprehending and initiating criminal proceedings against the culprit's post-incident.
What are the Initiatives Taken by Governments to Prevent the Issue?
- Law against mob lynching:
- As of now only three states Manipur, West Bengal and Rajasthan have enacted laws against mob lynching.
- The Jharkhand Assembly has passed Prevention of Mob Violence and Mob Lynching Bill, 2021 which has been returned by governor recently for reconsideration of a few provisions.
- Awareness Campaigns:
- Ranchi Police launched a mass awareness drive across Ranchi district to prevent mob lynching through poster campaigns.
- Aurangabad Police have launched an awareness campaign in all the eight districts of Marathwada to curb incidence of mob lynching.
- Victim Compensation:
- The Goa government announced in victim compensation scheme that in case a person dies of mob violence, the family will get Rs 2 lakh.
- Social Media Monitoring:
- In the southern city of Hyderabad, police are trying to stop mob violence through a social media campaign using hashtags #HyderabadKillsRumors.
Way Forward
- Pay a “minimum uniform amount” to the victims of lynchings and mob violence.
- Lynchings have no place in a democratic society like India. As a country that prides itself on being democratic, it is crucial that mob violence is eradicated.
- All the states and Centre should look forward to bringing comprehensive legislation on the matter as brought by states like Manipur, West Bengal and Rajasthan.
- Measures need to be taken to curb the spread of fake news and hate speech.
About National Federation of Indian Women:
- The National Federation of Indian Women is a women's organization in India, and it serves as the women's wing of the Communist Party of India.
- It was founded on June 4, 1954, by leaders from Mahila Atma Raksha Samiti, including Aruna Asaf Ali.
Akhil Bharatiya Shiksha Samagam and ULLAS Initiative
Why in News?
Recently, the Prime Minister (PM) of India inaugurated Akhil Bharatiya Shiksha Samagam a two-day event. The event is organized to mark the third anniversary of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
- Additionally, the Union Minister of Education launched the ULLAS: Nav Bharat Saksharta Karyakram mobile application.
What are the Key Highlights of Akhil Bharatiya Shiksha Samagam?
- The PM released the first installment of funds under the PM SHRI Scheme, supporting the establishment of schools that nurture engaged, productive, and contributing citizens, in alignment with the NEP 2020 vision.
- The PM also released education and skill curriculum books translated into 12 Indian languages, enhancing learning by allowing students to study in their mother tongue.
What is ULLAS: Nav Bharat Saksharta Karyakram?
- About:
- The ULLAS (Understanding Lifelong Learning for All in Society) is a transformative initiative launched by the Indian government to promote lifelong learning and bridge the gaps in basic literacy and critical life skills among citizens aged 15 and above.
- The program aims to empower individuals with essential knowledge and skills for personal and national development.
- ULLAS User-Friendly Mobile Application serves as a digital gateway to diverse learning resources via the DIKSHA portal.
- Key Features of ULLAS: Nav Bharat Saksharta Karyakram:
- Lifelong Learning Focus:
- Emphasizes continuous learning throughout life.
- Fosters a culture of knowledge-sharing and personal development.
- Digital and Financial Literacy:
- Equip participants with digital literacy skills.
- Promotes financial awareness and empowerment.
- Critical Life Skills:
- Impart important life skills such as legal literacy and digital literacy.
- Enhances citizenship and empowerment.
- Incentives for Student Volunteers:
- Provides credits in school/university for student volunteers.
- Offers appreciation through certificates, letters, and felicitations.
- Lifelong Learning Focus:
What are the Other Government Initiatives Related to Educational Reforms?
- National Programme on Technology Enhanced Learning.
- Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan
- PRAGYATA
- Mid Day Meal Scheme
- Beti Bachao Beti Padhao
- PM SHRI Schools
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following provisions of the Constitution does India have a bearing on Education? (2012)
- Directive Principles of State Policy
- Rural and Urban Local Bodies
- Fifth Schedule
- Sixth Schedule
- Seventh Schedule
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3, 4 and 5 only
(c) 1, 2 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans- (d)
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
MSME CARD
Recently, the Ministry of Micro Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME), in association with the National Payment Corporation of India (NPCI) had launched the MSME RuPay Credit Card on a pilot basis, pan-India for Udyam registered MSMEs.
- The MSME RuPay Credit Card provides a simplified payment mechanism to MSMEs to meet their business-related operational expenses like digital payments, utility bills payments, tax/statutory payments, etc.
- MSME borrowers also take benefit of interest-free credit period on their business spending as per the bank's policy.
- NPCI, an umbrella organization for operating retail payments and settlement systems in India, is an initiative of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and Indian Banks’ Association (IBA) under the provisions of the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007, for creating a robust Payment & Settlement Infrastructure in India.
Read more: Credit Growth for MSMEs
Mahila Samman Savings Certificate Scheme (MSSC)
The Mahila Samman Savings Certificate Scheme (MSSC) is a small savings scheme launched by the Ministry of Finance, to commemorate the Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav, aimed at encouraging women investors.
- Women of any age group, including girl children, can open an MSSC account with a minimum deposit of Rs 1000 and a maximum deposit of Rs. 2 Lakhs for a two-year period until March 2025.
- So far, 14,83,980 accounts have been opened with total deposits of Rs 8,630 crore under the scheme.
- The scheme offers an attractive interest rate of 7.5% p.a., compounded quarterly, along with the provision for partial withdrawal and premature closure of the account is allowed at any time after six months of opening but with the interest rate reduced by 2%.
Cross-Border Wildfire: Eagle Bluff Threatens Osoyoos and British Columbia
Recently, a wildfire, initially named 'Lone Pine Creek' that started in Washington, USA crossed the border into the Canadian province of British Columbia.
- This rapidly spreading fire, now known as 'Eagle Bluff’ and estimated to cover 885 hectares (2,200 acres) on the Canadian side and around 2,000 hectares on the U.S. side.
- British Columbia as well as other parts of Canada are already reeling from drought, which has caused several wildfires in the country in July 2023.
- This event also reminded of the 2021 wildfires in British Columbia, which were blamed on a heat dome in the Pacific Northwest.
Read more: Wildfire, Heat dome
MPLADS Fund Allocation for Covid-19 Relief
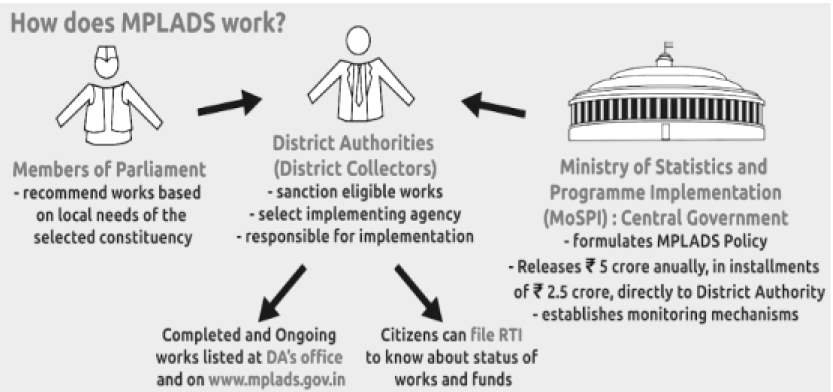
Recently, the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation provided valuable insights into the Members of Parliament Local Area Development Scheme (MPLADS) during a written reply in the Rajya Sabha.
- MPLADS scheme enables the members of parliaments (MPs) to recommend developmental work in their constituencies with an emphasis on creating durable community assets based on locally felt needs.
- The annual allotment under the MPLAD Scheme has remained unchanged since the Financial Year 2011-12.
- However, in response to the Covid-19 pandemic, a total of Rs. 6,320 crores from MPLADS funds were allocated to the Ministry of Finance for the Financial Years 2020-21 and 2021-22.
Read more: Members of Parliament Local Area Development Scheme